Strayer 11 (1900-1950)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
World War I
(1914 - 1918) European war in which an alliance including Great Britain, France, Russia, Italy, and the United States defeated the alliance of Germany, Austria-Hungary, Turkey, and Bulgaria. Consisted mostly of trench warfare.

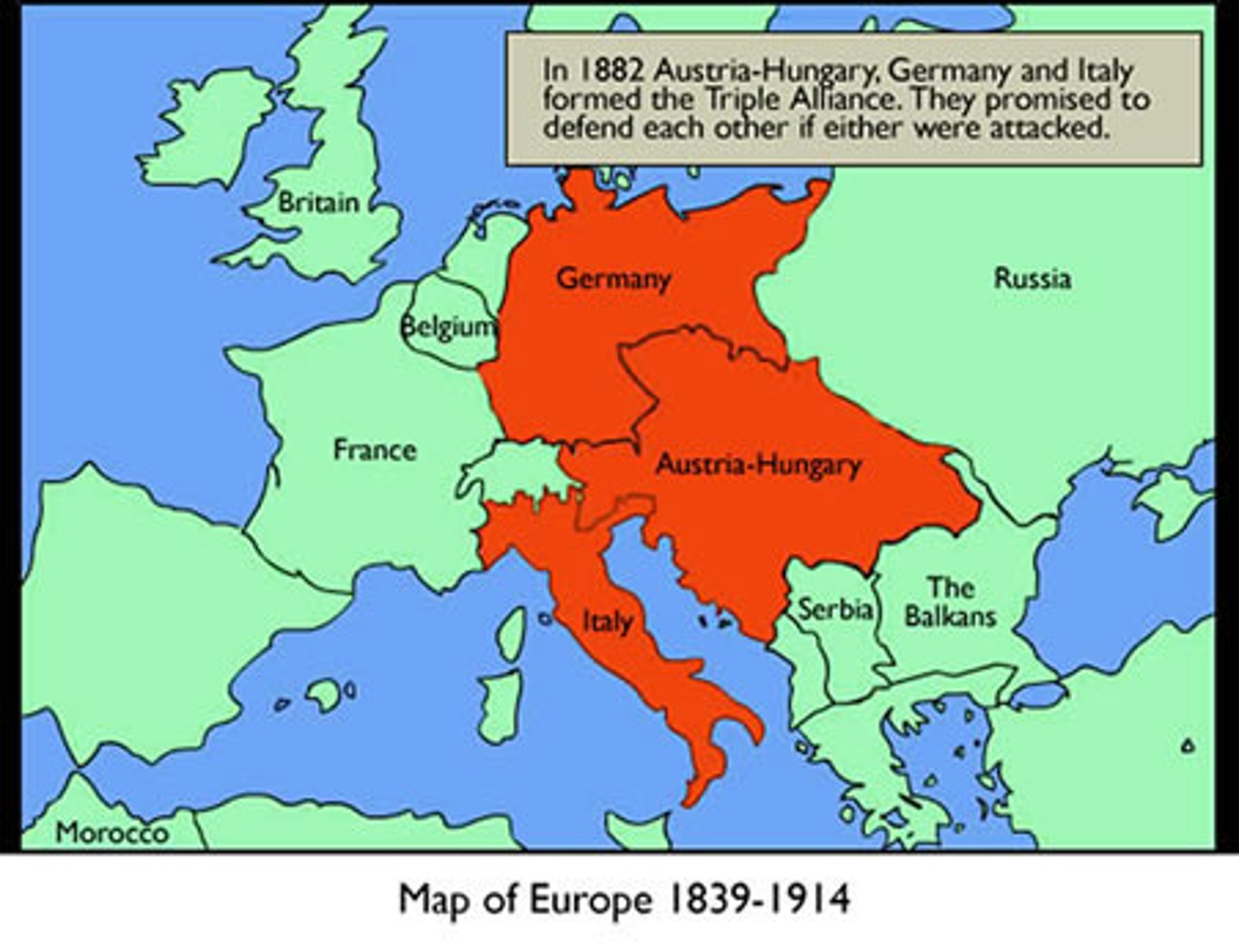
Triple Alliance
An alliance between Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy in the years before WWI.
Triple Entente
A military alliance between Great Britain, France, and Russia in the years preceding World War I.
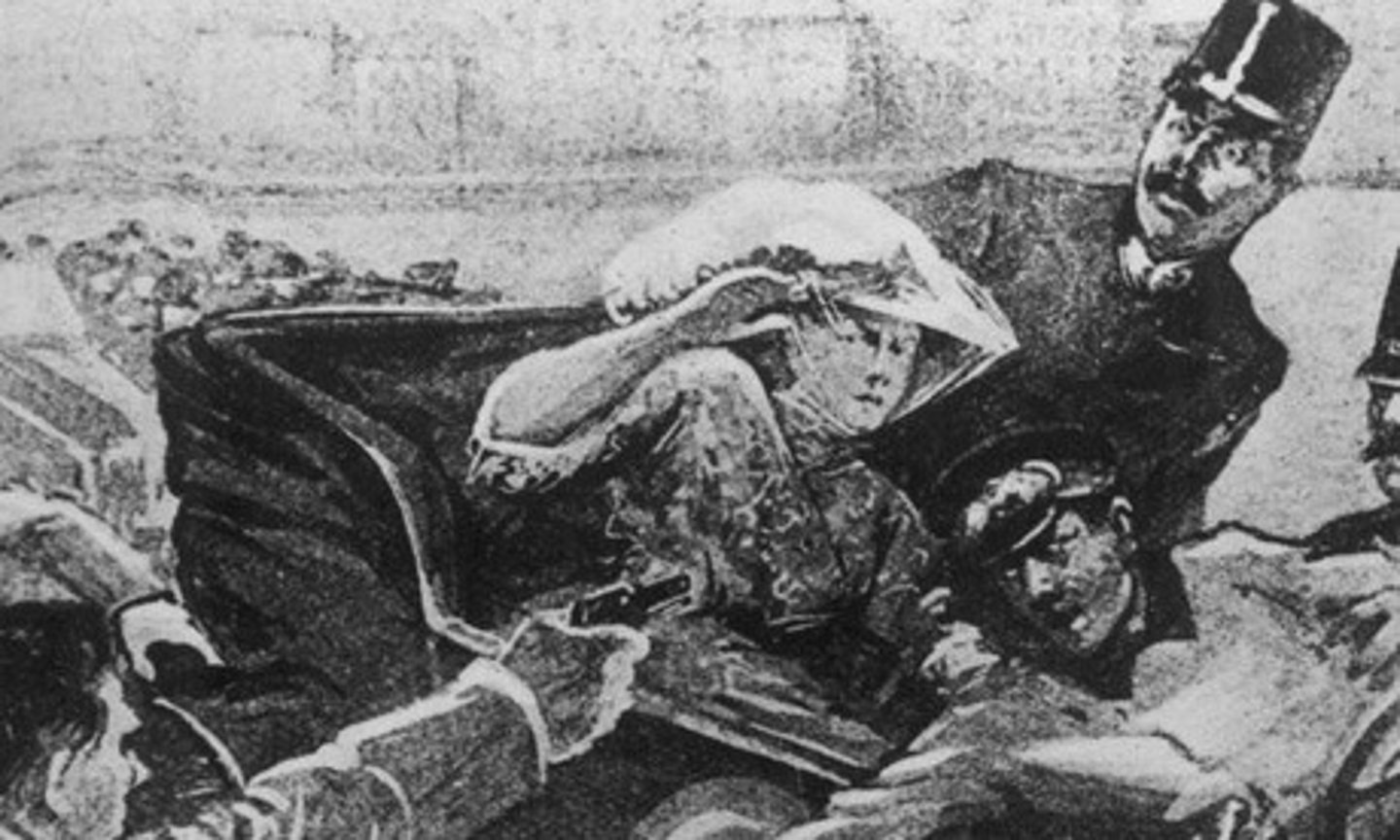
Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Archduke of Austria Hungary assassinated by a Serbian in 1914. His murder was one of the causes of WW I.
Total War
A conflict in which the participating countries devote all their resources to the war effort

