exam 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/314
Earn XP
Description and Tags
more exam like questions: https://quizlet.com/320246285/micro-exam-chapter-3-4-flash-cards/
Last updated 9:59 PM on 9/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
315 Terms
1
New cards
microbiology
study of organisms too small to be seen w the human eye
2
New cards
what are the sub disciplines of microbiology?
* bacteriology
* mycology
* food microbiology
* environmental microbiology
* forensic microbiology
* virology
* parasitology
* mycology
* food microbiology
* environmental microbiology
* forensic microbiology
* virology
* parasitology
3
New cards
when was microbiology born and by who?
* 1674
* anthony van leeuwenhoek saw bacteria/protozoa with his homemade microscope. called organisms “animacules”. used lens to peer into a drop of lake water.
* robert hooke was the first to see a microorganism. observed “microscopical mushroom”. later identified as common bread mold.
* anthony van leeuwenhoek saw bacteria/protozoa with his homemade microscope. called organisms “animacules”. used lens to peer into a drop of lake water.
* robert hooke was the first to see a microorganism. observed “microscopical mushroom”. later identified as common bread mold.
4
New cards
theory of spontaneous generation
* theory of how microorganisms originated
* “organisms can arise spontaneously from non living matter”
* “organisms can arise spontaneously from non living matter”
5
New cards
who were the 3 detractors of the theory of spontaneous generation?
* francesco redo
* louis pasteur
* john tyndall
* louis pasteur
* john tyndall
6
New cards
louis pasteur
* developed the swan necked flask
* father of modern microbiology
* showed air is filled w/ microorganisms in 1861
* proved by filtering air through a cotton plug, trapping microorganisms
* identified organisms in cotton as same organisms contaminating infusions
* father of modern microbiology
* showed air is filled w/ microorganisms in 1861
* proved by filtering air through a cotton plug, trapping microorganisms
* identified organisms in cotton as same organisms contaminating infusions
7
New cards
ferdinand cohn
german botanist that discovered endospores in 1876
8
New cards
robert koch
established the role of endospores in disease transmission
9
New cards
what was anthrax caused by?
bacillus anthracis
10
New cards
microbes
* responsible for the production of oxygen and nitrogen
* key elements for all living organisms
* key elements for all living organisms
11
New cards
why are microorganisms decomposers?
bc they are responsible for the breakdown of wide variety of materials
12
New cards
bioremediation
use organisms to degrade environmental waste
* clean up oil spills
* treat radioactive waste
* degrade PCBs, DDT
* clean up oil spills
* treat radioactive waste
* degrade PCBs, DDT
13
New cards
what products can bacteria synthesize?
* ethanol
* pesticides
* antibiotics
* dietary amino acids
* pesticides
* antibiotics
* dietary amino acids
14
New cards
genetic engineering
introduce genes of one organisms into an unrelated organism to confer new properties on the organism
15
New cards
golden age of microbiology
* 1854 - 1918
* time of great interest in the study of microorganisms
* lead to the initiation of prevention and treatment of disease
* time of great interest in the study of microorganisms
* lead to the initiation of prevention and treatment of disease
16
New cards
what are factors associated w emerging diseases?
* changing lifestyles
* genetic changes in organisms
* genetic changes in organisms
17
New cards
reasons for resurgence of old diseases
* increased travel
* unvaccinated individuals susceptible to infection
* increase in immune compromised population
* unvaccinated individuals susceptible to infection
* increase in immune compromised population
18
New cards
example of chronic disease caused by microbes
gastric ulcers (H.pylori)
19
New cards
why are host-bacterial interactions beneficial?
* simulate immune system
* outnumber cells in the body 10:1
* keep disease causing organisms from breaching hose defenses
* estimated 10k species of bacteria reside in and on the body
* outnumber cells in the body 10:1
* keep disease causing organisms from breaching hose defenses
* estimated 10k species of bacteria reside in and on the body
20
New cards
why are microorganisms a great model to study?
* metabolism same as higher forms of life
* genetic properties mimic other organisms
* building blocks of macromolecules same as other life forms
* genetic properties mimic other organisms
* building blocks of macromolecules same as other life forms
21
New cards
what is a domain?
a group in which all living things (organisms) can be classifies in
22
New cards
what are the 3 domains?
