Septal Defects - Left side of Heart
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What is Mitral Stenosis/Atresia?
Thickened mitral orifice & immobile
Small left ventricle (hypoplastic left heart) due to decreased inflow
Left ventricular inflow disturbance type is considered…
Mitral Stenosis or Atresia
What is seen with Mitral Stenosis if aortic atresia is present?
Myocardial thickness is increased
Secondary to increased left ventricular pressure overload
____ chamber view compares placement of mitral valve with slightly apical position of tricuspid valve.
4 [LVOT view may be used too]
Check for mobility of leaflets
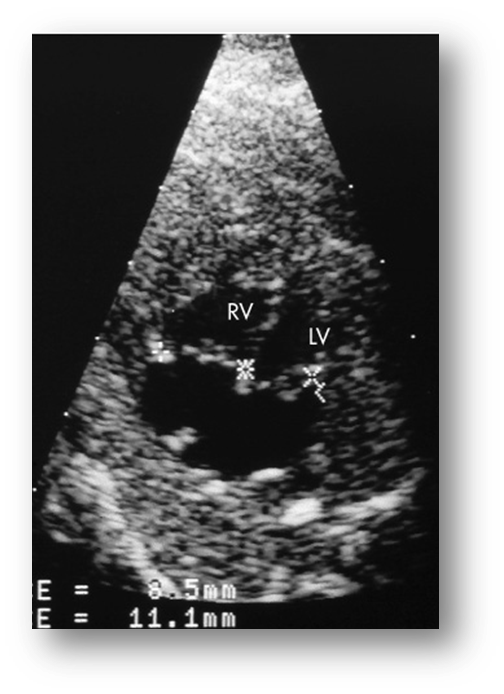
Mitral Stenosis
Left ventricular outflow disturbance type is considered…
Abnormal Aortic Valve
Critical Aortic Stenosis
Aortic valve between LV & Aorta normally has _____ semilunar cusps
3
Semilunar cusps can be seen best in _____ and ______ axis planes.
Long
Short
If development of aortic valve is interrupted: Bicuspids =
2 leaflets with asymmetric cusps
If development of aortic valve is interrupted: Unicuspid =
1 leaflet with central opening & aortic stenosis
What causes a Critical Aortic Stenosis?
Infection or virus
Causing Aortic leaflets to thicken & close prematurely
Critical Aortic Stenosis results in…
Enlarged, dysfunctional LV because LVOT is obstructed
Thin LV walls & bulge into RV
What is an aortic stenosis?
Abnormal development of these cusps, aortic valve results in the thickened domed appearance
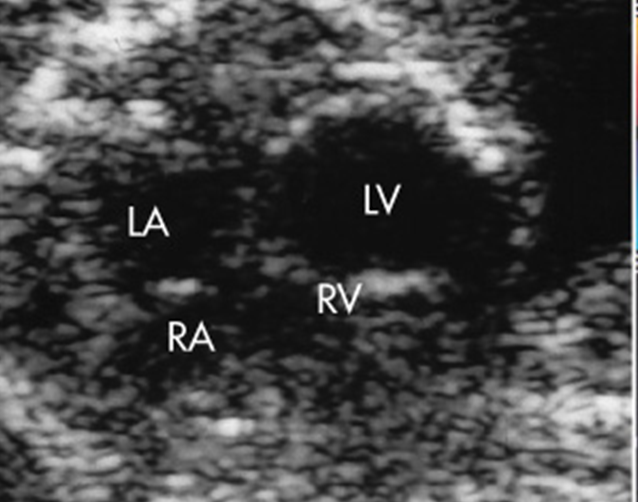
Critical Aortic Stenosis
When a small left ventricle is seen, what should the sonographer suspect?
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
Underdevelopment characteristics
What syndromes are associated with Hypoplastic left heart syndrome?
Coarctation of aorta
Hypoplasia of aortic arch
Autosomal Recessive Traits
What causes Hypoplastic left heart syndrome?
Unknown cause, may be due to decrease perfusion and filling of the left ventricle
What is the prognosis of Hypoplastic left heart syndrome?
