Depressant Module- Narcotic Analgesics, Benzos, Barbiturates, Nitazenes, Phenibut, and Pregabalin
1/205
Earn XP
Description and Tags
7.2 Benzodiazepines and Designer Benzodiazepines Drug Chemistry SOP 7.2 Fentanyl and Heroise ictions that you should be reviewing. 7.2 Benzodiazepines and Designer Benzodn the Depressant lecture, here are the pertinent SOP seian 7.2 Nitazenes 7.2 Phenibut 7.2 Pregabalin 7.2 Selection, Verification and Validation of Test Methods Drug Chemistry SOP 6.4 Equipment - Balances, Microscopes, GC/MS, AgilentTOF Drug Chemistry SOP 7.3 Sampling Drug Chemistry SOP 7.7 Ensuring the Validity of Results Drug Chemistry SOP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
206 Terms
What is an Alkaloid?
A basic nitrogen-containing compound of plant origin, many of which are physiologically active when administered to humans.
Define Opium.
The highly addictive narcotic derived from the unripe seed pods of the opium poppy. The dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy. The milky juice is air dried and forms a brownish gummy mass. This is further dried and powdered to make the official powdered opium.
What are the GCMS Parameters for Alprazolam ran on (BENZO01012020)?
Acquisition Method: BENZO01012020. Internal Standard(s): 4-(1H-Indol-3-yl) Butan-2-one. Solvent(s): Ethyl Acetate. Control Concentration(s): ~60/250ug/mL. Split Ratio: 5:1.
What are the GCMS Parameters for Alprazolam ran on (30BENZO01012020)?
Acquisition Method:30BENZO01012020. Internal Standard(s): 4-(1H-Indol-3-yl) Butan-2-one. Solvent(s): Ethyl Acetate. Control Concentration(s): 250ug/mL. Split Ratio: 30:1
What are the GCMS Parameters for Isonitazene ran on (UNK09062011)?
Acquisition Method: UNK09062011. Internal Standard(s): 4-(1H-Indol-3-yl) Butan-2-one. Solvent(s): Methanol. Control Concentration(s): 250ug/mL. Split Ratio: 30:1
What are the GCMS Parameters for Metonitazene ran on (UNK09062011)?
Acquisition Method: UNK09062011. Internal Standard(s): 4-(1H-Indol-3-yl) Butan-2-one. Solvent(s): Methanol. Control Concentration(s): 250ug/mL. Split Ratio: 30:1
What are the GCMS Parameters for Protonitazene ran on (UNK09062011)?
Acquisition Method: UNK09062011. Internal Standard(s): 4-(1H-Indol-3-yl) Butan-2-one. Solvent(s): Methanol. Control Concentration(s): 250ug/mL. Split Ratio: 30:1
What are the GCMS Parameters for N-Pyrrolidino Etodesnitazene ran on (UNK09062011)?
Acquisition Method: UNK09062011. Internal Standard(s): 4-(1H-Indol-3-yl) Butan-2-one. Solvent(s): Methanol. Control Concentration(s): 250ug/mL. Split Ratio: 30:1
What are the GCMS Parameters for N-Pyrrolidino Protonitazene ran on (UNK09062011)?
Acquisition Method: UNK09062011
Internal Standard(s): 4-(1H-Indol-3-yl) Butan-2-one.
Solvent(s): Methanol. Control Concentration(s): 250ug/mL.
Split Ratio: 30:1
What kind of Phenibut samples need to be extracted before GC/MS analysis? What solvent is the approved solvent for an extracted sample?
Liquid/ Edible submissions of Phenibut. n-Butyl Chloride.
What is the GC/MS Parameters for Phenibut samples ran on (PHEN08232023) Phenibut Program- 15m Column?
Acquistion Method:PHEN08232023.
Internal Standard(s): Dibucaine.
Solvent(s): Ethyl Acetate, or for extracted samples n-Butyl Chloride.
Control Concentration(s): ~250ug/mL.
Split Ratio: 5:1
What is the GC/MS Parameters for Phenibut samples ran on (PHEN08232023-30M) Phenibut Program- 30m column?
