Understanding Alexia and Agraphia in Communication Disorders
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Alexia
acquired reading disorder (impacting oral reading and/or reading comprehension)
Agraphia
acquired writing disorder
Grapheme
smallest unit that signals a difference in meaning in a writing system (e.g., "p", "sh", "ch", "i")
Allograph
variations of a grapheme
Case
upper vs. lower
Print type
cursive vs. print
Pseudoword
not a word in the language, but follows phonological rules (e.g., for English "blaf")
Cognitive architecture
mental operations involved in a brain function
Peripheral alexia
affects earlier processing stages of reading; difficulty visually perceiving written word
Central alexia
affects later processing stages of reading; difficulty attaching sound or meaning to written word
Pure alexia
impairment in the simultaneous, parallel identification and processing of letters in a written word
Neglect alexia
Impairment in correctly identifying initial or final letters in words
Attentional alexia
incorrect productions of letters in a word as a result of interference from other letters in the word
Visual alexia
production of a word that is visually similar to the target word
Surface alexia
a type of central alexia
Phonological alexia
a type of central alexia
Deep alexia
a type of central alexia
Alexia without agraphia
significant reading impairment without significant writing impairment (rare)
Lesion site for Pure alexia
Left occipital cortex and splenium of corpus callosum
Lesion site for Neglect alexia
Visual processing areas (variable)
Lesion site for Attentional alexia
Visual processing areas (variable)
Lesion site for Visual alexia
Visual processing areas (variable)
Surface alexia
Impaired lexical reading with impaired oral reading of irregularly spelled words (e.g., "yacht"), relatively intact reading of regularly spelled words (e.g., "bat") and pseudowords, and regularization errors due to over-reliance on nonlexical reading route.
Phonological alexia
Impaired nonlexical reading characterized by impaired pseudoword reading, lexicalization errors (e.g., blaf -> black), and absence of semantic errors in oral reading.
Deep alexia
Impaired lexical and non-lexical reading with impaired oral reading of pseudowords (e.g., blaf), semantic, visual, and morphological errors in oral reading, and easier reading of concrete, imageable words.
Central alexias
Types of alexia that involve impairments in the central processes of reading.
Lesion site for Surface alexia
Left temporal / temporo-parietal (variable).
Lesion site for Phonological alexia
Left perisylvian, left superior temporal cortex (variable).
Lesion site for Deep alexia
Extensive left hemisphere lesion.
Lexical writing route
Accesses word forms and generates spelling for familiar word forms.
Lexical semantic route
Accesses the semantic system needed for written confrontation naming.
Lexical nonsemantic route
Bypasses the semantic system.
Nonlexical writing route
Does not access word forms and is used to process words not in spelling vocabulary.
Peripheral agraphia
Impairment of peripheral processes that convert graphemes into motor commands for writing.
Central agraphia
Impairment of central linguistic processes that generate spellings for words and pseudowords.
Allographic agraphia
Impairment in generating or selecting correct letter shapes in handwriting, with oral spelling spared.
Apraxic agraphia
Impairment related to the motor planning of writing.
Motor nonapraxic agraphia
Impairment in writing that is not due to apraxia.
Spatial / afferent agraphia
Impairment affecting the spatial aspects of writing.
Mixed writing profiles
Commonly observed in individuals with various types of agraphia.
Lesion site for Allographic agraphia
Left parieto-occipital cortex.
Apraxic agraphia
Poor letter formation not attributed to impaired letter shape knowledge or to sensorimotor, extrapyramidal, or cerebellar dysfunction affecting writing hand.
Oral spelling, typing, and anagram tasks
Preserved in apraxic agraphia.
Motor nonapraxic agraphia
Impairment in regulating movement force, speed, and amplitude in handwriting.
Micrographia
Example of motor nonapraxic agraphia seen in Parkinson's disease.
Spatial / afferent agraphia
Impaired ability to use sensory feedback for control and execution of writing.
Common errors in spatial / afferent agraphia
Duplications or omissions of letters or strokes, difficulty keeping line of writing straight, difficulty maintaining spacing between letters and words.
Surface / lexical agraphia
Impaired lexical writing / spelling with over-reliance on non-lexical route.
