IB Exam 2
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
first mover advantages
advantages accruing to the first to enter a market
timing of entry
entry is early when a firm enters a foreign market before other foreign firms and late when a firm enters after other international businesses have established themselves
location economies
cost advatnages from performing a value creation activity at the optimal location for that activity
low cost strategy
lowering production costs
differentiation strategy
increasing the attractiveness of a product
efficiency frontier
all the different positions that a firm can assume with regard to adding value to the product and low cost, assuming that the internal operations align with their strategy
controls
the metrics used to measure the perfomance of subunits and make judgements about how well managers are running those subunits
pressures for cost reductions
lower cost for more profit
differentiation and localization raise prices
conflicting demands
more intense when producing commodities
pressures to be locally responsive
diferences in consumer tastes and preferences
differences in infrastructure
host government demands (regulations)
differences in distribution channels (supermarkets ex)
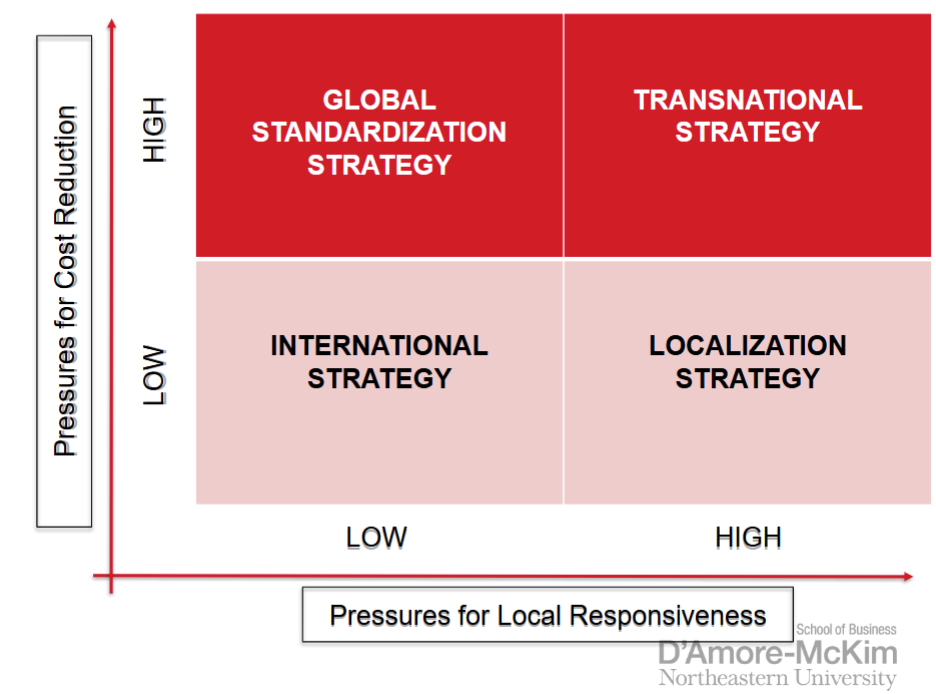
global standardization
a firm focuses on increasing profitability and profit growth by reaping the cost reduction that come from economies of scale, learning effects, and location economies
pursure low cost strategy on a global scale
try not to customize their product to local conditions (expensive)
makes sense when there are strong pressures for cost reductions and demands for local responsiveness are minimal
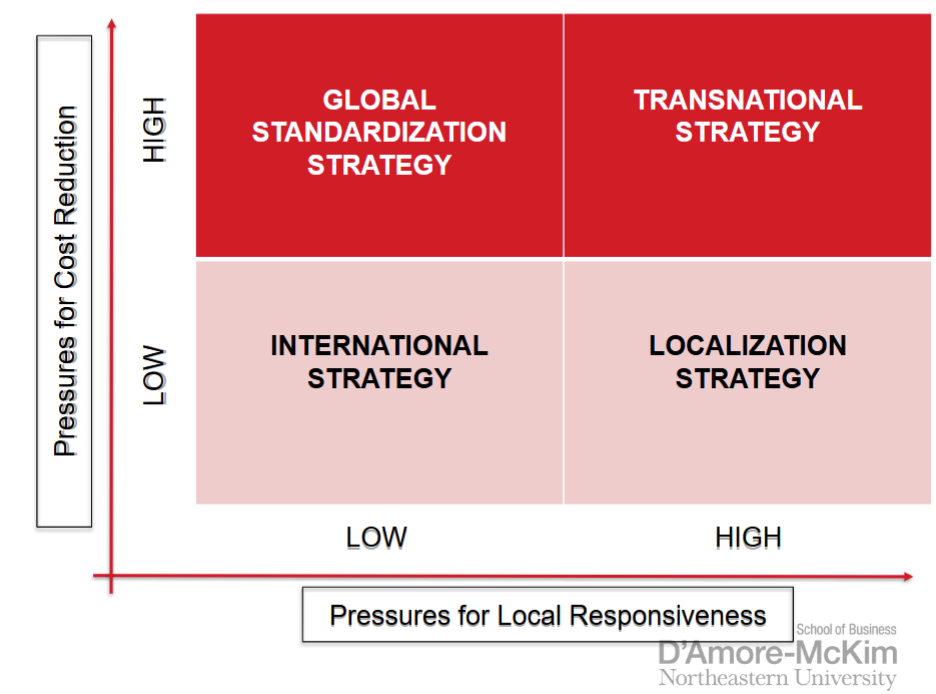
localization strategy
increasing profitability by customizing the firm’s goods or services so that they provide a good match to tastes and preferences in different national or regional markets
most appropiate when it comes to tastes and preferences of the product across nations and regions
customization limits the ability of a firm to capture the cost reductions associated with mass producing
added value or increased demand allows them to make up the lost money with a higher price
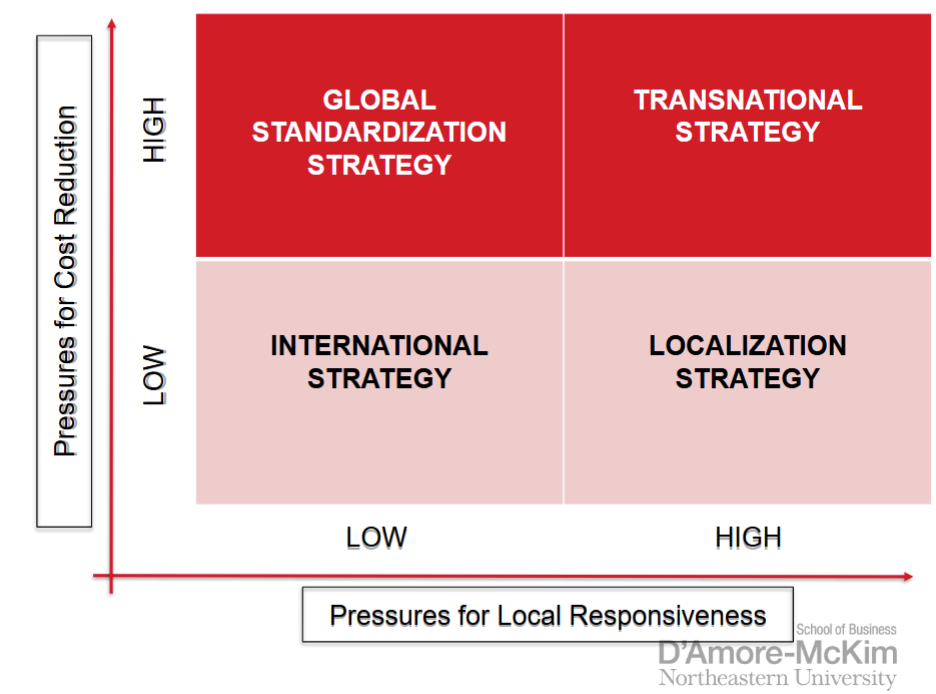
transnational strategy
trying to simultaneously achieve low cost through location economies, economies of scale, and learning effects
differentiate their product offering across geographic markets to account for local differences
foster a multidirectional flow of skills between different subsidiaries in the firm’s global network of operations
conflicting demand
difficult to implement