* bacteria
* archaea
* eukarya
* archaea
* eukarya
23
New cards
characteristics of bacteria
* unicellular
* prokaryotic
* lacks nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
* has peptidoglycan
* prokaryotic
* lacks nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
* has peptidoglycan
24
New cards
characteristics or archaea
* unicellular
* prokaryotic
* can live in extreme environmental conditions
* lacks peptidoglycan
* prokaryotic
* can live in extreme environmental conditions
* lacks peptidoglycan
25
New cards
characteristics of eukarya
* true nucleus and membrane bound organelles
* contains chromosomes
* algae can be unicellular or multicellular
* protozoa is unicellular (protists)
* fungi can be uni or multi
* helminths can be multi or parasitic
* contains chromosomes
* algae can be unicellular or multicellular
* protozoa is unicellular (protists)
* fungi can be uni or multi
* helminths can be multi or parasitic
26
New cards
infectious agents (non-living)
* viruses
* viroids
* prions
* usually consist of only a few molecules found i living cells
* called agents not organisms
* viroids
* prions
* usually consist of only a few molecules found i living cells
* called agents not organisms
27
New cards
prokaryotes
* pre - nucleus
* “pro” “karyote”
* “pro” “karyote”
28
New cards
bacteria and archaea microbial world
* both single celled organisms
* contain no membrane bound nucleus or organelles
* DNA stores in nucleoid (clump of DNA)
* cytoplasm is surrounded by rigid cell wall
* contain no membrane bound nucleus or organelles
* DNA stores in nucleoid (clump of DNA)
* cytoplasm is surrounded by rigid cell wall
29
New cards
eukaryote
true nucleus
“eu” “karyote”
“eu” “karyote”
30
New cards
eukarya microbial world
* organisms that contain membrane bound nucleus
* contain internal organelles
* makes organism more complex
* ex: mitochondria
* may be single/uni or multicellular
* contain internal organelles
* makes organism more complex
* ex: mitochondria
* may be single/uni or multicellular
31
New cards
domain bacteria
* common in human infection, widely diverse
* prominent features:
* specific shapes (rod, spherical, spiral)
* rigid cell walls, responsible for cell shape and contain peptidoglycan
* multiply by binary fission, one cell divides into two and cells are genetically identical to the first
* some bacteria are motile and move by means of flagella
* prominent features:
* specific shapes (rod, spherical, spiral)
* rigid cell walls, responsible for cell shape and contain peptidoglycan
* multiply by binary fission, one cell divides into two and cells are genetically identical to the first
* some bacteria are motile and move by means of flagella
32
New cards
domain archaea
* cell wall lacks peptidoglycan
* same shapes as bacteria
* multiplies by binary fission
* moves by means of flagellum(archaellum)
* found in extreme temperatures and environmental conditions (ex:high conc. of salt)
* same shapes as bacteria
* multiplies by binary fission
* moves by means of flagellum(archaellum)
* found in extreme temperatures and environmental conditions (ex:high conc. of salt)
33
New cards
domain eukarya - algae
* diverse group that includes single and multicellular organisms
* all contain chloroplasts
* structure used to absorb light to be converted into energy
* usually found near surface waters
* contain rigid cell walls
* distinct from bacterial cell walls (contain polysaccharides and glycoproteins)
* all contain chloroplasts
* structure used to absorb light to be converted into energy
* usually found near surface waters
* contain rigid cell walls
* distinct from bacterial cell walls (contain polysaccharides and glycoproteins)
34
New cards
domain eukarya - fungi
* diverse single and multicellular organisms
* single/uni cellular = yeast
* multicellular = molds
* gain energy from organic materials
* decomposers
* mostly found on land
* single/uni cellular = yeast
* multicellular = molds
* gain energy from organic materials
* decomposers
* mostly found on land
35
New cards
domain eukarya - protozoa
* single/uni cellular organisms
* found in water and on land
* complex
* larger than prokaryotes
* lacks rigid cell wall
* gains energy from organic matter
* most are motile
* means of motility is diverse and a feature of classification
* found in water and on land
* complex
* larger than prokaryotes
* lacks rigid cell wall
* gains energy from organic matter
* most are motile
* means of motility is diverse and a feature of classification
36
New cards
domain eukarya - helminths
* multicellular parasites
* derive nutrients from host organisms
* include round and tapeworms
* derive nutrients from host organisms
* include round and tapeworms
37
New cards
nomenclature
* binomial naming system
* first word is genus and always capitalized, often abbreviated
* second word is species, not capitalized
