Energy transfers - Nutrient cycles
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What drives nutrient cycles?
Saprobionts
What are saprobionts?
Either bacteria or fungi that feed on dead or decaying matter through the process of saprotrophic nutrition
Describe how saprobionts work.
Extracellular enzymes are secreted by the
saprobiont. These enzymes break down organic compounds into inorganic ions
Describe the structure of fungi.
- Chitin cell wall
- Often multinucleated
- They contain a mycelium which is made of hyphae threads
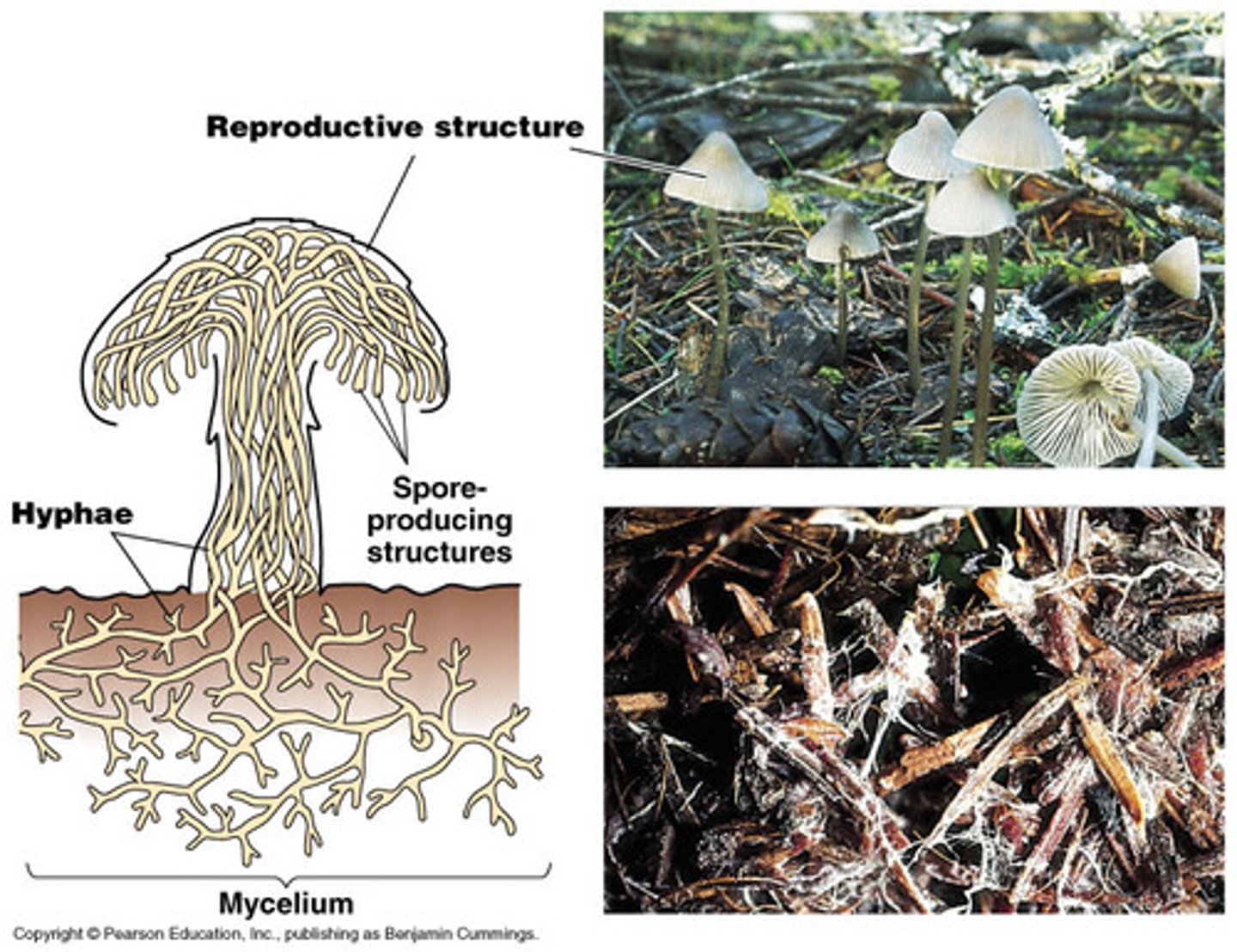
What is a symbiotic relationship?