Propaganda
information, especially of a biased or misleading nature, used to promote or publicize a particular political cause or point of view.

Treaty of Versailles
the treaty imposed on Germany by the Allied powers in 1920 after the end of World War I which demanded exorbitant reparations from the Germans
Reparations
Payments imposed on Germany post-World War I in money, territory, military, and resources
League of Nations
an international organization formed in 1920 to promote cooperation and peace among nations

Russian Revolution
1917 uprising leading to Bolshevik control.
Bolsheviks
Led by Vladimir Lenin it was the Russian communist party that took over the Russian government during WWI

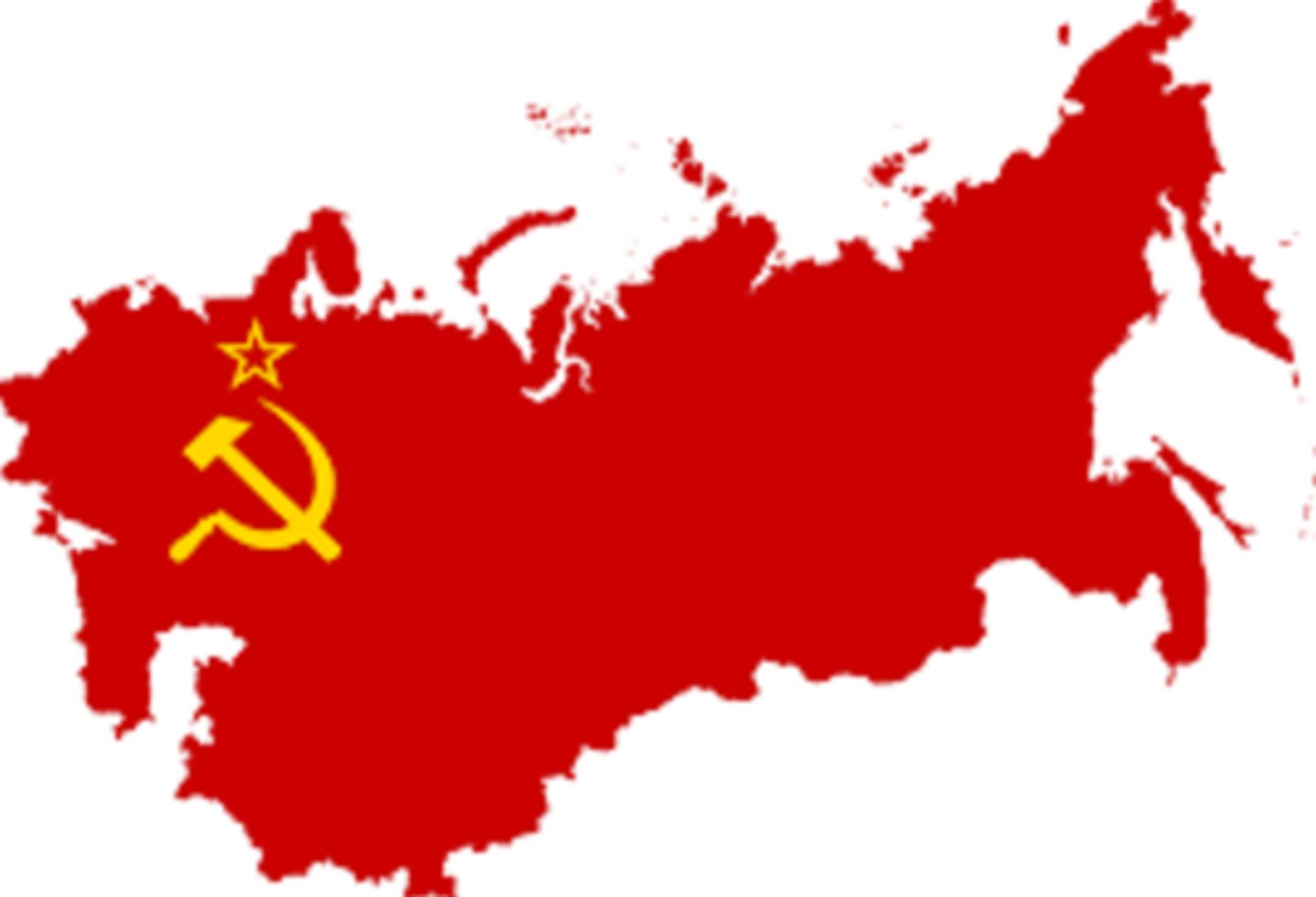
USSR
Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. Created by Lenin in 1922.
Stalin
Russian leader who succeeded Lenin as head of the Communist Party and created a totalitarian state by purging all opposition (1879-1953)

Collectivization
a system in which private farms are eliminated and peasants work land owned by the government

New Deal
A series of reforms enacted by the Franklin Roosevelt administration between 1933 and 1942 with the goal of ending the Great Depression.

Fascism
A governmental system led by a dictator having complete power, forcibly suppressing opposition and criticism, regimenting all industry, commerce, etc., and emphasizing an aggressive nationalism and often racism.

Mussolini
founded fascism and ruled Italy for almost 21 years, most of that time as dictator. He dreamed of building Italy into a great empire, but he led his nation to defeat in World War II (1939-1945) and was executed by his own people.

Nazi Party
German political party joined by Adolf Hitler, emphasizing nationalism, racism, and war. When Hitler became chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party became the only legal party and an instrument of Hitler's absolute rule.