Phonological agraphia
Impaired nonlexical writing/spelling with over-reliance on lexical route.
Deep agraphia
Impaired lexical and nonlexical writing / spelling with similar errors as phonological agraphia plus semantic errors.
Semantic agraphia
Impairment of conceptually mediated writing tasks, with relatively spared writing to dictation.
Graphemic output buffer impairment
Impaired short-term storage of graphemic information leading to errors with grapheme order and identity in all spelling tasks.
Narrative writing sample - Broca's aphasia
Task: Written picture description.
Narrative writing sample - Wernicke's aphasia
Task: Written picture description.
Narrative writing sample - conduction aphasia
Task: Written picture description.
Functional reading and writing
Reading and writing impairment impact everyday functioning.
Examples of functional reading and writing
Reading newspapers, magazines, books, environmental signs, prescriptions, recipes, and other instructions.
Terminology: alexia, agraphia, grapheme, allograph, pseudoword
Key terms related to reading and writing impairments.
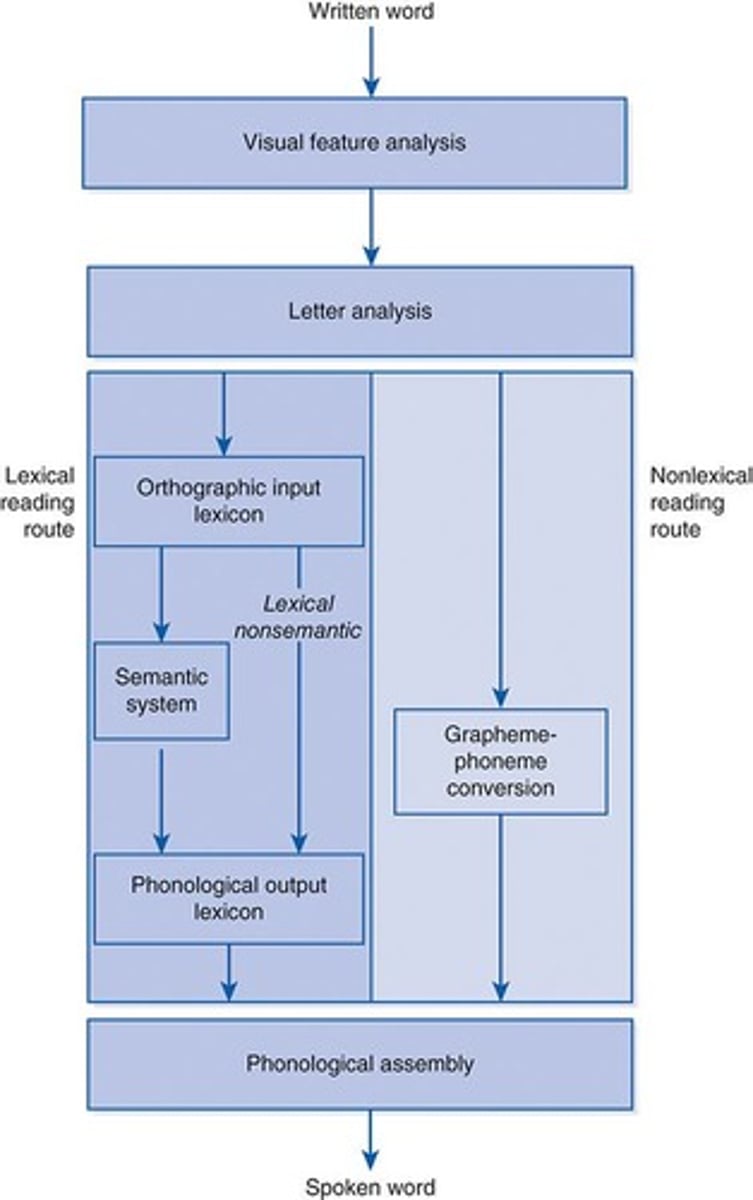
Dual route model of reading
A model describing the processes involved in reading.
