2.2 motion of charged particles in electric fields
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
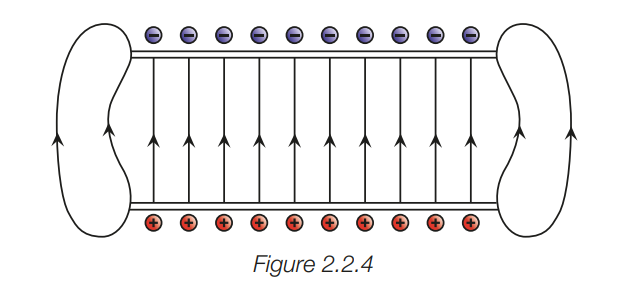
draw and describe the electric field produced by two oppositely charged parallel conducting plates
uniform between the plates and away from the edges is uniform
represented by evenly spaced electric field lines
means a positive test charge experiences the same force no matter where it is placed
near and beyond the edges of the plates the electric field is non-uniform
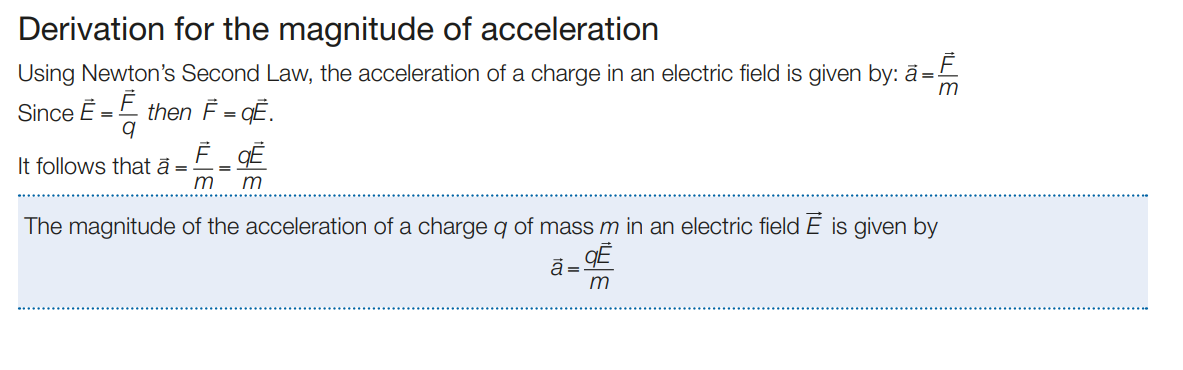
derive the formula for the accelleration of a charge q of mass m in an electric field
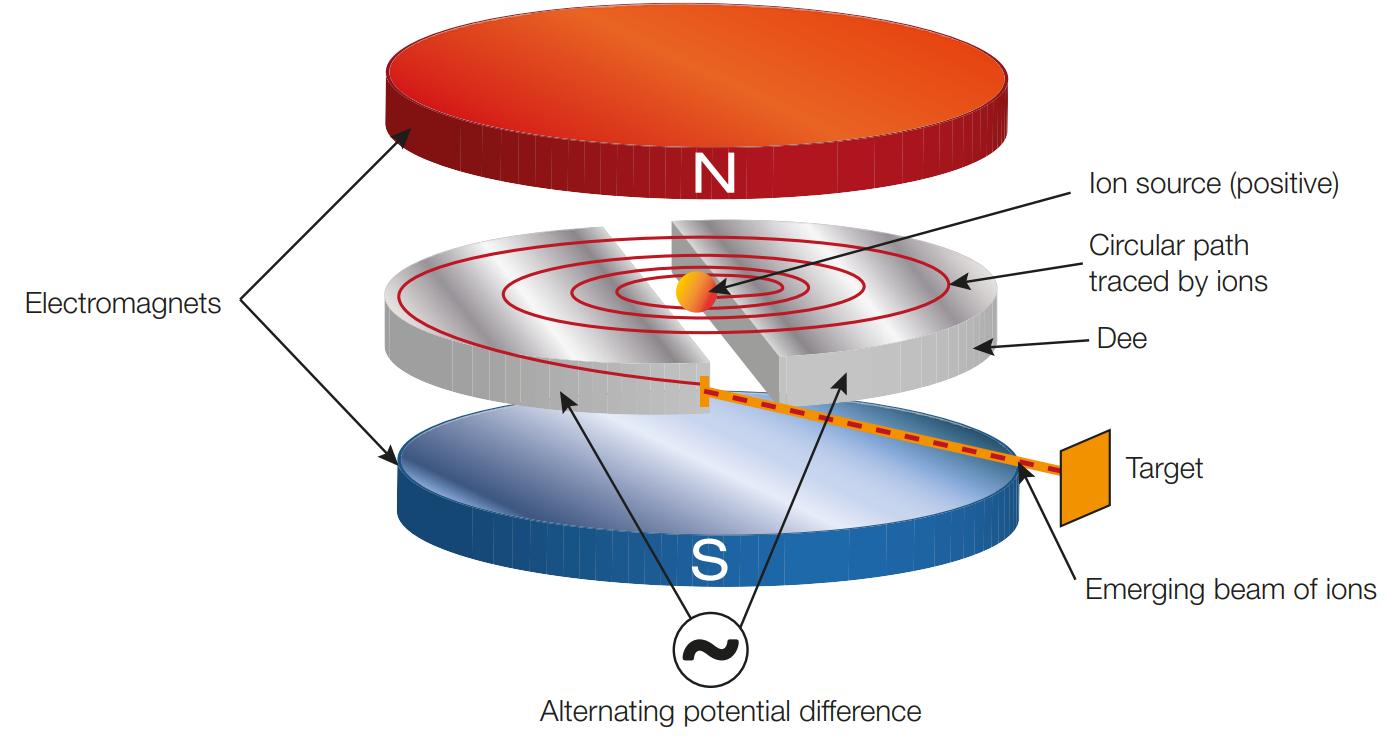
how do cyclotrons utilise electric fields
cyclotron is composed of two hollow D-shaped copper conductors called Dees
the potential difference in the gap between the dees produces a uniform electric field
when the charges enter the electric field they are accellerated as the electric field exerts a force on the charges, due to f=ma, the charges gain speed
the magnetic field created by electromagnets above and below the dees cause the charged particles to move in a semi circular path through the dees so that they return to the electric field
