PARA311: Prelim - Sarcomastigophora
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Amoeba
Equipped with the ability to extend their cytoplasm in the form of pseudopods (false feet), which allows them to move.
Significant Amoeba in Humans
Entamoeba
Naegleria
Acanthamoeba
Entamoeba Species
Entamoeba coli
Entamoeba hartmanni
Entamoeba dispar
Entamoeba moshkovskii
Enatamoeba gingivalis
Entamoeba histolytica (pathogenic)
The only pathogenic Entamoeba spp.
Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba polecki
A zoonotic protozoans of pigs and monkey.
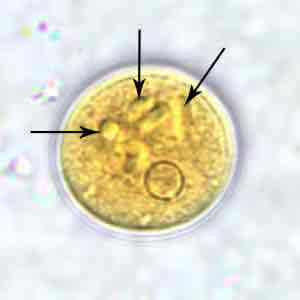
Wet mount stained with iodine
Entamoeba polecki
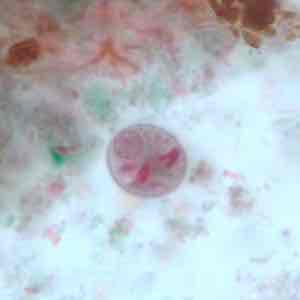
Trichrome Stain
Entamoeba polecki
Free living protozoans found mainly in freshwater.
Naegleria and Acanthamoeba
Trophozoite
Escystation; delicate, fragile and motile (pseudopods)
Cysts
Non-feeding stage, have protective cell wall. Encystation.
Entamoeba
Characterized by vesicular nucleus with comparatively small karyosome located at or near its center and with varying characteristic of the peripheral chromatin attached to the nuclear membrane.
Entamoeba that is non lumen dwelling protozoan.
Entamoeba gingivalis
Entamoeba whose infective stage is not the cystic stage.
Entamoeba gingivalis
He first described E. histolytica
Losch (Russian)
E. histolytica (T)
Size: 16-60 um
Motility: pseudopods
Cytoplasm: hyaline-like (ectoplasm); hematophagous (with ingested RBCs
Nucleus: karyosome is located centrally
E. histolytica (C)
Size: 10-20 um
Nuclei: quadrinucleated mature cysts
Cytoplasm: chromatoidal bar