Multiple surgeries need to be done and eventually a transplant may be needed to improve the prognosis
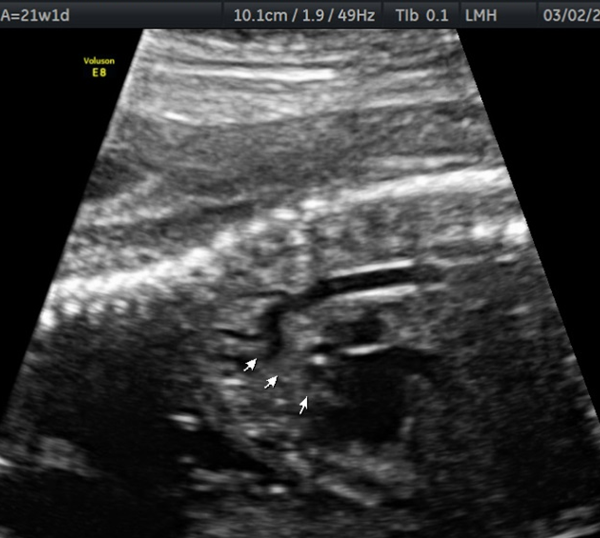
Blockage in Aortic Arch
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
When something is found in the wrong place, what should the sonographer suspect?
Transposition of the Great Vessels
With Transposition of Great Vessels: where does the Aorta arise from?
Right ventricle & supplies systemic circulation with deoxygenated blood
With Transposition of Great Vessels: where does the PA arise from?
Left ventricle & supplies the lungs with oxygenated blood
With Transposition of Great Vessels, vessels do NOT ________, they run ______ to each other.
Crisscross
Parallel
What is the best way to view Transposition of Great Vessels?
Parasternal short-axis
4 chamber view
What abnormalities are associated with Transposition of Great Vessels?
Pulmonary stenosis
Underdevelopment of RT and LT ventricle
Valve anomalies
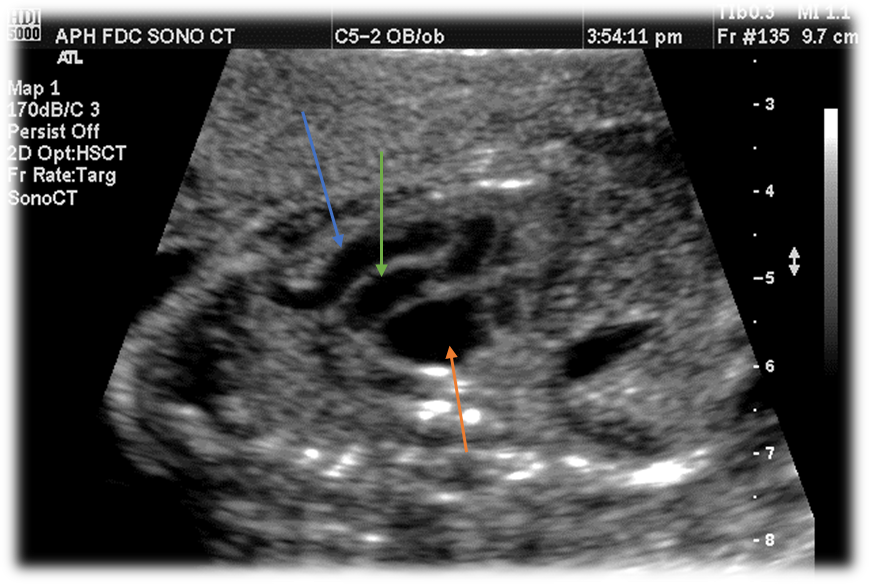
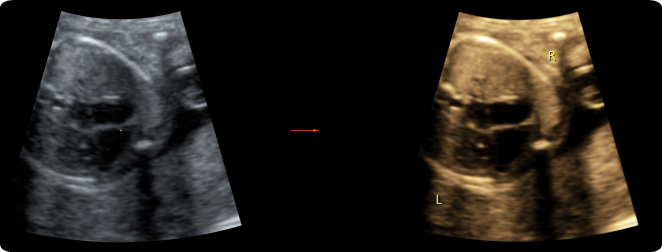
Label this image.
Blue - Aorta
Green - Pulmonary Artery
Orange - Left atrium
With Transposition of Great Vessels, the ____ ____ ____ may appear normal.
4-chamber view
Will see the vessels run parallel when we are attempting to obtain our 3-vessel view
What is Truncus Arteriosus?
Single great artery where the pulmonary trunk, aorta, coronary arteries arises from the same spot
Single large truncal artery arising from the base of the heart
How does Truncus Arteriosus develop?
