Retinal Venous Occlusions
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
external compression of the vein by an atherosclerotic artery, intraluminal thrombosis, or inflammation of the vein
what are the theorized causes of retinal vein occlusions?
hypertension
what is the leading cause of retinal vein occlusions?
dilated & ruptured capillaries, edema
describe the appearance of the capillaries with a retinal vein occlusion
abnormalities of the vessel wall
abnormalities in blood viscosity/coagulation
abnormalities in blood flow/velocity
what is Virchow’s triad for thrombosis in general?
increased BMI & waist circumference, increased BP, higher fasting blood glucose, higher LDL/triglycerides/total cholesterol, lower HDL
what are the systemic associations with retinal vein occlusion?
sudden, painless loss of vision
what is the presenting sx of a CRVO?
increases
the risk of a CRVO _____ with increased IOP
non-ischemic CRVO
type of CRVO
less severe presentation & better prognosis
VA is moderately reduced
no APD (usually)
VA improves to 20/40 or better in 2/3 of pts
less capillary non-perfusion on IVFA
no neovascular complications
ischemic CRVO
type of CRVO
much more severe
VA is markedly reduced, usually 20/200 or worse
+APD
massive hemorrhaging in all 4 quadrants
severe ME & possible disc edema
more cotton wool spots
significant capillary dropout & non-perfusion on IVFA/OCTA
neovascularization of the iris is very common
carotid doppler, BP & CV work-up
what should you do to manage an ischemic CRVO?
BP & CV workup
what should you do to manage a non-ischemic CRVO?
anti-VEGF injections, intravitreal steroid implants/injections, PRP
what is the tx for a CRVO?
can permanently fix the problem (decreases oxygen demand below the needed threshold)
what is the advantage of PRP for a CRVO w/ neovascularization over just anti-VEGF injections?
ERM formation, night vision loss, peripheral vision loss, longer tx sessions
what are the disadvantages of PRP tx for a CRVO w/ neovascularization over just anti-VEGF injections?
low rate of SE, work very well
what is the advantage of anti-VEGF injections for a CRVO w/ neovascularization?
requires repeated injections (issues with cost, transportation, visit fatigue)
what is the disadvantage of anti-VEGF injections for a CRVO w/ neovascularization?
endophthalmitis, elevated IOP
what are the SE of anti-VEGF injections?
BRVO
rarely ischemic, more commonly non-ischemic
VA compromised only if edema/blood reaches the macular or there is long-term macular ischemia
neovascularization is more rare
usually temporal
collaterals
form over 6-24mo w/ a BRVO/CRVO then often regress & close, thicker & ropey vessels
anti-VEGF w/ early loading doses then tx & extend
what is the standard of tx for a BRVO w/ macular edema?
monitor w/o tx
what is the standard of tx for a BRVO w/o macular edema?
grid/focal laser therapy, steroid implants/injections, evaluate BP, CV workup
what are additional tx options after anti-VEGF injections for a BRVO?
papillophlebitis
may be an inflammatory variant of a CRVO
often strikes at a younger age
disc edema typically out of proportion w/ retinal hemorrhaging, 4 quadrant hemorrhaging out to the periphery
condition is self limiting over the course of several months & complete recovery is the norm
can be related to APA syndrome
vague prodrome of scintillating, colored lights w/ visual disturbances
enlarged blind spot on visual field
mild VA reduction (20/30)
dilated/tortuous veins
what are some presenting signs/sx of papillophlebitis?
hypoperfusion syndrome
occurs when the eye lacks blood perfusion secondary to carotid artery blockage or ophthalmic artery blockage
complaint of dull, chronic ache in affected eye
difficulty w/ light/dark adaptation
TIA sx (amaurosis fugax)
possible bruit/decreased pulse strength in carotid
peripheral dot/blot hemorrhages
dilated veins
relatively spares posterior pole
what are some signs/sx of hypoperfusion syndrome?
neovascularization
iritis
sluggish pupil
conjunctival congestion
corneal edema
severely reduced VA
complaint of dull/chronic ache in affected eye
difficulty w/ light/dark adaptation
TIA sx (amaurosis fugax)
possible bruit/decreased pulse strength in carotid
peripheral dot/blot hemorrhages
dilated veins
what are the signs/sx of ocular ischemic syndrome?
question about TIA
check carotids
arrange for carotid testing
ESR
C-reactive protein
CBC
lipid panel
when presented w/ the ocular findings of OIS or hypoperfusion, what things should you consider doing?
systemic management
PRP/cryotherapy/anti-VEGF injections
what is the tx of OIS?
