Blood pressure, heart & thermoregulation NOT FINISHED
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is the cardiovascular system involved in?
Transporting nutrients and other material , via the blood, to and from various parts of the body
To fulfil the function of the cardiovascular system blood must be?
continuously circulated throughout the body
How is blood circulated continuously around the body?
it is a closed system => blood won’t come out unless soemthing like a cut happens
heart => pump
blood vessels => system of tubes
What kind of tissue is blood?
it is a fluid connective tissue
Components of blood?
-plasma
-leucocytes
-erythrocytes
-platelets (not visible)
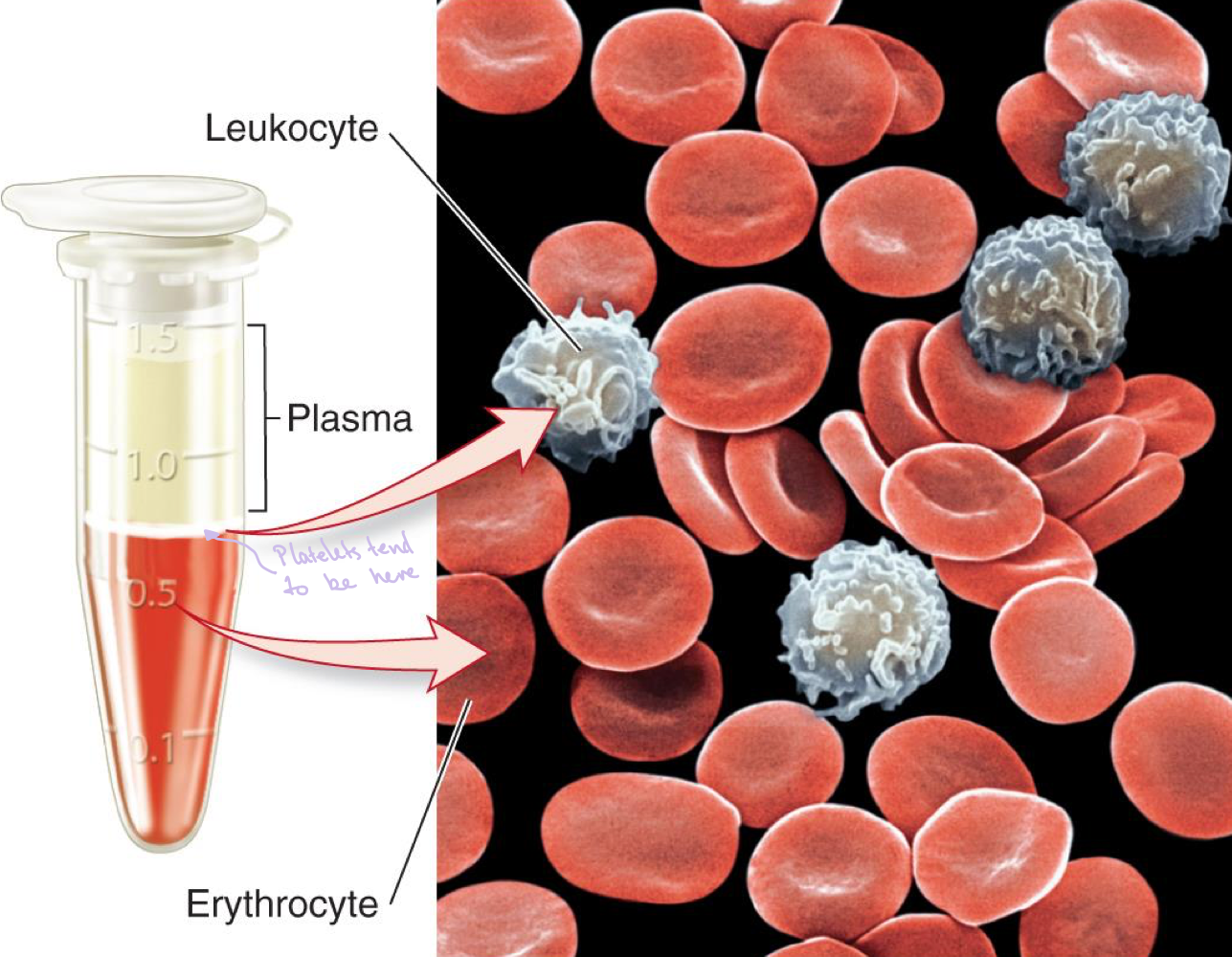
Plamsa?
-30-60% of total blood volume
-water, dissolved organic and inorganic nutrients
-dissolved O2, waste products of metabolism
-hormones
-proteins (important for blood clotting)
-pH buffers and osmotic balance.
