Cause & Mechanisms for Evolution, The Scientific Method, Chapter 3.3, Chapter 3.2 Flashcards, Chapter 3.1 Flashcards, 5.1 Flashcards, Chapter 5.3: Human Nervous System, Chapter 5.4, Chapter 4: Evolution, Evidence for Evolution
1/220
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
221 Terms
Selective Pressures
environmental factors that influence the survival and reproductive success of individuals (can be biotic or abiotic)
Traits
characters/adaptations inherited from parents
Adaptations
traits that have evolved overtime through evolution to improve an individual's fitness
Inheritance
transmission of DNA to offspring
genes
segments of DNA carrying info for development of specific traits
Alleles
different versions of a gene
Allele frequency
the relative frequency of a specific allele in a population relative to total number of alleles
Natural Selection
individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce passing the traits on
types of natural selection
directional, stabilizing, disruptive
Directional
selection of one extreme trait
stabilizing
selection of average/intermediate trait
Disruptive
selection of both extremes
Genetic drift
random changes in allele frequency especially in smaller populations because each individual holds more weight
Bottleneck effect
original population in cup and more diverse, but an event (the bottleneck) favors only one trait and whittles down the diverse gene pool
Founder effect
genetic drift that occurs after a small number of individuals colonize a new area and gene pool there is limited to only small group
Mutations
random changes in DNA that create new alleles and introduce them to population
artificial selection
humans favor a specific trait and select only animals with that to breed
sexual selection
certain traits allow an individual to reproduce more
Gene flow (migration)
movement of alleles from one population to another through migration
What 5 circumstances must be met for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
1. No mutations occur
2. No gene flow
3. Random Mating
4. Large Population so no Genetic Drift
5. No selection
Step one
observation
step two
question
step three
background knowledge
step four scientific method
create the hypothesis
step five of the scientific method
experiment
step six scientific method
analyze results
step seven
conclusion
Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)
A semipermeable boundary that surrounds the cell and controls what enters or exits.
Homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment despite changes outside.
Phospholipid
A molecule with a water-attracting (polar) head and water-repelling (nonpolar) tails that makes up the membrane.
Lipid Bilayer
Two layers of phospholipids that form the basic structure of the cell membrane.
Selective Permeability
The ability of the cell membrane to control which substances can pass through.
Concentration Gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance across a space.
Water Potential
the physical property that predicts the direction in which water will flow (from high h2o pot. to low h2o pot.)
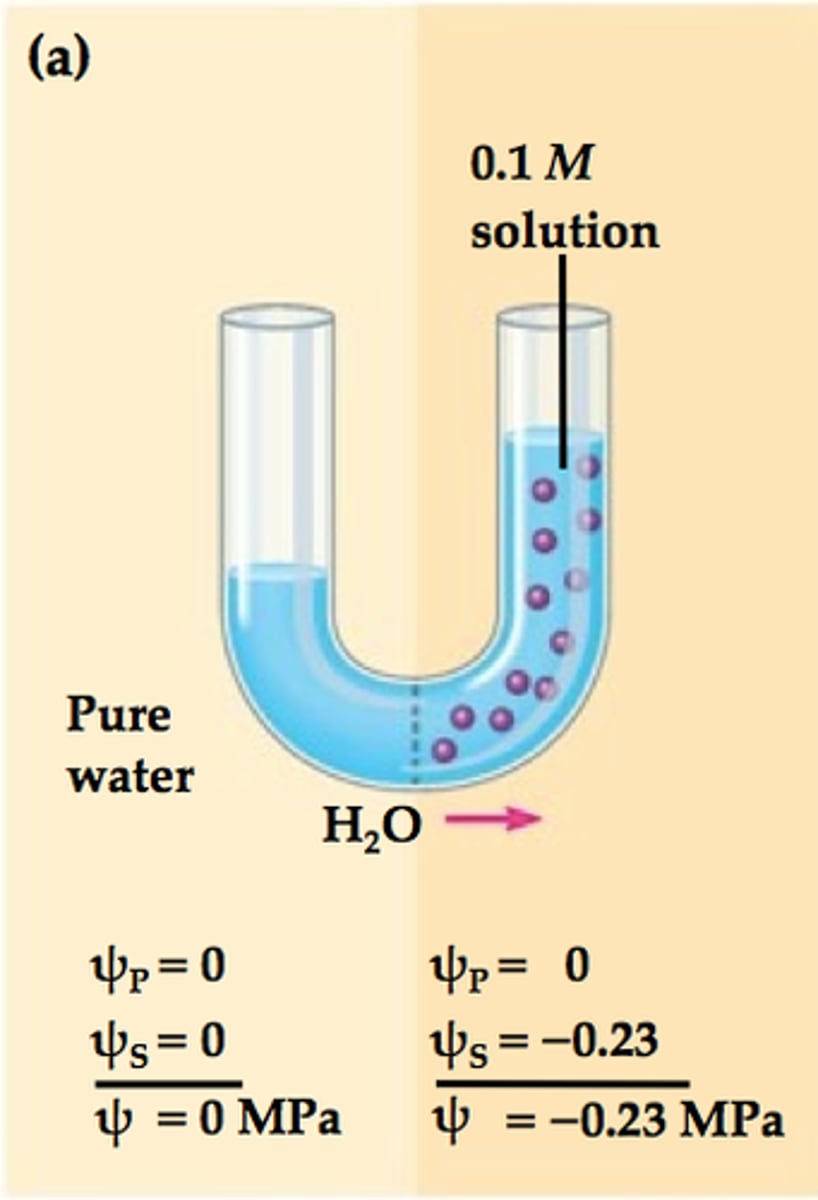
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from high to low concentration—no energy required.
