Microbiology: Key Concepts, Microorganisms, and Disease Prevention
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
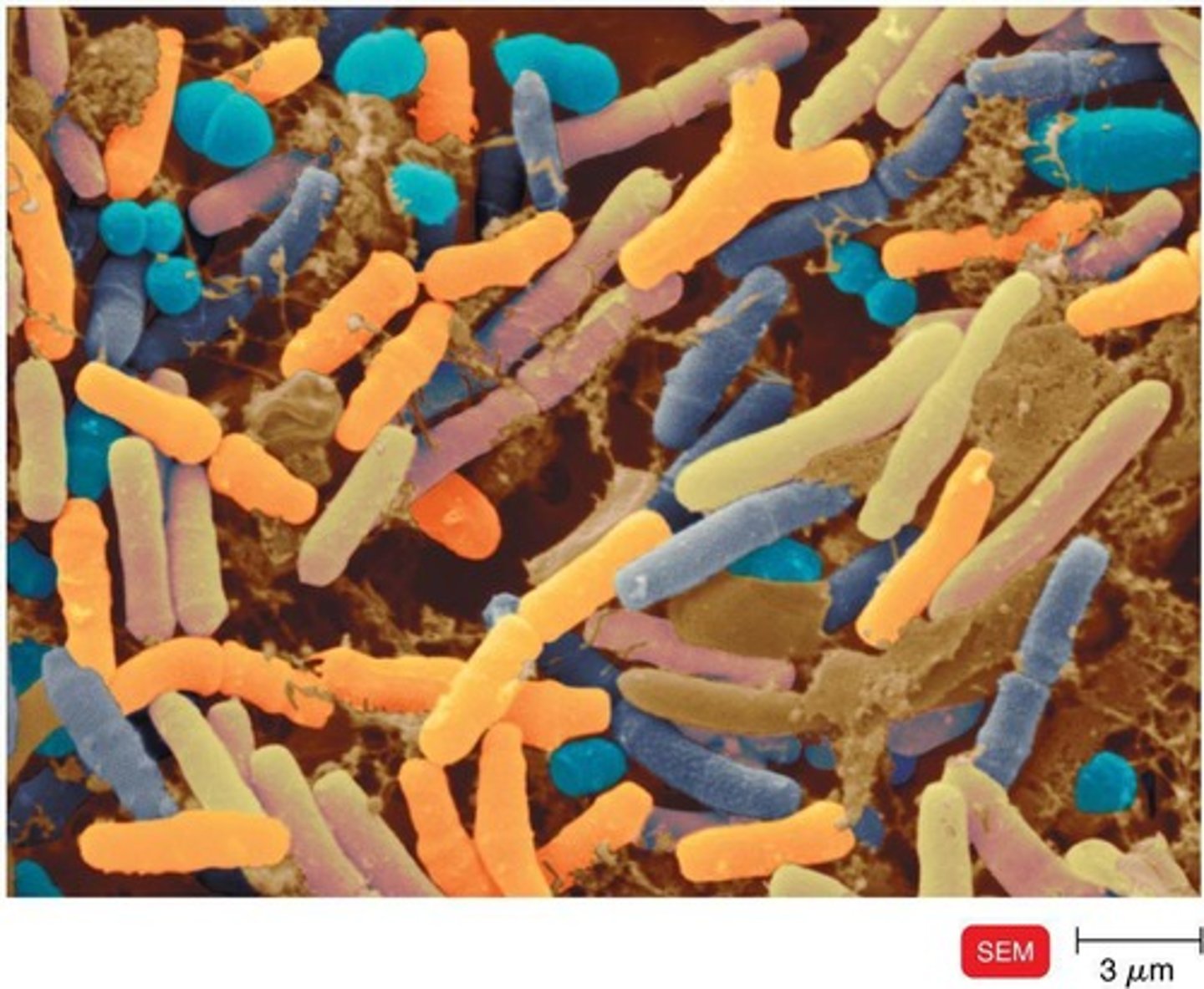
What are microorganisms?
Living things too small to be seen with the unaided eye.
How do microorganisms interact with hosts?
They can interact in beneficial, neutral, or detrimental ways.
Why are microorganisms important for ecological balance?
recycle nutrients, decompose wastes, generate oxygen through photosynthesis, and form symbiotic relationships that support food webs and ecological balance.