the electric field is reversed when the charges return to the gap so that they once again accellerate accross the electric field
the process repeats many times and the charges eventually exit the cyclotron having accumulated a large amount of kinetic energy and thus speed
the charges do not gain energy while inside the dees as there is no electric field within a hollow conductor
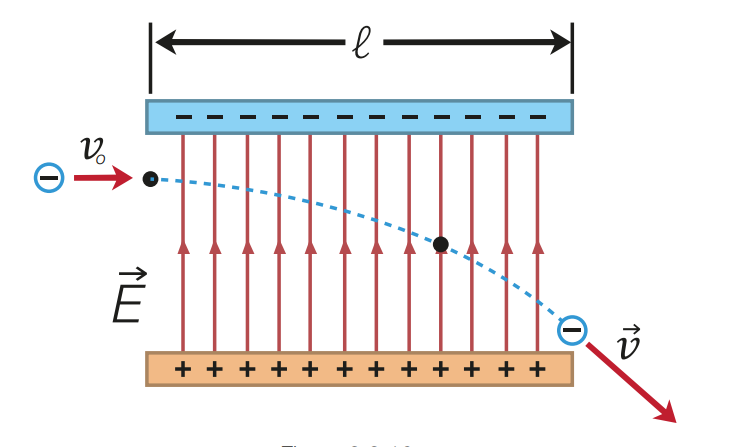
describe the morion of charged particles at an angle to a uniform electric field
consider a negative charge entering a uniform electric charge between two parallel conducting plates
the charge enters in a direction which is perpendicular to the electric field
the electric field exerts a constant force towards the lower plate
the electric field does not exert a force on the charge in the horizontal direction
therefore the component of velocity perpendicular to the electric field remains constant
results in a parabolic path towards lower plate
the magnitude of vertical accelleration of a charge can be calculated using a=(qE)/m
the direction depends on the particle’s charge and the charge of the plates of the conductors