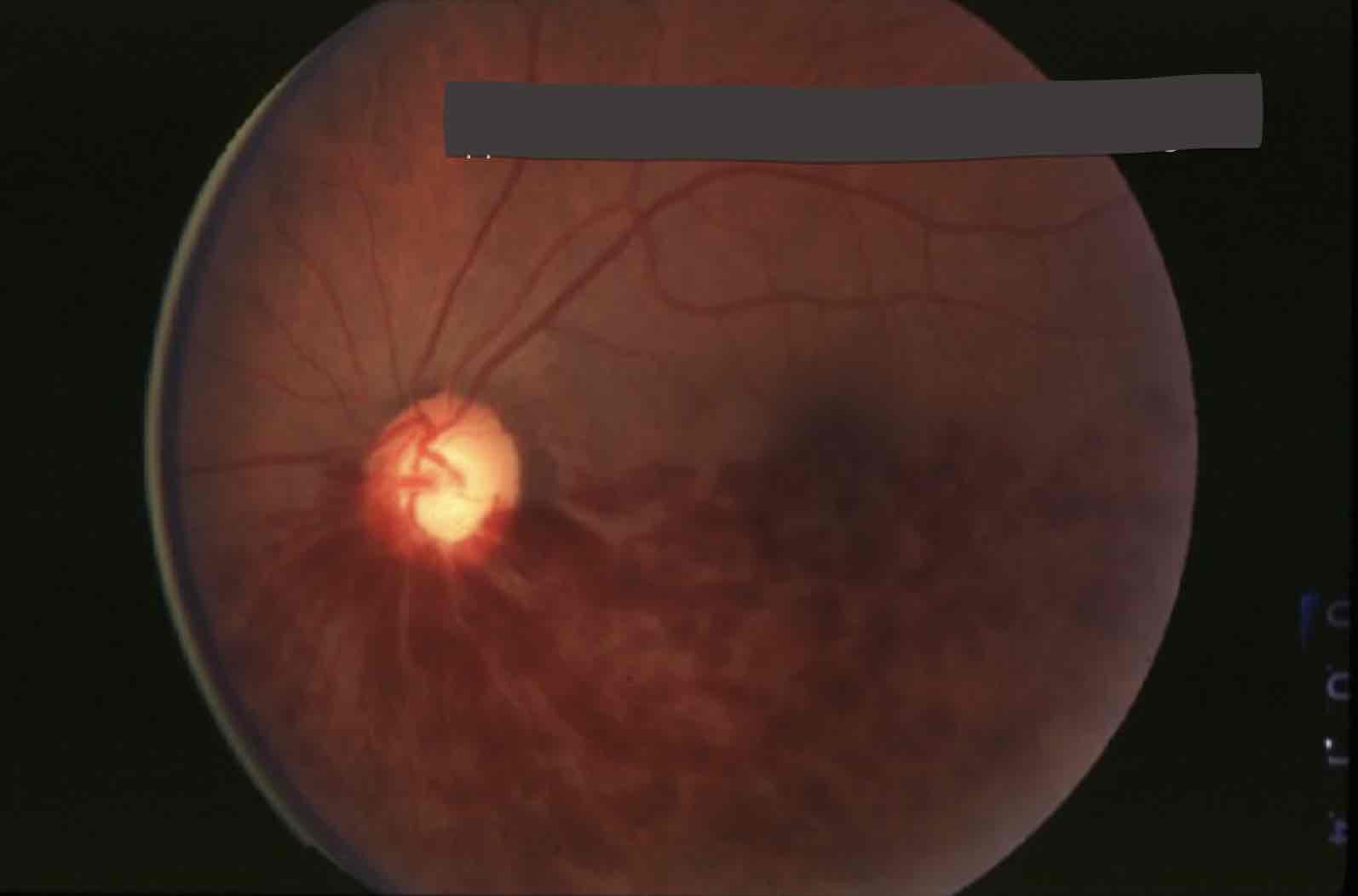
ischemic CRVO
ischemic CRVO
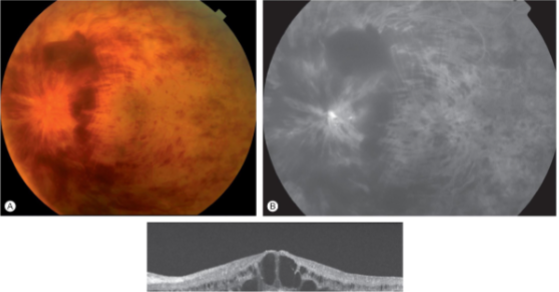
non-ischemic CRVO
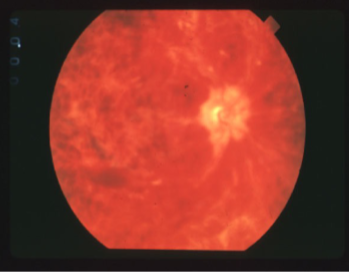
hemicentral RVO w/ collaterals
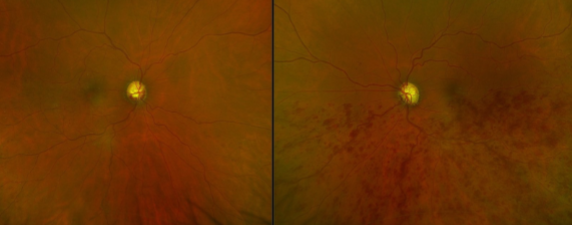
combined CRAO/CRVO
