Biochem Lect 31: TCA Cycle
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Aerobic Metabolism
-
grow only without O2/ROS, use fermentation for energy only
obligate anaerobes
can handle presence of O2/ROS, use fermentation for energy only
aerotolerant anaerobes
(tolerant, don’t use O2)
can handle presence of O2/ROS, can use O2/ROS for energy if available
facultative anaerobes
(use O2)
dependent on O2
obligate aerobes
aerotolerant/facultative anaerobes and obligate aerobes contain ___________ to handle O2
detoxifying enzymes (detoxify ROS)
Which 3 processes are considered part of aerobic metabolism?
TCA cycle, ETC, oxidative phosphorylation
Aerobic metabolism (including TCA cycle) usually occurs in cytoplasm or mitochondria?
mitochondria
electrons are transferred to someone with higher _______ potential
reduction (reduce = gain e-)
2 main categories of redox coenzymes
1) NAD/NADPH
2) FAD/FMN
NAD = ?
NADPH = ?
NAD = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
NADPH = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
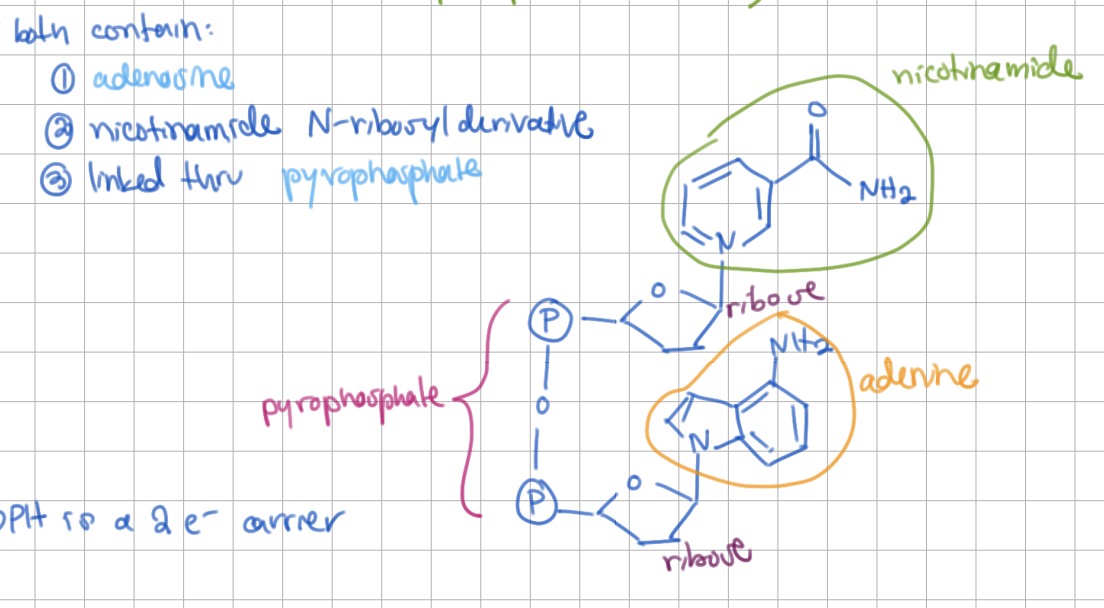
NAD/NADPH structure - both contain:
_______
nicotinamide N-ribosyl derivative
linked thru _______
NAD/NADPH structure - both contain:
adenosine
nicotinamide N-ribosyl derivative
linked thru pyrophosphate
FAD = ?
FMN = ?