Leucocytes?
-defend body against infections and disease
Haematocrit meaning?
percent volume of how much of the body’s blood is composed of red blood cells
Erythrocytes?
-haematocrit => 40-65%
-250 million haemoglobin molecules/red cell
-haemoglobin contains 4 proteins subunits
-each protein subunit contains 1 heme molecule that binds 1 O2 molecule
-each haemoglobin can bind 4 O2 molecules
Capillaries?
site of gas exchange and nutrient exchange
-red blood cells go one by one as their diameter is about the same as capillaries
Platelets?
play a crucial role in the formation of blood clots
The heart in action?
-the upper chambers contract then the lower chambers will contract
What makes cardiac muscle cells contract?
the release of calcium leads to muscle contraction
Myogenetic heart?
signalling mechanism that causes the heart to beat
-resides within the heart
generates its own electrical impulses for contraction, meaning the heart muscle (myocardium) has the ability to initiate and regulate its own rhythm without needing external nerve signals.
Artial excitation?
-starts at the SA node, spreads through the atria causing them to contract and fill the ventricles with blood
Ventrical excitation?
-the signal moves to the AV node which causes the ventricles to contract and pump blood out
SA node ?
-the pacemaker of the heart, initiating the electrical impulses
AV node?
-slows down the electrical impulse to allow the ventricles to fill with blood before contracting
What does ECG stand for?
electrocardiogram
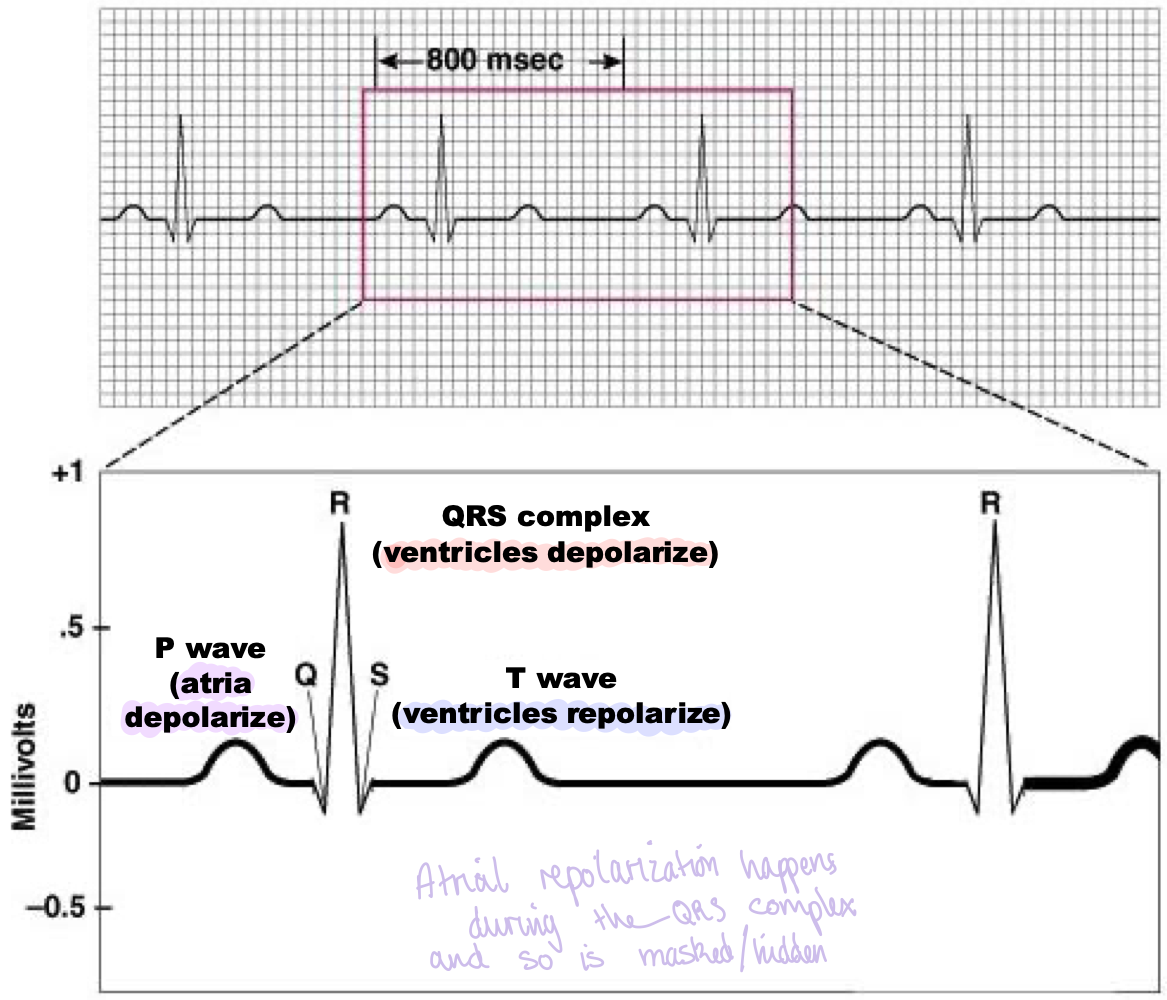
What happens at the P wave?