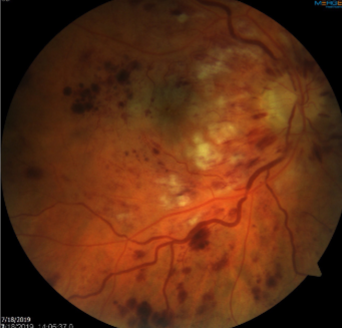
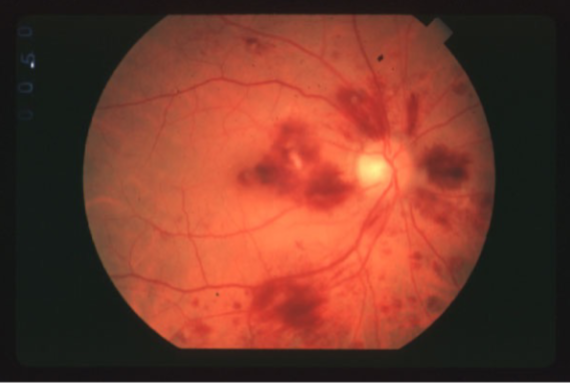
collaterals & sclerosed vein post occlusion
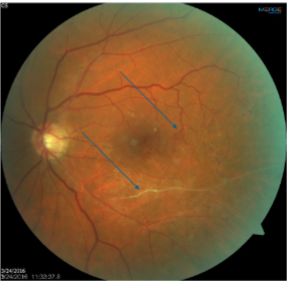
collaterals
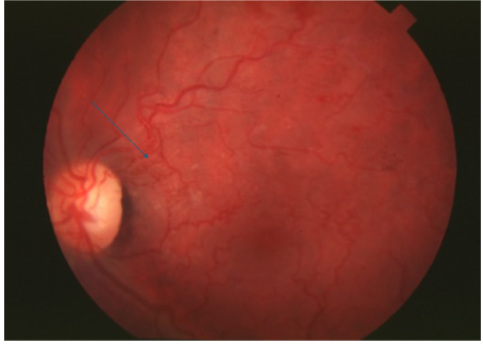
collaterals
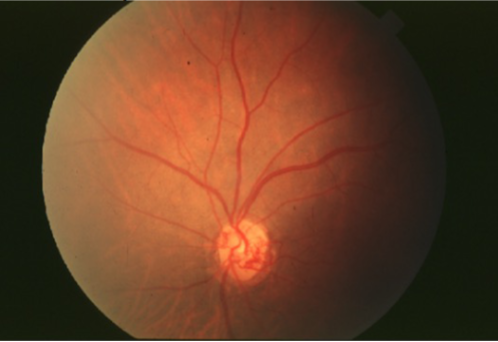