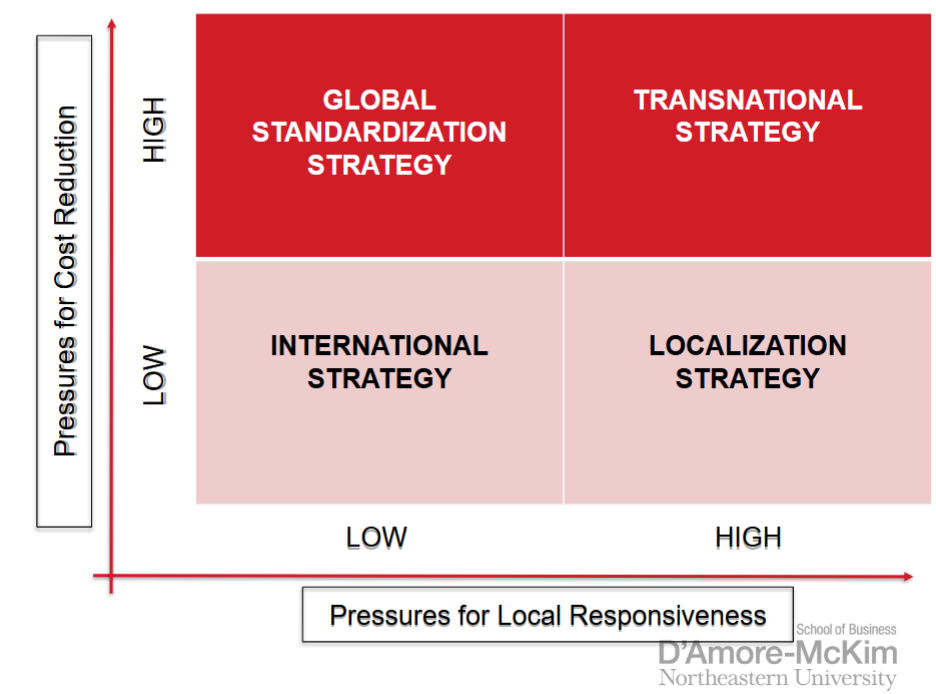
international strategy
taking product first produced for their domestic market and selling them internationally with only minimal local customization
selling a product that serves universal needs
organizational strcuture
the 3 part strcuture of an organization, including its formal division into subunits such as product divisions, its location of decision-making responsibilities within that structure, and the establishment or integration mechanisms to coordinate the activities of all subunits
organizational architecture
the totality of a firm’s organizations, including formal organizational strcture, control systems and incentives, organzational strcutre, processes, and people
core competencies
firms skills that competitors cannot easily match or imitate
learning effects
cost saving from learning by doing
economies of scale
cost advantages associated with large scale production
3 main factos for the success of an alliance
partner selection
allaince structure
alliance management
cross border trade and investment
lowering of barriers
tariffs on the rise
3 conditions for profitability
elements of the organizational architecture must be internally consistent
architecture must match and fit the strategy of the firm
strategy and architecture must make sense given the competitive conditions prevailing the firms markets
centralized decision making
concentrated at top levels of mangement
facilitate coordination
ensure that decisions are consistent with organizational objectives
give top levele managers the means to bring about needed organizational changes
decentralized decision making
distributed across different levels
more individual freedom
greater flexibility
better decisions: decisions are made closer to the spot by individuals who have better information than managers several levels up in a hierarchy
horizontal differentiation
how the firm divides itself into subunit
across the organization at the same level of hierarchy
vertical differentiation
hierarchical levels in an organization
top to lower levels
product divisional structure
each division is responsible for a distinct product line
self contained, largely autonomous entity with its own functions
headquarters retains control for the overall strategic direction
international division structures
organized on geography
export the product manufactured at home to foreign subsidiaries
dual structure can conflictand problems with coordination between domestic and foreign operations
many firms start off with this structure
worldwide product divisional structure
adopted by firms that are reasonably diversified, and accordingly, originall had domestic structures based on product divisions