atria depolarise
What happens during the QRS complex?
ventricles depolarise
What happens at the T wave?
ventricles repolarise
Where does the atria repolarise?
this occurs during the QRS complex and so is hidden/masked on the ECG
What are the 2 circuits?
-pulmonary circuit
-systemic circuit
Pulmonary circuit?
anything that goes to the lungs
-carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation and then returns oxygenated blood back to the heart
Systemic circuit?
anything that goes w]anywhere else (not the lungs)
-carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart
Distribution of blood at rest?
some organs (kidney, liver, gastrointestinal) receive blood in excess of their metabolic needs
What organ can least tolerate disrupted blood supply?
brain
-irreparable damage can happen if blood supply is disrupted >4 mins
Pressure exerted by blood?
-how much it’s pushing against the walls
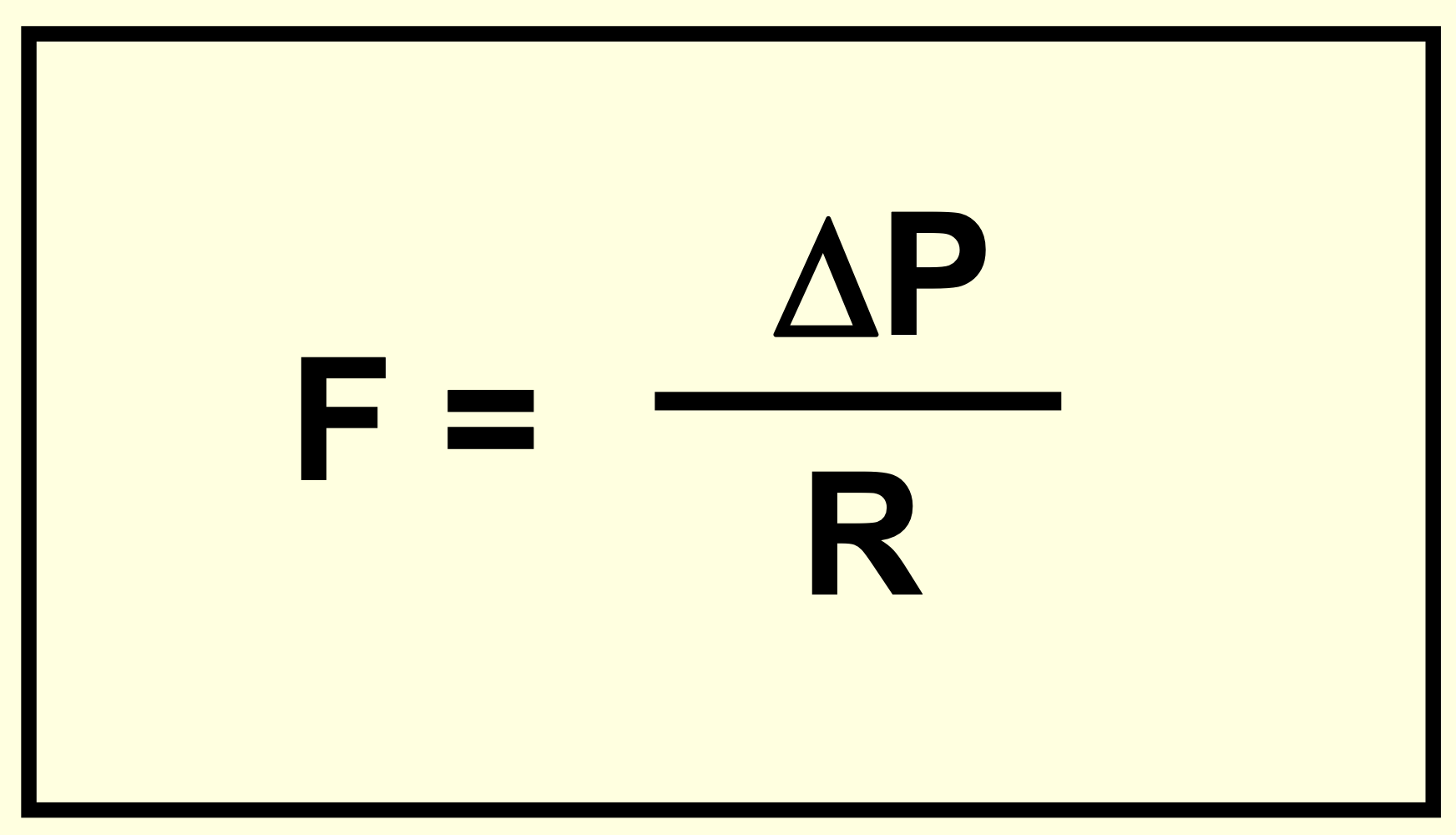
Blood pressure equation (flow)?
