Lecture 5 - Proteins: Amino Acids and Structure
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
1
New cards
protein
one type of biological polymers
large biological molecules consisting of one or more chains of amino acids
made up if one or multiple polypeptide chains
large biological molecules consisting of one or more chains of amino acids
made up if one or multiple polypeptide chains
2
New cards
peptide
short chain of amino acid monomers linked by polypeptide bonds
3
New cards
amino acid
biologically important organic compound made from amine and carboxylic acid functional groups, along with a side chain specific to each amino acid
4
New cards
amine group - primary
pka 9-10
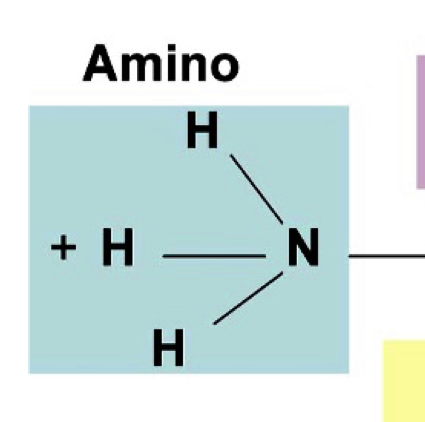
5
New cards
carboxyl group - alpha carbon
pka 1.5-2.5
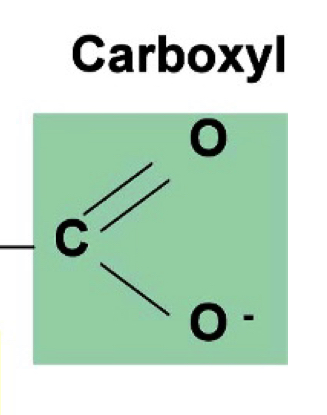
6
New cards
Glycine (gly)
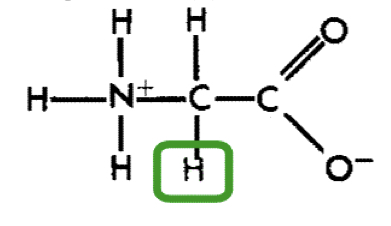
7
New cards
L-Alanine (ala)
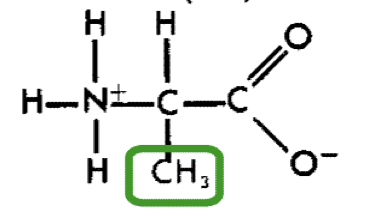
8
New cards
L-Valine (Val)
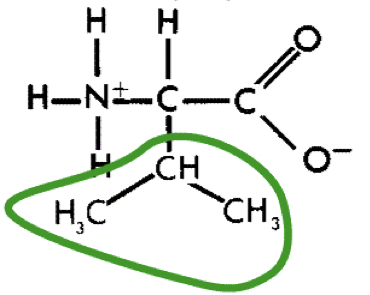
9
New cards
L-Isoleucine (ileu)
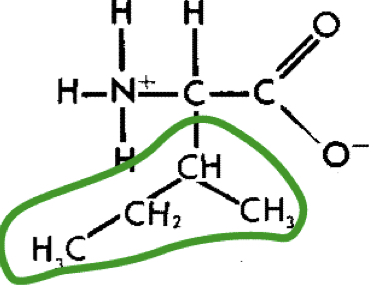