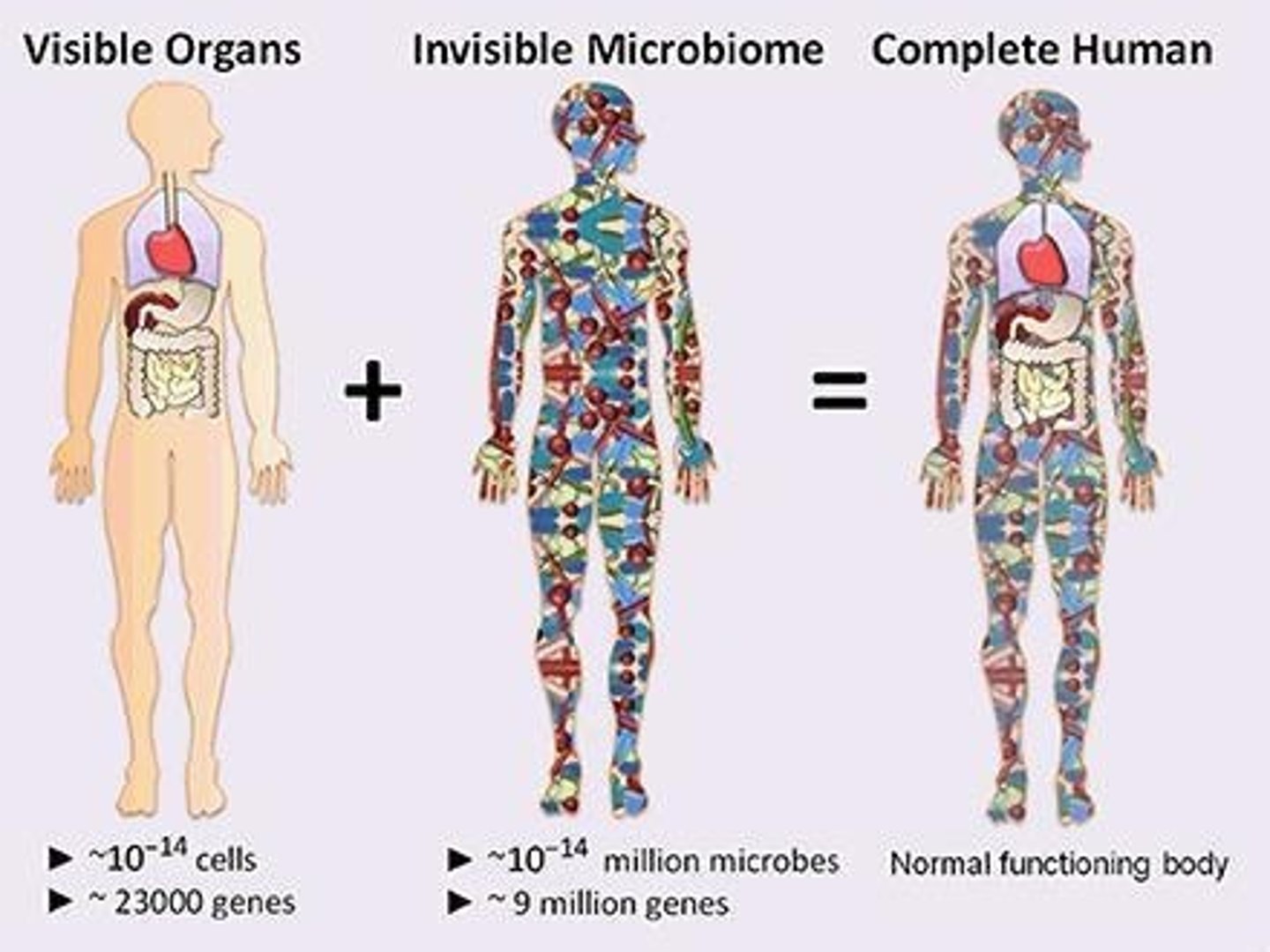
What is the human microbiome?
The normal microbiota in and on the body that are needed to maintain good health.
What are some uses of microorganisms?
They are used to produce foods and chemicals.
The adult is composed of ____ ______ body cells and harbors another ____ ______ bacterial cells
30 trillion; 40 trillion
What is a key characteristic of bacteria?