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a membrane.
Passive Transport
Movement of substances across the membrane without energy
Active Transport
Movement of substances across the membrane using energy (from low to high concentration).
Simple Diffusion
Substances move directly through the membrane.
Aquaporins
Channel proteins for water that facilitate its movement across the membrane.
Hypotonic Solution
Less dissolved stuff outside, causing the cell to swell as water moves into the cell.
Hypertonic Solution
More dissolved stuff outside, causing the cell to shrink as water moves out of the cell.
Isotonic Solution
Equal concentration inside and out, causing the cell to stay the same as water moves in and out equally.
Facilitated Diffusion
Substances move from high to low concentration using proteins.
Channel Proteins
Proteins that are always open, providing a fast pathway for substances.
Gated Channel Proteins
Proteins that open or close in response to signals.
Carrier Proteins
Proteins that change shape to carry molecules across the membrane.
Amphipathic Proteins
Proteins with both hydrophilic/polar and hydrophobic/nonpolar regions.
Endocytosis
Membrane folds inward to bring substances into the cell in vesicles.
Exocytosis
Vesicle fuses with membrane to send substances out of the cell.
Barrier Function
Keeps the inside of the cell separate from the outside.
Transport Function
Controls what enters and exits (via diffusion, transport proteins, etc.).
Communication Function
Proteins can send and receive signals.
Structure Function
Provides shape and allows interaction with the environment.
9 of Life Characteristics
HOME HERD; homeostasis, organization (cell theory), metabolism, (response to) environment, heredity, evolution, reproduction, development
Characteristic Sub-Cellular Units
Not alive on their own.
Atom
Basic unit of matter (e.g., carbon, oxygen).
Ion
Atom with unequal protons and electrons.
Cation
type of ion with + charge (more protons).
Anion
type of ion with − charge (more electrons).
Molecule
Two or more atoms joined together.
Nonpolar
describes a molecule with no charge; avoids polar/charged molecules and clusters together; only types of
Polar
Slight + and − areas; attract opposite charges.
Charged
Full + or − charge.
How can molecules diffuse through the membrane
Small nonpolar molecules diffuse freely through the cell membrane; small uncharged polar molecules can cross slowly; large polar molecules and ions require transport proteins.
Biomolecules
Large molecules made of many atoms.
Lipids
Biomolecule that stores energy, make up cell membranes (most are non-polar)
Nucleic Acids
Biomolecule that Stores genetic info (DNA, RNA).
Proteins
Biomolecule that helps with digestion, metabolism, and DNA replication (enzymatic activity), transportation through cell membrane, and communication with other cells
What is an enzyme
type of protein that helps chemical reactions take place under milder conditions (the artificial way of speeding up chemical reactions)
Carbohydrates
Biomolecule that Stores energy, help in cell communication by attaching to proteins on cell membrane
Nucleus
Organelle that Stores DNA; controls cell.
Mitochondria
Organelle that Makes energy (ATP) from chemical reactions (has TONS of enzymes)
Ribosomes
Organelle that Makes proteins with amino acids from info from RNA
Vesicles
Organelle that Transports materials in cell. Jobs: transporting, secreting (get rid of junk), lysosomes (break down waste)
Vacuole
Organelle that Stores water and nutrients (large in plants).
Lysosomes
Organelle that is a type of vesicle and breaks down waste.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER & SER)
Rough: makes and processes proteins with ribosomes Smooth: makes lipids and detoxes substances
Rough ER
Organelle that Makes proteins (has ribosomes).
Smooth ER
Organelle that makes and stores lipids
Golgi Apparatus
Gets lipids and proteins from ER, sorts and modifies them, sends them off in vesicles.
Chloroplast
(Organelle in plants only) Converts sunlight into energy (photosynthesis).
Prokaryotic cells
No nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, but do have ribosomes. includes bacteria and archaea
Eukaryotic cells
Larger, complex, with nucleus, membrane bound organelles, DNA tightly wrapped around histone proteins in chromosomes, cellulose in plant cell walls. Includes Protists, plants, fungi, and animals
Tissue
Group of similar cells doing a specific function.
Organ
Group of tissues working together.
Organ System
Group of organs doing a larger job.
Organism
Comprised of multiple organ systems; an individual living being that shows all characteristics of life and can reproduce to create a new organism.
Population
A group of the same species living in one area.
Community
All the different species in one area.
Ecosystem
All biotic communities + abiotic parts of an area.
Biome
A large region with a specific climate and ecosystems.
Biosphere
Everywhere life exists on Earth. Includes: air, water, land
Cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all living things.
Unicellular organisms
Organisms made of one cell, such as bacteria.
Multicellular organisms
Organisms made of trillions of cells, such as humans.
Cell theory
The principle that all living things are made of cells, and all cells come from earlier cells.
Unity and Diversity of Cells
All cells share a common ancestry and core structures but can look and act differently based on their function.
Core Structures Found in ALL Cells
Cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA, and ribosomes.
Cell membrane
Controls what enters and exits the cell; acts as a protective boundary.