10
New cards
L-Leucine (leu)
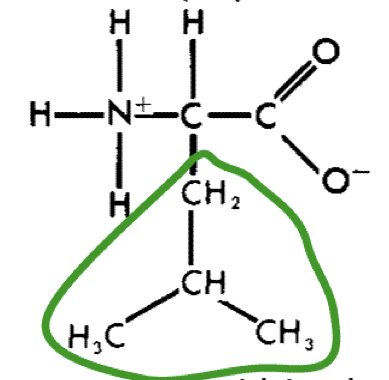
11
New cards
L-Serine (ser)
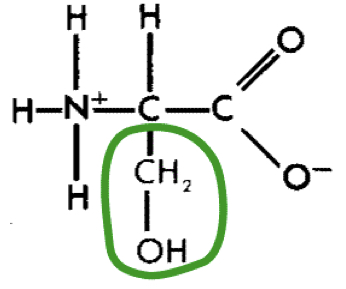
12
New cards
L-Theronine (thr)
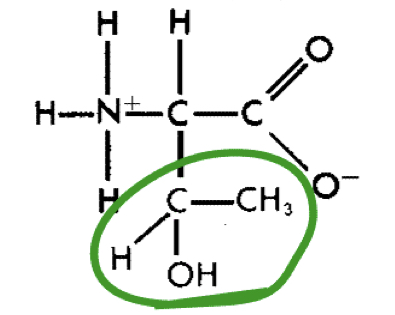
13
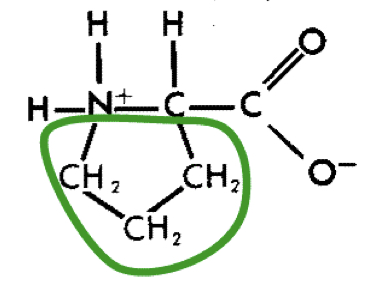
New cards
L-Proline (pro)
14
New cards
L-Aspartic acid (asp)
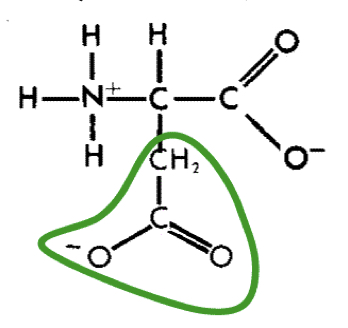
15
New cards
L-Glutamic acid (glu)
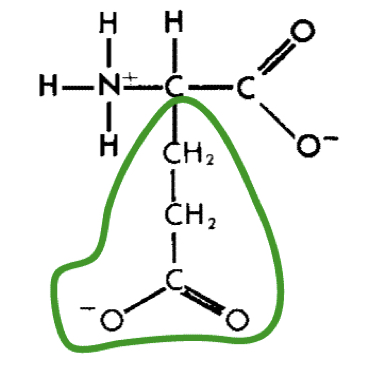
16
New cards
L-Lysine (lys)
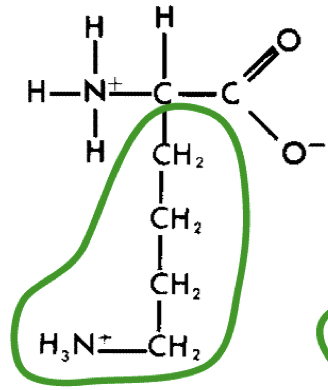
17
New cards
L-Arginine (arg)
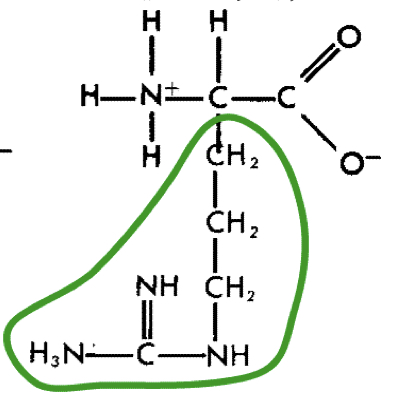
18
New cards
L-Asparagine (asn)
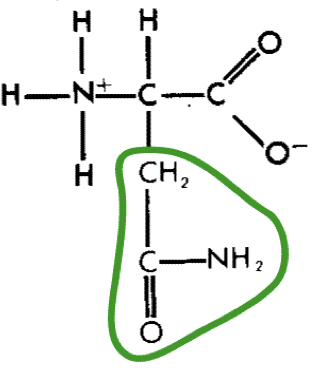
19
New cards
L-Glutamine (gln)
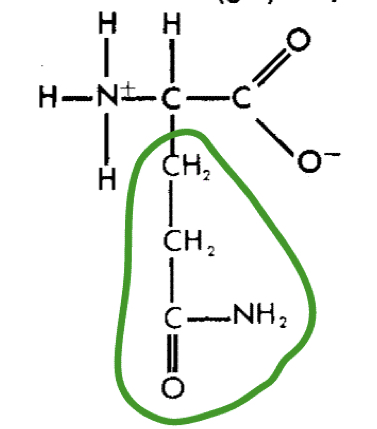
20
New cards
L-Cystein (cys)
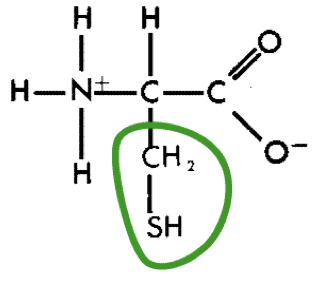
21
New cards
L-Methionine (met)
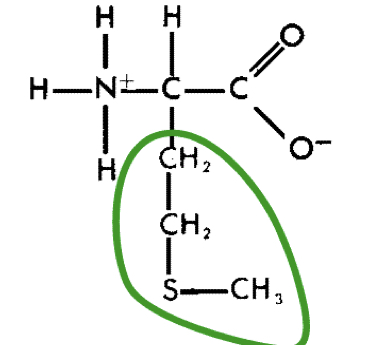
22
New cards
L-Tryptophan (trp)
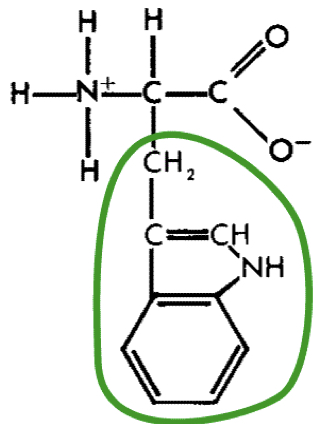
23
New cards
L-Phenylalanine (phe)
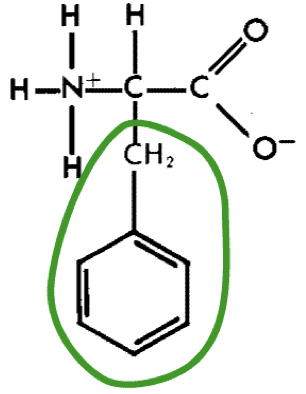
24
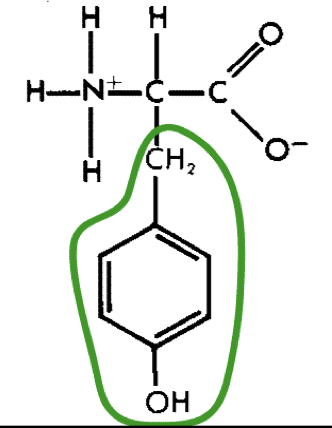
New cards
L-Tyrosine (tyr)
25