collaterals
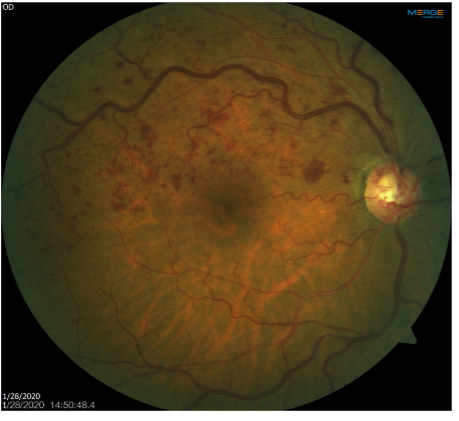
collaterals
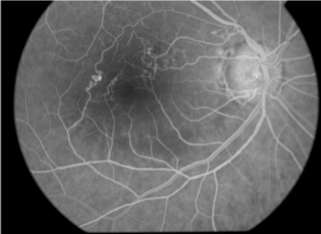
BRVO S/P laser tx
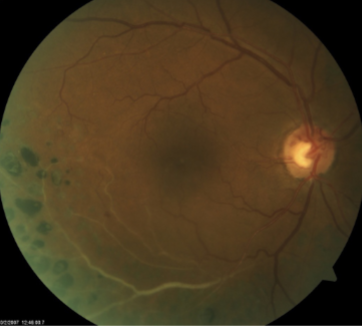
papillophlebitis
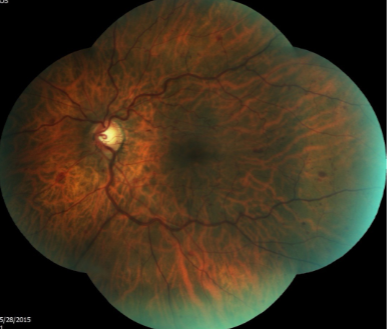
papillophlebitis
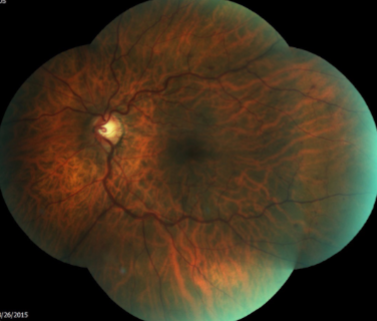