* ex: E. coli
* when writing out full name, its always italicized or underlined
* first word is genus and always capitalized, often abbreviated
* second word is species, not capitalized
* ex: E. coli
* when writing out full name, its always italicized or underlined
38
New cards
viruses
* contain certain protein coat surrounding nucleic acid
* essentially protein bag of nucleic acid
* viruses termed ‘obligate intracellular parasites”
* must have host machinery to replicate
* inactive outside of host
* all forms of life can be infected by viruses
* frequently kill hosts
* some live harmoniously with host
* essentially protein bag of nucleic acid
* viruses termed ‘obligate intracellular parasites”
* must have host machinery to replicate
* inactive outside of host
* all forms of life can be infected by viruses
* frequently kill hosts
* some live harmoniously with host
39
New cards
viroids
* smaller and simpler than viruses but require host cell for replication
* consist of a single short piece of RNA
* contain no protective protein coat
* generally cause diseases in plants
* consist of a single short piece of RNA
* contain no protective protein coat
* generally cause diseases in plants
40
New cards
prions
* infectious proteins that have no nucleic acid
* responsible for 6 neurodegenerative diseases
* Animal disease
* scrapie in sheep
* mad cow disease in cattle
* Human disease
* kuru (contaminated brain tissue, found amongst population that practices cannibalism)
* creutzfeldt jakob (brain tissue)
* responsible for 6 neurodegenerative diseases
* Animal disease
* scrapie in sheep
* mad cow disease in cattle
* Human disease
* kuru (contaminated brain tissue, found amongst population that practices cannibalism)
* creutzfeldt jakob (brain tissue)
41
New cards
size of microbial world
* large range
* smalles virus approx. 1/1,000,000th size of largest eukaryotic cell
* basic unit of length is a meter (m) and all other units are fractions of a meter
* smalles virus approx. 1/1,000,000th size of largest eukaryotic cell
* basic unit of length is a meter (m) and all other units are fractions of a meter
42
New cards
light microscopy
* light passes through specimen, then through series of magnifying lenses
* most common and easiest to use, bright-field microscope
* most common and easiest to use, bright-field microscope
43
New cards
magnification of light microscopy
* microscope has 2 magnifying lenses
* ocular lens and objective lens
* called compound microscope
* lenses combine to enlarge objects
* 10x(100x) = 1000x
* ocular lens and objective lens
* called compound microscope
* lenses combine to enlarge objects
* 10x(100x) = 1000x
44
New cards
resolution of light microscopy
* usefulness of microscope depends on its ability to resolve two objects that are very close together
* enhanced with lenses of higher magnification (100x) and by the use of immersion oil
* oil reduces light refraction (bending or light)
* enhanced with lenses of higher magnification (100x) and by the use of immersion oil
* oil reduces light refraction (bending or light)
45
New cards
contrast of light microscopy
* reflects the number of visible shades in a specimen
* higher contrast achieved for microscopy through specimen staining
* light microscopes that increase contrast
* phase contrast
* interference
* dark-field
* fluorescence
* confocal scanning laser
* higher contrast achieved for microscopy through specimen staining
* light microscopes that increase contrast
* phase contrast
* interference
* dark-field
* fluorescence
* confocal scanning laser
46
New cards
phase contrast microscope
* amplifies differences between refractive indexes of cells and surrounding medium
* uses set of rings and diaphragms to achieve resolution
* uses set of rings and diaphragms to achieve resolution
47
New cards
fluorescence microscope
* used to observe organisms that are naturally fluorescent or are tagged with fluorescent dye
* fluorescent molecule absorbs ultraviolet light and emits visible light
* image fluoresces on dark background
* fluorescent molecule absorbs ultraviolet light and emits visible light
* image fluoresces on dark background
48
New cards
confocal scanning laser microscope
* constructs 3D image of thicker structures
* provides detailed sectional views of internal structures of an intact organism
* provides detailed sectional views of internal structures of an intact organism
49
New cards
electron microscope
* uses electromagnetic lenses, electrons and fluorescent screen to produce image
* resolution increased 1000 fold over brightfield microscope
* magnification increased to 100,000x
* 2 types of electron microscopes
* transmission- internal structures
* scanning- surface
* resolution increased 1000 fold over brightfield microscope
* magnification increased to 100,000x
* 2 types of electron microscopes