A close biological interaction between two species where both organisms benefit
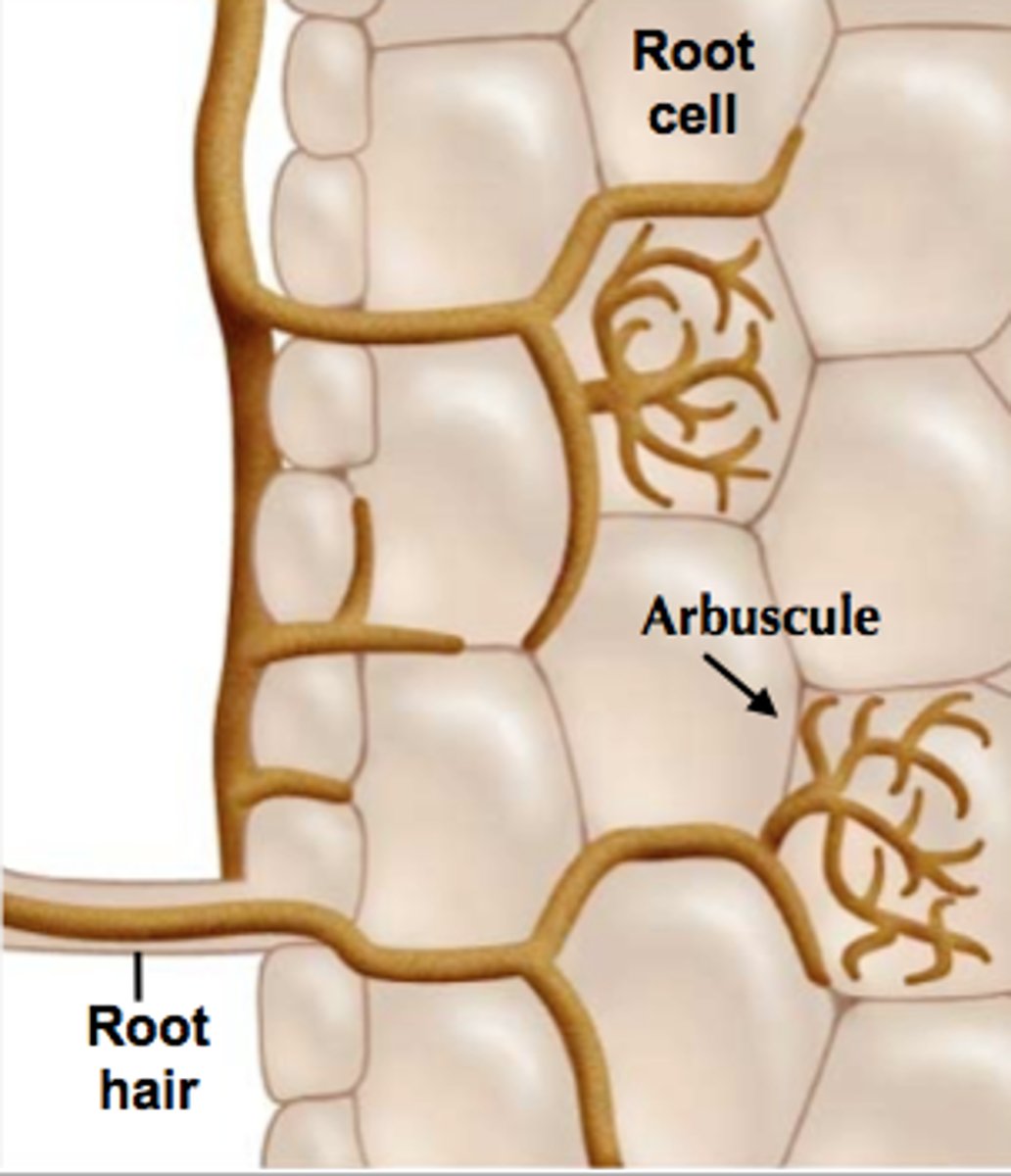
What is a symbiotic association of plant roots and fungi called?