papillophlebitis
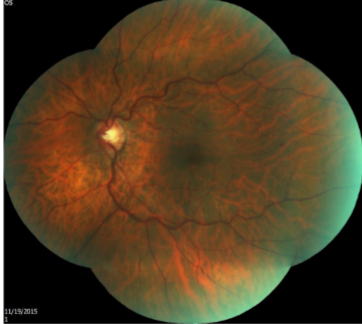
papillophlebitis
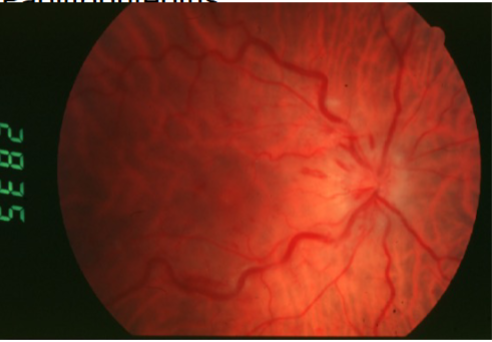
papillophlebitis
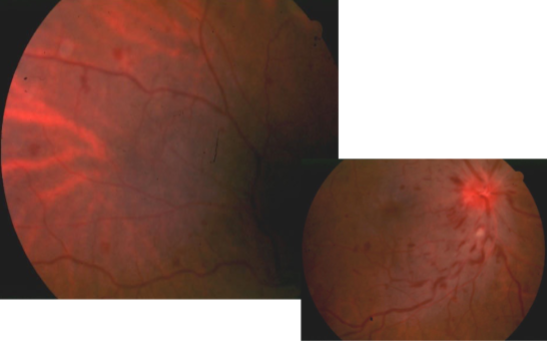
papillophlebitis
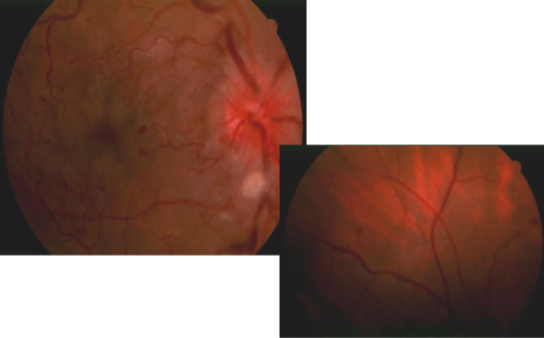
papillophlebitis