Acquistion Method: PHEN08232023-30M.
Internal Standard(s): Dibucaine.
Solvent(s): Ethyl Acetate, or for extracted samples n-Butyl Chloride.
Control Concentration(s): ~250ug/mL.
Split Ratio: 5:1
What is the GC/MS Parameters for Phenibut samples ran on (30PHEN08232023) Phenibut Program- 15m column 30:1 split?
Acquistion Method: 30PHEN08232023.
Internal Standard(s): Dibucaine.
Solvent(s): Ethyl Acetate, or for extracted samples n-Butyl Chloride.
Control Concentration(s): ~250ug/mL.
Split Ratio: 30:1
What is the GC/MS Parameters for Phenibut samples ran on (30PHEN08232023-30M) Phenibut Program- 30m column 30:1 split?
Acquistion Method: 30PHEN08232023-30M.
Internal Standard(s): Dibucaine.
Solvent(s): Ethyl Acetate, or for extracted samples n-Butyl Chloride.
Control Concentration(s): ~250ug/mL.
Split Ratio: 30:1
What are the GCMS Parameters for Pregabalin ran on (UNK09062011)?
Acquisition Method/Mode: UNK09062011
Internal Standard(s): Dibucaine
Solvent(s): Chloroform
Control Concentration(s): ~250ug/mL.
What is the plant from which opium is obtained?
Papaver Somniferum (The opium poppy). Opium is found in the gummy, milky juice exuded through a cut made in the unripe pod of the poppy after the petals of the flower have dropped.
List the alkaloids present in opium poppy.
Morphine, Codeine, Noscapine, Papaverine, and Thebaine are the main ones. Opium contains ~20 alkaloids.
Which Alkaloids are the primary constituents in opium?
Morphine (9-15%), Codeine (0.1-2.5%), Noscapine (4-8%), Papaverine (0.8-1%), Thebaine (0.3-1.5%). Meconic Acid (a non-alkaloid unique to opium (3-5%)).
What is the difference between opiates and opioids?
Opiates are substances that are directly derived from the poppy plant while opioids are substances that have morphine-like effects but are not found in the opium plant.
Define opiate and give an example.
Refers to those substances that are directly derived from the opium poppy. Ex. Morphine, Opium, Codeine.
Define opioid and give an example.
Refers to those substances that have morphine-like effects but are not found in the opium poppy. Ex. Heroin, Hydromorphone, Fentanyl, Oxycodone, Methadone, Meperidine, Propoxyphene, and codeine.
What is a natural opiate, and give an example of one?
An opiate from direct extraction from the opium poppy. Ex. Opium, Morphine, and Codeine.
What is a semi-synthetic opiate and give an example of one?
Opium derivative made from naturally occurring opium alkaloid. (Refined Poppy Derivatives) Ex. Codeine, Heroin, Hydromorphone (Dilaudid), and Oxycodone (Percodan).
What is a synthetic opiate and give an example of one?
Compounds not produced from a naturally occurring opium alkaloid but have similar narcotic-analgesic pharmacological effects. (Not based on Opium Poppy) Ex. Methadone, Meperidine, and Propoxyphene (Darvon).
What functional groups are present in the morphine molecule?
2 Hydroxyl Groups: C3-phenolic OH, C6-allylic OH.
Ether linkage at C4-C5
Basic Tertiary Amine at C17.
1 Benzene Ring
2 Partially unsaturated cyclohexane.
Piperidine
Tetrahydrofuran
Heterocycles
Unsaturation between C7&C8
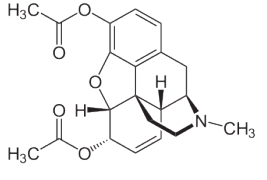
To get to Heroin, what changes on the morphine structure?
The hydroxy groups of C-3 and C-6 are replaced with acetoxy groups. (An acetyl group attached to an oxygen).
Which of the opioid receptors is the most important?
The mu receptor (u).
What structures are necessary to retain morphine’s action at the opioid receptor?
