Physical Growth And Developement
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Four areas of child development
Physical:
Motor maturation
Growth of body and CNS
Height and weight
Sensory capacity
Muscular and physical coordination
Cognitive
Intellectual processes
Change and stability in mental abilities
Language
Communication and understanding
Socio-emotional
Personality, emotional life, social relationships
Five periods of child development
Pre-natal
Infancy (birth-18 months) and Toddlerhood (18-24 months):
Infancy: identify familiar faces, use basic utensils and respond to facial expressions, learn few words and may walk on their own
Toddlerhood: pretend games, play with other children, follow 2-part directions and say names of familiar people, run
Early Childhood (3-5) Middle Childhood (6-11)
Early: likes and dislikes, count, colors, name, address, play
Middle: problem-solving skills, confidence, friendships, interests and reading skills
Adolescence (12-adulthood): independence, opinions, puberty, dating, sexuality
Schema
Cognitive structures that first appear during childhood and help children organize knowledge that helps them learn ways to view the world and adapt
Can create bias
Child’s developmental milestones
Mark stages of growth, each represents a higher level of function than its predecessor
Normative vs. Individual vs. Dynamic development
Normative: typical capabilities
Individual: vary from the norm and has continuity within each child’s pathway
Dynamic development: sequence and changes over time and their interaction
Nature vs Nurture in Growth and Development
Basic Brain Structures are present at birth → nature
Experiences influence brain connections → nurture
What 4 Factors affect Physical Development?
Heredity: determines growth hormones
Nutrition: breastfeeding vs bottle, malnutrition, obesity
Infectious Diseases: immunization
Emotional well-being: neglect can cause cognitive delay and increased risk for psychological disorders and stunted physical growth
Infant (birth-18m) physical development
Small faces, large eyes
Touch, pain, vision is sharp at 6m, hearing, smell, taste, voice recognition
Cranium nearer to adult size but no new neurons
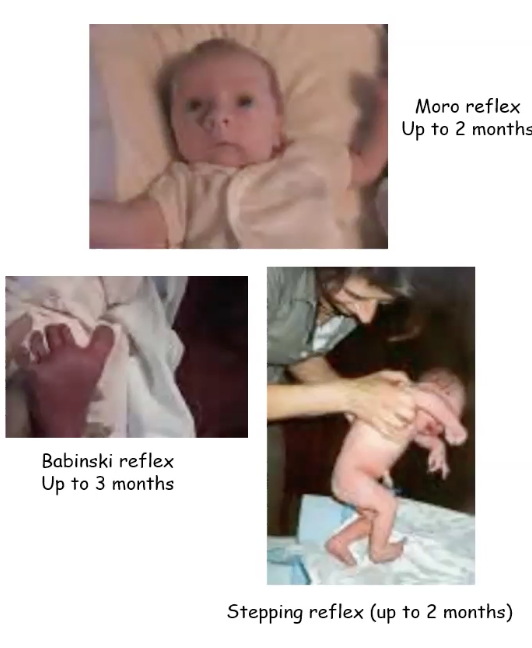
27 major reflexes
Motor development start with self locomotion and continues depending on environment and culture
Everything in mouth at 4m
Sit without support 6m
Crawls 9m
Grip and grasp 9-12m
Walk 1yr
Eat with spoon 18m
Toddler (18m- 2yr) physical development
Naps, adult-dependent
Climbs 18m
Handedness 18m
Developing fine motor skills
Runs (2yr)
Health and safety issues
Early Childhood (3-5yr) physical development
Walks erect
Overeating and sleep related issues
Rides tricycle
Alternates feet in stair climbing
Tooth decay is prevalent at this life stage
Fine motor skills and artistic development
Hand preference develops
Health and safety issues such as minor illnesses, accident, temperament
4 year old
Dresses except for back buttons
Cant set limits until exhausted
Scribbles and finger paints
5 year old
Enjoys hand skills
Draws recognizable man
Dancing
Fights
rapid muscle growth
Middle Childhood (6-11) growth and development
Beginning of lose tooth time
Greater apetite
Sexual groeth latency
Physicsl play increases
Colds, sore throatgs, etc
Nervous habits
Adolescence (12y+)
Begins with puberty
Beggins 2-3 years earlier in girls
Growth spurts that precedes sexual maturity
Sleep and eating disorders