FAD = flavine adenine dinucleotide
FMN = flavin mononucleotide
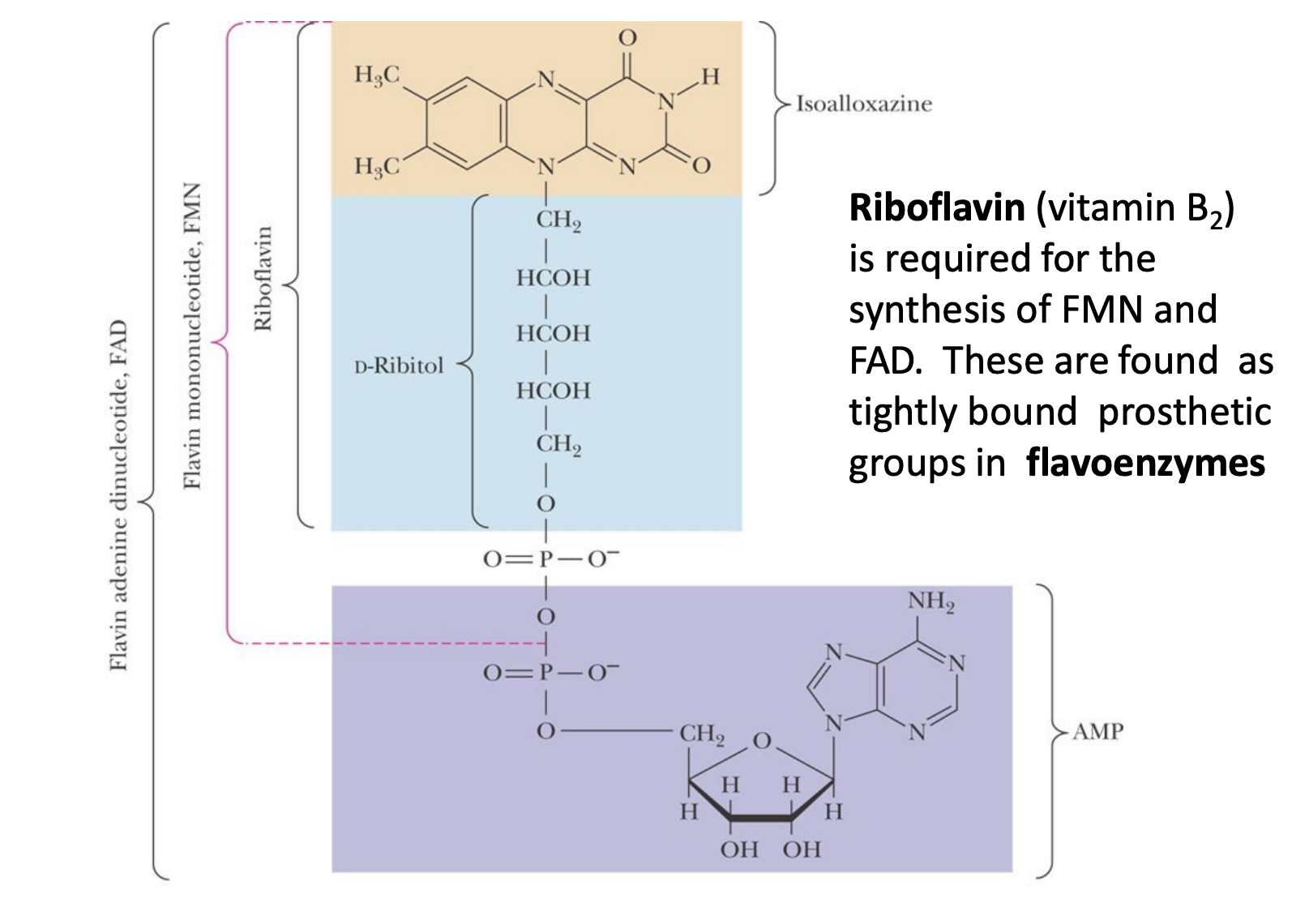
FAD/FMN structure
________ (_________) are tightly bound prosthetic groups in _________ (FAD/FMN).
FAD/FMN structure
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) are tightly bound prosthetic groups in flavoenzymes (FAD/FMN).
NADPH carries ___ electrons and transfers ___ at a time.
FAD/FMN carries ___ electrons and tranfers ___ at a time.
NADPH carries 2 electrons and transfers 2 at a time.
FAD/FMN carries 2 electrons and transfers 1 or 2 at a time.
TCA/Citric Acid/Krebs Cycle
-
Overall reactants and products of TCA cycle
Acetyl CoA + Oxaloacetate → energy (NADH2, FADH2)
Acetyl Coa can be made in many ways, for example…
from pyruvate !!
fatty acid catabolism
some reactions in amino acid metabolism
TCA Cycle 2 phases overall (_ reactions)
1) acetyl-CoA + Oxaloacetate → ______
2) ??
TCA Cycle 2 phases overall (8 reactions)
1) acetyl-CoA + Oxaloacetate → 2 CO2 released
2) Oxaloacetate is regenerated
Phase I has ___ reactions, Phase II has ___ reactions
5, 3
What are the regulated steps of TCA cycle?