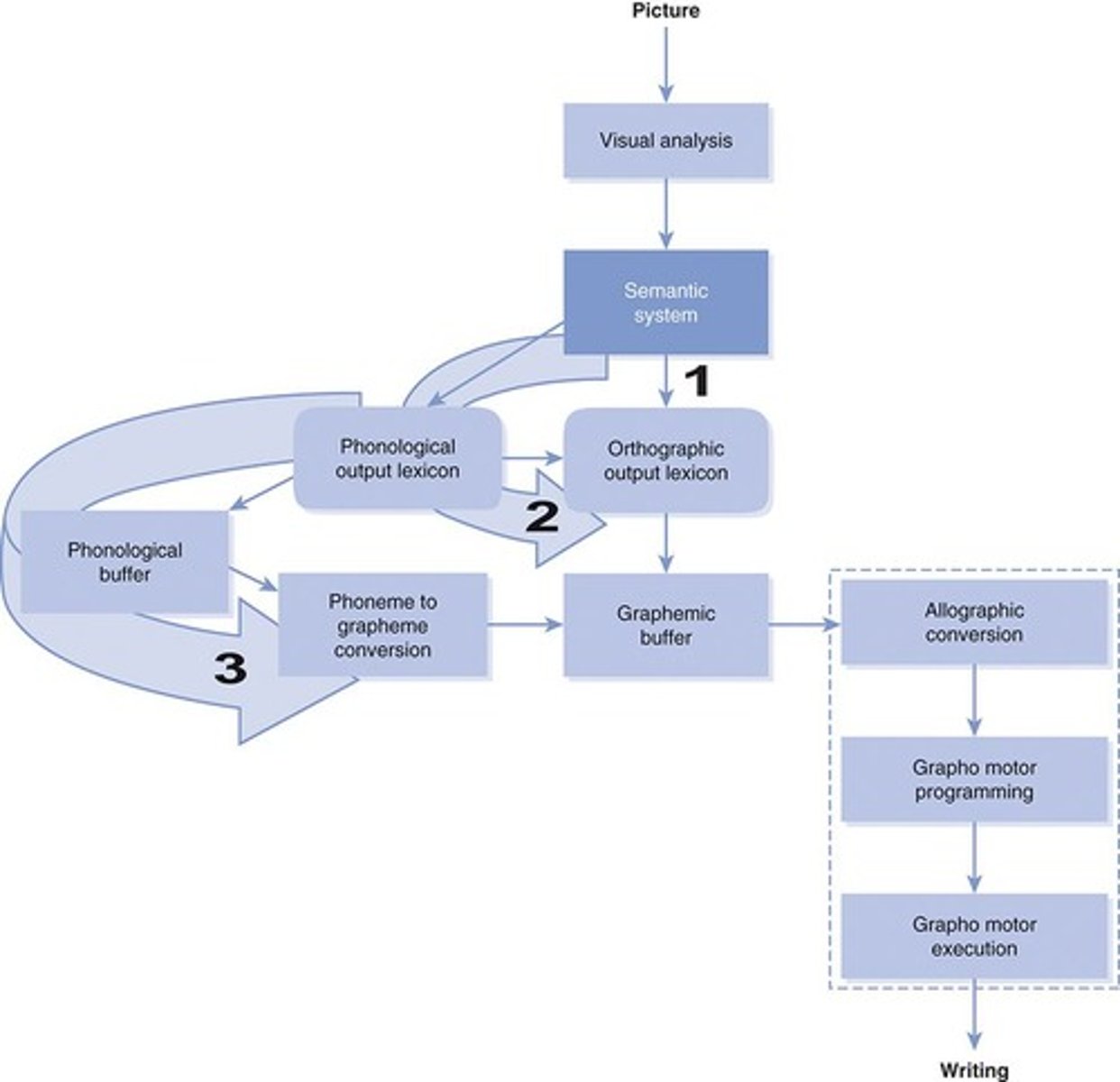
Neuropsychological model of writing
A model describing the processes involved in writing.
Central vs. peripheral agraphia
Classification of agraphia based on underlying cognitive processes.
Relationships between reading, writing, and speaking
Understanding how these skills interact and affect communication.
Communication and participation implications of alexia and agraphia
Impact of reading and writing impairments on daily life and social interactions.