Bacteria are unicellular organisms with prokaryotic cells.
What is the cell wall composition of most bacteria?
Most bacteria have a peptidoglycan cell wall.
How do bacteria reproduce?
They divide by binary fission.
How do bacteria obtain nutrition?
Organic/inorganic chemicals or photosynthesis
What are archaea?
Prokaryotic cells that lack peptidoglycan in their cell walls.
Name three types of archaea.
Methanogens, extreme halophiles, and extreme thermophiles.

What type of cells do fungi have?
Eukaryotic cells with a true nucleus.

How do fungi obtain nutrients?
By absorbing organic material from their environment.
What are protozoa?
Unicellular eukaryotes that obtain nourishment by absorption or ingestion.

Protozoa may be motile via
pseudopods, cilia, or flagella
How do algae obtain nourishment?
By photosynthesis.
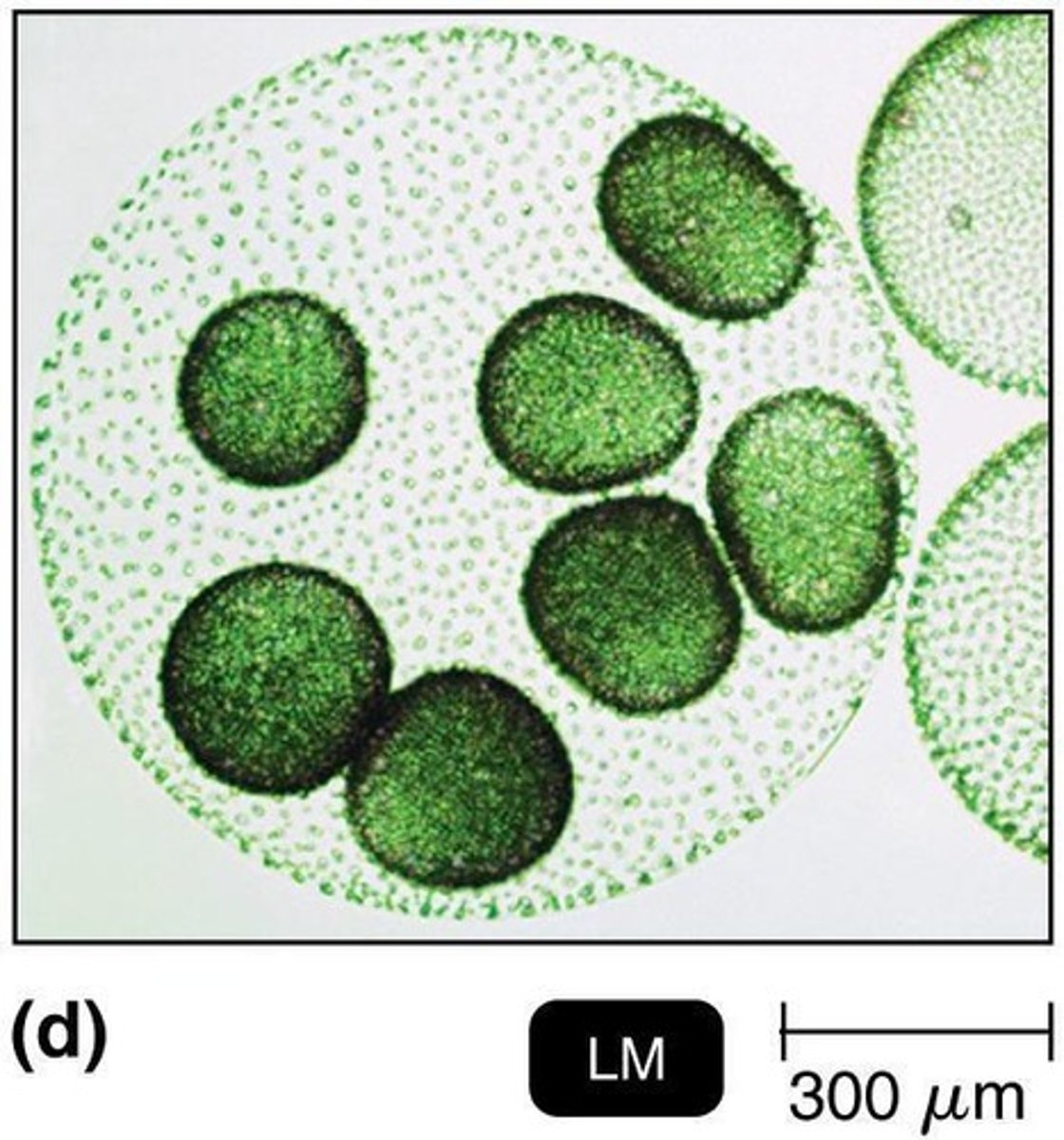
What do algae produce that is used by other organisms?