1, 3, 4
Phase I
-
Summary of Phase I (Reactants → Products)
1) Acetyl-CoA + Oxaloacetate → Citrate
2) Citrate → Isocitrate
3) Isocitrate → ɑ-Ketoglutarate
4) ɑ-Ketoglutarate → Succinyl CoA
5) Succinyl-CoA → Succinate
Summary of Phase I (Enzymes)
1) Citrate Synthase
2) Aconitase
3) Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
4) ɑ-Ketoglutanate Dehydrogenase Complex
5) Succinyl-CoA Synthetase
Summary of Phase I (Extras)
1) -ΔG
2)
3) +CO2, +NADPH/H+, -ΔG
4) +CO2, +NADPH/H+, +CoA-SH
5) +GTP, -CoA-SH
Step 1: ________ → ________ (E = ________)
-
-
Step 1: Acetyl-CoA + Oxaloacetate → Citrate (E = Citrate Synthase)
aldol condensation + hydrolysis
-ΔG (regulated)

Step 2: ________ → ________ (E = ________)
-
-
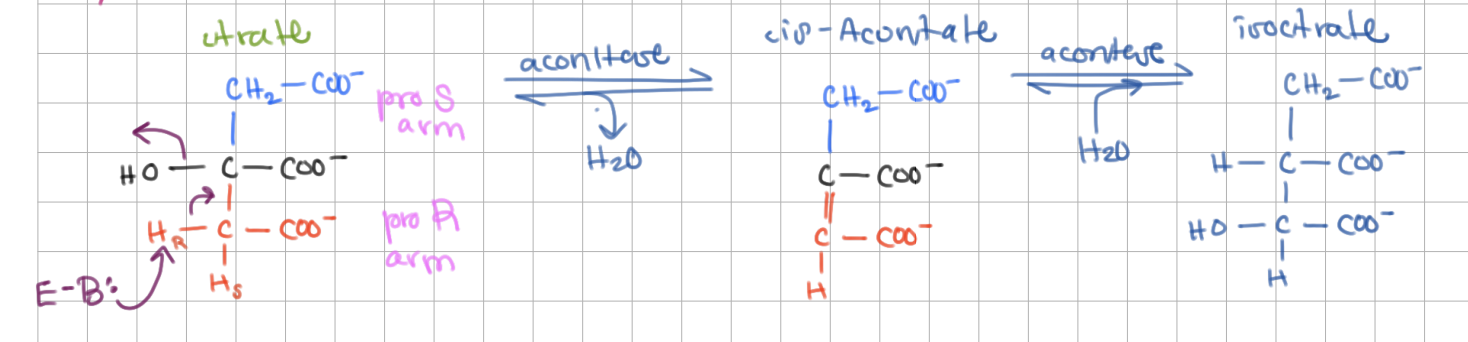
Step 2: Citrate → Isocitrate (E = Aconitase)
dehydration/rehydration
intermediate step involving cis-Aconitate
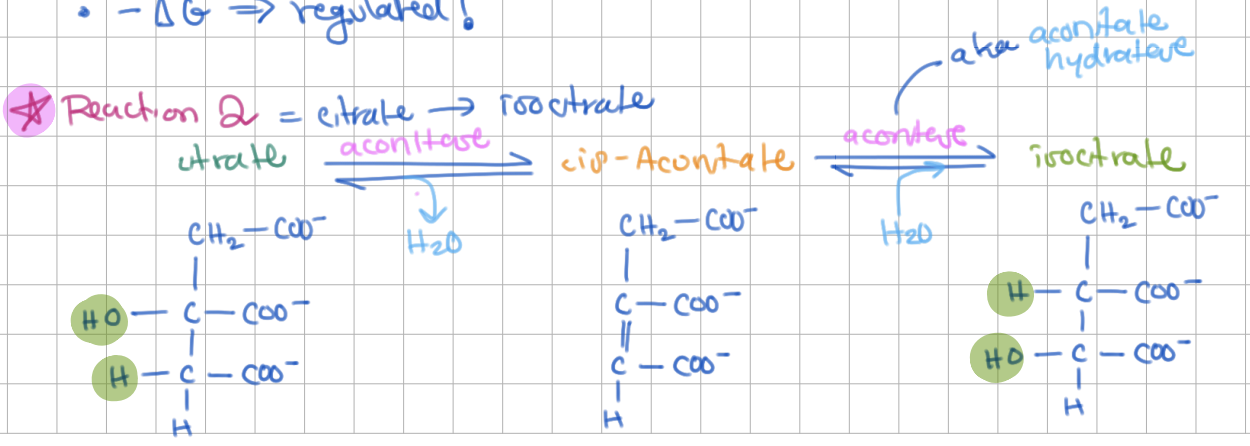
Aconitase removes the pro R/S H arm of citrate via a ______
R, Fe-S cluster
Aconitase contains a ___Fe-___S cluster bound to a protein by 3 ___.
Inactive form = ___Fe-___S (binding ____ activates aconitase)
Aconitase contains a 4Fe-4S cluster bound to a protein by 3 Cys.