allows for worldwide coordination of value creation activities of each product division
helps realize location economies and experience effects
facilitiates the transfer of core competencies
does not allow for local responsiveness
worldwide area strucure
favored by firms with low degree of diversification and a domestic structure based on function
divides the world into autonomous geographic areas
decentralizes operational authority
facilitates local responsiveness
fragments an organization into highly autonomous entities
global matrix structure
tries to minimize the limitations of the worldwide area structure and the worldwide product divisional structure
horizontal differentiation proceeds along 2 dimensions
product division and geographic area
dual decision making responsibility should be shared by the product divison and various areas of the firm
does not always work as well as it states
lead to power struggles between the areas and the product divisions
difficult to be accountable
which markets to enter
benefits, costs, and risks associated with doing business in that country
size of the market, the purchasing power of consumers, future wealth
living standards and economic growth
future economic growht
economically advanced and politically stable countries
suitability of its product offering
when should a firm enter its market
early
first mover advantages
ability to build sales volume
ability to create switching costs that tie customers into their products or services
pioneering costs (CON)
late
other international businesses have already established themselves
on what scale should firms enter these markets
large scale
more commitment
difficult to reverse
first mover advantages
lack of flexibility
small scale
limit exposure while learning about a foreign maket
reduces risk
lack of commitment makes it more difficult to build market share
exporting
many firms start off as exporters and then move to other modes
PRO
avoid costs
achieve experience curve and location economies
CON
not appropiate if lower cost locations from manufacturing the product can be found abroad
high transportation costs
tariff barriers
delegation of marketing, sales, and service
turnkey projects
the contractor agrees to handle every detail of the project for a foreign client, including the training of operating personnel
PRO
earning great economic returns from the know how required to assemble and run a technologically complex process (especially where FDI is limited by host government)
less risky than conventional FDI
CON
no long term interest in the country to which they enter