* transmission- internal structures
* scanning- surface
50
New cards
transmission electron microscope (TEM)
* used to observe fine detail
* directs beam of electrons of specimen
* electrons pass through or scatter at surface
* shows dark and light areas
* specimen preparation through
* thin sectioning
* freeze fracturing or freeze etching
* directs beam of electrons of specimen
* electrons pass through or scatter at surface
* shows dark and light areas
* specimen preparation through
* thin sectioning
* freeze fracturing or freeze etching
51
New cards
scanning electron microscope (SEM)
* used to observe surface detail
* beam of electrons scan surface of specimen
* specimen coated with metal, usually gold
* electrons are released and reflected into viewing chamber
* some atomic microscopes capable of seeing single atoms
* beam of electrons scan surface of specimen
* specimen coated with metal, usually gold
* electrons are released and reflected into viewing chamber
* some atomic microscopes capable of seeing single atoms
52
New cards
dyes and staining
* cells are frequently stained to observe organisms
* dyes carry + or - charge
* molecules bind to certain cell structures
* dyes divided into basic or acidic based on charge
* dyes carry + or - charge
* molecules bind to certain cell structures
* dyes divided into basic or acidic based on charge
53
New cards
basic dyes
* carry a + charge and bond to cell structures that contain - charge
* commonly stain the cell
* more commonly used than acidic dyes
* common basic dyes:
* methylene blue
* crystal violet
* safranin
* malachite green
* commonly stain the cell
* more commonly used than acidic dyes
* common basic dyes:
* methylene blue
* crystal violet
* safranin
* malachite green
54
New cards
acidic dyes
* carry a - charge and repelled by cell structures that contain - charge
* commonly stain the BACKGROUND
* commonly stain the BACKGROUND
55
New cards
staining procedures
* simple stain uses one basic stain to stain the cell
* allows for increased contrast btwn cell and background
* all cells stained the same color
* no differentiation btwn cell types
* allows for increased contrast btwn cell and background
* all cells stained the same color
* no differentiation btwn cell types
56
New cards
differential stains
* used to distinguish one bacterial group from another
* uses a series of reagents
* 2 most common differential stains:
* gram stain
* acid fast stain
* uses a series of reagents
* 2 most common differential stains:
* gram stain
* acid fast stain
57
New cards
gram stain
* most widely used procedure for staining bacteria
* developed over a century ago- Dr. Hans Christian Gram
* bacteria separated into 2 groups:
* gram +, stained purple/blue
* gram -, stained red/pink
* developed over a century ago- Dr. Hans Christian Gram
* bacteria separated into 2 groups:
* gram +, stained purple/blue
* gram -, stained red/pink
58
New cards
4 reagents in gram stain
* primary stain
* crystal violet: stains the cell
* mordant
* grams iodine: holds primary dye to cell
* decolorizer
* removes primary dye from gram - cell
* counter/secondary stain
* recolors cells that lose stain through decolorization
* crystal violet: stains the cell
* mordant
* grams iodine: holds primary dye to cell
* decolorizer
* removes primary dye from gram - cell
* counter/secondary stain
* recolors cells that lose stain through decolorization
59
New cards
acid fast stain
* stains organisms that resist conventional staining
* used to stain members of genus mycobacterium (TB, hansen’s disease)
* high lipid concentration in cell wall prevents uptake of dye therefore harsh methods are needed to stain these organisms
* once stained, these cells are very resistant against decolorizers
* used to stain members of genus mycobacterium (TB, hansen’s disease)
* high lipid concentration in cell wall prevents uptake of dye therefore harsh methods are needed to stain these organisms
* once stained, these cells are very resistant against decolorizers
60
New cards
capsule stain
* example of negative stain: india ink
* allows capsule to stand out around organism
* allows capsule to stand out around organism
61
New cards
endospore stain
* staining enhances endospore
* uses heat to facilitate staining
* uses heat to facilitate staining
62
New cards
flagella stain
* staining increases diameter of flagella
* makes it more visible
* makes it more visible
63
New cards
shapes of prokaryotic cells
* coccus
* spherical
* bacillus
* rod or cylinder, not to be confused with genus
* coccobacillus
* short, round rod
* vibrio
* curved rod
* spirillum
* spiral
* spirochete
* helical
* pleomorphic
* ability to vary in shape
\
* spherical
* bacillus
* rod or cylinder, not to be confused with genus
* coccobacillus
* short, round rod
* vibrio
* curved rod
* spirillum
* spiral
* spirochete