Piperidine Ring
Nitrogen
Hydroxyl in the C3 position
List the structure modifications to morphine and the effect on activity.
Removal of the Hydroxy group at C-3: Removal of OH reduces activity.
Removal of oxygen in Tetrahydrofuran increases activity.
The Hydroxy at C-6: Oxidation, coupled with the reduction of the double bond at 7,8 increases activity. Acetylation increases activity.
The reduction of the double bond between C-7 and C-8 increases activity.
The introduction of OH at the 14 hydrogen position increases activity.
The Nitrogen Group: N-CH2CH2Ph increases activity. N-CH2CH=CH2 creates antagonist.
List the following as having increased or decreased potency compared to morphine. Codeine
5x less potent than morphine.
List the following as having increased or decreased potency compared to morphine. Hydrocodone.
Less potent than Morphine, but much more potent than codeine.
List the following as having increased or decreased potency compared to morphine. Hydromorphone
7x more potent than morphine.
List the following as having increased or decreased potency compared to morphine. Oxycodone
Equal to or greater than morphine in potency.
List the following as having increased or decreased potency compared to morphine. Oxymorphone
8x more potent than morphine.
List the following as having increased or decreased potency compared to morphine. Heroin
2x as potent as morphine.
List the following as having increased or decreased potency compared to morphine. Fentanyl
50-100 x more potent than morphine.
List the following as having increased or decreased potency compared to morphine. Propoxyphene
Less potent than morphine.
List the following as having increased or decreased potency compared to morphine. Meperidine
Less potent than morphine.
List the following as having increased or decreased potency compared to morphine. Methadone
Less potent than morphine.
What is the purpose of the modification that created heroin?
Conversion of two -OH groups to -OAc facilitates crossing of the BBB. Due to presence of 2 acetyl groups, heroin passes the blood-brain barrier rapidly. Results in rapid onset of action and is metabolized to morphine in the brain. Renders the molecule more fat soluble.
What modification to morphine would create an antagonist?
The modification of the nitrogen group: N-CH2CH=CH creates antagonist.
Modification of the tertiary amine: Increasing the chain length.
What compound is utilized in emergency opioid overdoses?
Naloxone commonly known as Narcan.
List the medical uses of narcotic analgesics.
Analgesia (Pain Relief) W/O loss of consciousness or major impairment of other sensory modalities, Sedation? , Respiratory Depression, Alleviate Suffering (Hydromorphone), Treatment of severe, painful dry coughing (Hydromorphone), Diarrhea (Codeine), Cough (Codeine), Moderate to severe IBS (Codeine), Antitussive (Hydrocodone), Reversal of Opioid Overdose by opioid receptor antagonist, Opioid Abuse Withdrawal/ Maintenance therapy in opiate addicts.
Give the controlled status of the following: Heroin
1
Give the controlled status of the following: Fentanyl
2
Give the controlled status of the following: Dextromethorphan
Non-controlled substance
Create a chart with the following characteristics: molecular formula, monoisotopic mass, acidic/basic/amphoteric. Fentanyl
Molecular Formula: C22H28N2O
Monoisotopic Mass: 336.2201635
Acidic/Basic/Amphoteric: Basic
Create a chart with the following characteristics: molecular formula, monoisotopic mass, acidic/basic/amphoteric. Heroin
Molecular Formula:C21H23NO5
Monoisotopic Mass: 369.15762283
Acidic/Basic/Amphoteric: Amphoteric
Create a chart with the following characteristics: molecular formula, monoisotopic mass, acidic/basic/amphoteric. Morphine
Molecular Formula: C17H19NO3
Monoisotopic Mass: 285.13649347
Acidic/Basic/Amphoteric: Amphoteric
Create a chart with the following characteristics: molecular formula, monoisotopic mass, acidic/basic/amphoteric. Hydrocodone
Molecular Formula: C18H21NO3
Monoisotopic Mass: 299.15214353
Acidic/Basic/Amphoteric: Basic
Give examples of narcotic analgesics that cannot be differentiated by DART TOF.