Inactive form = 3Fe-4S (binding Fe2+ activates aconitase)
Step 3: ________ → ________ (E = ________)
-
-
Step 3: Isocitrate → ɑ-Ketoglutarate (E = Isocitrate Dehydrogenase)
oxidative decarboxylation (+CO2, +NADPH/H+)
-ΔG (regulated)
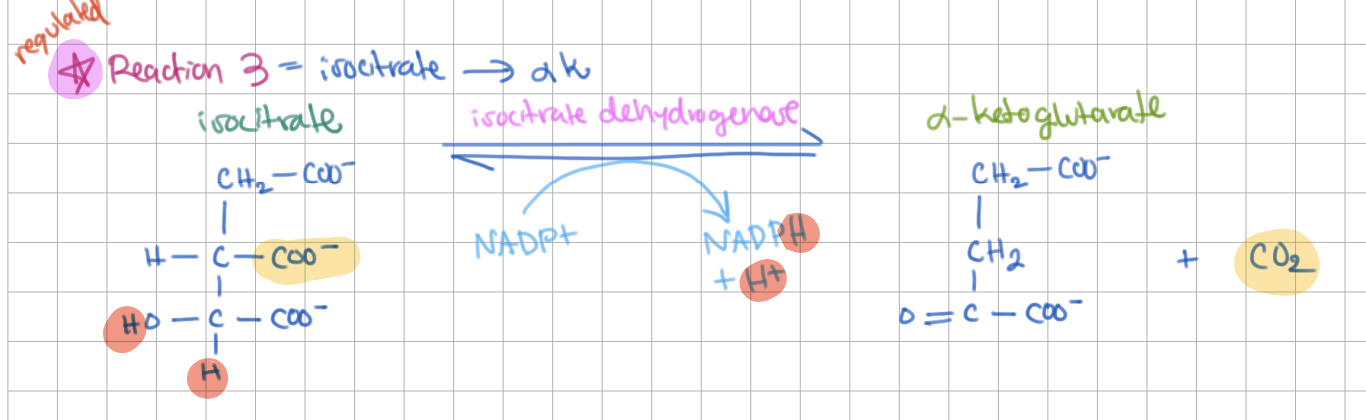
Step 3 mechanism (oxidative decarboxylation):
1) isocitrate —oxidized—> ____(1)____
2) ____(1)____ —decarboxylated—> ____(2)____
3) ____(2)____ —> ɑkg
Step 3 mechanism (oxidative decarboxylation):
1) isocitrate —oxidized—> oxalosuccinate
2) oxalosuccinate —decarboxylated—> enol intermediate
3) enol intermediate —> ɑkg
Step 4: ________ → ________ (E = ________)
-
-
Step 4: ɑ-Ketoglutarate → Succinyl CoA (E = ɑ-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Complex)
2nd oxidative decarboxylation (+CO2, +NADPH/H+)
add CoA-SH
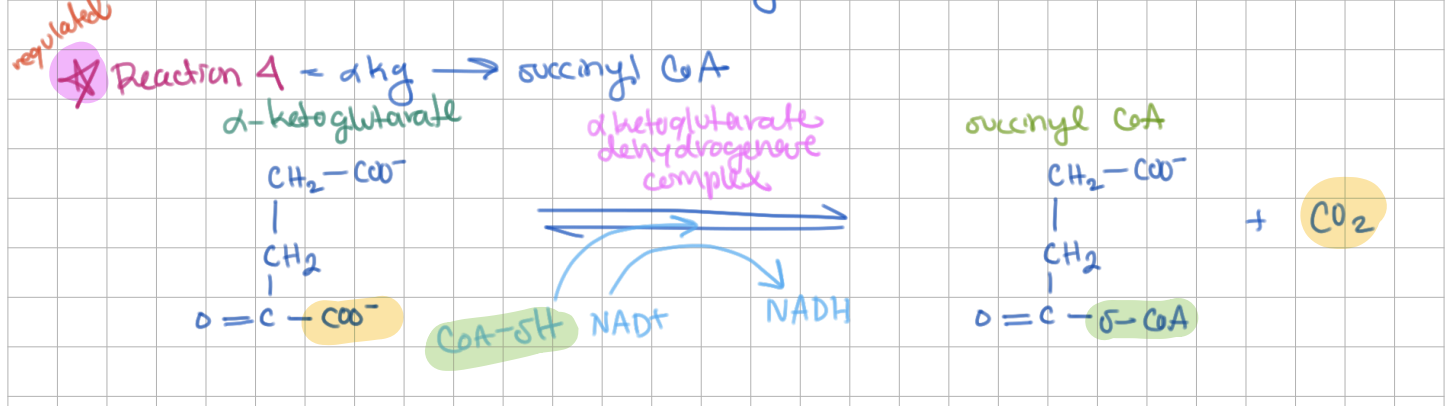
ɑkg dehydrogenase complex involves what 3 enzymes?