Blitzkrieg
"Lighting war", typed of fast-moving warfare used by German forces in WWII
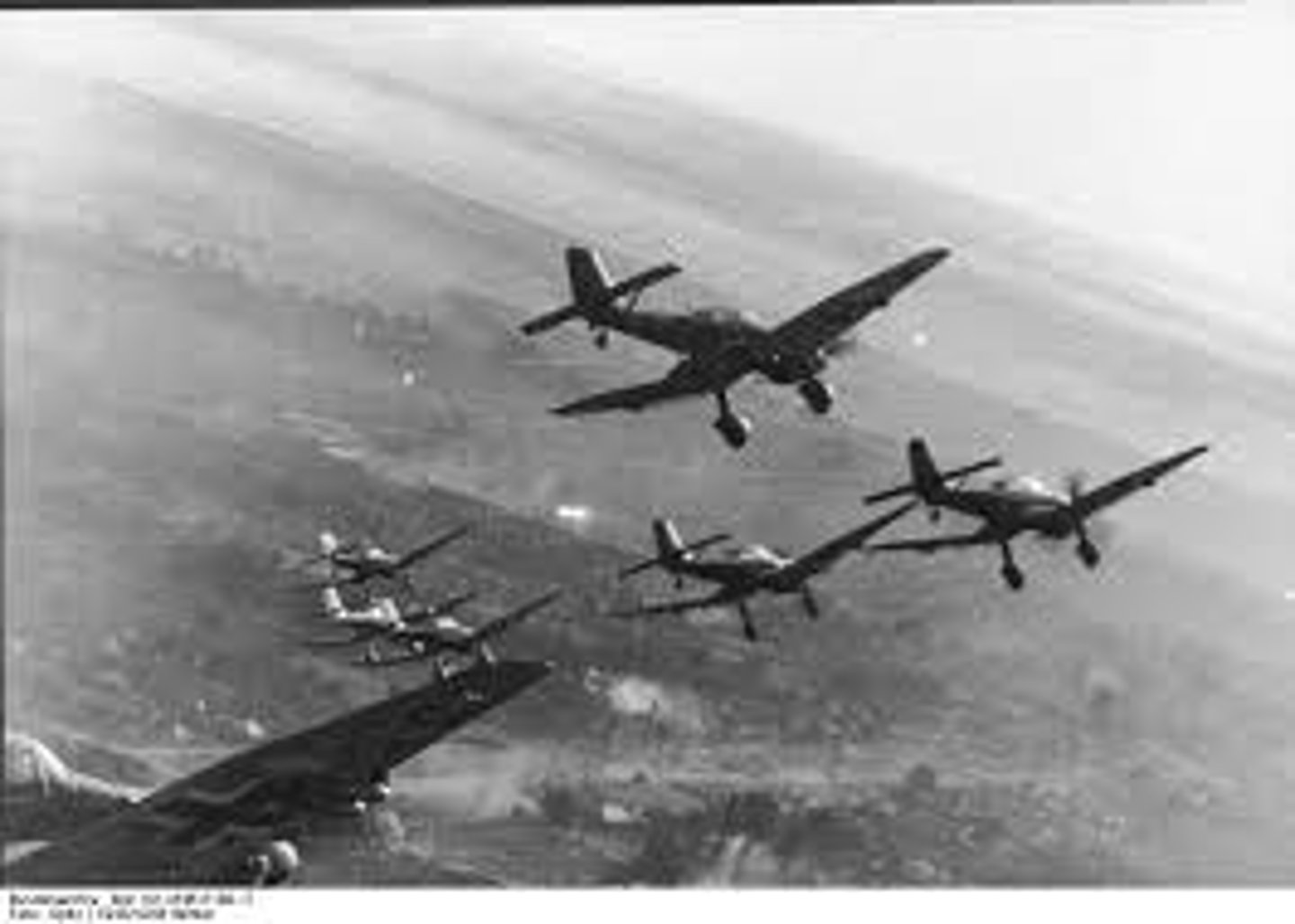

Holocaust
A methodical plan orchestrated by Hitler to ensure German supremacy. It called for the elimination of Jews, non-conformists, homosexuals, non-Aryans, and mentally and physically disabled.
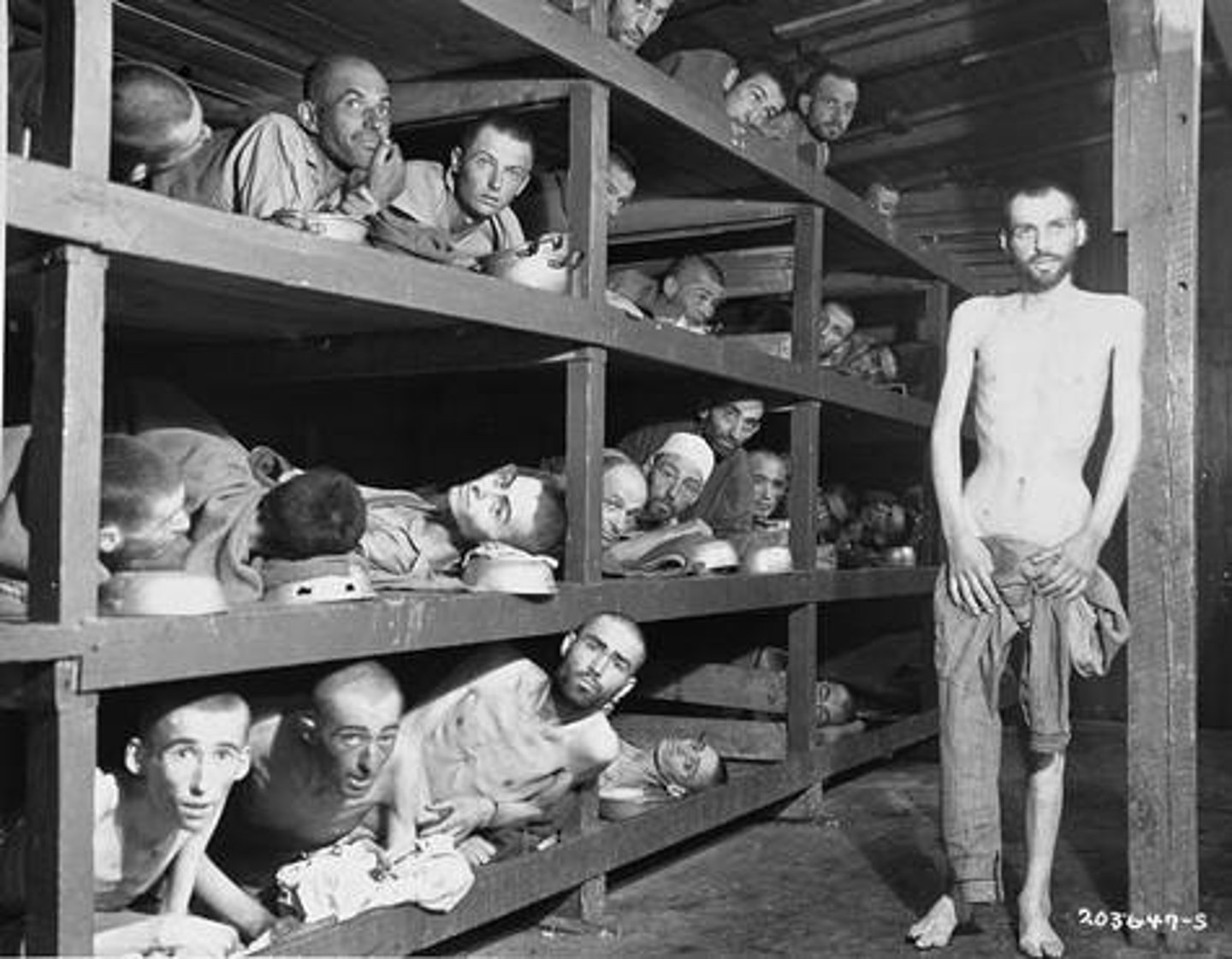

