ANTH 2030 Practical 2 Study Guide for Labs 4-5
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
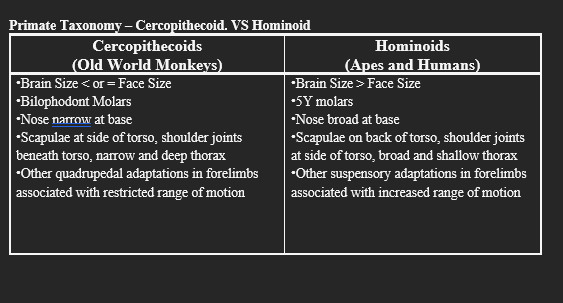
Cercopithecoidea
A superfamily of Old World monkeys.
Hominoidea
A superfamily that includes apes and humans.
Epiphyseal closure
The process that indicates the age of an individual based on the fusion of bone ends.
Osteoarthritis
A degenerative joint disease that can lead to the fusion of vertebrae.
Minimum Number of Individuals (MNI)
The largest group of the same bone from the same side, used to estimate the number of individuals represented.
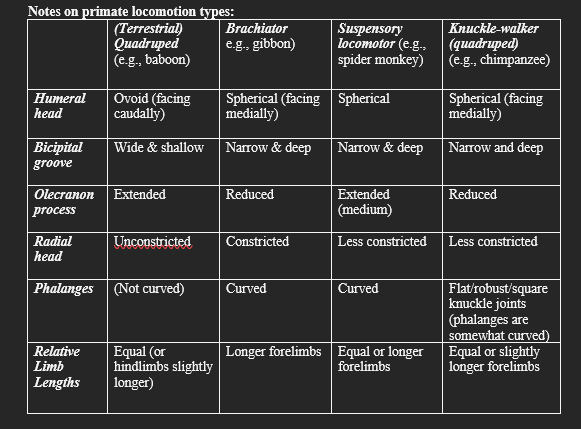
Quadrupedal locomotion
Movement using all four limbs, can be arboreal or terrestrial.
Suspensory/Brachiator locomotion
Movement that involves hanging or swinging from branches.
Bipedal locomotion
Movement that involves walking on two legs.
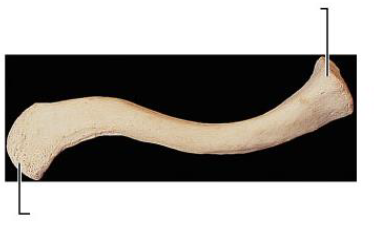
Clavicle
features acromial and sternal ends.
Scapula
A bone that connects the humerus to the clavicle, featuring acromion process, coracoid process, and glenoid fossa.
Humerus
The upper arm bone, featuring
the humeral head,
bicipital groove,
olecranon fossa,
medial epicondyle,
trochlea.
Ulna
The inner forearm bone, featuring the semilunar notch, radial facet, and olecranon process.
Radius
The outer forearm bone, featuring the radial head, ulnar notch, styloid process, and radial tuberosity.
Vertebrae
The bones that make up the spine, differentiated into cervical, thoracic, and lumbar types.
Features
Centrum
Transverse Foramina
Rib Facets
Lack of Centrum (C1, “The Atlas”)
Dens or Odontoid Process (C2, “The Axis)
C1 (The Atlas)
The first cervical vertebra, which lacks a body/centrum.
C2 (The Axis)
The second cervical vertebra, which has the dens/odontoid process.
Transverse Foramina
Holes in cervical vertebrae that allow for the passage of blood vessels.
Rib facets
Surface features on thoracic vertebrae that articulate with ribs.
Cervical vertebrae
Yes transverse foramina
No rib facets.
Thoracic vertebrae
Yes rib facets
No transverse foramina.
Lumbar vertebrae
No rib facets
No transverse foramina.
Bicipital groove
A feature of the humerus that is wide and shallow in quadrupeds.
Olecranon process
A feature of the ulna that is extended in quadrupedal locomotion.
Radial head
The proximal end of the radius, which is unconstricted in quadrupeds.
Phalanges
Finger bones that can be curved or flat depending on locomotion type.
Brain Size in Cercopithecoids
Brain size is less than or equal to face size.
Brain Size in Hominoids
Brain size is greater than face size.
Bilophodont Molars
A type of molar found in Cercopithecoids.
5Y Molars
A type of molar found in Hominoids.