if a process’s technology is a competitive advantage, they run the risk of loosing the control of their technology
licensing
arrangment whereby a licensor grants the rights to intangible property to another entity for a specific period of time, and in return, the licensor receives royalty fee from the licensee
patents, inventions, formulas, processes, deisgns, copyrights, and trademarks
PRO
not having to bear the development costs and risk associated with opening a foreign market
avoids barriers to investment
easier to respond to customer needs
CON
lack of control over operations
potential for creating a competitor
requires a firm to coordinate strategic moves across countries by using profits earned in one country to support competitive attacks in another
franchising
a specialized form of licensing in which the franchiser not only sell intaginble property to the franchisee, but also abide by strict rules on how it does busienss
PRO
the firm is relieved of the many costs and risks of opening a foreign market on its own
very similar to those of licensing
CON
quality control
joint ventures
entails establishing a firm that is jointly owned by two or more otherwise independent firms
50-50
PRO
benefit from a local partners knowledge of the host country’s competitive conditions, culture, language, political systems and business
a firm might gain by sharing these costs and risks with a local partner
political considerations make it the only feasible option
CON
risks giving control of its technology to its partners
may not have the tight control to realize learning effects or location economies
shared ownership can lead to conflicts and battles for control if goals and objectives differ or change over time
greenfield investment
PRO
reduce the risk of losing control over core competencies
tight control in different countries necessary for global strategic cooridnation
greatest opportunity for long term growth
CON
firm bears the full cost and risk of setting up overseas operations
slower to establish
large investment and risk
foreign acquisition
PRO
quick to execute
less risky than greenfield ventures
immediate local expertise
CON
acquiring firm overpays for the acquired firm
cultures of the acquiring and acquired firm clash
anticipated synergies are slow and difficult to achieve
inadequate pre-acquistion screening
management know how
risk of losing control over management skills to franchisees or joing venture partners is not that great
geocentric
staffing with no matter nationality
ethnocentric
staffing done from home country
polycentric
home country nationals tkae care of management while host country nationals are recruited