Mycorrhiza (where fungus penetrates plant)
How does a mycorrhiza help plants?
- Hyphae increase plants root system SA
- It helps plants to absorb more inorganic ions and water
How does a mycorrhiza help fungi?
Plant supplies sugars to fungi that it made via photosynthesis
Structure of mycorrhiza.
How much of the atmosphere is N?
78%
Why is N2 so stable?
Because it has a triple covalent bond
Can plants use N2?
No because it is very difficult to separate (they can only use N in other compounds)
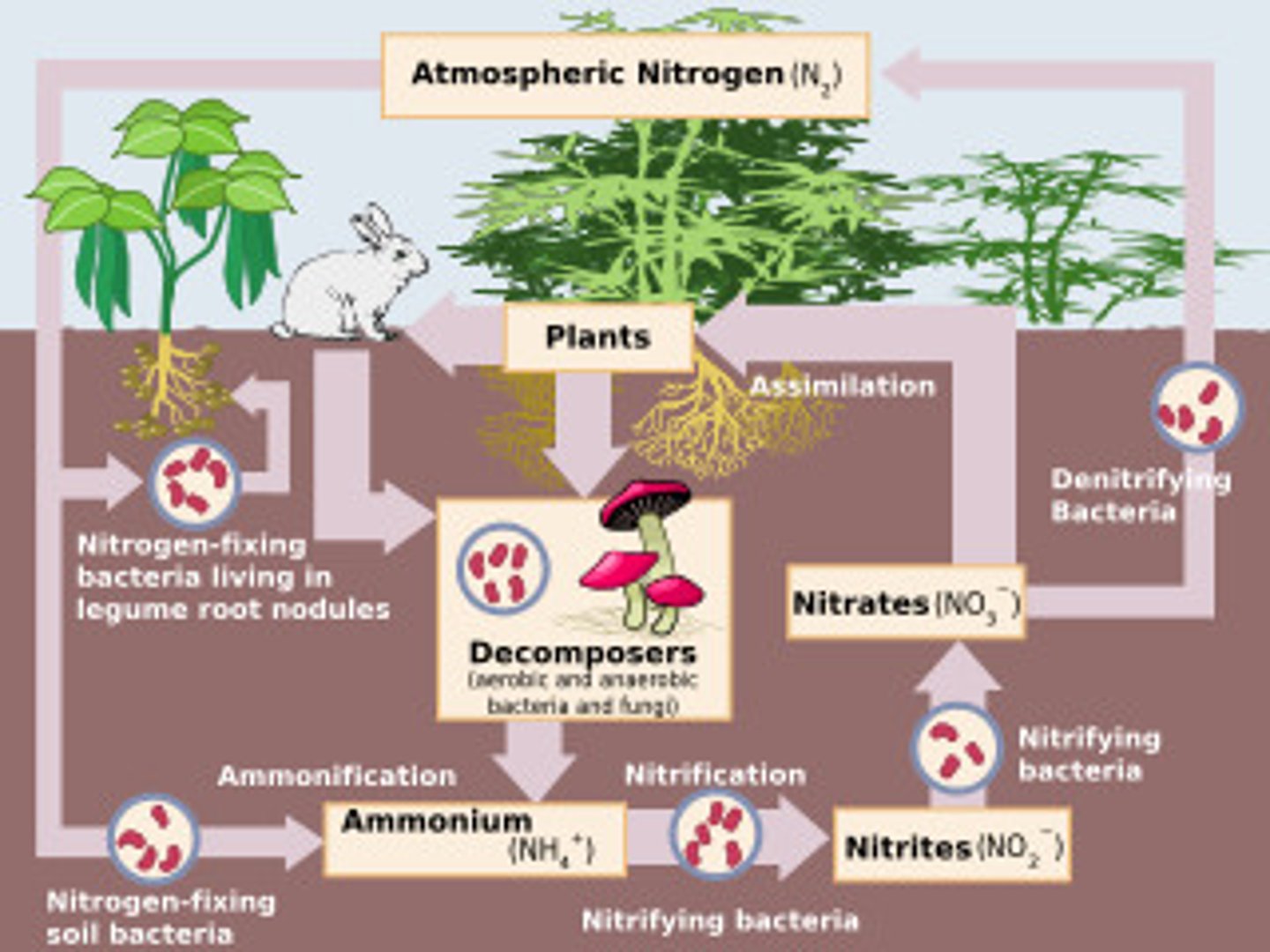
List the processes involved in the nitrogen cycle.