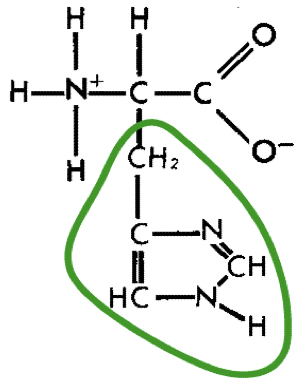
New cards
L-Histidine (his)
26
New cards
acidic amino acids
asp & glu
27
New cards
basic amino acids
arg, his, & lys
28
New cards
neutral amino acids
ala, asn, cys, gln, gly, his, ile, leu, met, phe, pro, ser, thr, trp, tyr, val
29
New cards
alpha carbon chiral in all amino acids except for…
glycine
30
New cards
all natural amino acids are L or R form?
Left
31
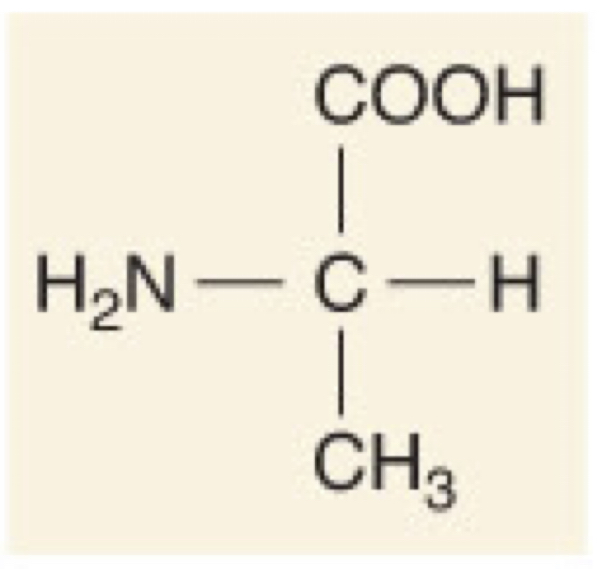
New cards
L-Alanine
32
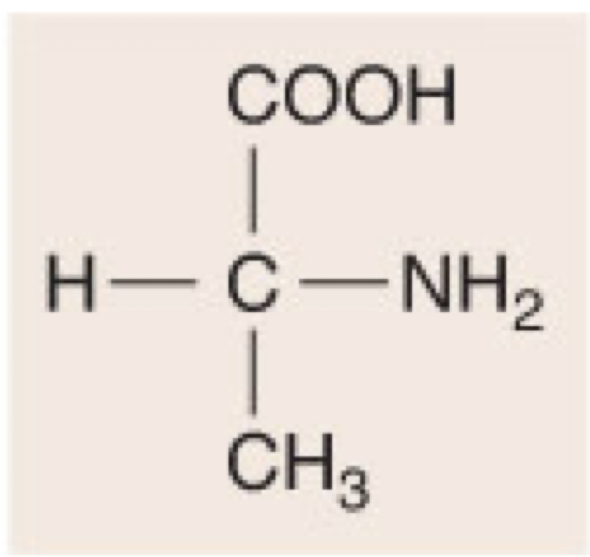
New cards
D-Alanine
33
New cards
L-Glyceraldehyde
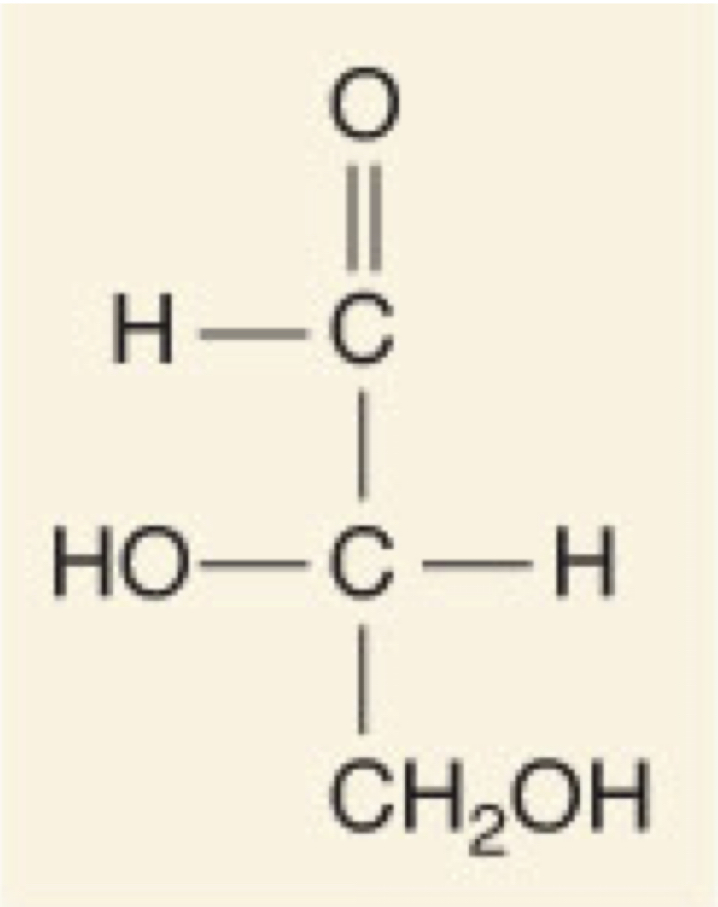
34
New cards
D-Glyceraldehyde
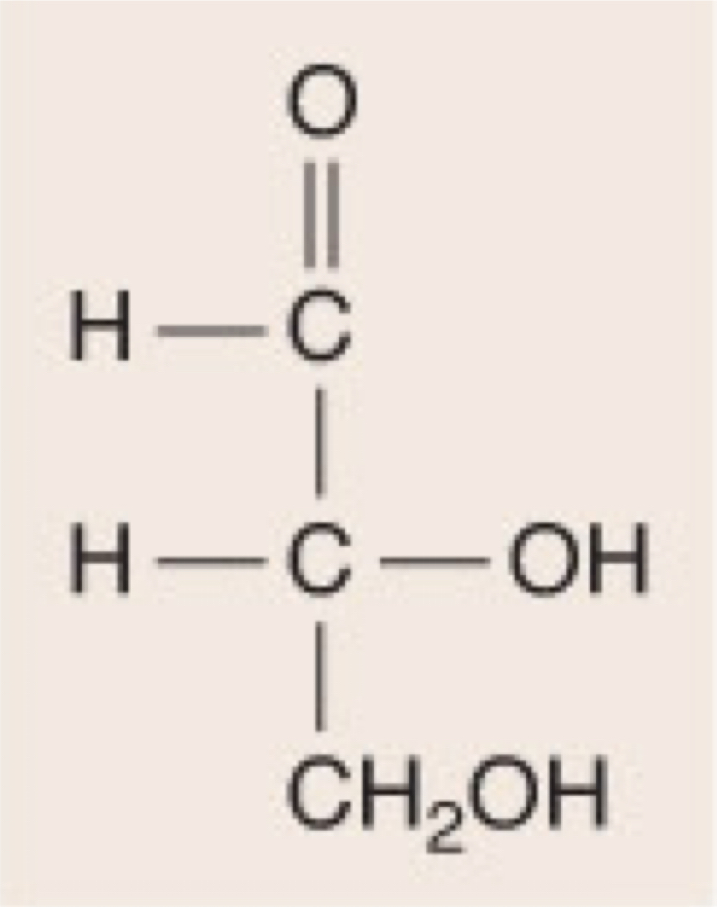
35
New cards
characteristics of polar amino acids
neutral, basic, acidic
36
New cards
characteristics of non-polar amino acids
alkyl, branched, aromatics, unique
37
New cards
Acidic negatively charged R Polar Amino acids
Asp and Glu
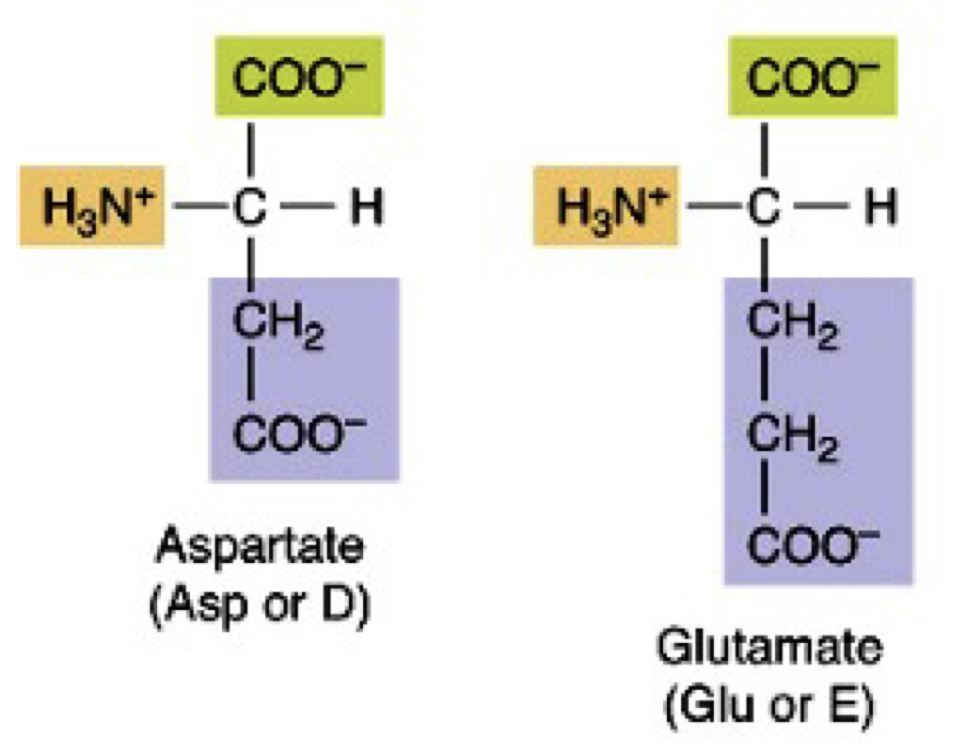
38
New cards
Basic positively charged R Polar Amino Acids
Lys, Arg, His
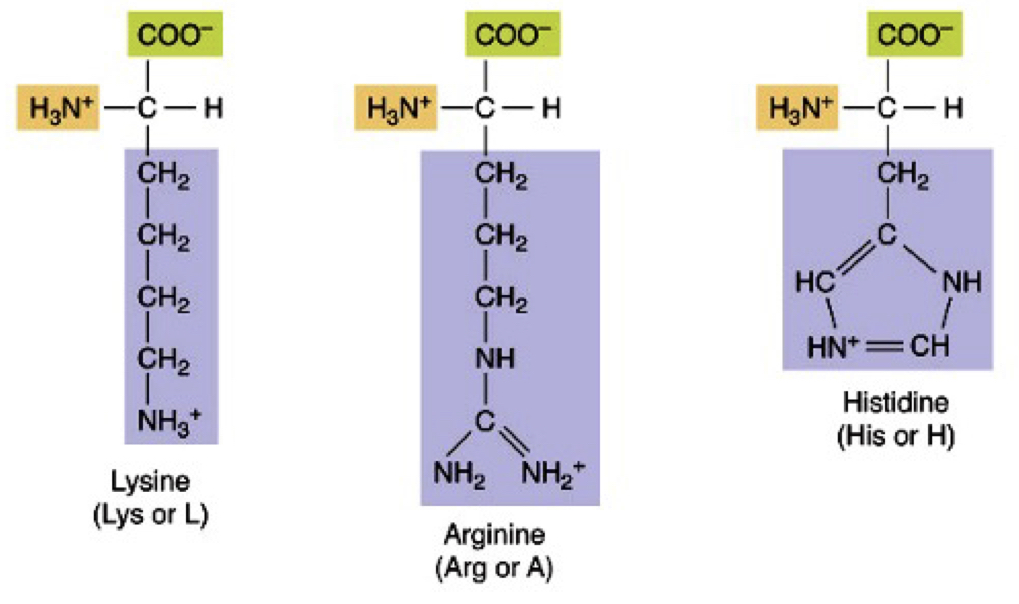
39
New cards
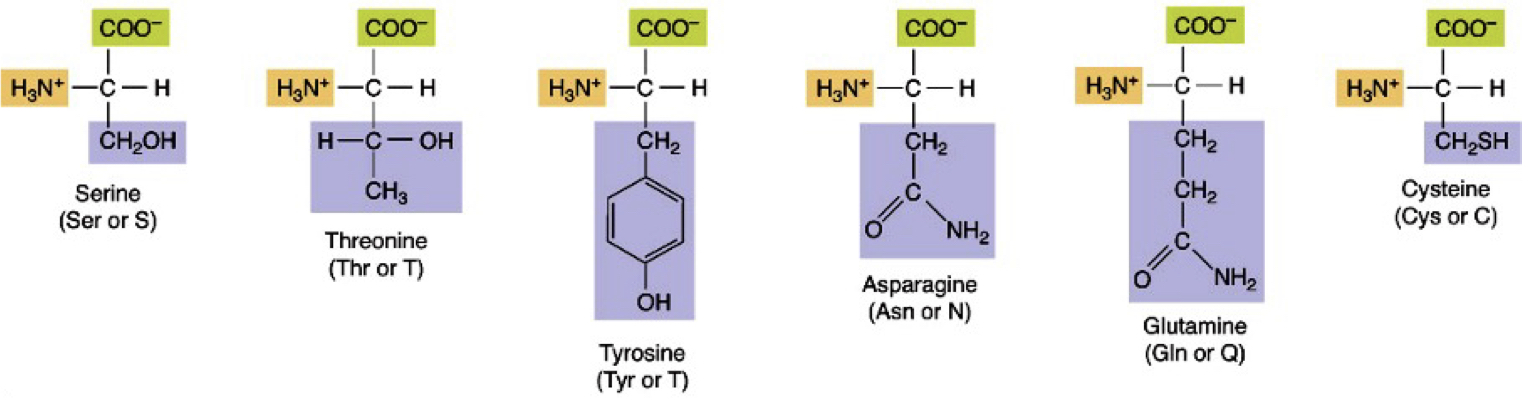