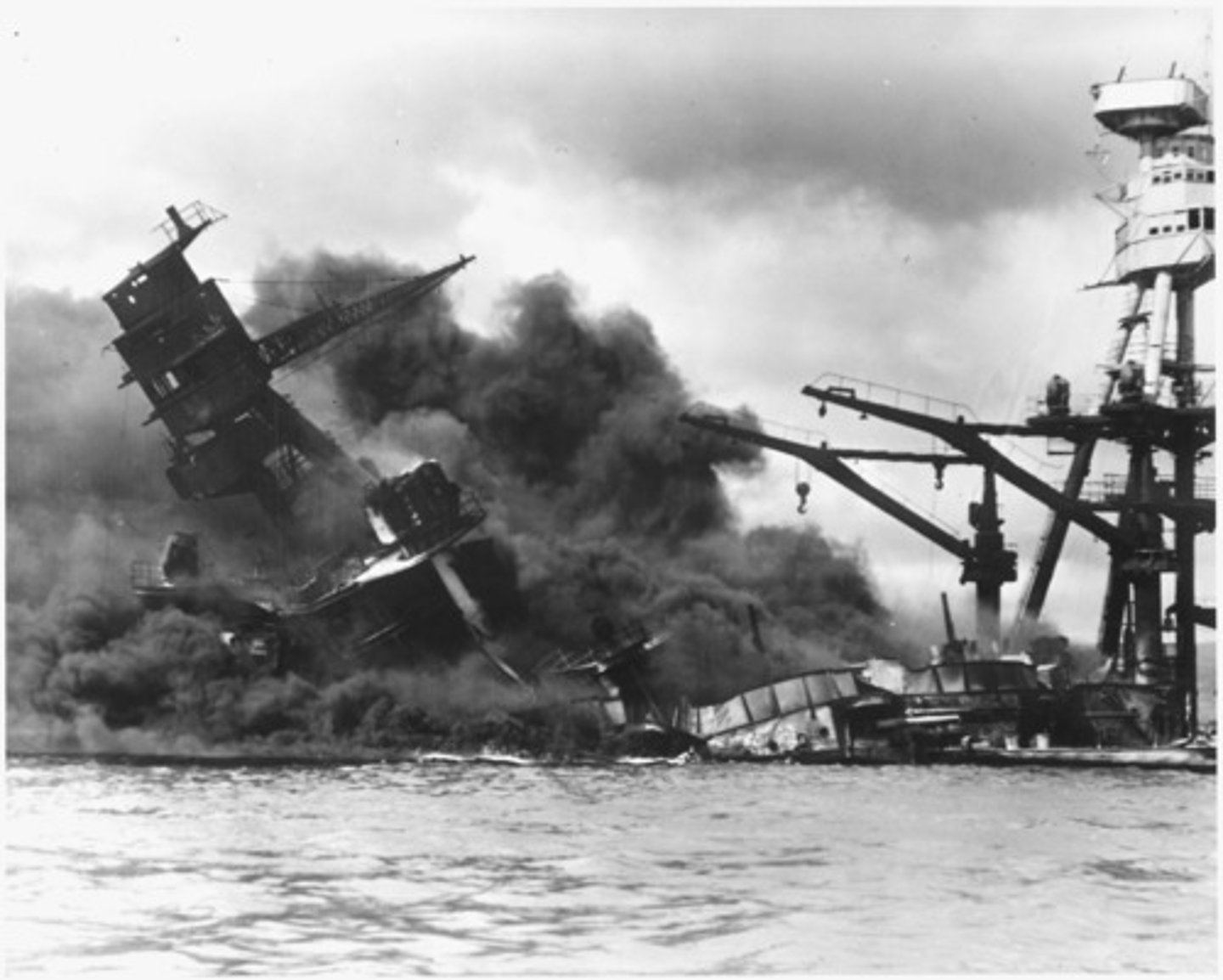
Pearl Harbor
United States military base on Hawaii that was bombed by Japan, bringing the United States into World War II. Pearl Harbor was attacked on December 7, 1941.

