Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/249
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:17 PM on 2/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
250 Terms
1
New cards
What are the components of the CNS?
\-Brain
\-Spinal Cord
\-Spinal Cord
2
New cards
What makes up the PNS?
\-Cranial and spinal nerves and their associated ganglia
\-Ventral horns of the spinal cord
\-Fiber bundles have names of nerve, nerve root, nerve trunk, nerve cord and ramus
\-Ventral horns of the spinal cord
\-Fiber bundles have names of nerve, nerve root, nerve trunk, nerve cord and ramus
3
New cards
What is the gray matter composed of?
\-Neurons (cell bodies)
→Also called ganglia or nuclei
→Also called ganglia or nuclei
4
New cards
What is the white matter composed of?
\-Composed of fiber tracts (axons/nerve fibers)
\- +/- wrapped in myelin sheath (fat)
\-Make up fiber bundles in CNS
\- +/- wrapped in myelin sheath (fat)
\-Make up fiber bundles in CNS
5
New cards
What do the fiber bundles in the CNS contain?
\-Groups of axons with common origin and common destination
→Tract
\-Common names for tracts that are used interchangeably
→Fasciculus, Brachium (arm in Greek), Peduncle, Column or Lemniscus
→Tract
\-Common names for tracts that are used interchangeably
→Fasciculus, Brachium (arm in Greek), Peduncle, Column or Lemniscus
6
New cards
What are the spinal cord and the rootlets of the alpha motor neurons wrapped in?
Pia mater
7
New cards
As these rootlets exit the spinal cord, what do they become wrapped in?
\-Arachnoid mater
\-Dura mater
\-Dura mater
8
New cards
What are the major divisions of the brain?
\-Hindbrain
\-Midbrain
\-Forebrain
\-Midbrain
\-Forebrain
9
New cards
What is the hindbrain?
\-Medulla
\-Pons
\-Cerebellum
\-Pons
\-Cerebellum
10
New cards
What is the midbrain?
Connects the hindbrain to the forebrain
11
New cards
What is the forebrain?
\-Cerebrum
\-Diencephalon
\-Diencephalon
12
New cards
What is the cerebral cortex?
Outer gray matter of cerebrum that contains nerve cell bodies
13
New cards
What is cerebral cortex composed of?
\-Gyri, sulci (fissures)
\-Two major grooves on the lateral surface of the brain
→Lateral Sulcus (Sylvian fissure)
→Central Sulcus (Rolandic or Sulcus of Rolando)
\-Cortical thickness varies among areas of the cerebrum
→Number of nerve cell layers
\-Two major grooves on the lateral surface of the brain
→Lateral Sulcus (Sylvian fissure)
→Central Sulcus (Rolandic or Sulcus of Rolando)
\-Cortical thickness varies among areas of the cerebrum
→Number of nerve cell layers
14
New cards
What are the 6 lobes of the brain?
\-Frontal
\-Occipital
\-Parietal
\-Temporal
\-Limbic
\-Insular
\-Occipital
\-Parietal
\-Temporal
\-Limbic
\-Insular
15
New cards
Does the central sulcus go all the way to the temporal lobe?
No
16
New cards
The corpus callosum is made up of what?
White matter
17
New cards
Directional Terms for the Brain
\-Superior/Dorsal
\-Anterior/Rostral
\-Posterior/Caudal
\-Inferior/Ventral
\-Anterior/Rostral
\-Posterior/Caudal
\-Inferior/Ventral
18
New cards
What are the types of neurons?
\-Unipolar
\-Bipolar
\-Multipolar
\-Bipolar
\-Multipolar
19
New cards
What is a unipolar neuron?
\-A cell body with a single neurite
\-Divides into peripheral and central processes
\-Found in dorsal root ganglion
\-Divides into peripheral and central processes
\-Found in dorsal root ganglion
20
New cards
What is a bipolar neuron?
\-One axon
\-One dendrite
\-One dendrite
21
New cards
What is a multipolar neuron?
\-Many neurites from cell body
→Most are dendrites
\-Found in brain and spinal cord
→Most are dendrites
\-Found in brain and spinal cord
22
New cards
What are the two types of synapses?
\-Electrical
\-Chemical
\-Chemical
23
New cards
What is an electrical synapse?
\-Bridges (tight junctions) connect one synapse to another
\-Ionic current
→Very fast, Little delay
\-20 nanometer synapse
\-Ionic current
→Very fast, Little delay
\-20 nanometer synapse
24
New cards
What is a chemical synapse?