Neutral Polar R no charge
ser, thr, tyr, asn, gln, cys
40
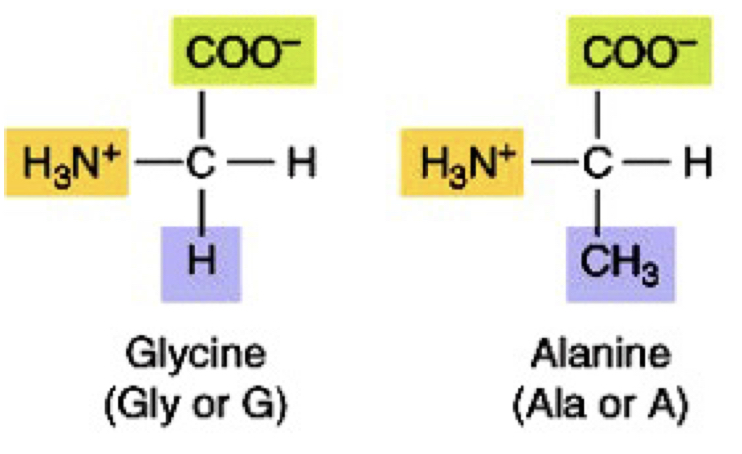
New cards
Alkyl non-polar amino acids
Gly, Ala
41
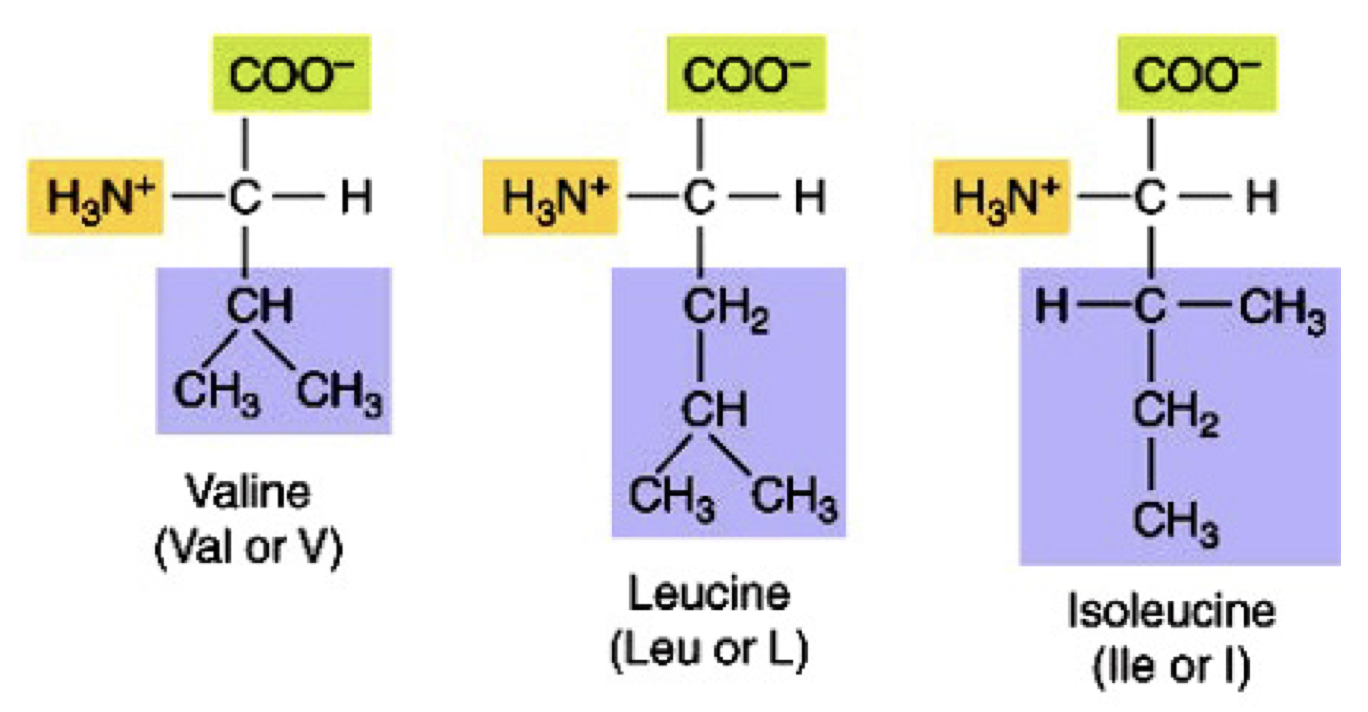
New cards
Branched chain non-polar amino acids
val, leu, ile
42
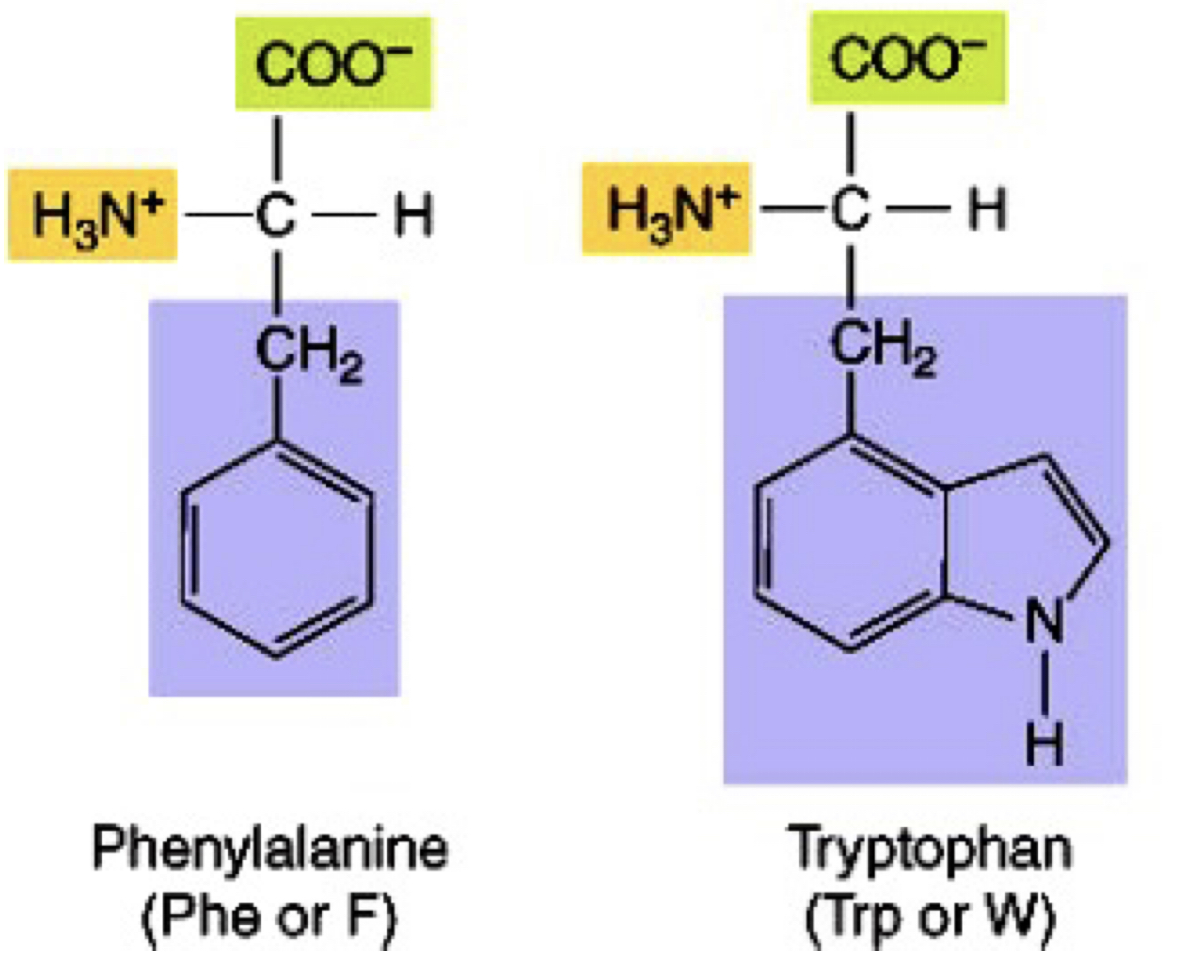
New cards
Aromatics non-polar amino acids
phe, trp
43
New cards
Thioether non-polar amino acid
met
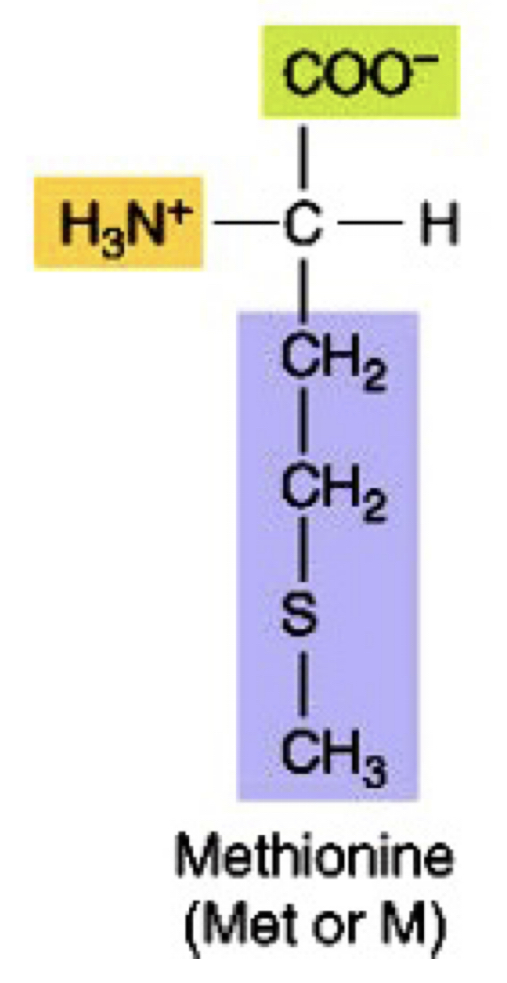
44
New cards
Secondary Amine non-polar amino acid
Pro
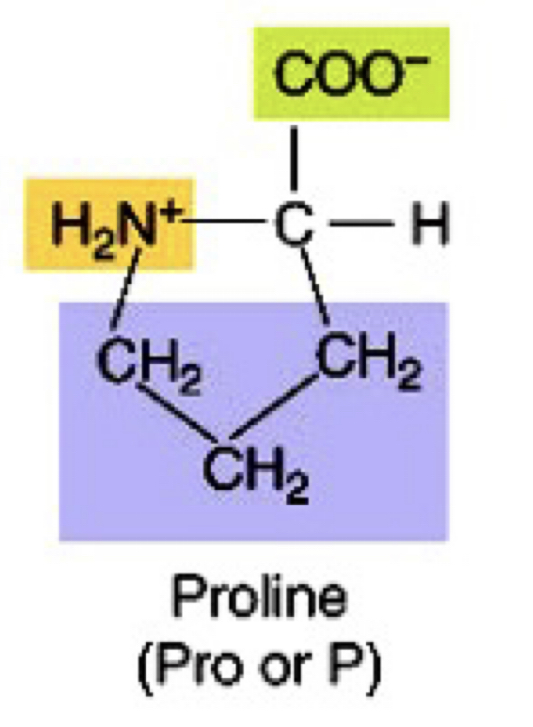
45
New cards
Essential amino acids in humans
(only available in food)
(only available in food)
Histidine, Isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, valine
46
New cards
Nonessential amino acids in humans
(can be synthesized in body)
(can be synthesized in body)
Alanine, arginine, aspartic acid, asparagine, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, __tyrosine__
47
New cards
Ketogenic amino acids
leucine, lysine (acetyl CoA, acetoacetyl CoA)
48
New cards
Glucogenic amino acids
glycine, serine, valine, histidine, arginine, cysteine, proline, alanine, glutamine, aspartate, asparagine, methionine (glycosis, gluconeogenics, krebs → sugar metabolism)
49
New cards
Both ketogenic and glucogenic
isoleucine, threonine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan
50
New cards
zwitterion
have both negatively and positively charged groups but the overall charge in the molecules is 0
51
New cards
isoelectric point pI
the ph value at which the overall charge of zwitterion is exactly zero
if R group does not have dissociable groups: pI=(pK1+pK2)/2
if R group has dissociable group: pI=pK3/pKR
if R group does not have dissociable groups: pI=(pK1+pK2)/2
if R group has dissociable group: pI=pK3/pKR
52
New cards
amine bond or peptide bond
covalent bond between amino group of one amino acid and alpha carboxyl group of another amino acid
53
New cards
dehydration reaction
energy dependent; GTP
54
New cards
In vivo formation of peptide bond
several proteins and a nucleic acid scaffold are involved; both protein type enzymes and ribozymes are involved
55
New cards
how much energy is needed to rotate a peptide bond?