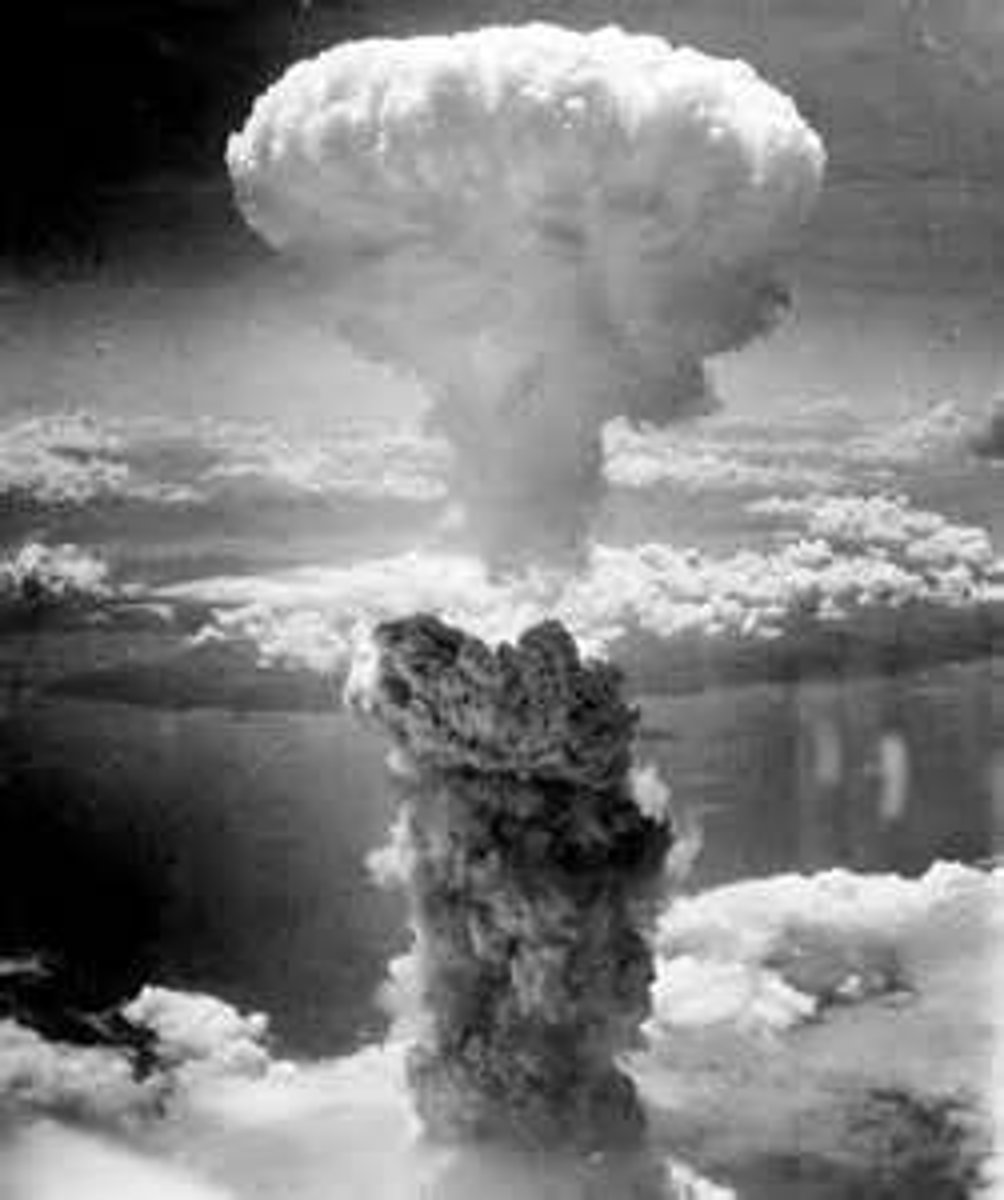
Atomic Weapons
These were developed during World War II as a result of the Manhattan Project. Two of these would be used on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.

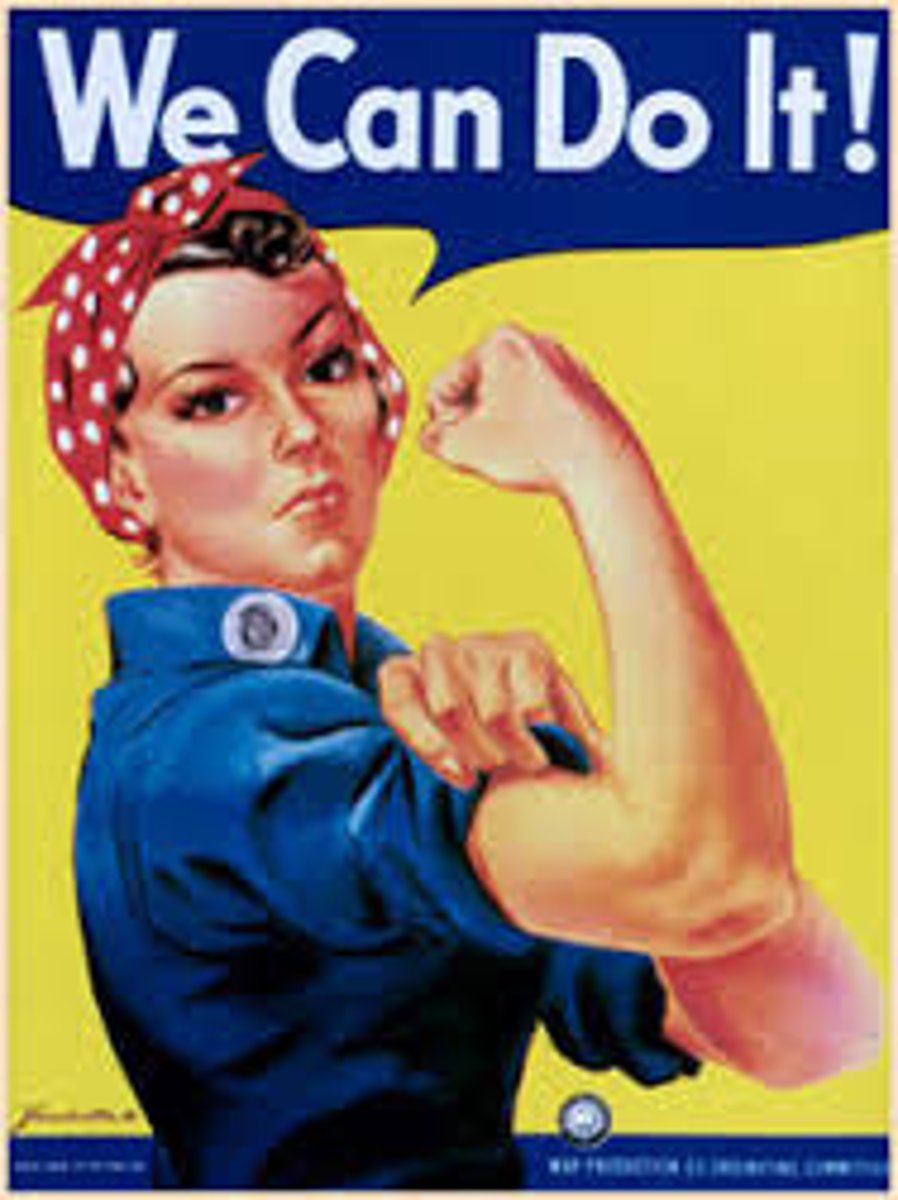
Rosie the Riveter
A propaganda character designed to increase production of female workers in the factories. It became a rallying symbol for women to do their part.

United Nations
An international organization formed after WWII to promote international peace, security, and cooperation.

Stalin's Terror
Stalin had more than 15 million people killed or sent to prison camps in Siberia. Used fear to exert power, killed and arrested many people

Mao Zedong
Leader of the Chinese Communist Party (1927-1976). He led the Communists on the Long March (1934-1935) and rebuilt the Communist Party and Red Army during the Japanese occupation of China (1937-1945).

Guomindang
Political party formed by Sun Yat-sen that ruled China from 1911 to 1949; enemy of the Communists. Often abbreviated at GMD.

Long March
The 6,000-mile (9,600-kilometer) flight of Chinese Communists from southeastern to northwestern China. The Communists, led by Mao Zedong, were pursued by the Chinese army under orders from Chiang Kai-shek.