\-Consist of presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons that are completely separated by synaptic cleft
\-Synaptic vesicles in presynaptic terminal contain neurotransmitters
\-Synaptic vesicles in presynaptic terminal contain neurotransmitters
25
New cards
What are ligand-gated receptors?
\-Modulate neurotransmitters effect
→Increase or decrease depending on state of postsynaptic neuron
→Increase or decrease depending on state of postsynaptic neuron
26
New cards
What is chemical conduction?
\-Occurs in one direction only
\-Transmission can be excitatory or inhibitory
\-Depolarization is a summation of activity at thousands of receptors
\-Transmission can be excitatory or inhibitory
\-Depolarization is a summation of activity at thousands of receptors
27
New cards
What are the main elements of a synapse?
\-Presynaptic terminal
\-Presynaptic receptors
\-Synaptic cleft
\-Postsynaptic receptors on postsynaptic terminal
\-Presynaptic receptors
\-Synaptic cleft
\-Postsynaptic receptors on postsynaptic terminal
28
New cards
What is capacitance?
The ability to store charges on opposite sides of 2 opposing surfaces
29
New cards
Is a NT intrinsically excitatory or inhibitory?
\-No
→Its effect at any given synapse is determined by the nature of the receptor to which it binds
→Its effect at any given synapse is determined by the nature of the receptor to which it binds
30
New cards
What ion do voltage-dependent channels at the presynaptic axon terminal depend on?
Calcium
31
New cards
IF stimulation of one presynaptic neuron evokes an excitatory response in one postsynaptic neuron, what occurs?
Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
32
New cards
IF stimulation of one presynaptic neuron evokes an inhibitory response in one postsynaptic neuron, what occurs?
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
33
New cards
The impact of any individual synapse depends on what?
\-Amount of transmitter released
\-Number of postsynaptic receptors present
\-Distance from trigger zone
\-History of activity at that synapse
\-Number of postsynaptic receptors present
\-Distance from trigger zone
\-History of activity at that synapse
34
New cards
What are ionotropic receptors?
\-Ligand-gated channel
\-Leads to a change in the channel and an ion flux
\-Really fast
\-Leads to a change in the channel and an ion flux
\-Really fast
35
New cards
What is a metabotropic receptor?
\-G-protein-coupled receptors
\-A neurotransmitter needs his buddy
\-Travels a little slower
\-Neuromodulators
\-A neurotransmitter needs his buddy
\-Travels a little slower
\-Neuromodulators
36
New cards
What is the most common neurotransmitter?
Acetylcholine
37
New cards
With a lumbar disc herniation, what can be lost/decreased?
\-Deep tendon reflexes
\-Bladder control
\-Bladder control
38
New cards
What is an epidural hemorrhage?
\-Blood between skull and dura mater
\-Mainly due to arterial bleed
\-Life threatening emergency
\-Mainly due to arterial bleed
\-Life threatening emergency
39
New cards
What is a subdural hemorrhage?
\-Bleeding between the dura and layers of meninges (below the dura and above the brain).
\-Mainly venous
\-Can be acute or chronic
\-Mainly venous
\-Can be acute or chronic
40
New cards
Where is the subarachnoid space located?
\-Between arachnoid mater and pia mater
\-Aneurysms occur here
\-Aneurysms occur here
41
New cards
What is included in the paracentral lobule?
\-Precentral gyrus
\-Postcentral gyrus
\-Postcentral gyrus
42
New cards
What are the four parts of the corpus callosum?
\-Rostrum
\-Genu
\-Body
\-Splenium
\-Genu
\-Body
\-Splenium
43
New cards
What is the function of the corpus callosum?
\-Connects the two hemispheres of the brain and allows the hemispheres to communicate with each other
\-Made up of white matter
→Axons that allow crossing from one side to the other
\-Made up of white matter
→Axons that allow crossing from one side to the other
44
New cards
What is the internal capsule?
\-It consists of ascending and descending tracts (motor and sensory) that connect the thalamus and the cerebral cortex
\-Allows information to go from the spinal cord to the cerebrum and vice versa
\-Allows information to go from the spinal cord to the cerebrum and vice versa
45
New cards
What are the parts of the internal capsule?
\-Anterior limb
\-Genu
\-Posterior limb
\-Retrolenticular division
\-Sublenticular division
\-Genu
\-Posterior limb
\-Retrolenticular division
\-Sublenticular division
46
New cards
What are corticofugal tracts?
\-Motor tracts
→We specifically need to know the corticospinal tract
→We specifically need to know the corticospinal tract
47
New cards
What is the corticospinal tract?