Hydrocodone and Codeine
Morphine and Hydromorphone
Butyryl Fentanyl and Isobutyryl Fentanyl
Methacryl Fentanyl and Cyclopropyl Fentanyl and Crotonyl Fentanyl
B-hydroxyfentanyl and Methoxyacetyl Fentanyl
(meta, para, ortho) -Fluoroisobutyryl Fentanyl
(meta, para, ortho)- Fluorobutyryl Fentanyl
(meta, para, ortho)- Fluorofentanyl
There have been instances where black pepper will pop positive for morphine.
What narcotic analgesics can be tested by FTIR?
Heroin Base and Heroin HCl
Morphine
List the fentanyl compounds that are that can be reported per the DC SOP. Include the controlled status for these compounds.
Acetyl Fentanyl -1
B-hydroxyfentanyl -1
Furanyl Fentanyl -1
Butyryl Fentanyl -1
Acryl Fentanyl -1
Isobutyryl Fentanyl -1
Methoxyacetyl Fentanyl -1
Methacryl Fentanyl -1
Cyclopropyl Fentanyl -1
Crotonyl Fentanyl- 1
(meta, para, ortho) Fluoroisobutyryl Fentanyl -1
(meta, para, ortho) Fluorobutyryl Fentanyl -1
(meta, para, ortho) Fluorofentanyl -1
Carfentanil -2
What is the challenge with the presence of 4-anilino-N-phenethyl-4-piperidine (4-ANPP) in GC/MS data?
It is a precursor and a degradant product of fentanyl. We don’t know if it’s in the precursor stage or degradation stage from analysis of GC/MS data.
What are the specific requirements for the fentanyl analogue GC/MS positive controls?
If using the FENTANYL071117 method, a mixture of Furanyl Fentanyl and Furanyl fentanyl 3- furancarboxamide isomer will be analyzed with the case samples and individual Furanyl Fentanyl and Furanyl fentanyl 3-furancarboxamide isomer controls to ensure proper assignments.
To ensure proper assignments, a mixture of Butyryl Fentanyl and Isobutyryl Fentanyl will be analyzed with the case samples and individual Butyryl Fentanyl and Isobutyryl Fentanyl controls.
To ensure proper assignments, a mixture of (meta, para, ortho) Fluoroisobutyryl Fentanyl, (meta, para, ortho) Fluorofentanyl, and (meta, para, ortho) Fluorobutyryl Fentanyl will be analyzed with the case samples and individual (meta, para, ortho) Fluoroisobutyryl Fentanyl, (meta, para, ortho) Fluorofentanyl, and (meta, para, ortho) Fluorobutyryl Fentanyl controls.
What is the reporting requirement for fentanyl/fentanyl analogue cases that meet a weight bearing charge?
Fentanyl and fentanyl analogues are compounds that represent a danger to public safety. As such, it may be important for local law enforcement agencies to know if one of these compounds are present in combination with other drugs such as heroin. For cases that qualify for a weight bearing charge, the fentanyl/fentanyl analogue will be identified and reported to the submitting agency.
What is the definition of sedative?
A drug that slows down the body’s functions. In low doses sedative-hypnotic drugs produce a calming effect (sedation) relieving anxiety, tension, and relaxing muscles.
What is the definition of hypnotic?
A drug that slows down the body’s functions. In high doses sedative-hypnotic drugs produce drowsiness and a sleep-like state (Hypnotics)
What is the definition of a depressant?
Substances that slow down brain activity. (CNS Depressant). Category of substances that slow down all mental and physical actions of the body with no analgesic properties.
What is the definition of anticonvulsant?
Anti-epileptic or anti-seizure. Prevent or reduce the severity and/or frequency of seizures.
What is the definition of muscle relaxant?
Spasmolytics and Neuromuscular Blockers. Affects skeletal function and decreases the muscle tone.
Define what a counterfeit pharmaceutical is.
Medication or pharmaceutical item which is produced and sold with the intent to deceptively represent its origin, authenticity, or effectiveness.
What is the difference between a sedative and a hypnotic?
Same drug, but in low doses produces a calming effect (sedation). In high doses the same drug produce drowsiness and a sleep-like state (Hypnotic).