Rape of Nanjing
Japanese attack on Chinese capital from 1937-1938 when Japanese aggressors slaughtered 100,000 civilians and raped thousands of women in order to gain control of China.
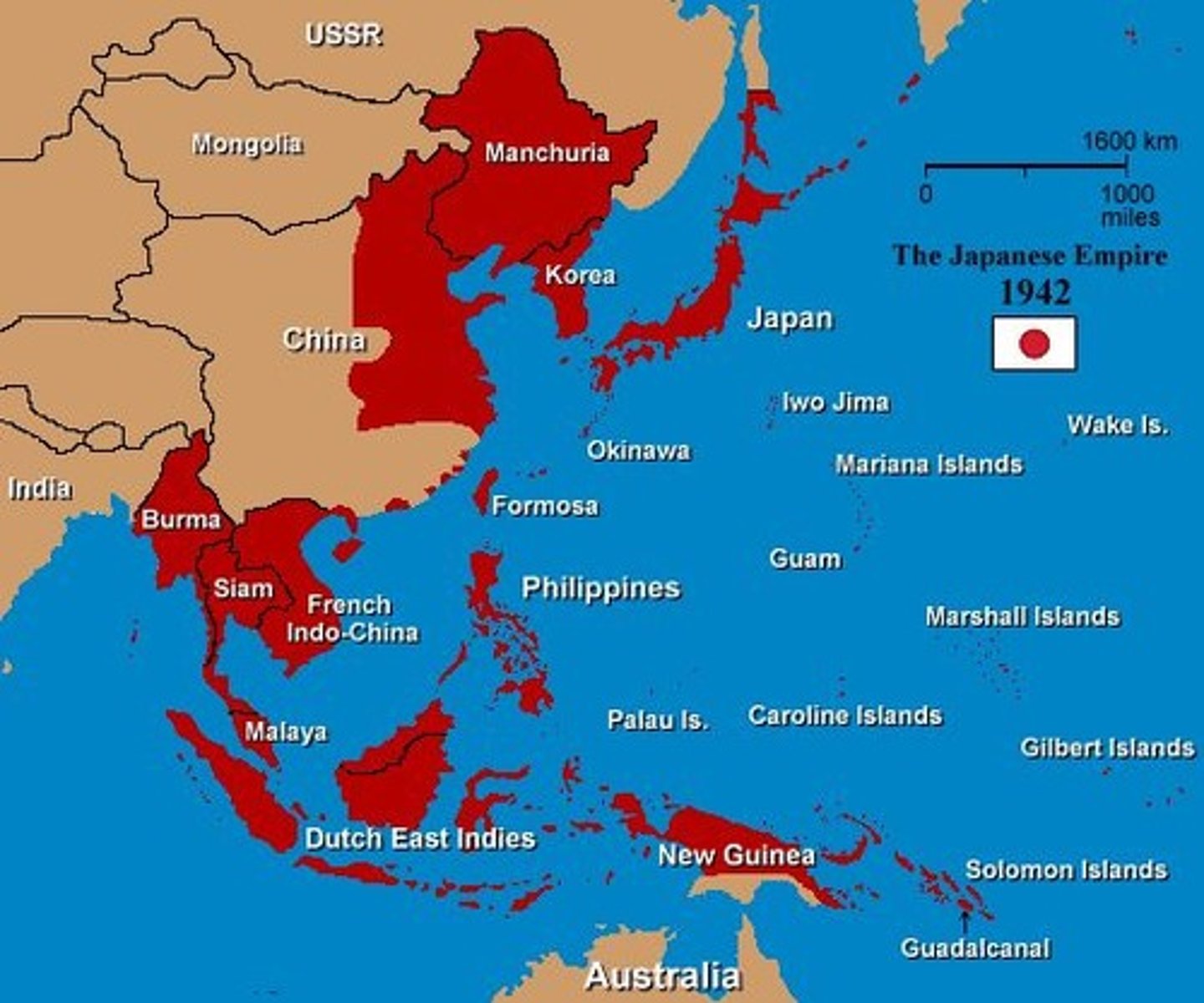
Japanese Expansion
1941-1942 refers to the opening of the Pacific War when the Empire of Japan attacked British, Dutch, Australian and American holdings in Southeast Asia and the Pacific Ocean to gain resources in order to break Japanese dependence on US resources
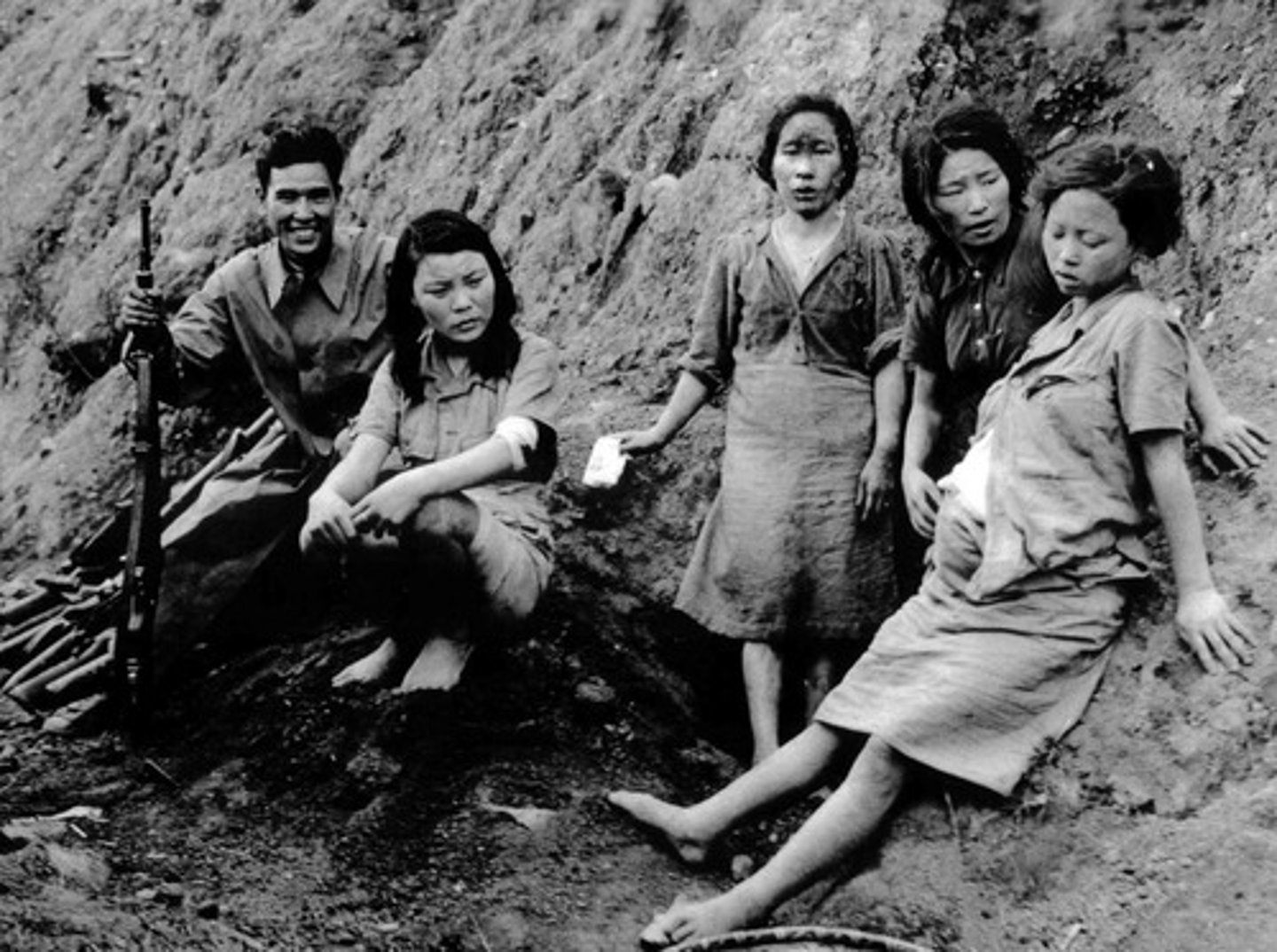
Comfort Women
women forcibly recruited by the Japanese army to serve in military brothels