Early in development, failure of the bulbus to divide into the great arteries causing that single vessel
What anomalies are associated with Truncus Arteriosus?
Mitral atresia
ASD
VSD
Univentricular heart
Aortic arch anomaly
What is the US findings of Truncus Arteriosus?
Abnormal large single vessel
Multiple cusps within great artery
May see hydrops, CHF, and effusions
What is the prognosis for Truncus Arteriosus?
Poor. Hydrops or pericardial fluid —> CHF
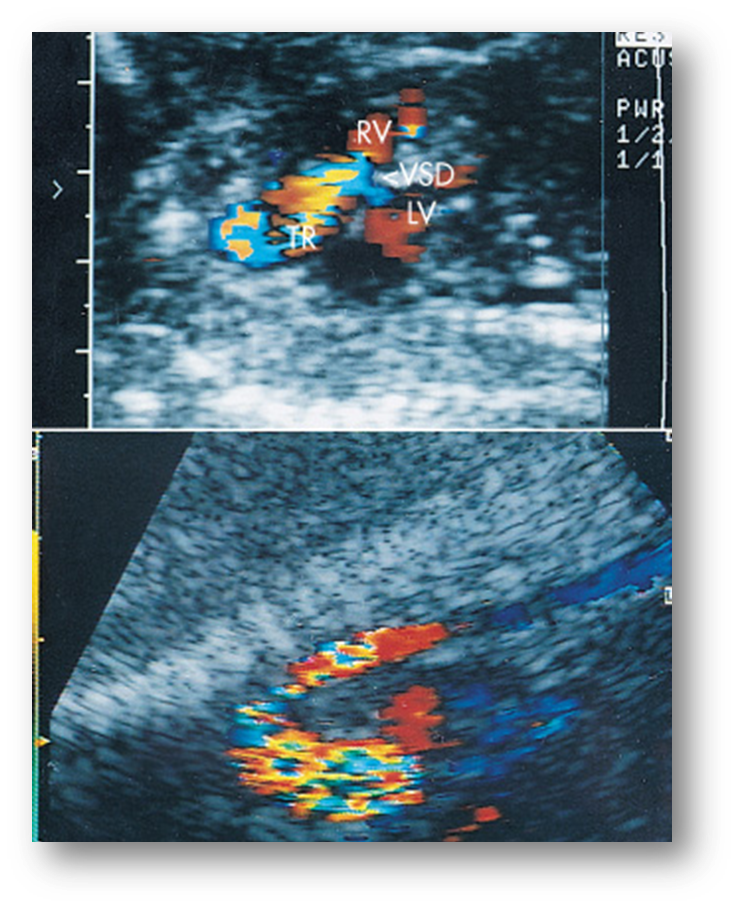
Truncus Arteriosus
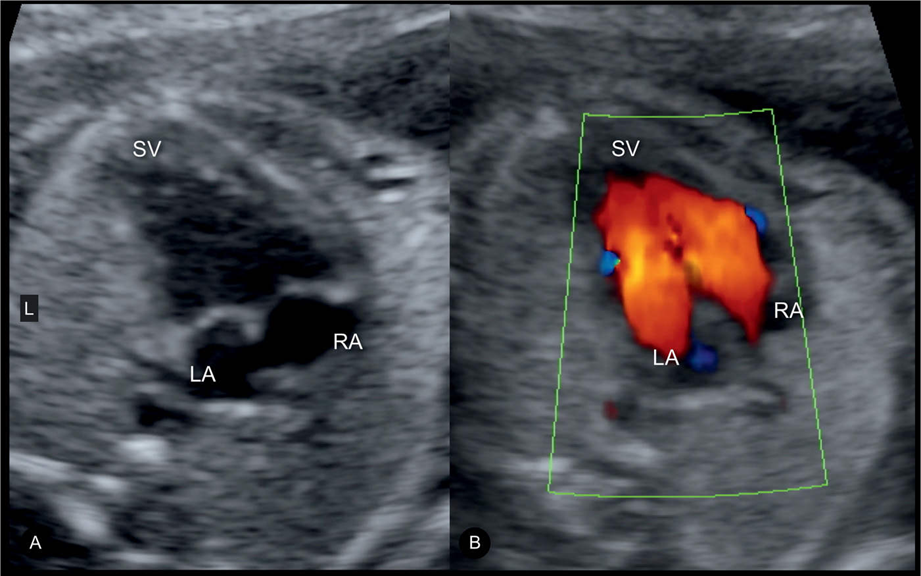
Single ventricle
What view is a single ventricle best evaluated in?