What is an example of a benzodiazepine?
Alprazolam, Diazepam, Lorazepam, Flunitrazepam, Clonazepam, Clonazolam, Etizolam, Flubromazepam, Flubromazolam, Phenazepam, Bromazolam, Deschloroetizolam, Chlordiazepoxide, Chlorazepate,Flurazepam, Oxazepam, Prazepam, Temazepam, and Triazolam.
What is an example of a barbiturate?
Pentobarbital, Thiopental, Methohexital, Amobarbital, Secobarbital, Phenobarbital, Butalbital, Babrital, Mephobarbital, and Barbituric Acid.
What is an example of a muscle relaxant?
Carisoprodol, Cyclobenzaprine, and Methocarbamol.
What is an example of a Non-benzodiazepine insomnia drug (Zzz drug)?
Zolpidem, Zopiclone, and Zaleplon.
List each of the following as (1) acidic/basic/amphoteric and (2) polar/non-polar. Alprazolam
Basic/Acidic/Amphoteric: Basic
Polar/Non-polar: Nonpolar
List each of the following as (1) acidic/basic/amphoteric and (2) polar/non-polar. Carisoprodol
Basic/Acidic/amphoteric: Amphoteric
Polar/Non-polar: Mostly Polar
List each of the following as (1) acidic/basic/amphoteric and (2) polar/non-polar. Zolpidem
Basic/Acidic/Amphoteric: Basic
Polar/Non-polar: Nonpolar
List each of the following as (1) acidic/basic/amphoteric and (2) polar/non-polar. Phenobarbital
Basic/Acidic/Amphoteric: Acidic
Polar/Non-polar: Polar
What sample types are associated with CNS Depressants?
Solids
Liquids
Pharmaceuticals/ Clandestine/ Tablet Fragments
Limited Samples
Residues
Pharmaceutical and Counterfeit Tablet Preparations, Capsules, Injectable Preparations, and Liquids.
Benzodiazepines: Tablets- Pharmaceutical and Counterfeit. Capsules, injectable preparations, and liquids.
Muscle Relaxants- Tablets
Explain the difference between commercially prepared pharmaceuticals and counterfeit pharmaceuticals.
Commercially Prepared pharmaceuticals are prepared in certified labs by accredited individuals. With commercially prepared pharmaceuticals you know exactly what you are getting in the preparation. However counterfeit pharmaceuticals are preparations made to imitate the likeness of commercially prepared pharmaceuticals and are produced in uncontrolled labs, therefore you are not sure what is in the counterfeit preparation.
Why are the following drugs of abuse? Barbiturate
THEY GET YOU HIGH. People take them to get high.
They carry a high risk of misuse, abuse, and addiction due to their rapid tolerance development and strong physical dependence potential.
They depress the central nervous system, leading to neural activity suppression and a sedative effect.
They are often used to counteract the stimulant effects from other drugs.
They are used to reduce anxiety, decrease inhibitions, and treat unwanted effects of other drugs.
Why are the following drugs of abuse? Benzodiazepine
People abuse them for the anti-anxiety calming effect, plus used in suicides.
Physical dependence will result from excessive use of any sedative-hypnotic drugs.
Benzodiazepines are a drug of abuse due to their effects, widespread availability, and potential for addiction
Why are the following drugs of abuse? Muscle Relaxants
Sedative and Muscle relaxing effects.
Why are the following drugs of abuse? Non-benzodiazepine insomnia drugs (ex. Zolpidem)
EXTREME RELAXATION.
Non-benzodiazepine insomnia drugs, such as zaleplon, zolpidem, and eszopiclone, are considered drugs of abuse because they have been associated with altered sleep architecture, psychomotor and memory impairment, rebound insomnia, withdrawal effects, tolerance, dependence, and abuse potential
List the effects of abuse for each of the following: Alprazolam
Physical Dependence will result from excessive use of any of the sedative-hypnotic drugs.
General Sluggishness
Drowsy with drooping eyelids
Staggered Walk
Irritability
Slurred speech without the odor of alcohol.