Oxygen and carbohydrates.
What are viruses?
Noncellular entities that are parasites of cells.
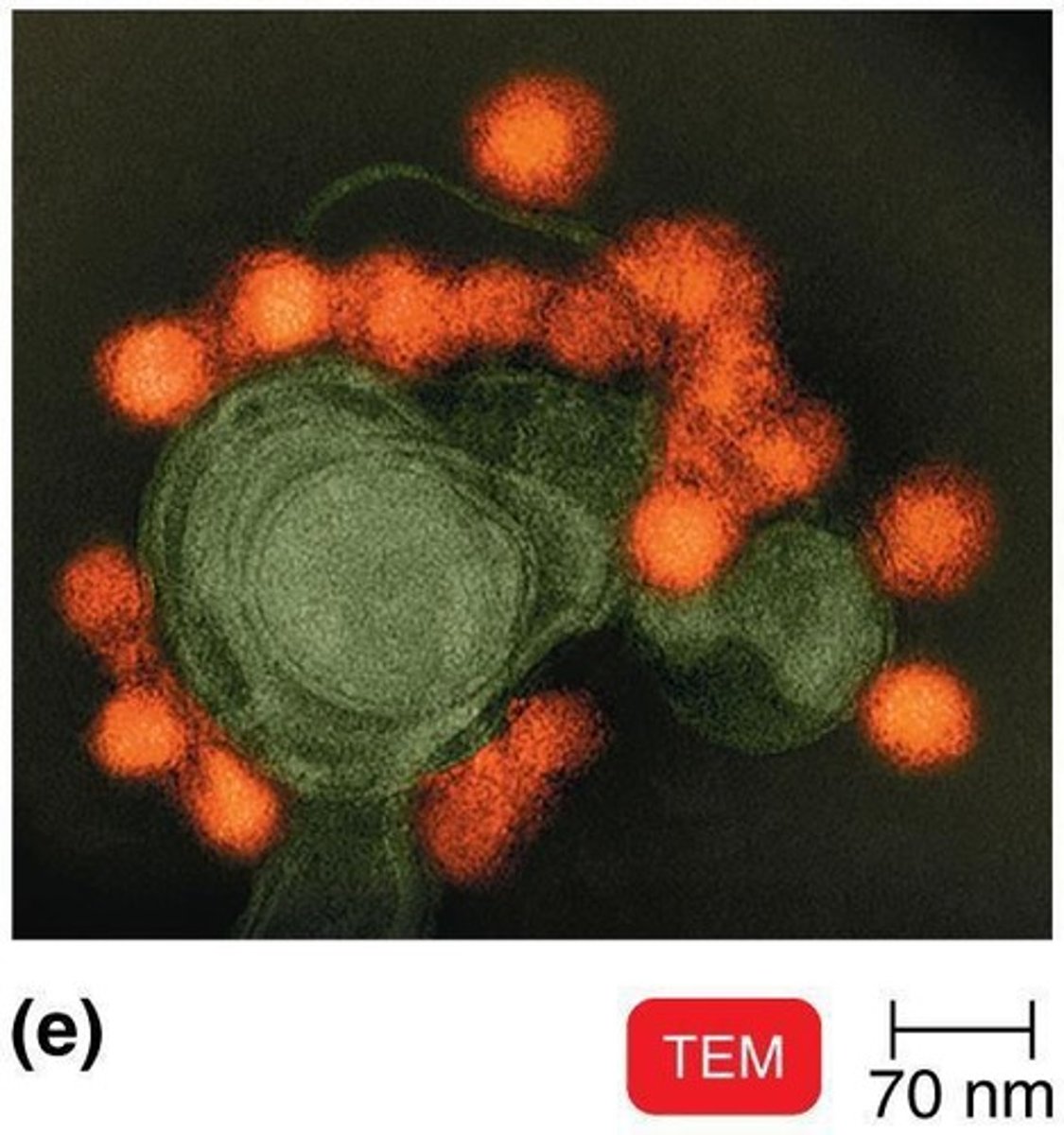
What is the structure of a virus?