\-A descending somatic motor tract
\-White matter
\-Efferent fibers converge and make a path through the internal capsule and brainstem to get to the spinal cord
\-Afferent fibers make a separate path upward to reach the cerebral cortex from the spinal cord
\-White matter
\-Efferent fibers converge and make a path through the internal capsule and brainstem to get to the spinal cord
\-Afferent fibers make a separate path upward to reach the cerebral cortex from the spinal cord
48
New cards
What is the corticobulbar tract?
\-Controls all voluntary movement for speech production. -Descends from motor cortex through internal capsule but terminates at cranial nerves.
49
New cards
If you have a tumor in the thalamus that grows laterally, what will be affected?
\-Loss of sensation on opposite side
→Superior thalamic radiation
\-If it travels even more lateral
→Motor deficits (paralysis, corticospinal tract)
→Superior thalamic radiation
\-If it travels even more lateral
→Motor deficits (paralysis, corticospinal tract)
50
New cards
If you have a tumor in the thalamus that grows superiolaterally, what will be affected?
\-Facial paralysis
→Affects corticobulbar tract
→Affects corticobulbar tract
51
New cards
Lesions of the internal capsule are usually due to what?
Hemorrhaging/bleeding
52
New cards
What s/s are produced if you have a lesion that affects the genu and posterior limb?
\-Lower ½ of opposite face weakness (Genu)
\-Contralateral hemianesthesia (Somatosensory radiation)
\-Contralateral spastic hemiplegia (Corticospinal tract)
\-Optic radiations
\-Auditory radiations
\-Contralateral hemianesthesia (Somatosensory radiation)
\-Contralateral spastic hemiplegia (Corticospinal tract)
\-Optic radiations
\-Auditory radiations
53
New cards
What do neurons do?
\-Generate & transmit the nerve impulse
\-Cell body is necessary for metabolism
\-Receives sensory input from external sources
\-Cell body is necessary for metabolism
\-Receives sensory input from external sources
54
New cards
What is conduction?
\-Speed and strength of a signal being transmitted by nerve cells
\-Nodes of Ranvier speed this up
\-Nodes of Ranvier speed this up
55
New cards
What is axoplasmic transport?
\-Neurotransmitters in nerve terminals
\-Reuptake mechanism
\-Reuptake mechanism
56
New cards
What types of cells are non-excitable and do not have axons?
Neuroglial cells
57
New cards
What is the purpose of the thalamus?
\-Act as relay center and directs impulses to cerebrum
\-Provides almost all the input to the cortex through thalamocortical projections
\-All sensory stuff has to go through here
\-Provides almost all the input to the cortex through thalamocortical projections
\-All sensory stuff has to go through here
58
New cards
Are all neurons in a column activated selectively by the same peripheral stimulus?
\-Yes
→EX: If your head itches, that stimulus will react with a motor response
→EX: If your head itches, that stimulus will react with a motor response
59
New cards
Where are pyramidal cells found?
In the motor cortex
60
New cards
T/F Cell layers provide the depth of the cortex?
True
61
New cards
What areas surround the primary visual cortex and deal with the information specific to it?
\-Secondary visual cortex
\-Unimodal visual cortex
\-Unimodal visual cortex
62
New cards
What are bidirectional connections with the limbic cortex?
\-Memory
\-Emotions
\-Emotions
63
New cards
What connections allow for the performance of highest-order mental functions requiring integration of abstract sensory and motor info from appropriate parts of the nervous system, together with info from the limbic cortex?
Use of adjective “association” or heteromodal association cortex
64
New cards
What is the primary motor cortex?
Precentral gyrus
65
New cards
What is the primary visual cortex?
Occipital lobe
66
New cards
Axons from neurons in the precentral gyrus influence contralateral motor systems directly through what?
Corticospinal and Corticobulbar tracts
67
New cards
Axons from neurons in the precentral gyrus influence contralateral motor systems indirectly through what?
Their projections to the red nucleus and reticular formation
68
New cards
Axons project to and receive influences from what?
Recurrent loops through the cerebellum and the basal ganglia
69
New cards
Stimulation of specific parts of motor cortex results in what?
Isolated movements on the contralateral side of the body
70
New cards
M1 corresponds to the primary motor area and precentral gyrus, which stimulates what?
\-Stimulation of specific parts of this area
→Bilateral movements of:
\-→Extraocular muscles
\-→Muscles of the upper 1/2 of the face
\-→Muscles of the tongue
\-→Muscles of the mandible
\-→Muscles of the larynx
\-→Muscles of the pharynx
→Bilateral movements of:
\-→Extraocular muscles
\-→Muscles of the upper 1/2 of the face
\-→Muscles of the tongue
\-→Muscles of the mandible
\-→Muscles of the larynx
\-→Muscles of the pharynx
71
New cards
What is homunculus?