4-chamber
What is present and absent in a heart that only has one ventricle?
One ventricle
Two atrium
Mitral and Tricuspid valves
What causes a single ventricle to form?
A VSD
What is Coarctation of the Aorta?
Discrete shelf like lesion present in aortic arch, at isthmus or more commonly ductal insertion near left subclavian artery
____% of cases are associated with other intracardiac malformations
90 [Type 1]
Characteristics describing Type 1 of Coarctation of the Aorta.
Most common
Focal narrowing at or just distal to ductus arteriosus
Post ductal coarctation
Characteristics describing Type 2 of Coarctation of the Aorta.
Narrowing is proximal to ductus arteriosus
Preductal coarctation
Ductal insertion near left subclavian
What are the US findings seen with Coarctation of the Aorta?
Left ventricle smaller than right ventricle
Bicuspid aortic valve, narrow area of the aorta
What anomalies are associated with Coarctation of the Aorta?
Aortic stenosis
Aortic insufficiency
VSDs
TPOGA
Truncus arteriosus
Double outlet right ventricle
Turners Syndrome
With Coarctation of the Aorta, a long segment of narrowing is associated with a ______.
VSD
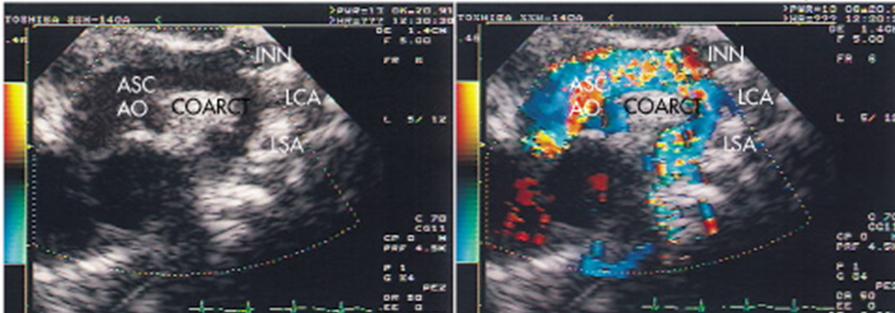
Coarctation of the Aorta
When an enlarged heart is seen, what should the sonographer suspect?
Cardiomegaly
What may cause the fetal heart to enlarge?
Hydrops
Increased flow
Intrinsic cardiac anomaly
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiac tumor

Cardiomegaly
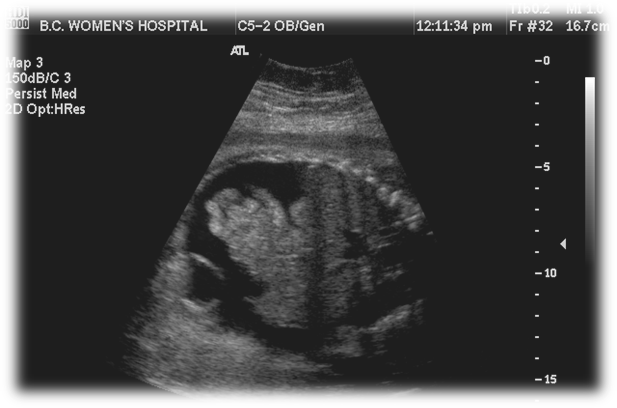
Fetal Hydrops
What is a Rhabdomyoma?
Most common [58%], benign & isolated cardiac mass
Very unusual
What is the best plane to evaluate a Rhabdomyoma?
4-chamber
There may be multiple
May involve the septum
A Rhabdomyoma mass is associated with…
Tuberous sclerosis
Regurgitation or obstruction due to placement of mass
Large = symptomatic & causes obstruction of outflow tract
What is the prognosis of a Rhabdomyoma tumor?