* helical
* pleomorphic
* ability to vary in shape
\
64
New cards
morphology of prokaryotic cells
* division along a single plane that may result in pairs or chains of cells
* pairs: diplococci
* chains: streptococii
* division along two or three perpendicular planes from cuboidal packets
* division along several random planes form clusters
* pairs: diplococci
* chains: streptococii
* division along two or three perpendicular planes from cuboidal packets
* division along several random planes form clusters
65
New cards
multicellular associations
* ex: myxobacteria
* when conditions are favorable, these organisms secrete a slime layer that allows the formation of a swarm of cells
* allows for release of enzymes which degrade organic material
* in the absence of water or nutrients the cells come together to form a fruiting body
* when conditions are favorable, these organisms secrete a slime layer that allows the formation of a swarm of cells
* allows for release of enzymes which degrade organic material
* in the absence of water or nutrients the cells come together to form a fruiting body
66
New cards
biofilms
* cells within biofilms alter their activities when a critical number is reached (staphylococcus and pseudomonas); dental plaque
67
New cards
cytoplasmic membrane
* delicate thin fluid structure surrounding cytoplasm of cell
* defines boundary
* serves as semipermeable barrier
* barrier btwn internal and external environment
* defines boundary
* serves as semipermeable barrier
* barrier btwn internal and external environment
68
New cards
what is the structure of a cytoplasmic membrane
* a lipid bilayer w/ embedded proteins
* bilayers consists of two opposing leaflets
* leaflets composed of phospholipids, each contain a hydrophilic phosphate head (- charge) and hydrophobic fatty acid tail
* bilayers consists of two opposing leaflets
* leaflets composed of phospholipids, each contain a hydrophilic phosphate head (- charge) and hydrophobic fatty acid tail
69
New cards
proteins embedded in a cytoplasmic membrane
* proteins fxn as receptors and transport gates
* integral proteins- span membrane
* peripheral proteins- on periphery either inside or outside of membrane
* provides mechanism to sense surroundings
* proteins are not stationary
* constantly changing position, called fluid mosaic model
* integral proteins- span membrane
* peripheral proteins- on periphery either inside or outside of membrane
* provides mechanism to sense surroundings
* proteins are not stationary
* constantly changing position, called fluid mosaic model
70
New cards
is the cytoplasmic membrane is selectively permeable? (T/F)
T
71
New cards
simple diffusion
* process by which molecules moved freely across the cytoplasmic membrane down a concentration gradient (high to low)
* water, certain gasses, small alcohols, small fatty acids and uncharged molecules pass through via simple diffusion
* water, certain gasses, small alcohols, small fatty acids and uncharged molecules pass through via simple diffusion
72
New cards
osmosis
* ability of water to flow freely across the semi permeable cytoplasmic membrane, usually through trans-membrane channels
* water flows to equalize solute concentrations inside and outside the cell
* water flows to equalize solute concentrations inside and outside the cell
73
New cards
directed movement in a cytoplasmic membrane
* movement of many molecules directed by transport systems
* transport systems employ highly selective proteins, transport proteins
* transport systems employ highly selective proteins, transport proteins
74
New cards
transport protein- cytoplasmic membrane
* permeases or carriers
* these proteins span membrane
* single carrier gen transports specific type molecules
* most transport proteins are produced in a response to need
* these proteins span membrane
* single carrier gen transports specific type molecules
* most transport proteins are produced in a response to need
75
New cards
transport systems in cytoplasmic membrane
* facilitated diffusion
* active transport
* group translocation
* active transport
* group translocation
76
New cards
facilitated diffusion
* rarely used by prokaryotes
* moves compounds across membrane, exploiting a concentration gradient
* via protein channel and carrier proteins
* moves compounds across membrane, exploiting a concentration gradient
* via protein channel and carrier proteins
77
New cards
active transport
* moves compound against a concentration
* requires energy, "going up-hill”
* requires energy, "going up-hill”
78
New cards
2 primary mechanisms in active transport
* those that use proton motive force
* MFS (major facilitator superfamily): as proton is brought in, another substance is either brought in or pumped out (ex: efflux pumps)
* those that use ATP
* require ATP as energy source