A nucleic acid core (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat, which may have an envelope.
Viruses coat
What are helminths?
Multicellular animal parasites, including flatworms and roundworms.
How are the microscopic stages of helminths identified?
By traditional microbiological procedures.
What are the three domains of life?
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
What does the domain Eukarya include?
Protists, fungi, plants, and animals.
What did Hooke's observations contribute to?
The development of the cell theory, which states that all living things are composed of cells.
Who was the first to observe microorganisms and in what year?
Anton van Leeuwenhoek in 1673.
What is spontaneous generation?
The idea that living organisms could arise from nonliving matter.
What did Francesco Redi demonstrate regarding maggots and decaying meat?
Maggots appear on decaying meat only when flies can lay eggs on it (1668).
What claim did John Needham make about microorganisms in nutrient broth?
He claimed that microorganisms could arise spontaneously from heated nutrient broth (1745).
What did Lazzaro Spallanzani suggest about Needham's results?
He suggested that Needham's results were due to microorganisms in the air entering his broth (1765).
What concept did Rudolf Virchow introduce in 1858?
The concept of biogenesis: living cells can arise only from preexisting cells.
What did Louis Pasteur demonstrate in 1861?
He demonstrated that microorganisms are in the air everywhere and provided proof of biogenesis.
What techniques did Pasteur's discoveries lead to in laboratories and medical procedures?
The development of aseptic techniques to prevent contamination by microorganisms.
What significant advancements occurred in microbiology between 1857 and 1914?
Rapid advancements in the science of microbiology.
Yeast are
unicellular fungi and eukarytotic
Molds and mushrooms are
multicellular fungi and eukaryotic
What did Pasteur discover about yeast and bacteria?
Yeast ferments sugars to alcohol, and bacteria can oxidize alcohol to acetic acid.
What is pasteurization?
A heating process used to kill bacteria in some alcoholic beverages and milk.
What relationship did Agostino Bassi and Pasteur show between microorganisms and disease?
They showed a causal relationship between microorganisms and disease.
What did Joseph Lister introduce to control infections in humans?
The use of a disinfectant to clean surgical wounds (1860s).
What did Robert Koch prove in 1876?
That microorganisms cause disease, using a sequence of procedures known as Koch's postulates.
What did Edward Jenner demonstrate in 1798?
That inoculation with cowpox material provides immunity to smallpox.
What did Pasteur discover about avirulent bacteria around 1880?
That they could be used as a vaccine for fowl cholera and he coined the word vaccine.
How are modern vaccines prepared?
From living avirulent microorganisms, killed pathogens, isolated components of pathogens, and recombinant DNA techniques.
What initiated the Second Golden Age of Microbiology?
The discovery of penicillin's effectiveness against infections.
What are the two types of chemotherapeutic agents?
Synthetic drugs (chemically prepared in the laboratory) and antibiotics (naturally produced by bacteria and fungi).
What did Paul Ehrlich introduce in 1910?
An arsenic-containing chemical called salvarsan to treat syphilis.
What did Alexander Fleming observe in 1928?
That the Penicillium fungus inhibited the growth of a bacterial culture and named the active ingredient penicillin.
What are the three fields of study in microbiology mentioned?
Bacteriology (study of bacteria), mycology (study of fungi), and parasitology (study of parasitic protozoa and worms).
What are some current research interests in immunology?
The study of AIDS and the action of interferons.
What advancements have molecular biology and electron microscopy provided in virology?
New techniques that enhance our knowledge of virology.
How has recombinant DNA technology impacted microbiology?
It has helped advance all areas of microbiology.
What is genomics in the context of microbiology?
The study of all of an organism's genes, used to study microbiomes in different environments.
What role do microorganisms play in biogeochemical cycles?
They are essential for life and support processes that recycle chemical elements.
How do microorganisms contribute to human welfare?
They degrade dead plants and animals, recycle elements, and are utilized in biotechnology.
What is bioremediation?