88 kJ/mol
56
New cards
configuration at peptide bond
planar, trans configuration → undergo little rotation as it is restricted
57
New cards
a lot of energy is needed to break a peptide bond
True
58
New cards
Peptide bond partial double bond
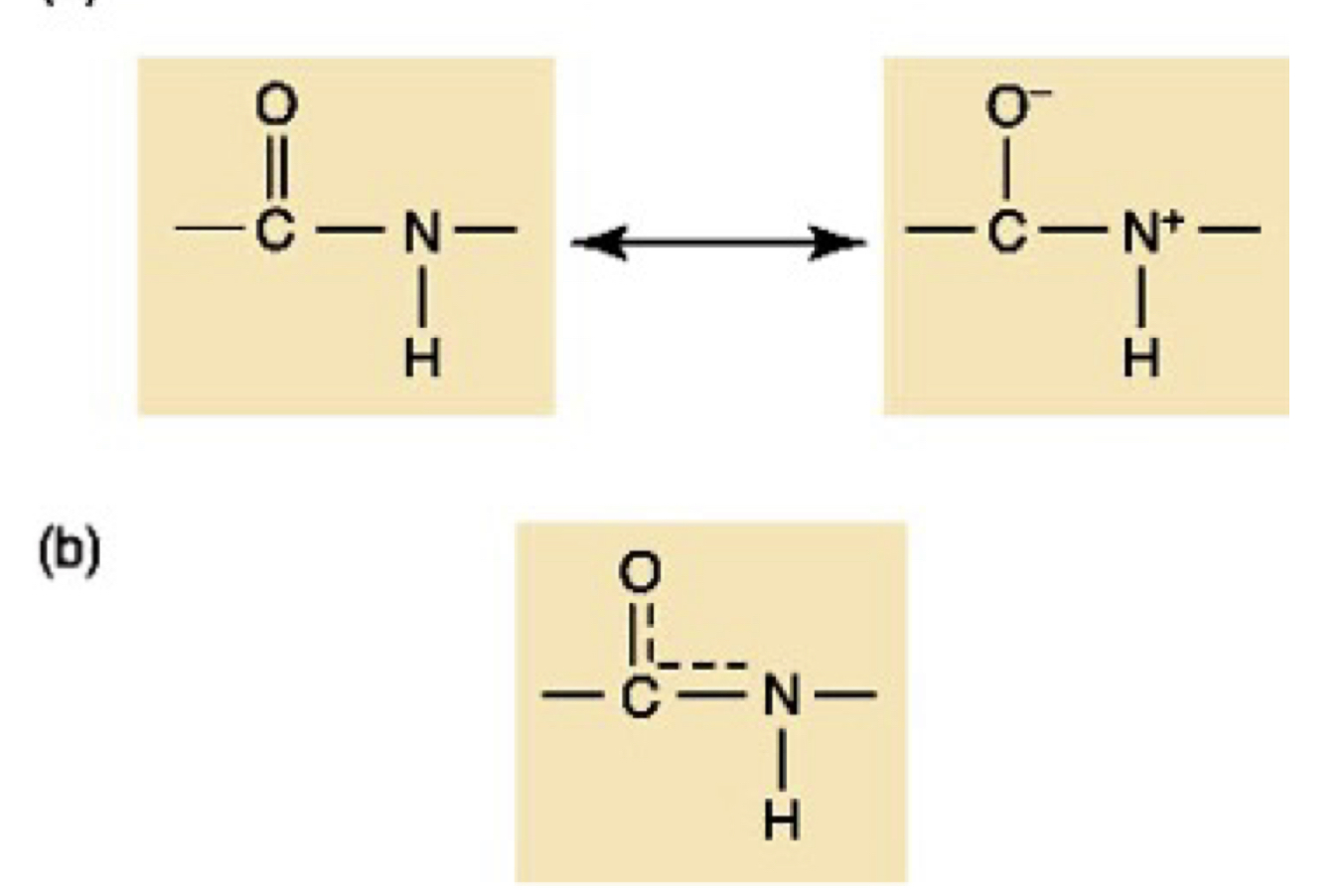
59
New cards
N-terminal end
free unbounded amino group
60
New cards
C-terminal end
free unbounded carboxyl group
61
New cards
what is the difference of a peptide and a protein
peptides are short chains or less than 25 amino acids and can have biological properties: functional
proteins have more than 25 amino acids and have one biological polymer: macromolecules
proteins have more than 25 amino acids and have one biological polymer: macromolecules
62
New cards
what does protein structure determine
function, it sets the foundation for its interaction with other molecules
63
New cards
4 levels of hierarchy in protein structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
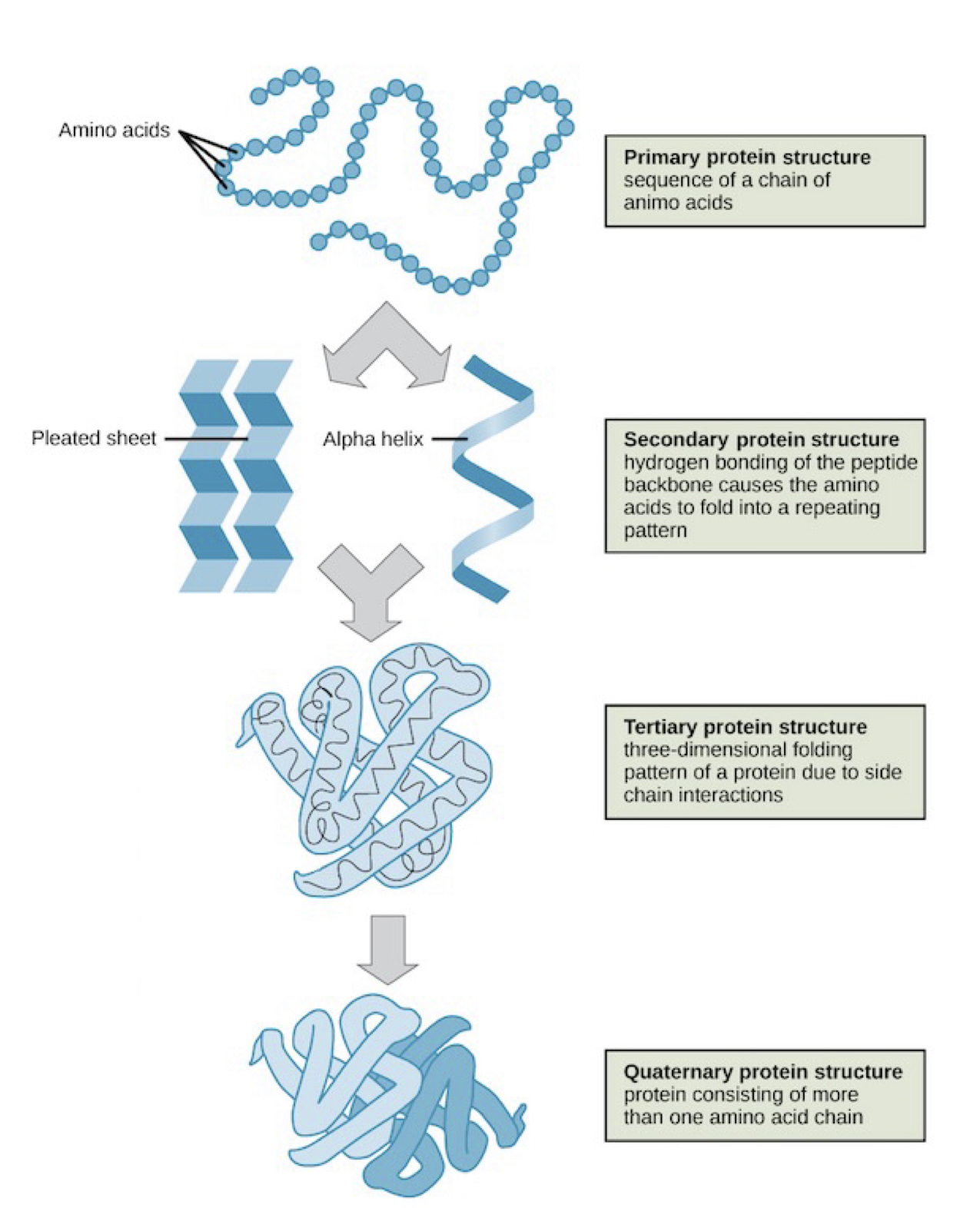
64
New cards
3 main types of secondary protein structure
beta sheet
alpha helix: spiral chain
coil/loop and turn
alpha helix: spiral chain
coil/loop and turn
65
New cards
(T or F) R groups determine amino acid water solubility (secondary protein structure)
T
66
New cards
which amino acid favors helix structure
glycine in collagen
67
New cards
which amino acids are helix breakers
proline
68
New cards
H bond and beta sheet does what
stabilizes this structure into a plated arrangement
69
New cards
Anti-parallel vs parallel beta sheets
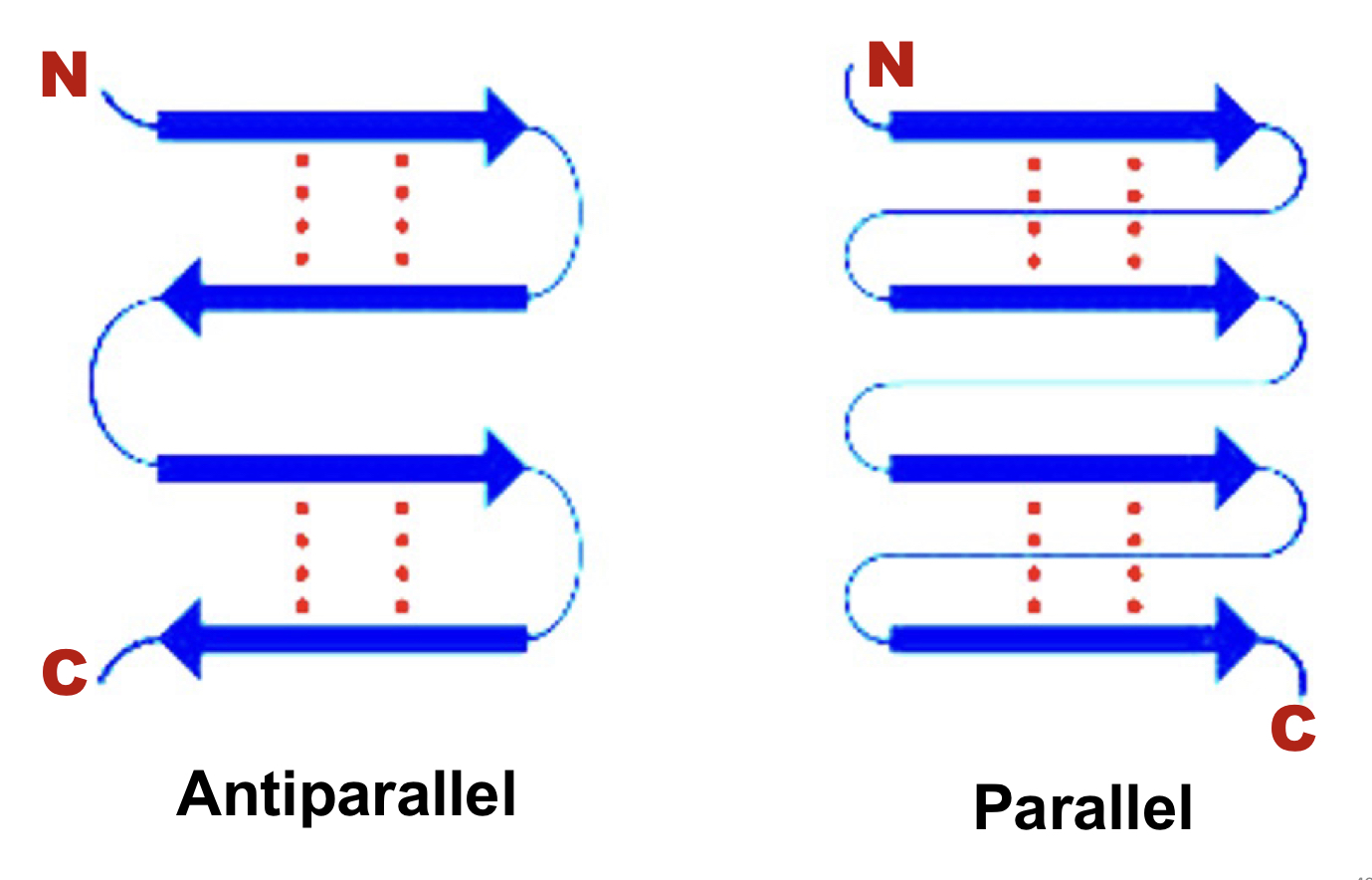
70
New cards
protein motifs
recognize specific signal/ligand
interact with DNA gene promoter
interact with some other proteins
interact with DNA gene promoter
interact with some other proteins
71
New cards
protein domains (motif/suer secondary structure)
perform a particular chemical or physical task/function
72
New cards
nuclear receptors