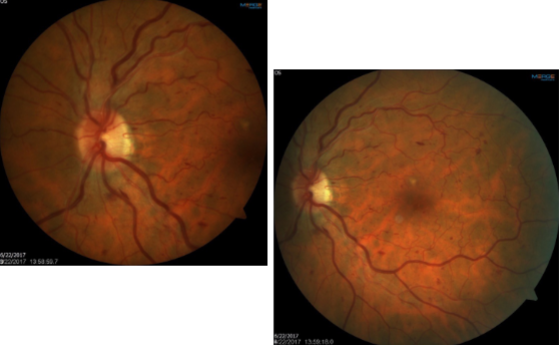
hypoperfusion syndrome
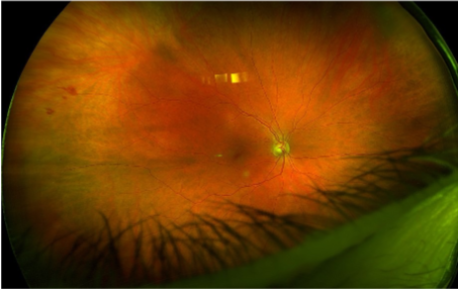
OIS
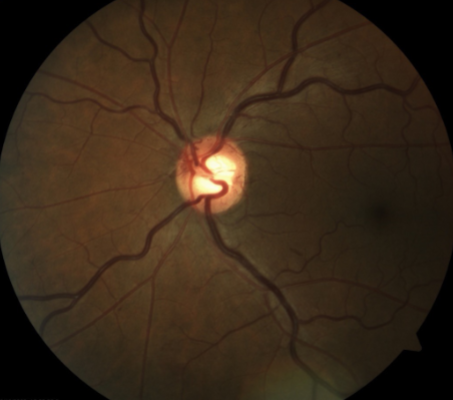
NVI
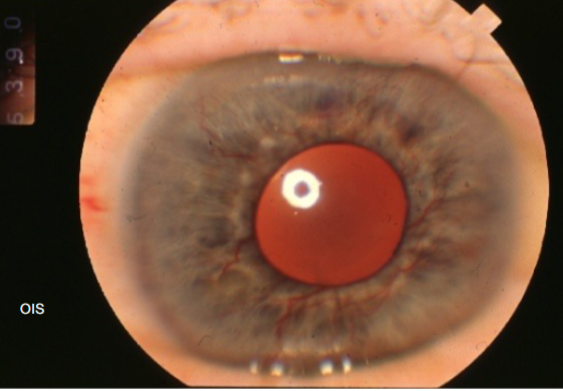
Non-ischemic CRVO
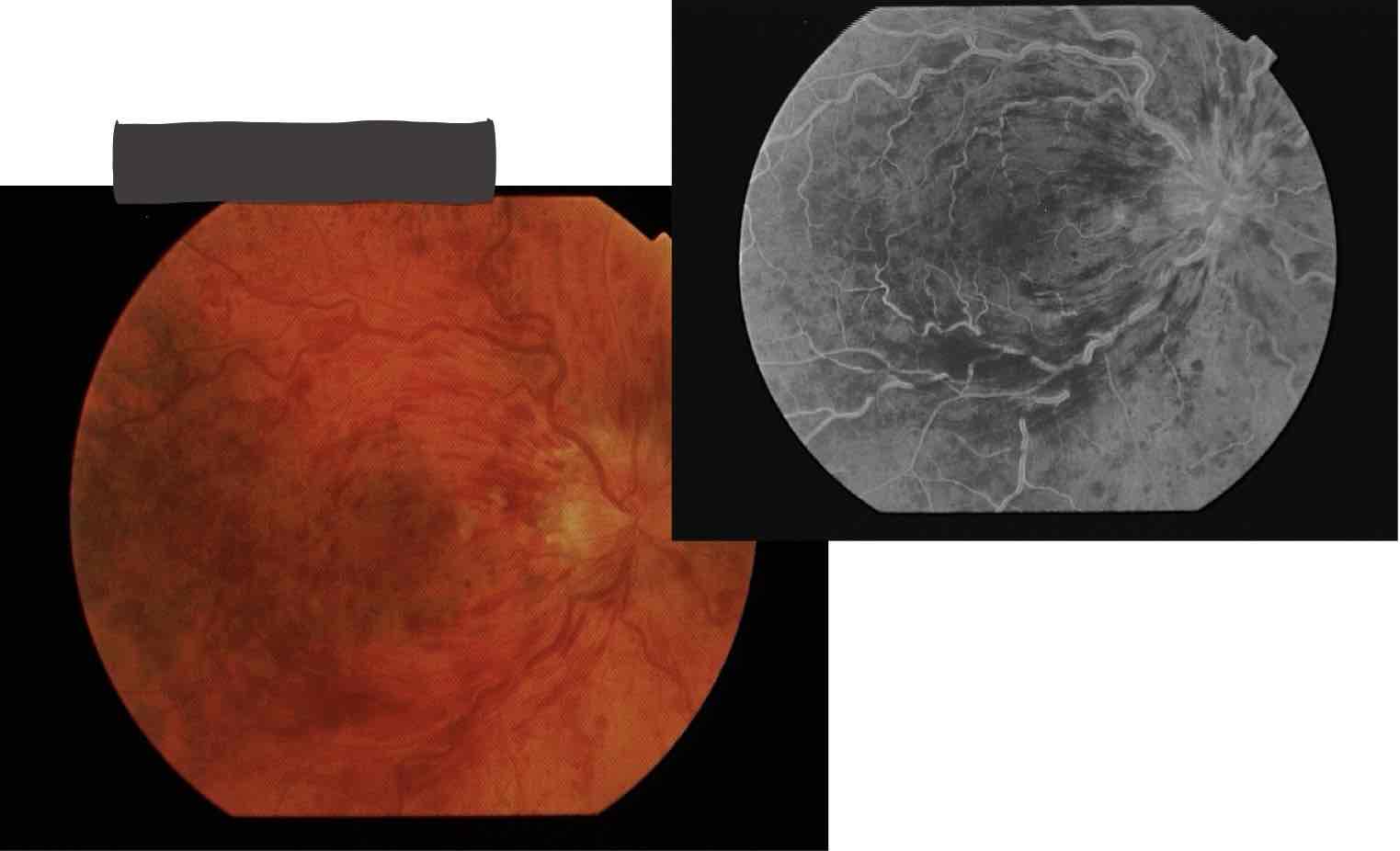
Hemicentral RVO