* binding proteins residing outside of the cytoplasmic membrane scavenge and deliver a given molecule to a specific transport complex within the membrane
* MFS (major facilitator superfamily): as proton is brought in, another substance is either brought in or pumped out (ex: efflux pumps)
* those that use ATP
* require ATP as energy source
* binding proteins residing outside of the cytoplasmic membrane scavenge and deliver a given molecule to a specific transport complex within the membrane
79
New cards
proton motive force- cytoplasmic membrane
* transporters allow protons into cell
* protons either bring in or expel other substances
* ex: efflux pumps used in antimicrobial resistance
* protons either bring in or expel other substances
* ex: efflux pumps used in antimicrobial resistance
80
New cards
ATP binding cassette system - CM
* use binding proteins to scavenge and deliver molecules to transport complex
* requires energy in form of ATP
* ex: maltose transport
* requires energy in form of ATP
* ex: maltose transport
81
New cards
group translocation- CM
* transport mechanism that chemically alters molecule during passage
* uptake of molecules does not alter concentration gradient
* uptake of molecules does not alter concentration gradient
82
New cards
phosphotransferase system- CM
* example of group transort system
* phosphorylates sugar (ex: glucose) molecule during transport
* phosphorylation changes molecule and therefore doesn’t change sugar balance across the membrane
* energy expended to phosphorylate the sugar is later regained (glycolysis)
* phosphorylates sugar (ex: glucose) molecule during transport
* phosphorylation changes molecule and therefore doesn’t change sugar balance across the membrane
* energy expended to phosphorylate the sugar is later regained (glycolysis)
83
New cards
secretion- CM
* primary mechanism used to secrete proteins synthesized by the cell
* recognizes “signal sequence”
* recognizes “signal sequence”
84
New cards
signal sequence
* serves as a tag marking those proteins destines for secretion
* signal sequence removed during process of secretion
* signal sequence removed during process of secretion
85
New cards
bacterial cell wall
* rigid structure
* surrounds cytoplasmic membrane
* determines shape of bacteria
* holds cell together
* prevents cell from bursting
* unique chemical structure
* distinguishes gram + from gram -
* surrounds cytoplasmic membrane
* determines shape of bacteria
* holds cell together
* prevents cell from bursting
* unique chemical structure
* distinguishes gram + from gram -
86
New cards
rigidity of cell wall
* due to peptidoglycan (PTG)
* only found in bacteria
* only found in bacteria
87
New cards
basic structure of peptidoglycan
* alternating series of two subunits
* NAG and NAM
* joined subunits form glycan chain
* glycan chain held together by string of four amino acids
* tetrapeptide chain
\- joined directly in gram + bacteria
\-joined indirectly by peptide interbridge in gram + bacteria
* NAG and NAM
* joined subunits form glycan chain
* glycan chain held together by string of four amino acids
* tetrapeptide chain
\- joined directly in gram + bacteria
\-joined indirectly by peptide interbridge in gram + bacteria
88
New cards
gram + cell wall
* relatively thick layer of PTG
* PTG is permeable to numerous substances
* (lipo)teichoic acid component of PTG
* gives cell - charge
* antigenic and induces immune responses that are species specific
* lipoteichoic acids are linked to cytoplasmic membrane
* PTG is permeable to numerous substances
* (lipo)teichoic acid component of PTG
* gives cell - charge
* antigenic and induces immune responses that are species specific
* lipoteichoic acids are linked to cytoplasmic membrane
89
New cards
gram - cell wall
* more complex than gram +
* only contains thin layer of PTG
* PTG sandwiched btwn outer membrane and cytoplasmic membrane
* region btwn outer membrane and cytoplasmic membrane is called periplasm
* most secreted proteins contained here
* proteins of ABC transport system located here
* only contains thin layer of PTG
* PTG sandwiched btwn outer membrane and cytoplasmic membrane
* region btwn outer membrane and cytoplasmic membrane is called periplasm
* most secreted proteins contained here
* proteins of ABC transport system located here
90
New cards
outer membrane- gram -
* constructed of lipid bilayer
* outer leaflet made of lipopolysaccharides
* outer membrane called the lipopolysaccharide layer or LPS
* LPS serves as barrier to a larger # of molecules
* small molecules or ions pass through channels called porins
* outer leaflet made of lipopolysaccharides
* outer membrane called the lipopolysaccharide layer or LPS
* LPS serves as barrier to a larger # of molecules
* small molecules or ions pass through channels called porins
91
New cards
what are the portions of LPS medically significant?