A process that uses bacteria to clean up toxic wastes.
How are bacteria used in sewage treatment?
They decompose organic matter.
What is biotechnology in relation to microorganisms?
Using microbes to make products such as foods and chemicals.
What is gene therapy?
A method where viruses carry replacements for defective or missing genes into human cells.
What are biofilms?
Bacterial communities that form slimy layers on surfaces.
Comes in masses, can cause infections, and are often resistant to antibiotics
Biofilms
What defines an infectious disease?
A disease in which pathogens invade a susceptible host.
What is an emerging infectious disease (EID)?
A new or changing disease showing an increase in incidence recently or has the potential to increase.
Name a significant contributor to microbiology known for the discovery of penicillin.
Alexander Fleming.
Who is known for the development of the germ theory of disease?
Louis Pasteur.
What is the significance of Edward Jenner in microbiology?
He developed the first successful smallpox vaccine.
Who is known for their work on the structure of DNA?
James Watson and Francis Crick.
What did Anton van Leeuwenhoek contribute to microbiology?
He is known as the father of microbiology for his work with microscopes and discovery of microorganisms.
What is the role of genetically modified bacteria in agriculture?
They protect plants from frost and insects and improve shelf life.
What is the importance of the host's resistance in disease contraction?
It is a crucial factor in determining whether a person will contract a disease.
What are some products that can be produced using recombinant DNA technology?
Proteins, vaccines, and enzymes.
What is the role of microbes in the recycling of chemical elements?
They degrade dead organisms and recycle nutrients for living plants and animals.
What are some roles of microbes in our lives?