a class of proteins that are responsible for sensing steroid and thyroid hormones, xenobiotics, and certain other molecules. In response, these receptors work with other proteins to regulate the expression of specific genes, thereby controlling the development, homeostasis, and metabolism of the organism
73
New cards
what does a protein require for it to be functional
multiple individual function components
74
New cards
DNA binding domain (DBD)
an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double or single stranded DNA
75
New cards
hydrophobic effects
causing no interaction with water
76
New cards
hydrophobic core
major determinant of native protein structure
77
New cards
electrostatic interactions
mainly van der waals force (short distance)
78
New cards
disulfide bonds
between two cysteine
79
New cards
metal ions
ionic force (iron in heme, zinc fingers-DNA binding protein)
80
New cards
relationship of configuration/ 3D structure of a protein and its function
* correct configuration or 3-D structure of a protein is essential for its function
* alteration of configuration or 3-D structure of a protein leads to alteration of its function
* activation & inhibition
* alteration of configuration or 3-D structure of a protein leads to alteration of its function
* activation & inhibition
81
New cards
Strategies to alter protein configuration
1. protein-protein interaction → chaperone protein driven folding and refolding
2. ligand binding → activators and inhibitors
3. phosphorylation and acytylation
82
New cards
chaperone protein
the protein that assists the non-covalent folding or unfolding and the assembly or disassembly of other macromolecular structures, such as other proteins
83
New cards
GroEL
a bacteria protein that helps folding of newly synthesized proteins or misfolding proteins
84
New cards
hydrophobic inner hole
required for protein folding
85
New cards
hydrophilic surface