* o specific polysaccharide side chain
* lipid A
* lipid A
92
New cards
o specific polysaccharide side chain- outer membrane, gram -
* directed away from membrane
* opposite location of lipid A
* used to identify certain species or strains
* opposite location of lipid A
* used to identify certain species or strains
93
New cards
lipid A- outer membrane (gram -)
* portion that anchors LPS molecule in lipid bilayer
* plays role in recognition of infection (endotoxin)
* molecule present w/ gram - infection of bloodstream
* plays role in recognition of infection (endotoxin)
* molecule present w/ gram - infection of bloodstream
94
New cards
PTG as a target- cell wall
* many antimicrobials interfere w/ the synthesis of PTG
* examples include penicillin and lysozyme
* produced in many body fluids (tears/saliva)
* breaks bond linking NAG and NAM
* destroys structural integrity of cell wall
* examples include penicillin and lysozyme
* produced in many body fluids (tears/saliva)
* breaks bond linking NAG and NAM
* destroys structural integrity of cell wall
95
New cards
penicillin- cell wall
* binds proteins involved in cell wall synthesis
* bind to and inhibit enzymes involved in cell wall synthesis (cross linking of peptidoglycan)
* more effective against gram + bacterium
* outer membrane of gram - prevents medication from reaching site of action
* derivatives produced to protect against gram -
\
* bind to and inhibit enzymes involved in cell wall synthesis (cross linking of peptidoglycan)
* more effective against gram + bacterium
* outer membrane of gram - prevents medication from reaching site of action
* derivatives produced to protect against gram -
\
96
New cards
cell wall of gram +
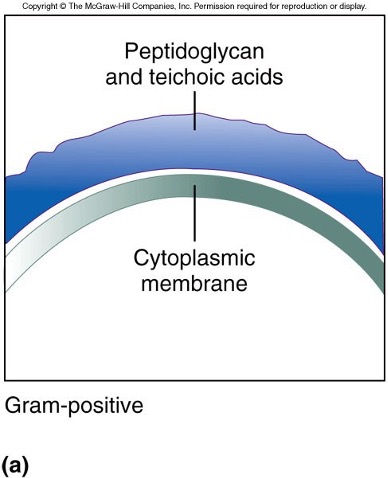
97
New cards
cell wall of gram -
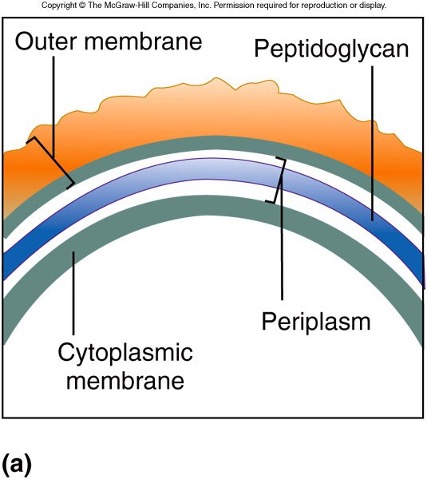
98
New cards
differences in cell wall
* gram + bacteria retain crystal violet iodine complex of gram stain
* gram - bacteria lose crystal violet iodine complex
* gram - bacteria lose crystal violet iodine complex
99
New cards
what are the external layers to the cell wall?
* capsules and slime layer
100
New cards
capsules and slime layer
* capsule is a distinct gelatinous layer
* slime layer is irregular diffused layer
* chemical composition of capsules and slime layers varies depending on bacterial species
* most are made of polysaccharides
* slime layer is irregular diffused layer
* chemical composition of capsules and slime layers varies depending on bacterial species
* most are made of polysaccharides