- Nitrogen fixation (via bacteria or lightning strikes)
- Ammonification (via saprotrophic nutrition)
- Nitrification
- Denitrification
What converts N2 into usable nitrogenous compounds?
Nitrogen fixing bacteria or lightning strikes
How do lightning strikes result in nitrogen fixation?
The amount of energy released by lightning is sufficient to convert N2 gas into various oxides of nitrogen
What do plants use nitrogen for?
Making proteins and nucleic acids
What are the two ways to produce ammonium?
- Nitrogen fixation via Rhizobium
- Ammonification via saprotrophic nutrition
What is the nitrogen fixing bacteria we need to know for the nitrogen cycle?
Rhizobium (species name)
What does Rhizobium do?
Convert N2 gas into ammonium ions (NH4+)
Where is Rhizobium found?
In the root nodules of legumes
What are root nodules?
Growths on the roots of leguminous plants such as peas, beans, and clover
Describe the process of ammonification.
Release of ammonium ions by bacteria which are involved in the digestion of proteins found in dead or waste organic matter
What are ammonium ions converted to and what is the name of the process?
Through the process of nitrification:
NH4+ is first converted to NO2- (nitrite ion)
NO2- is then converted to NO3- (nitrate ion)
What bacteria converts NH4+ to NO2- during nitrification?
Nitrosomonas
What bacteria converts NO2- to NO3- during nitrification?
Nitrobacter
How are nitrate ions converted back to N2 and what is the process called?
Process is denitrification and this is done by denitrifying bacteria
Give an example of a denitrifying bacteria.
Thiobacillus
Under what conditions does denitrification take place?
In anaerobic conditions such as waterlogged soil