Revolutionary Right
Also known as Radical Nationalism, this was a movement in Japanese political life ca. 1930-1945 that was marked by extreme nationalism, a commitment to elite leadership focused around the emperor, and dedication to foreign expansion.

WWII in Asia
WWII in Europe
A struggle essentially to halt German imperial expansion and aggression in Europe, fought by a coalition of allies that included Great Britain, the Soviet Union, and the United States. Started with German invasion of Poland

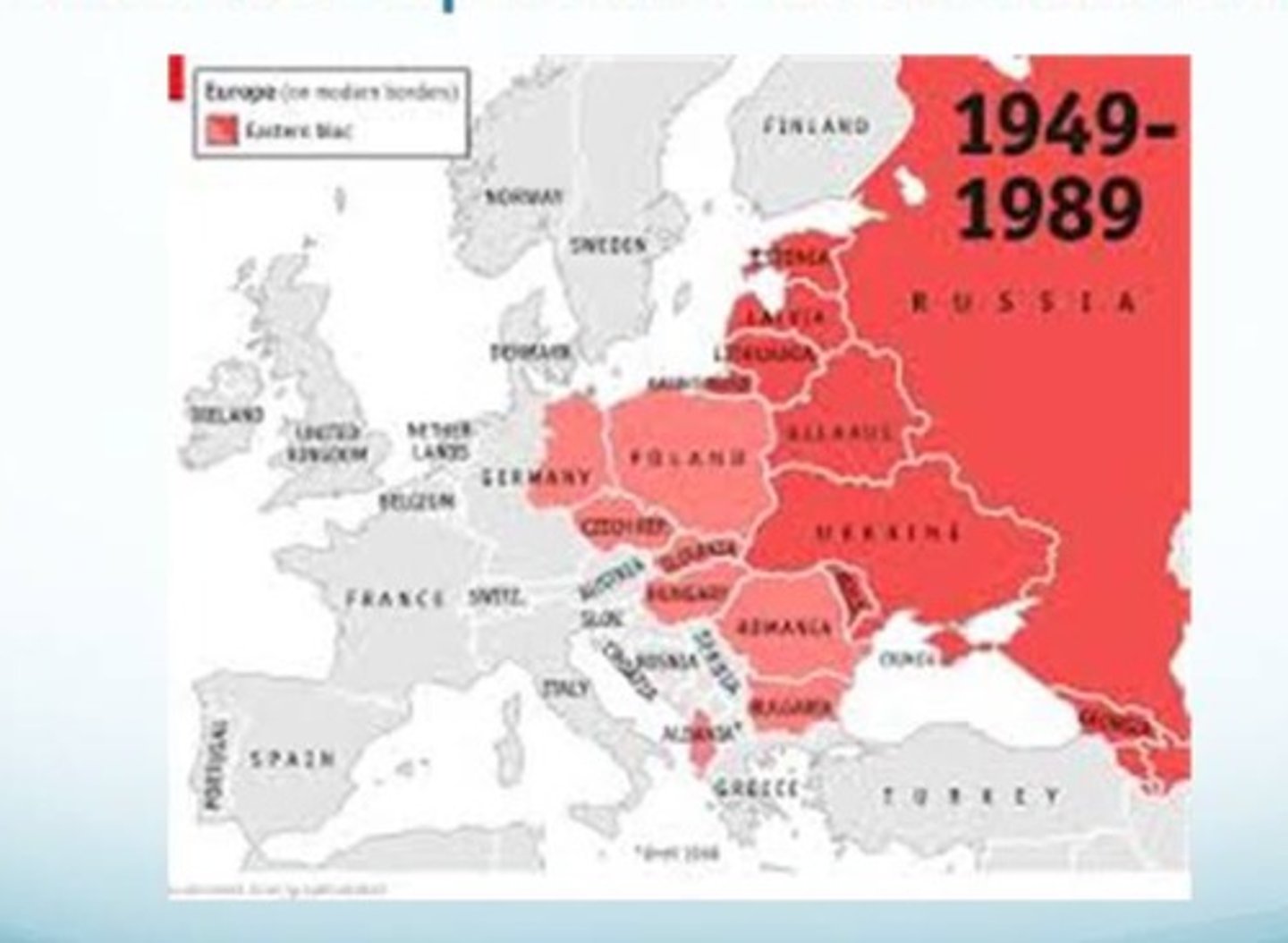
Communism in Eastern Europe
Expansion of post-World War II communism to Poland, East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria, imposed with Soviet pressure rather than growing out of domestic revolution.
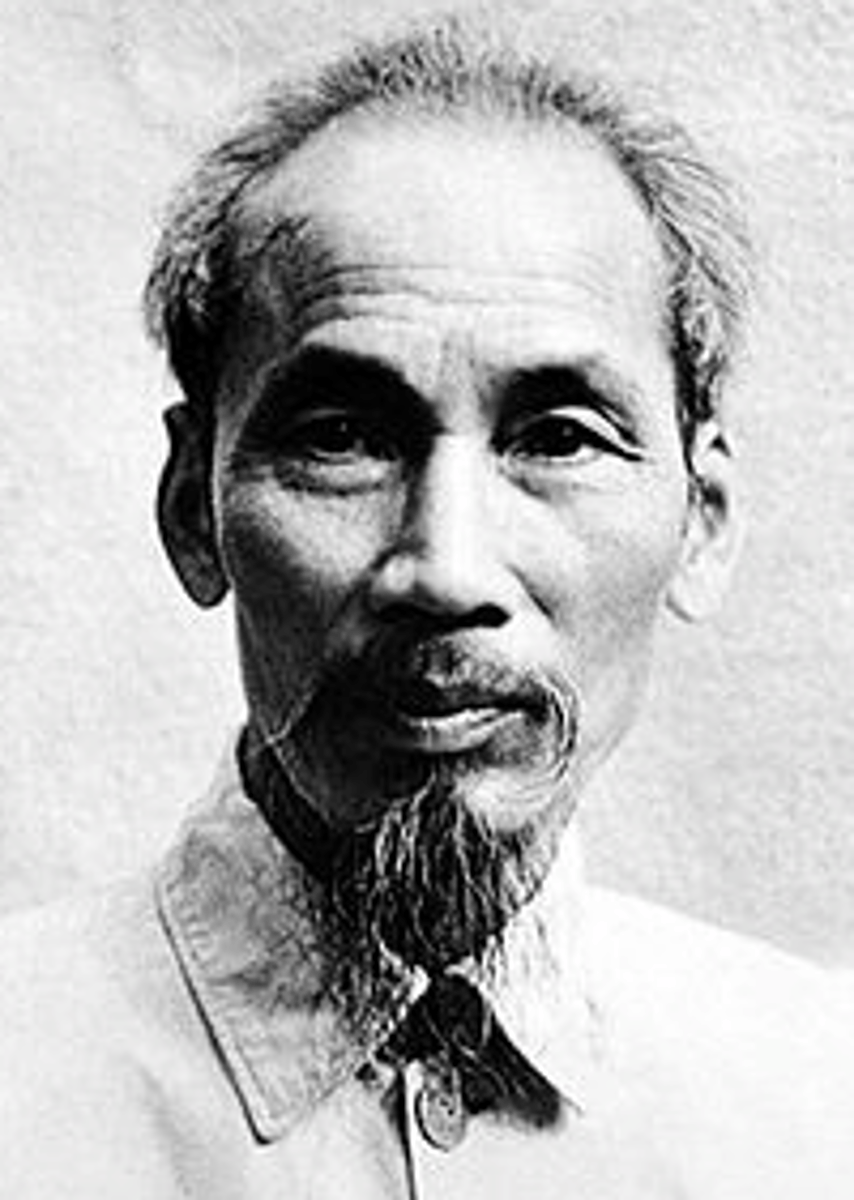
Ho Chi Minh
1950s and 60s; communist leader of North Vietnam; used guerilla warfare to fight anti-communist, American-funded attacks under the Truman Doctrine; strategy drew out war and made it unwinnable