Sternum
No Features
Ribs
No Features
Sacrum
Feature Alae
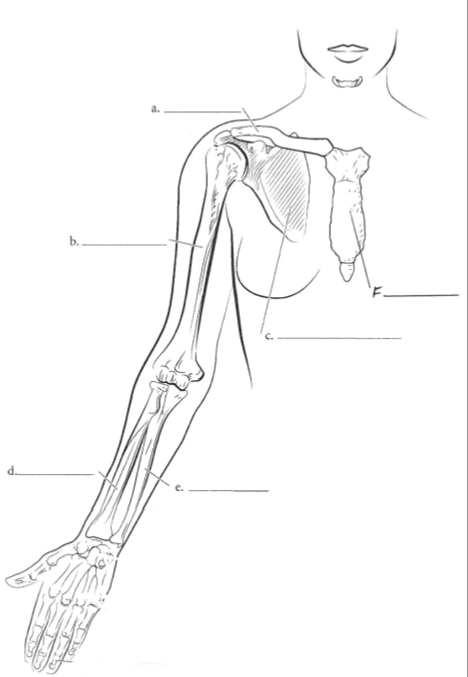
a. Clavicle
b. Humerus
c. Scapula
d. Radius
e. Ulna
f. Sternum
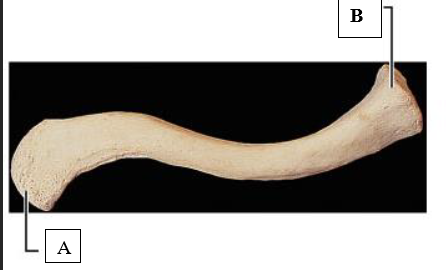
The Clavicle
a. Acromial end
b. Sternal end
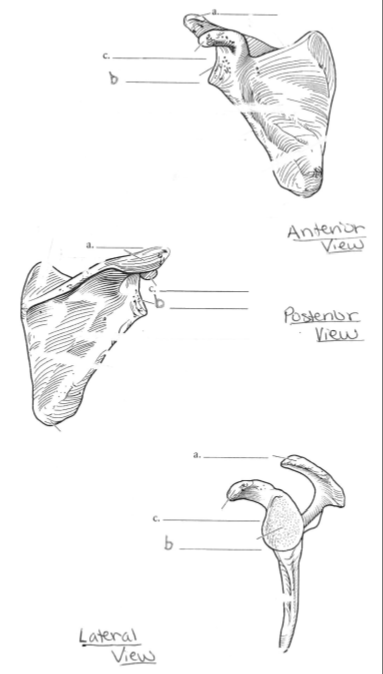
The Scapula
a. Acromion Process
b. Glenoid Fossa
c. Coracoid Process
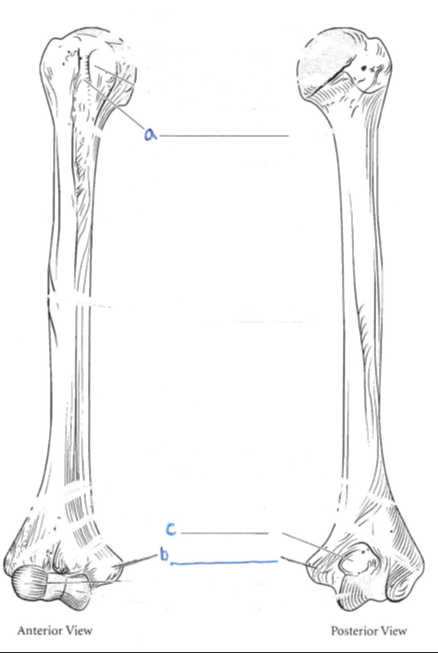
The Humerus
Features:
a. Bicipital Groove
b. Medial Epicondyle
c. Olecranon Fossa
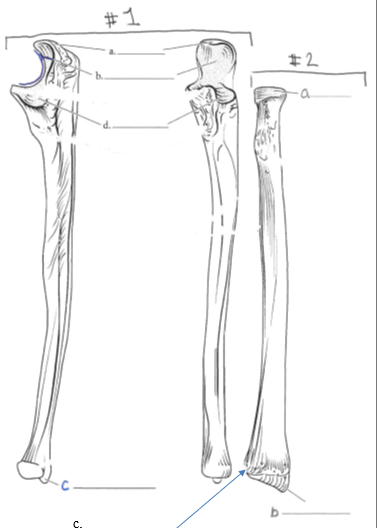
The Ulna and Radius
#1: The Ulna
Features:
a. Olecranon process
b. Semilunar notch
d. Radial notch
#2: The Radius
Features:
a. Radial head
b. Styloid process
c. Ulnar notch
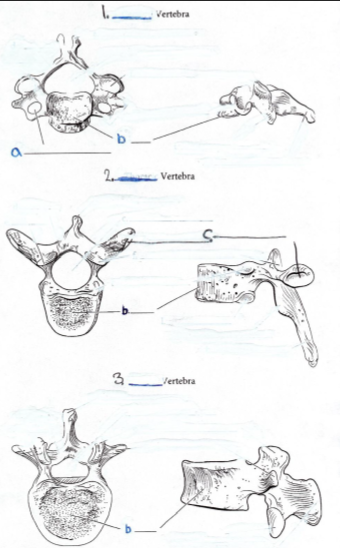
1. Name the Type of Vertebra: Cervical
Features:
a. Transverse foramina
b. Centrum/body
2. Name the Type of Vertebra: Thoracic
Features:
b. Centrum/body
c. Rib facet
3. Name the Type of Vertebra: Lumbar
Feature:
b. Centrum/body
Osteoarthritis
Identifications: Bony lipping. ridges, spurs on synovial joints
Causes: aging, physical activity, localized trauma, infection
Osteophytosis
Identifications: Bony lipping. ridges, spurs on cartilaginous joints (between centrum at each vertebrae)
Causes: aging, physical activity, localized trauma, infection