attracts misfolding proteins
86
New cards
binding protein
stabilized correctly folded protein
87
New cards
myoglobin (Mb) and Hemoglobin (Hb)
oxygen binding proteins in mammals
88
New cards
myoglobin (Mb)
monomer oxygen binding protein → tighly bound to one heme molecule
89
New cards
Hemoglobin (Hb)
tetramer oxygen binding proteins → 2 alpha and 2 beta chains. Bind to 4 heme molecules
90
New cards
myoglobin
a red protein containing heme that carries and stores oxygen in muscle cell
91
New cards
tetramer
2 alpha and 2 beta protomers/subunits → binding to 4 heme molecules
92
New cards
Bohr effects
hemoglobins oxygen binding affinity is inversely related both to acidity and to the concentration of carbon dioxide
93
New cards
what is the result of a decrease in blood ph or an increase in blood co2 concentration
hemoglobin proteins releasing their loads of oxygen → carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid
94
New cards
what muscle does during exercise
generate lactate and more co2 generated
95
New cards
what does a decrease in carbon dioxide pressure or increase in ph
hemoglobin picking up more oxygen
96
New cards
transportation of O2 and CO2 between lung and tissues: carbonic anhydrase
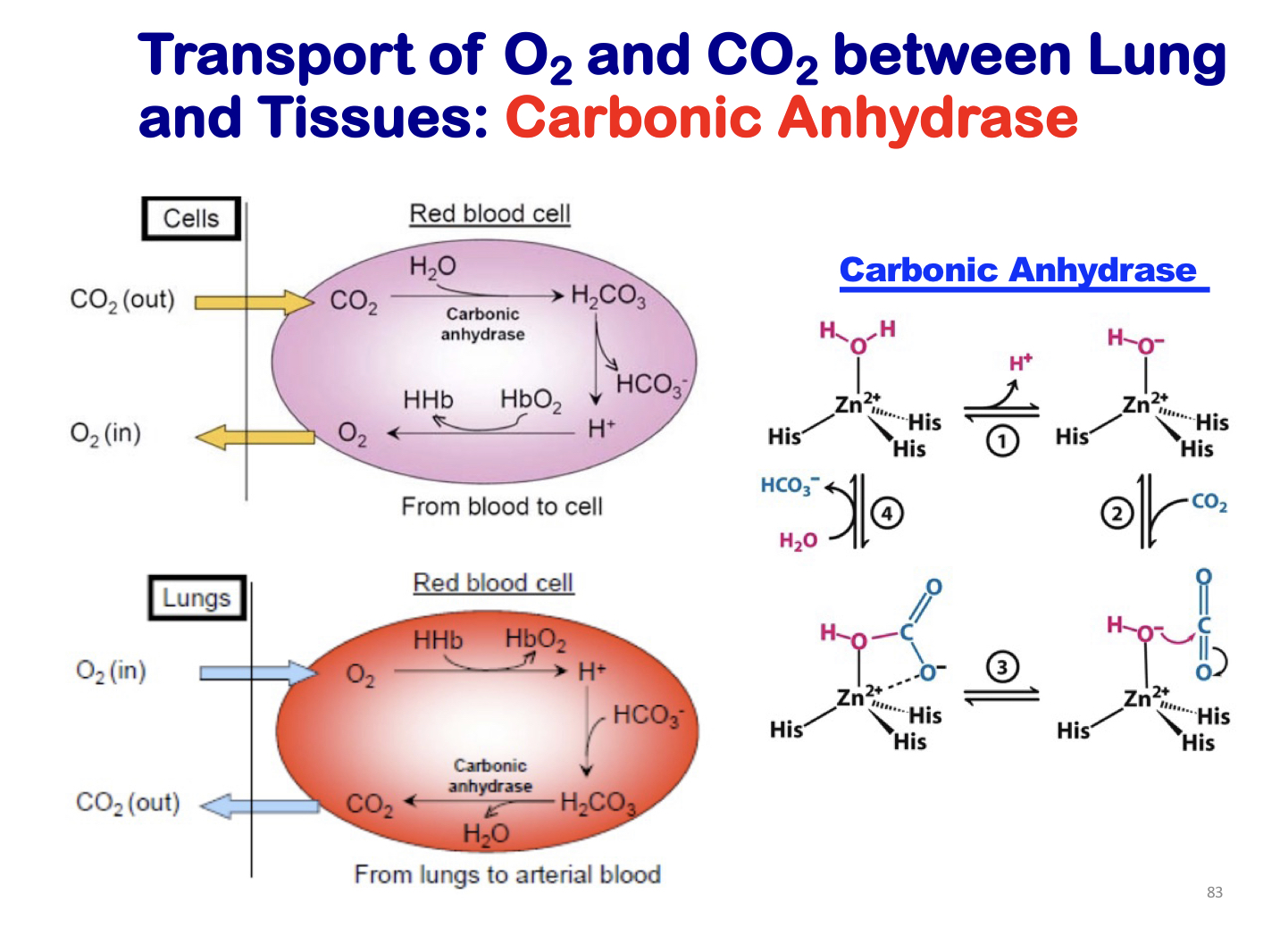
97
New cards
CO2 pressure is higher in muscle than lungs which leads to
O2 binding to hemoglobin in lung but O2 released in muscle
98
New cards
Discuss why the oxygen will dissociate from hemoglobin or why more oxygen will be delivered to muscle in an active tissue, such as the muscle during physical exercise
* CO2 pressure is high
* Temperature is high
* lactate is generated
* blood shunt from liver to muscle
→ lowering pH
* Temperature is high
* lactate is generated
* blood shunt from liver to muscle
→ lowering pH
99
New cards
Bohr effect → left shift
more binding → less CO2 and higher pH
100
New cards
Bohr effect → right shift
less binding → more CO2 and pH