1) ɑkg dehydrogenase
2) dihydrolipoyl transuccinylase
3) dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
Step 5: ________ → ________ (E = ________)
-
-
-
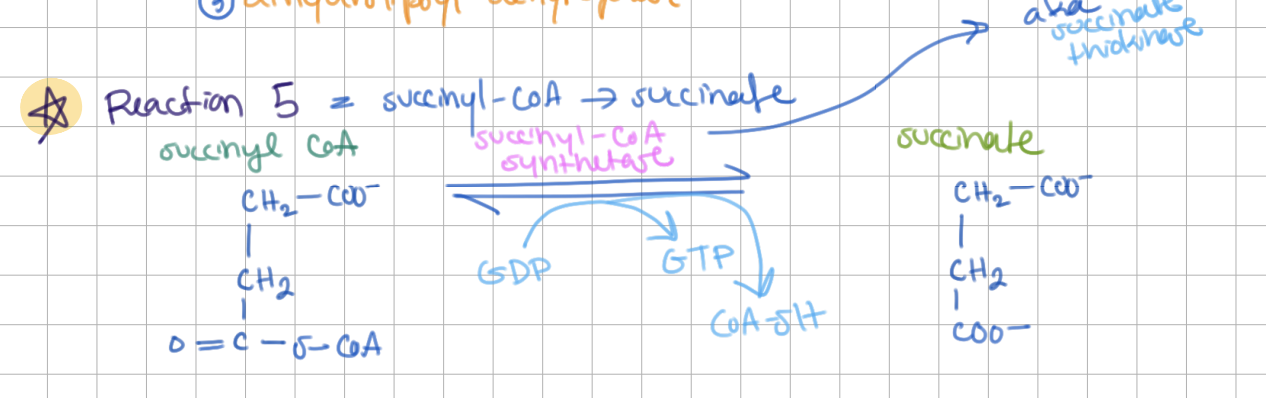
Step 5: Succinyl-CoA → Succinate (E = Succinyl-CoA Synthetase)
+GTP (synthetase)
remove CoA-SH
coupled with SLP
Phase II
-
Summary of Phase II (Reaction Name)
6) Oxidation (single → double bond)
7) Trans-Hydration
8) Oxidation (OH → ketone)
Summary of Phase II (Reactants → Products)
6) Succinate → Fumarate
7) Fumarate → Malate
8) Malate → Oxaloacetate
Summary of Phase II (Enzymes)
6) Succinate Dehydrogenase
7) Fumarase
8) Malate Dehydrogenase
Summary of Phase II (Extras)
6) +FADH2
7) -H2O
8) +NADH
Step 6: ________ → ________ (E = ________)
-
-
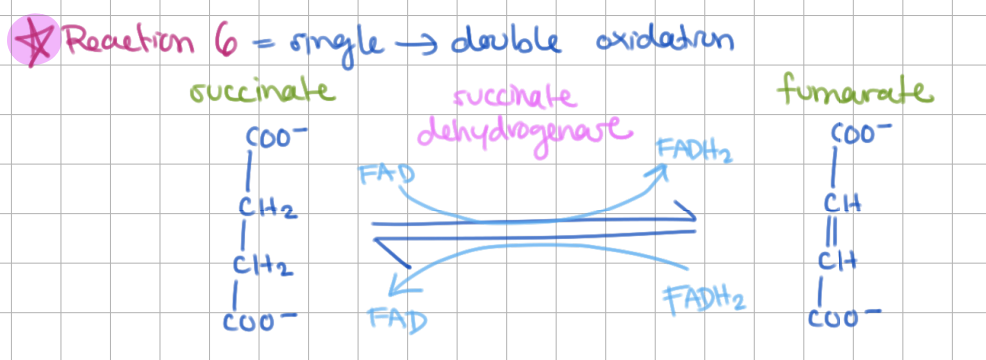
Step 6: Succinate → Fumarate (E = Succinate Dehydrogenase)
trans-oxidation = oxidation of single to double bond
+FADH2
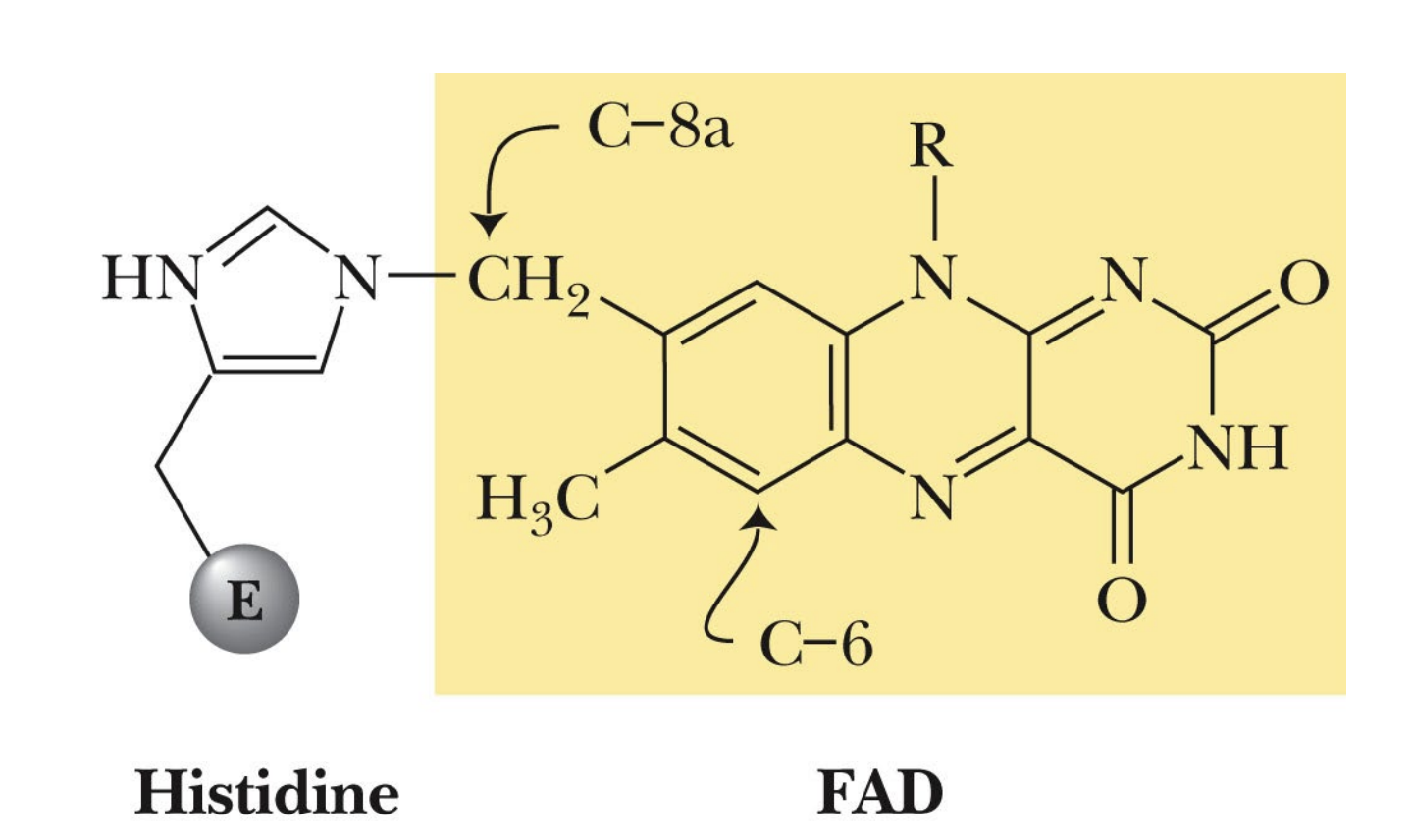
FAD is covalently bound to ___________________.