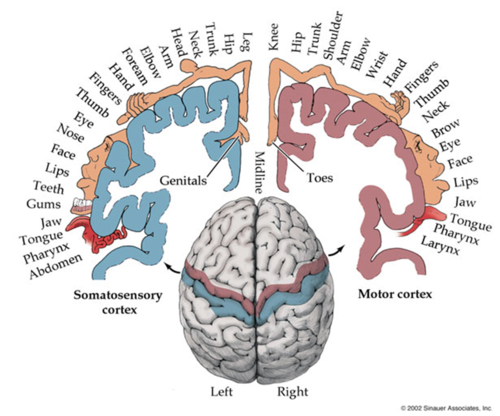
72
New cards
What does the premotor area do?
\-Receives inputs from sensory cortex, thalamus, and basal ganglia
\-Stores programs of motor activity as a result of past experiences
\-Programs activity for the primary motor area
\-Involved in controlling coarse postural movements through its connections with the basal ganglia
\-Stores programs of motor activity as a result of past experiences
\-Programs activity for the primary motor area
\-Involved in controlling coarse postural movements through its connections with the basal ganglia
73
New cards
Which hemisphere is dominant for speech?
Left
74
New cards
Speech is the motor production of spoken words using what?
\-Larynx
\-Tongue
\-Face
\-Tongue
\-Face
75
New cards
Directional Terms for the Spinal Cord
\-Anterior/Ventral
\-Posterior/Dorsal
\-Superior/Rostral
\-Inferior/Caudal
\-Posterior/Dorsal
\-Superior/Rostral
\-Inferior/Caudal
76
New cards
In the brain where is the gray and white matter located?
\-Gray = outer
\-White = inner
\-White = inner
77
New cards
What another term for bumps on the brain?
Gyri/ Gyrus
78
New cards
Whats another term for grooves of the brain?
Sulci
79
New cards
Where is the lateral fissure located?
Between the frontal and temporal lobes
80
New cards
What are other terms for the lateral fissure?
\-Lateral sucli
\-Sylvian fissure
\-Sylvian fissure
81
New cards
Where is the central sulcus located?
Between the frontal and parietal lobe
82
New cards
What are other terms for the central sulcus?
\-Central fissure
\-Fissure of Rolando
\-Rolando fissure
\-Fissure of Rolando
\-Rolando fissure
83
New cards
The limbic lobe of the brain is associated with what?
\-Emotions
\-Homeostasis
\-Homeostasis
84
New cards
The insular lobe of the brain is associated with what?
\-Emotions
→Pain
→Fear
→Sadness
→Happiness
→Pain
→Fear
→Sadness
→Happiness
85
New cards
The frontal lobe of the brain is known for what?
\-Memory
\-Problem solving
\-Motor function
\-Problem solving
\-Motor function
86
New cards
The parietal lobe of the brain is known for what?
\-Sensory (but not vision)
→Temperature
→Touch
→Taste
\-Movement
→Temperature
→Touch
→Taste
\-Movement
87
New cards
The occipital lobe of the brain is known for what?
Vision
88
New cards
The temporal lobe of the brain is known for what?
\-Hearing
\-Language interpretation
\-Language interpretation
89
New cards
What is the order of meninges from deep to superficial?
\-Pia mater
\-Arachnoid mater
\-Dura mater
\-Arachnoid mater
\-Dura mater
90
New cards
T/F The spinal cord spans from caudal medulla oblangota to L1/2
TRUE
91
New cards
What structures anchor the spinal cord to the dura mater?
Denticulate ligaments
92
New cards
Know your myotomes
Do the dance!
93
New cards
In what location does the dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal cord join to form a spinal nerve?
Intervertebral foramina
94
New cards
In the spinal cord, what is the arrangement of gray and white matter?
\-White = outer
\-Gray = inner
\-Gray = inner
95
New cards
How many pairs of Spinal Nerves are there?
31 pairs
96
New cards
The anterior horn of the spinal cord sends signals in which direction (To/Away) the CNS?
Away
97
New cards
The posteiror horn sends signals in which direction (To/Away) the CNS?
To
98
New cards
What matter is composed of neurons?
Gray
99
New cards
What matter is composed of fiber tracts?
White
100
New cards
What type of hemorrhage is commonly due to injury to menengial arteries and is considered a life threatening conditon?
Epidural space hemorrhage