Chinese Revolution of 1949
saw the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) led by Mao Zedong defeat the Kuomintang (KMT) and establish the People's Republic of China (PRC), ending the Chinese Civil War and leading to significant social and political changes

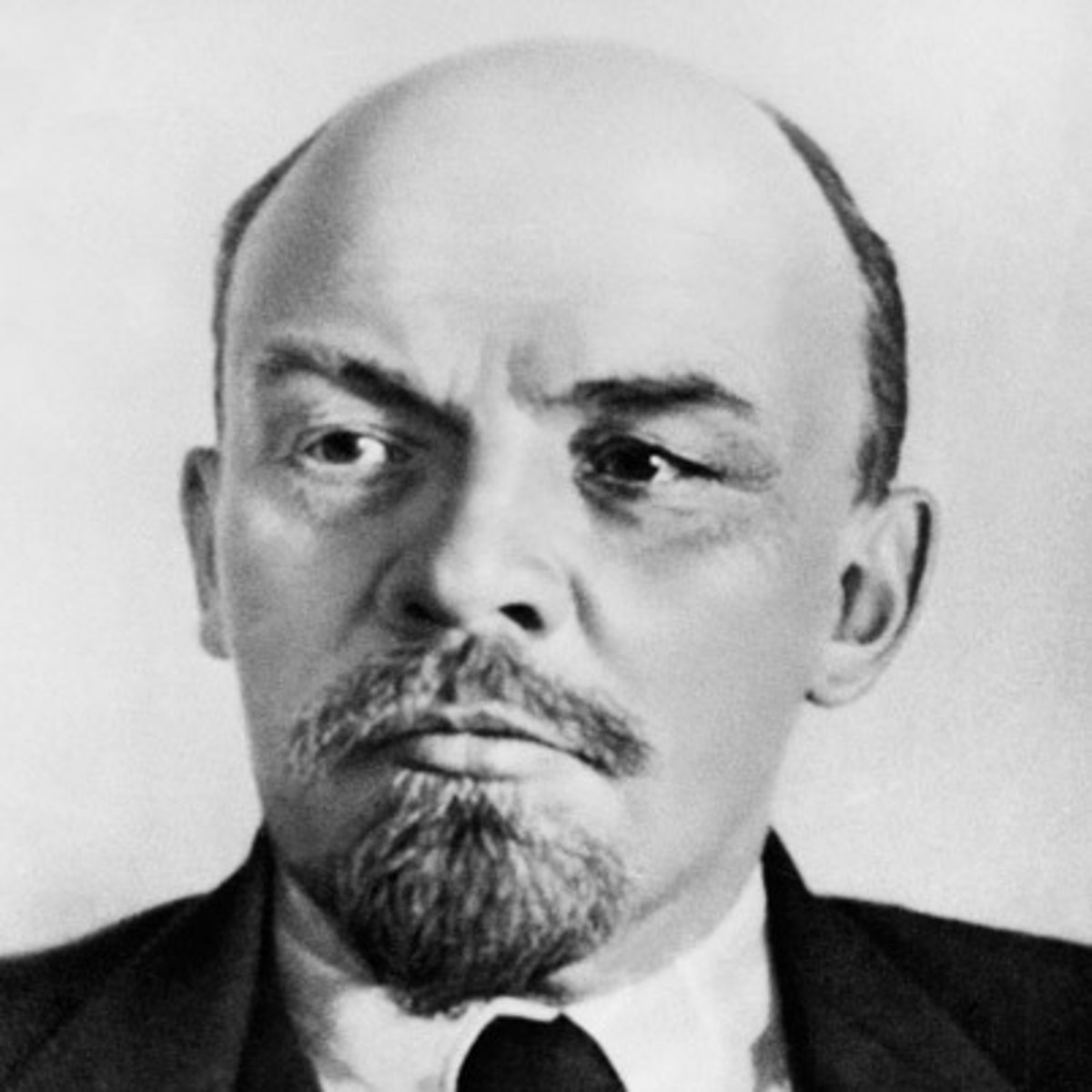
Lenin
a Russian revolutionary leader and the founder of the Soviet state, known for leading the Bolshevik Revolution in 1917 and establishing the first communist government in Russia

Great Depression
a severe global economic downturn that began in 1929 with the stock market crash and lasted until the late 1930s, characterized by widespread unemployment, poverty, and a sharp decline in industrial production