Depends on: size, location, and type
Leads to CHF, Pericardial fluid, Hydrops & possible Death
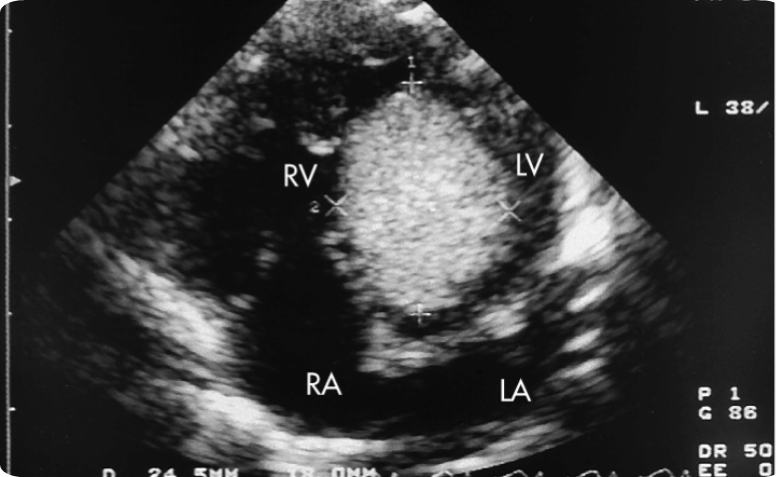
Rhabdomyoma
What is Ectopic Cordis?
Abnormal development of primitive heart OUTSIDE the embryonic disk
Stemming from a ventricle wall defect
What anomalies are associated with Ectopic Cordis?
Facial defects
Skeletal defects
Ventral wall defects
Cardiac anomalies
CNS malformations
What specific cardiac anomalies are associated with Ectopic Cordis?
Tetralogy of Fallot
Transposition of great vessels
What specific CNS malformations are associated with Ectopic Cordis?
Meningocele
Cephalocele
What is the prognosis for Ectopic Cordis?
Poor
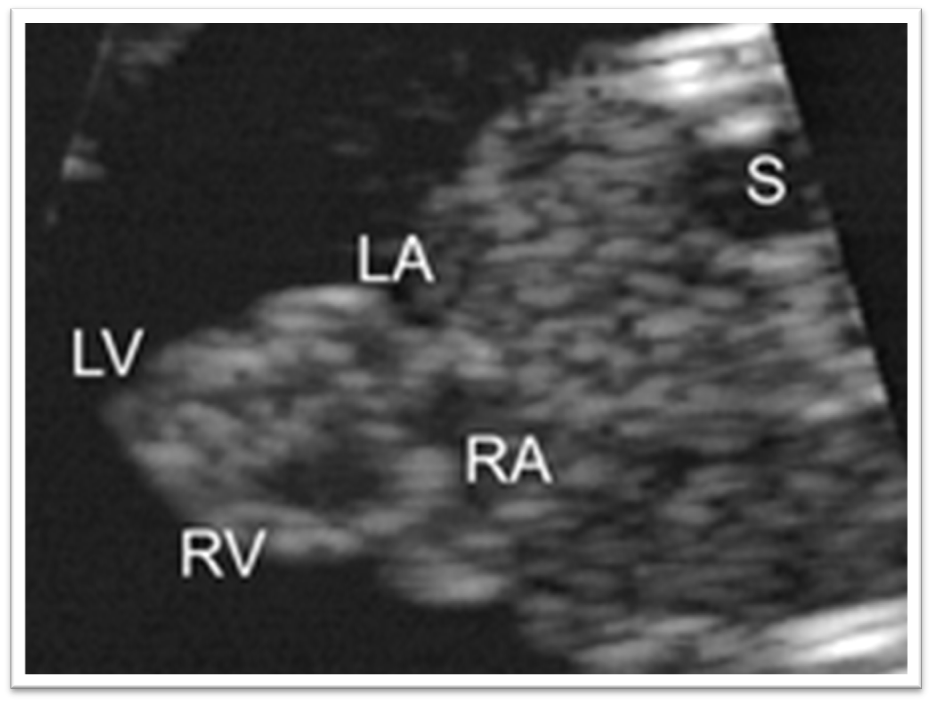
Ectopic Cordis
What are Dysrhythmias?
Fetal heart undergoes multiple changes
Progression of cardiac electrical system _________ to cause normal sinus rhythm
Matures
It is not uncommon to see decelerations in HR or even a pause, but what other factors may be causing this?
Fetus may be lying on umbilical cord
Transducer pressure is too great
What may be done to help the fetal heart resume normal rhythm?
Give time to recover
Change position of mother
Release transducer pressure