Overdose symptoms (Confusion, cramping, delirium, hallucinations, convulsions, tremors, and unconsciousness).
Dizziness/Vertigo
Drowsiness/Fatigue
Nausea, vomit, upset stomach
Decreased mental alertness
List the effects of abuse for each of the following: Pentobarbital
Hallucinations
Weak or Shallow Breathing
Slow heart rate/ weak pulse
Respiratory Depression.
Development of Physical Dependence/ Substance Use Disorder
Memory Issues
Learning Issues
Slower rates of thinking/cognition
Increased risk of liver cancer
Slurred Speech but w/o odor of alcohol
General Sluggishness
Staggered Walk
Irritability
Overdose Symptoms (Confusion, cramping, delirium, hallucinations, convulsions, tremors, and unconsciousness)
List the effects of abuse for each of the following: Zolpidem
Fatigue
Headache
Dizziness/ Vertigo
Struggle to maintain balance
Nausea
Tummy issues
Changes in appetite
Body Shakes/ Tremors
Redness of eyes
Confused, anxious, or upset behavior
“sleepwalking
List the effects of abuse for each of the following: Carisoprodol
Impairment of physical or mental capabilities.
Dizziness
Nausea/ Vomiting
Increased Heart rate
Tremors
Fainting
Anxiety and/or Insomnia
At high doses or when mixed with other drugs, the drug can cause:
The inability to control bodily movements.
Amnesia.
Agitation.
Respiratory depression.
Loss of consciousness.
Coma.
Death.
Side Effects
Loss of muscle coordination.
Weakness.
Dizziness.
Fainting.
Seizures.
Double vision.
Poor judgment.
Confusion.
Headache.
Depression.
Tremors.
Increased heart rate.
Nausea.
Vomiting.
Long-term effects of abuse: The drug is a carcinogen.
List the medical use(s) for each of the following: Alprazolam
Treat anxiety disorders and relieve symptoms of anxiety. Slow down the nervous system and produce a calming effect.
List the medical use(s) for each of the following: Carisoprodol
A muscle relaxer that blocks pain sensations between the nerves and the brain.
Carisoprodol is a muscle relaxer that blocks pain sensations between the nerves and the brain. It is used to relax certain muscles in your body and relieve the discomfort caused by acute (short-term), painful muscle or bone conditions.
List the medical use(s) for each of the following: Pentobarbital
Sedative
Preanesthetic: Used to induce sleep before surgery
Emergency Control of Seizures
Short-term treatment of insomnia
List the medical use(s) for each of the following: Phenobarbital
To treat or prevent seizures
Short-term sedative used to help you relax
List the medical use(s) for each of the following: Zolpidem
Treatment of insomnia
What is the controlled status for each of the following: a. Alprazolam
4
What is the controlled status for each of the following: Diazepam
4
What is the controlled status for each of the following: Flubromazolam
1
What is the controlled status for each of the following: Phenobarbital
4
What is the controlled status for each of the following: Carisoprodol
4
What is the controlled status for each of the following: Zolpidem
4
What is the definition of narcotic?
The term narcotic is derived from the greek word narkotikos, which implies a state of lethargy or sluggishness. Pharmacologists classify narcotic drugs as substances that produce a stuporous, sleeplike state and may or may not relieve pain.
What is the definition of analgesic?
An agent producing diminished sensation to pain without loss of consciousness : a drug that is used to relieve pain and produce analgesia
What is the definition of Tolerance?
A decrease in response to a drug that is used repeatedly.
In pharmacology, tolerance refers to the processes that result in the reduction of therapeutic effectiveness.
What is the definition of Anxiolytic?
(anti-anxiety drugs) Drugs that are used to reduce anxiety.
What is the controlled Status for: Protonitazene?
Schedule 1
What is the controlled Status for: Etizolam?
Schedule 1 Synthetic Controlled Substance
What is the controlled status of phenibut in Alabama?
Schedule 2 in Alabama
Federally they are scheduled as non-controlled Substance
What is the controlled status of Gabapentin?
Schedule 5