Why do farmers not want waterlogged soil?
It encourages denitrification which converts the useful compounds the plant needs back into N2 which it cannot use. This means yield is less
How can nitrogen be artificially delivered to plants?
Fertilisers
Diagram of the nitrogen cycle.
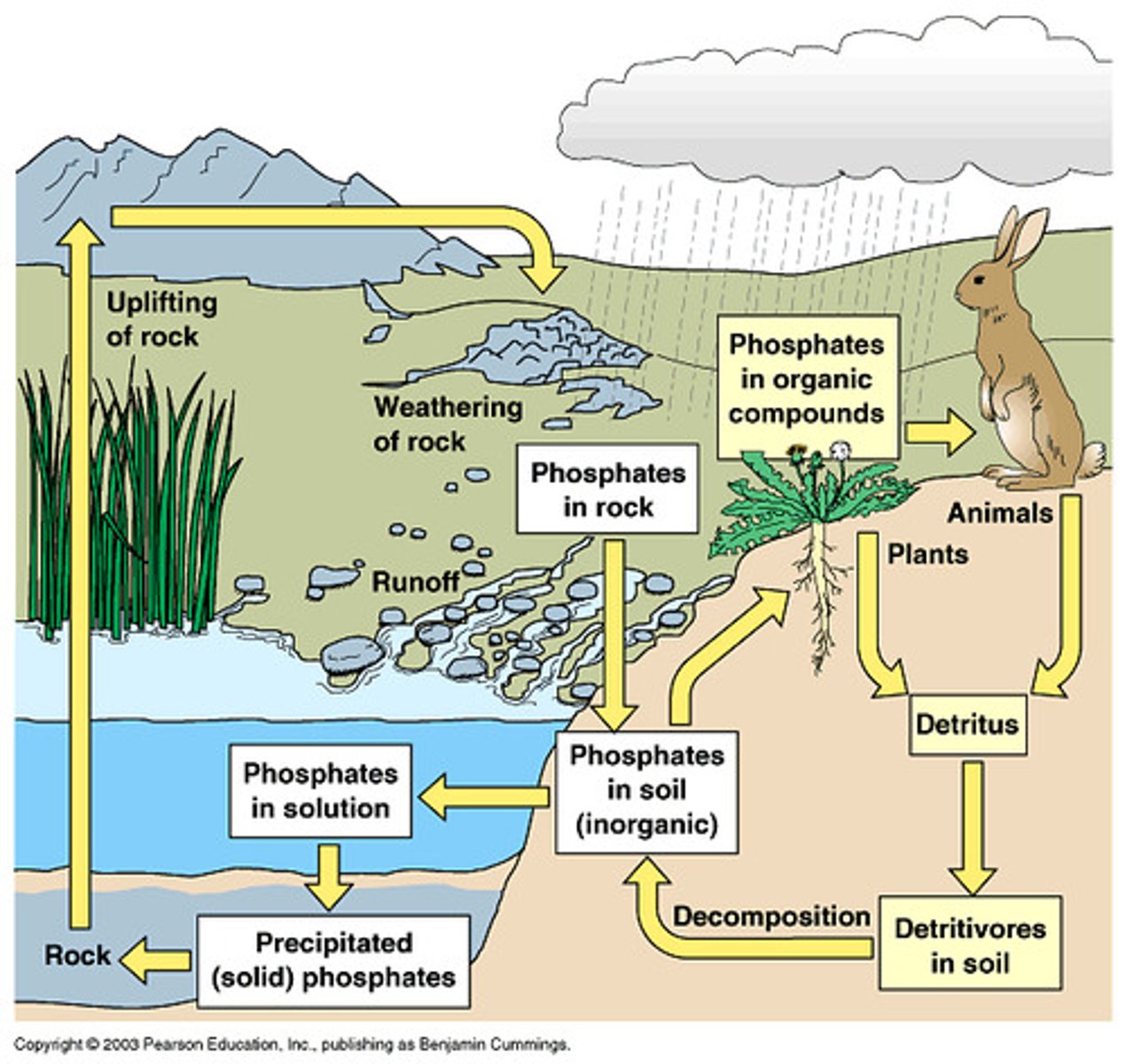
How is phosphorus useful to plants?
Used in DNA, ATP and cell membranes
Where and in what state is phosphorous found?
- In rocks as a phosphate ion (PO4 3-)
- In decomposing animal and plant matter (decomposed by bacteria)
- In fertilised fields as runoff
How can PO4 3- be made useful to plants?
Rocks can be dissolved by weathering and rain to release the ions in water into the soil
Where can phosphate ions go after entering the soil (that is not uptaken by plants)?
They can end up in rivers, lakes and the sea
What happens to phosphate ions when in the sea or a river?
They are incorporated into sediments or algae
How to plants take up phosphate ions?
They absorb them through their root systems
Once phosphate ions have been consumed by plants and alge, what happens to them?
These plants are eaten my consumers so the ions travel up the food chain
What is special about bird poo?
It contains high concentrations of phosphate ions and is thus used as fertiliser
Diagram of phosphorous cycle
What is the purpose of fertilsiers?
Because crop growth/livestock grazing depletes soil of nutrients, fertilisers replace these to ensure plants have enough to keep growing and producing a high yield
What are some common fertilisers and what are they made of?
- NPK containing nigtogen, phosphorous and potassium
- Organic fertilisers made of manure
What is a disadvantage of fertilisers?