The ___ carbon of FAD is linked to ____ of this enzyme.
FAD is covalently bound to succinate dehydrogenase.
The C8a carbon of FAD is linked to His of this enzyme.
Succinate dehydrogenase has 3 types of Fe-S clusters…
1) 2Fe-2S
2) 3Fe-4S
3) 4Fe-4S
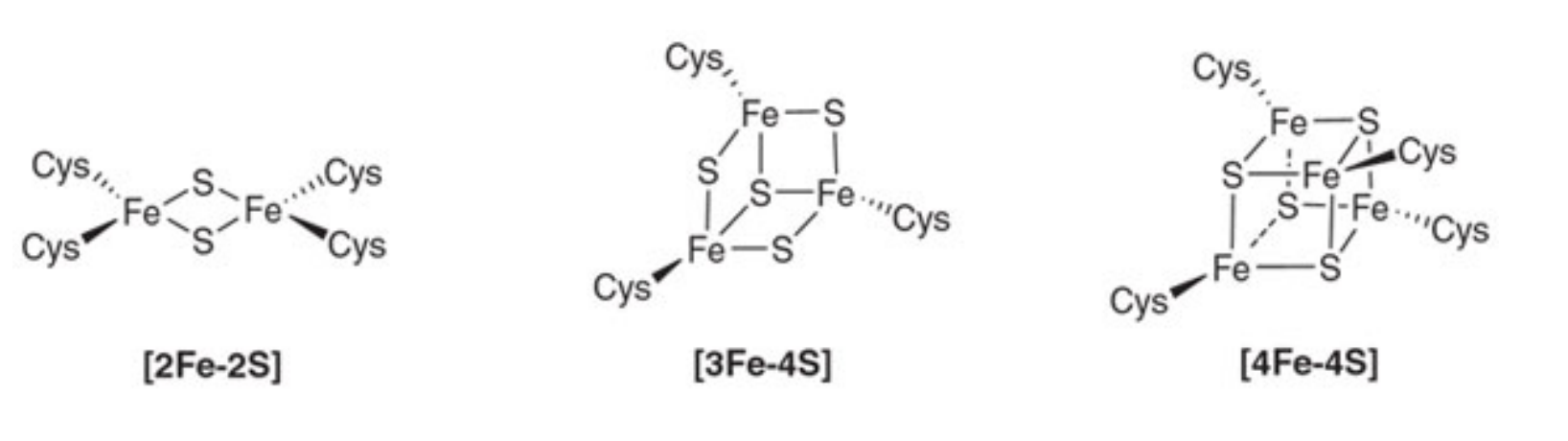
Fe-S clusters are “redox centers” that participate in ___ e- redox rxns (involving ___ and ___ oxidation states)
Fe-S clusters participate in 1 e- redox rxns (involving Fe2+ and Fe3+ oxidation states)
_________ = multiple redox centers close to each other (makes redox rxns easier)
electron wire
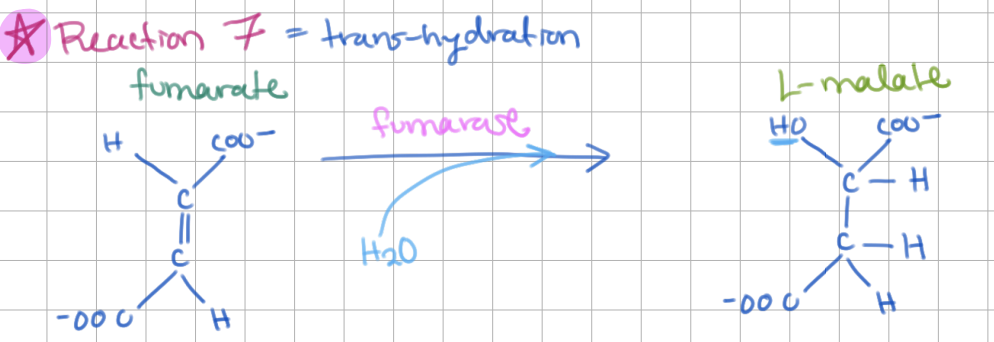
Step 7: ________ → ________ (E = ________)
-
Step 7: Fumarate → Malate (E = Fumarase)
trans-hydration (-H2O) = hydration across double bond
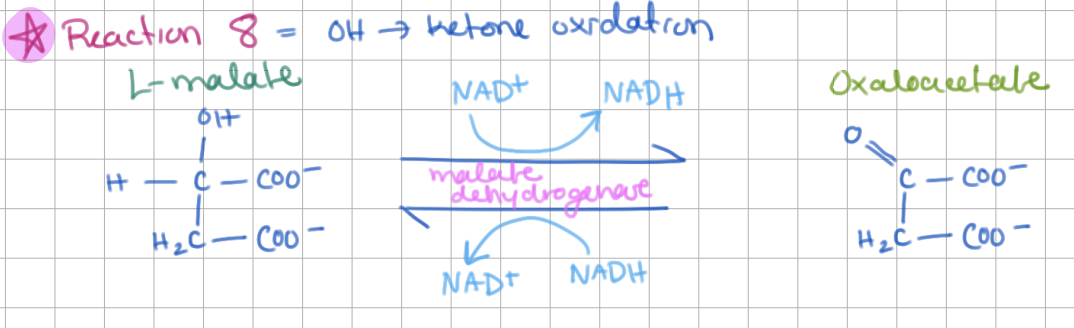
Step 8: ________ → ________ (E = ________)
-
Step 8: Malate → Oxaloacetate (E = Malate Dehydrogenase)
OH → ketone oxidation (+NADH)
TCA Cycle Yield
-