They decompose organic waste, generate oxygen by photosynthesis, produce chemical products (e.g., ethanol, acetone, vitamins), and create fermented foods (e.g., vinegar, cheese, bread).
Vitamins B and K
Vitamins that do not need to be ingested, synthesized by intestinal bacteria
How do microorganisms help prevent food spoilage and disease?
Knowledge of microorganisms allows humans to prevent food spoilage and understand the causes and transmission of diseases to prevent epidemics.
What is the microbiome?
A group of microbes that live stably on/in the human body, helping to maintain good health and prevent the growth of pathogenic microbes.
What is normal microbiota?
The collection of acquired microorganisms on or in a healthy human being, which can prevent the growth of pathogens and produce growth factors such as vitamins B and K.
What factors contribute to the body's resistance to disease?
Resistance factors include skin, stomach acid, and antimicrobial chemicals.
Who established the system of scientific nomenclature?
Carolus Linnaeus in 1735.
What are the two parts of a scientific name?
The genus and the specific epithet.
How is the scientific name formatted?
It is italicized or underlined, with the genus capitalized and the specific epithet in lowercase.
What does Escherichia coli honor?
It honors the discoverer, Theodor Escherich, and describes the bacterium's habitat in the large intestine.
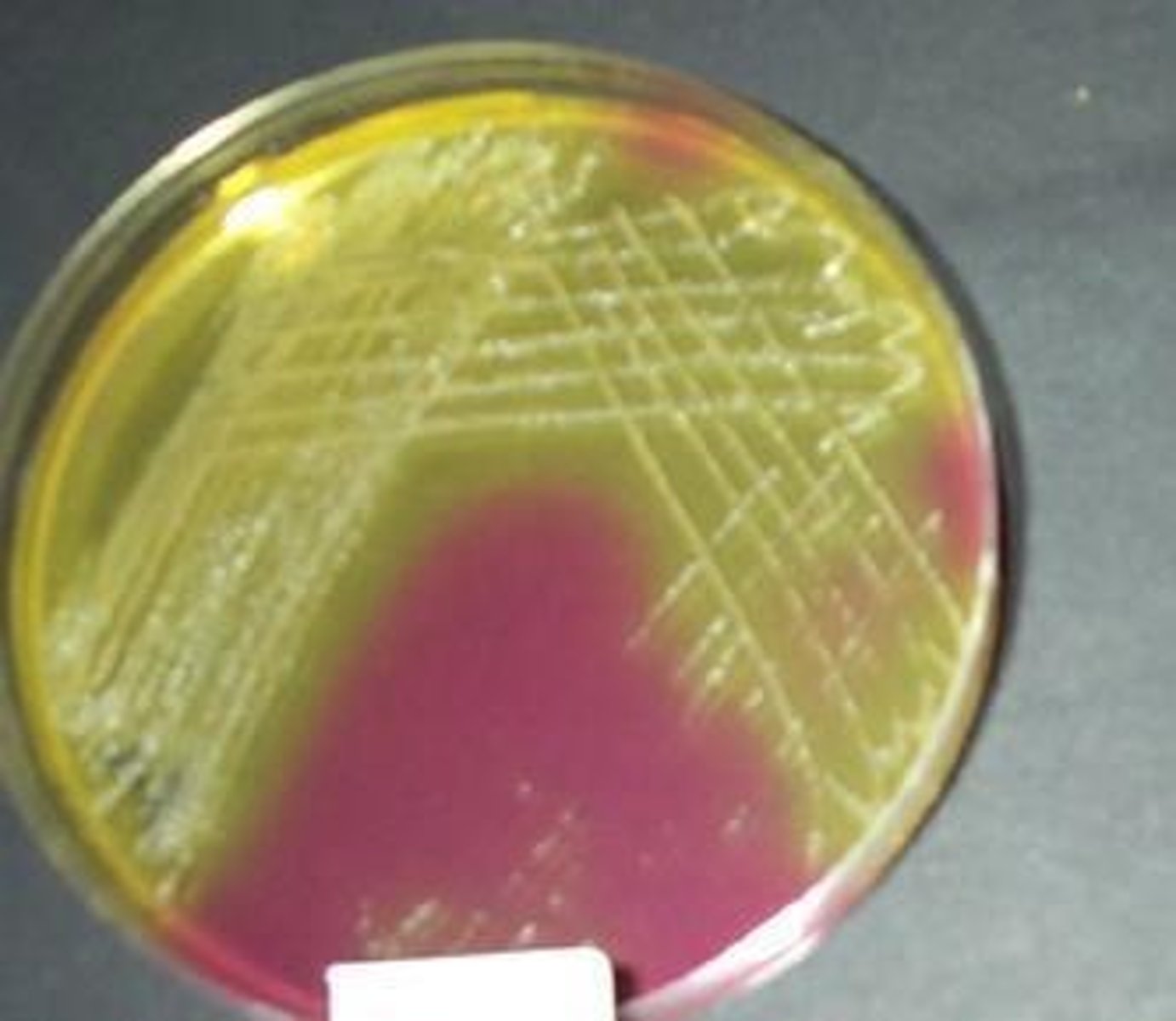
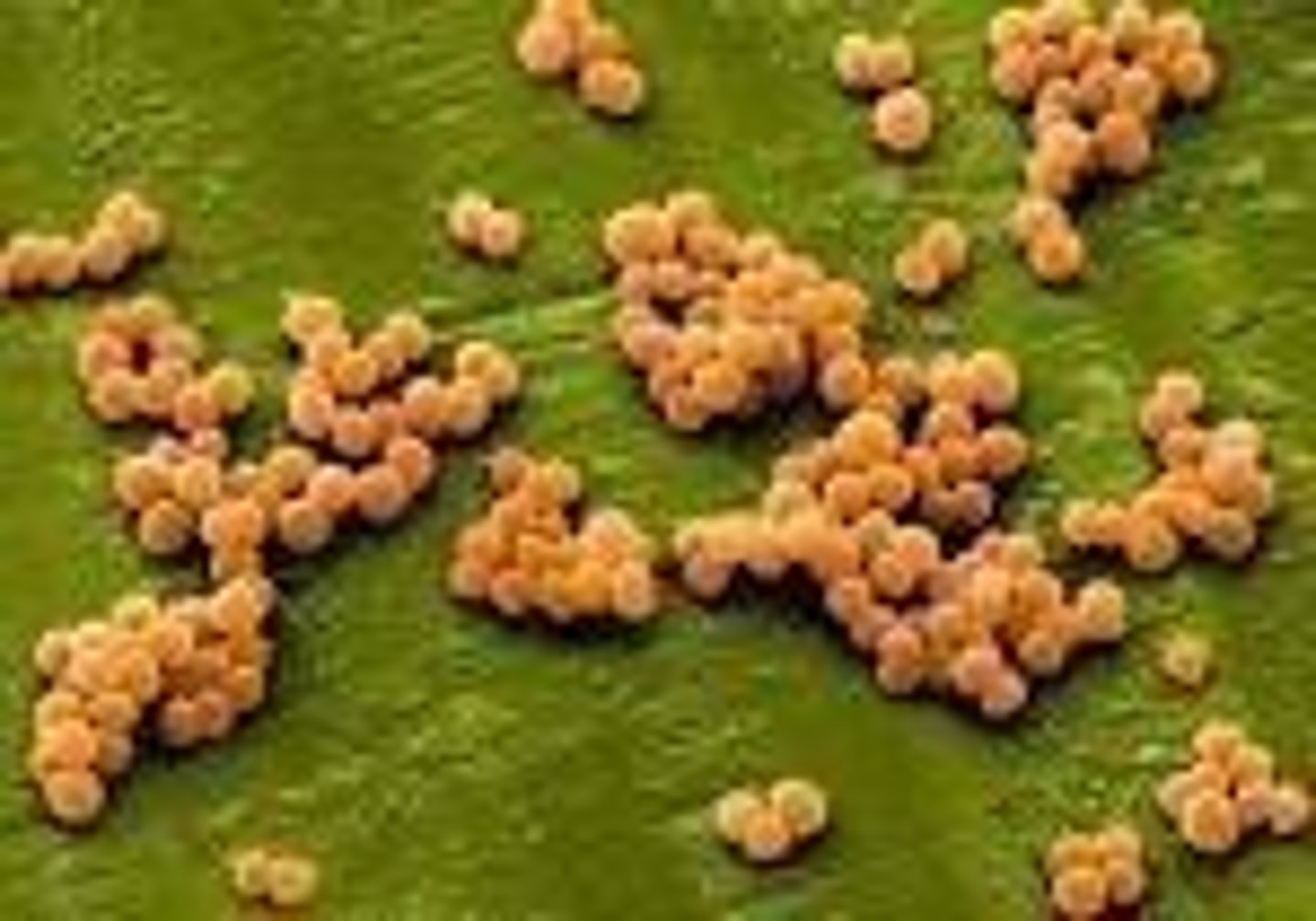
What does Staphylococcus aureus describe?
It describes the clustered (staphylo-) spherical (coccus) cells and the gold-colored (aureus) colonies.
What are the main types of microorganisms?
Bacteria, Archaea, Fungi, Protozoa, Algae, Viruses, and Multicellular Animal Parasites.
What are key characteristics of bacteria?
They are prokaryotes, single-celled, have peptidoglycan cell walls, divide via binary fission, and may swim using flagella.
What distinguishes Archaea from bacteria?