Non organic fertilisers are very soluble so their runoff can result in eutrophication (organic fertilisers less so)
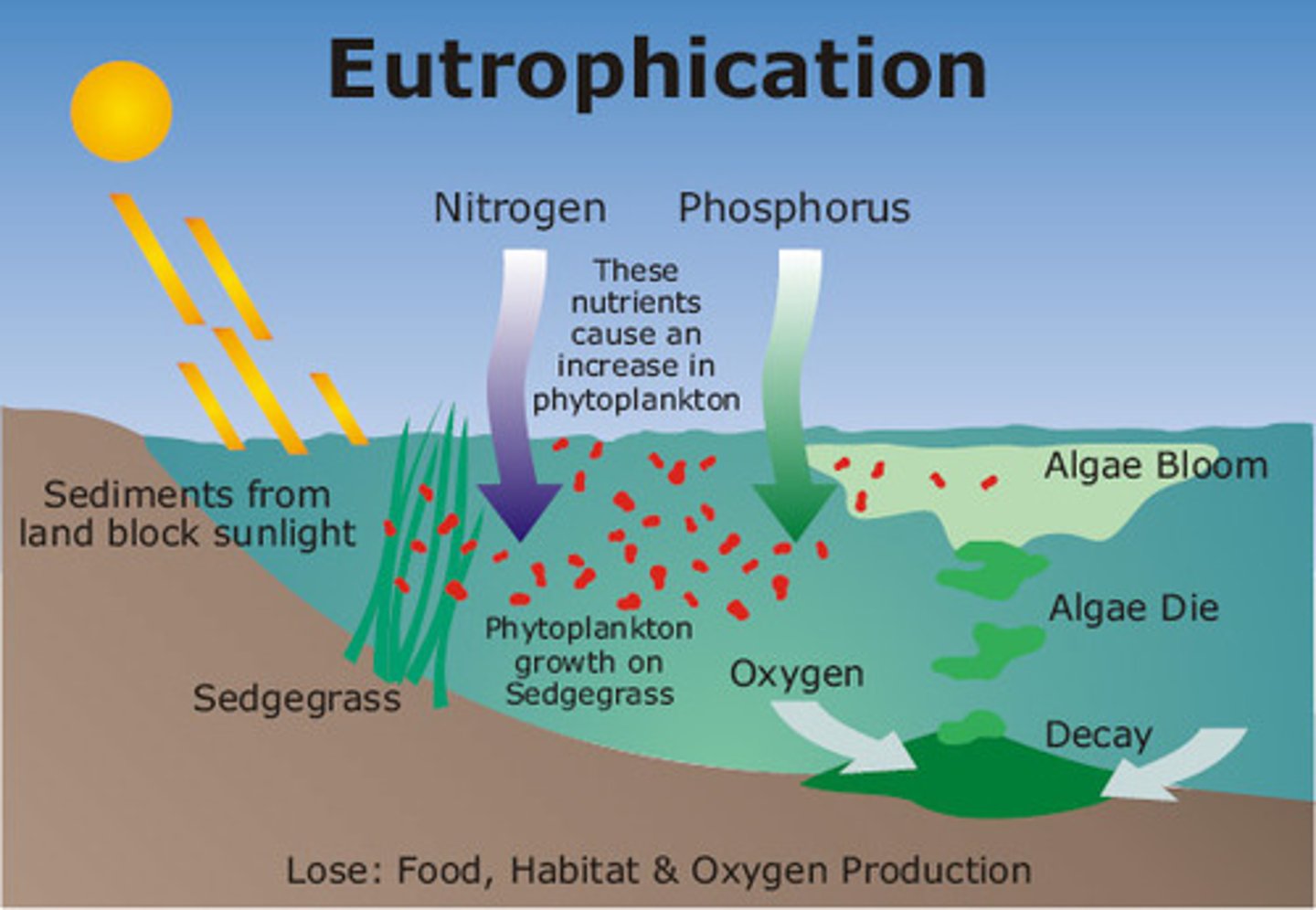
Describe the stages of eutrophication.
1. Fertiliser runoff from field enters rivers
2. Nutrients in fertilisers help algae to bloom
3. Large algal growth on the surface blocks sunlight reaching the plants underwater
4. Underwater plants can't photosynthesise
5. This means oxygen is not being released into the water
6. Plants die and are decomposed by bacteria
7. Respiration from the dead plants uses up O2 in the water
8. There is much less O2 in the water
9. Fish cannot respire so they die
10. Damage is done to ecosystems
Diagram of eutrophication.