oxidation of glucose to CO2 is a ___ e- oxidation
oxidation of glucose to CO2 is a 24 e- oxidation
Products of 1x TCA Cycle
___ CO2
___ NADH
___ FADH2
___ ATP
Products of 1x TCA Cycle
2 CO2
3 NADH
1 FADH2
1 ATP
Products of 1x TCA Cycle + Glycolysis
___ CO2
___ NADH
___ FADH2
___ ATP
Products of 1x TCA Cycle + Glycolysis
6 CO2
10 NADH
2 FADH2
4 ATP
10 NADH + 2 FADH2 → ___ ATP
10 NADH + 2 FADH2 → 34 ATP (varies)
TCA Cycle is at the center ________ and ________ pathways
catabolic, anabolic
anaplerotic reactions
“filling up” reactions
(replenish TCA cycle intermediates)
carbon source of anaplerotic reactions
CO2
The most important anaplerotic enzyme is ________ which catalyzes ________ → ________, providing a link between glycolysis and the TCA cycle.
The most important anaplerotic enzyme is pyruvate carboxylase which catalyzes pyruvate → oxaloacetate, providing a link between glycolysis and the TCA cycle.
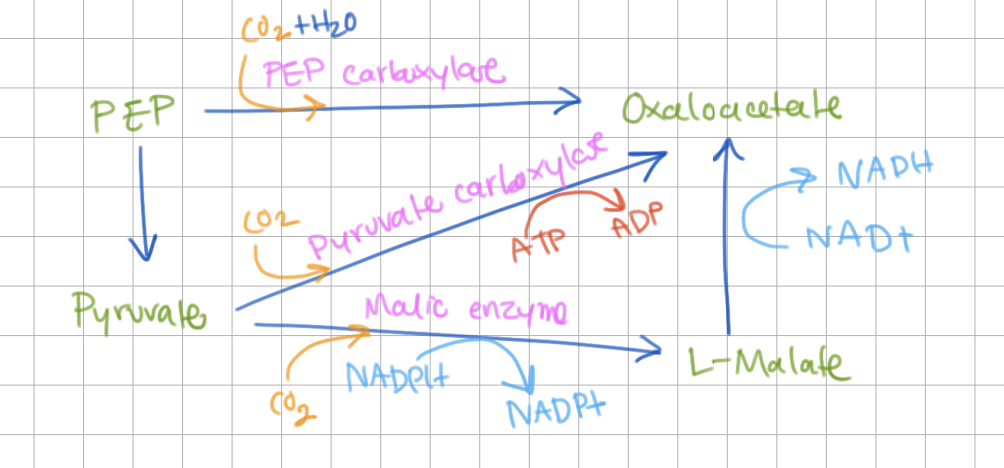
pyruvate carboxylase is activated by ________.