F => flow
ΔP => pressure gradient
R => resistance
Blood pressure equation (arterial pressure)?
F => cardiac output
ΔP => mean arterial pressure (map)
R => total peripheral resistance
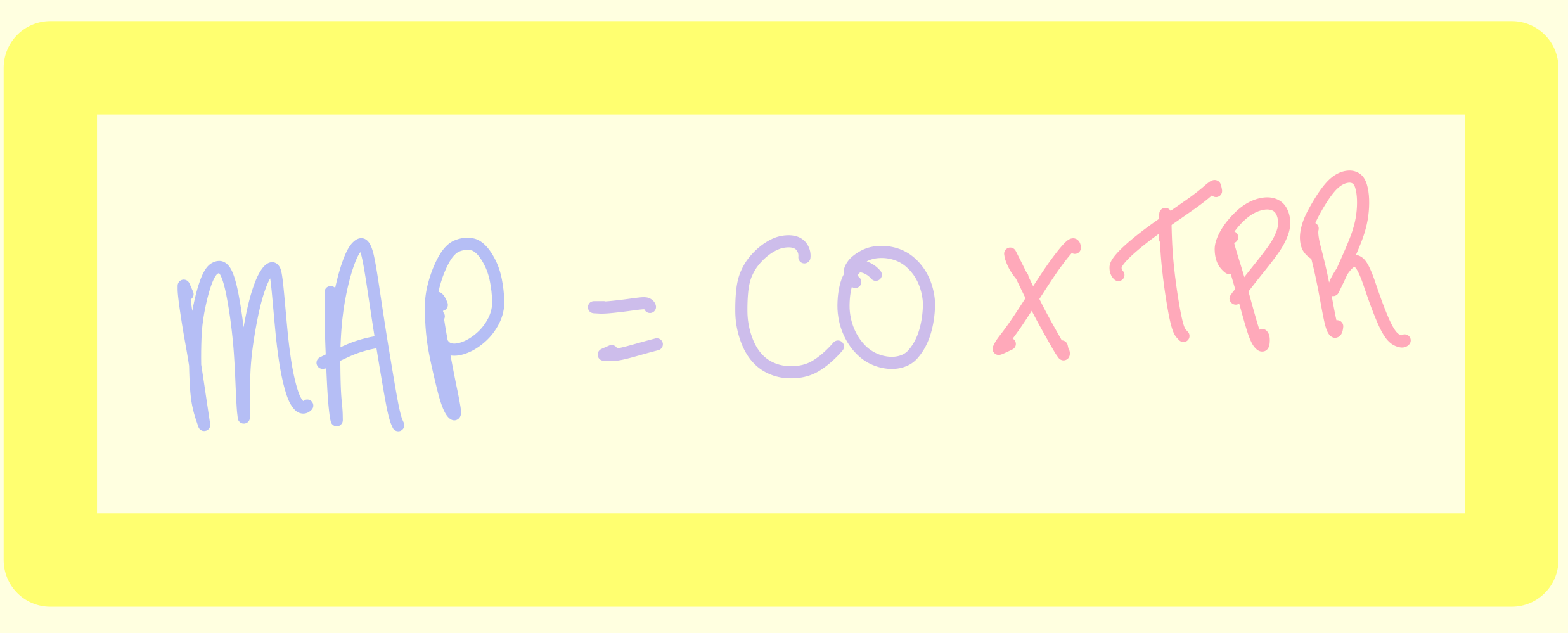
Pressure gradient?
the difference in pressure between the beginning and en dof vessel
What gradient does blood flow follow?
blood flows from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure
What happens when the heart contracts?
it exerts pressure on the blood, which is main driving force for flow through a veesel
What does resistance do to blood pressure?
due to resistance in the vessel, the pressure drops as blood flows