Archaea lack peptidoglycan cell walls and often live in extreme environments.
What are key characteristics of fungi?
They are eukaryotes with distinct nuclei, chitin cell walls, and absorb organic chemicals for energy.
What are the characteristics of protozoa?
They are unicellular eukaryotes without cell walls, may be motile, and can be free-living or parasitic.
What are the characteristics of algae?
Eukaryotes with cellulose cell walls, found in various environments, and use photosynthesis for energy.
What are multicellular animal parasites?
Eukaryotic organisms that are not strictly microorganisms, including parasitic flatworms and roundworms, known as helminths.
What are some examples of helminths?
Ascaris (roundworm), Trichuris (whipworm), Hymenolepis (tapeworms), Toxocara (roundworm), and Necator (hookworm).
Who developed the classification of microorganisms and in what year?
Carl Woese developed the classification in 1978.
What are the three domains of life based on cellular organization?
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
What significant contribution did Robert Hooke make in 1665?
He reported that living things are composed of little boxes, or 'cells', marking the beginning of cell theory.
Who was the first to observe microbes and what did he call them?
Anton van Leeuwenhoek observed microbes and referred to them as 'animalcules'.
What is biogenesis?
The hypothesis that living cells arise only from preexisting living cells.
What experiment did Francesco Redi conduct in 1668, and what were the results?
He filled jars with decaying meat; jars covered with fine net had no maggots, opened jars had maggots, and sealed jars had no maggots.
What was John Needham's experiment in 1745 and its outcome?
He put boiled nutrient broth into covered flasks, resulting in microbial growth.
What did Lazzaro Spallanzani do in 1765, and what were the results?
He boiled nutrient solutions in sealed flasks, which resulted in no microbial growth.