acetyl-CoA
(if acetyl CoA > oxaloacetate, more oxaloacetate will be made)
TCA Cycle regulation (steps ___, ___, ___ + _________ reaction)
ATP/AMP/ADP inhibits/activates
NADH/NAD+ inhibits/activates
succinyl CoA inhibits/activates
TCA Cycle regulation (steps 1, 3, 4 + pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction)
ATP inhibits, AMP activates
NADH inhibits, NAD+ activates
succinyl CoA inhibits
NAD+ = high/low energy signal, NADH = high/low energy signal
ATP = high/low energy signal, AMP/ADP = high/low energy signal
succinyl CoA = signal that __________
NAD+ = low energy signal, NADH = high energy signal
ATP = high energy signal, AMP/ADP = low energy signal
succinyl CoA = signal that cycle is saturated
-
*NADH = High
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Regulation
-
PDH complex catalyzes what reaction?
pyruvate → acetyl CoA
PDH complex contains what 3 enzymes?
1) pyruvate dehydrogenase
2) dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
3) dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
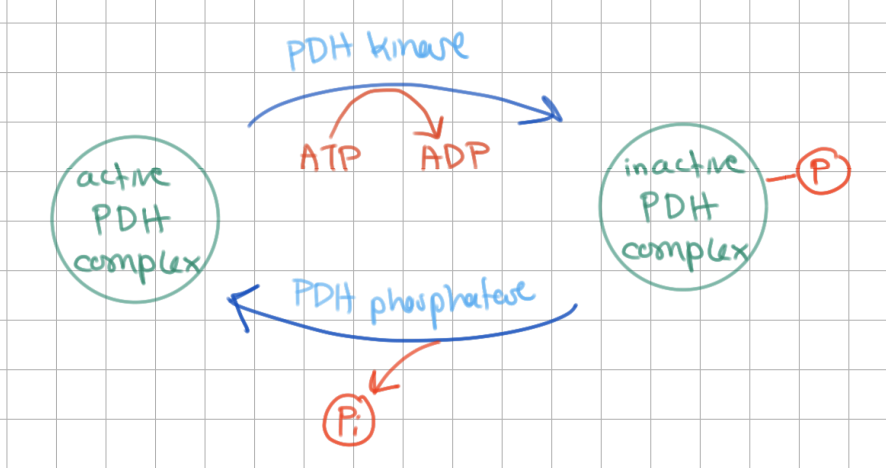
_______________ inactivates PDHC in 2 ways: ________, __________
PDH kinase inactivates PDHC in 2 ways: allosterically, serine phosphorylation
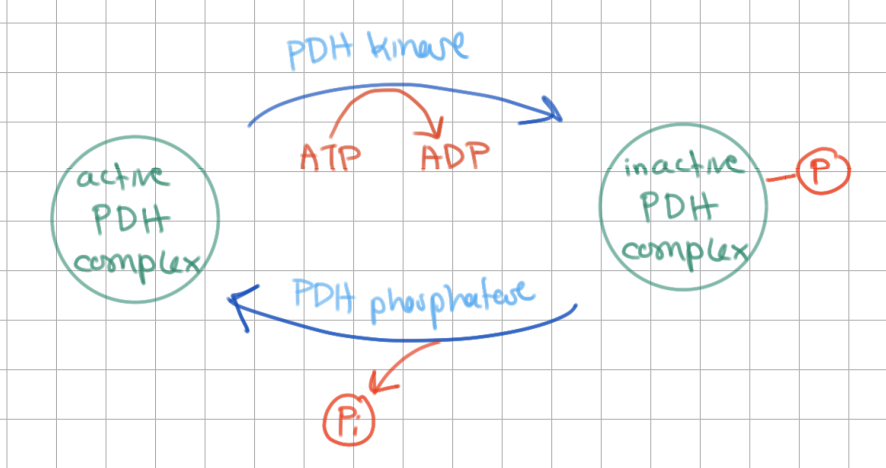
PDH kinase is activated by ________ and ________
NADH and acetyl CoA
(opposite of PDH Complex)
_______________ activates PDHC
PDH phosphatase activates PDHC