Schizophrenia- Neurological Disorders
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
what is the most severe neuropsychiatric illness
schizophrenia
how many people have schizophrenia world wide
20+ million
how many people in the US have schizophrenia
2.2 million
does schizophrenia have a sex difference?
no
how many hospital beds are occupied by schizophrenia patients
1/3
when do symptoms start with schizophrenia patients
18-25 years
what are positive symptoms
hallucinations, delusions, and paranoia
what are negative symptoms
loss of motivation, apathy, asocial behavior, loss of affect and speech
what are cognitive symptoms
impaired working memory, reduced attention span, disorganized thoughts, speech, and movement, impaired executive function
what is an example of disorganized movement
catatonia and child like behavior
what does catatonia look like
immobile and unresponsive
do you need all symptoms to be diagnosed?
no
what are negative symptoms misdiagnosed as
depression
what usually causes someone to be diagnosed with schizophrenia
a psychotic break
what is a the prodromal phase
withdrawn
what are symptoms in teenagers (early symptoms)
withdrawing from friends/family, not doing well in school, trouble sleeping, feeling irritable/depressed, lacking motivation
what are NOT symptoms in teenagers
NOT hallucinations, delusions, disorganization
before medication how were schizophrenia patients treated?
sedations and physical restraint
what type of symptoms do anti-psychotic drugs treat
positive symtoms
how was chlorpromazine created
double blind study created to test efficacy, too much can cause movement problems, created to be a sedative anti-histamine, eliminated post surgical shock
when did doctors used to know if the patient had enough chlorpromazine
when it caused PD symptoms
what is the heritability coefficient for schizophrenia
0.79
what are moderate risk factors
winter birth (higher risk for viral infection), maternal malnutrition, perinatal injury, solar flares at birth, growing up in urban area, minority groups
is there physical changes in the brain with people with schizophrenia
larger ventricles due to brain atrophy and disorganization of pyramidal cells in hippocampus
what areas of the brain have functional differences
amygdala, hippocampus, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, and ventrolateral prefrontal cortex
is there one specific gene for schizophrenia
no, there are many different gene
what does chlorpromazine do
D2 receptor antagonist
what is increased release of dopamine linked to
psychotic behavior
when is dopamine the highest is schizophrenia patients
during the psychotic episode
what type of symptoms does dopamine release address?
positive symptoms only
when people are given chlorpromazine during surgery what happens
they are consciousness but disinterested
what happens to NMDA receptors in schizophrenia
hypofunction (insufficient)
what blocks NMDA receptors
PCP and ketamine
what does PCP and ketamine cause
both positive and negative symptoms
what does glutamate do to dopamine
controls dopamine activity
what does GABA have to do in schizophrenia
an enzyme involved with the synthesis of GABA is decreased in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
what does an EEG measure
electrical activity
what do gamma waves do in the brain
bind info and working memory, allow words and mouth movement to sync
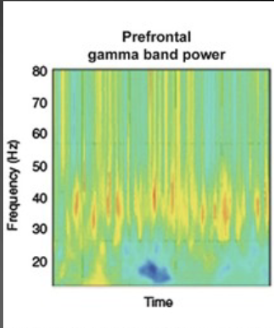
normal gamma waves
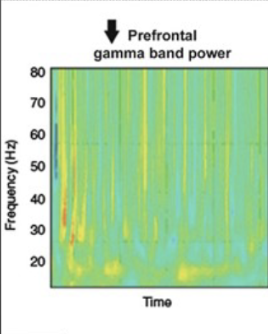
schizophrenia
why do auditory hallucinations occur
internal voice seems like an external sound, info binding issue
what happens to dendrites with schizophrenia patients
smaller pyramidal cell bodies and dendrites with fewer spines
what happens to dendrites in adolescent schizophrenia patients
over pruning, causing symptoms to start
what happens to oligodendrocytes
less of them, could be due to fewer axons?
what happens to white matter volume in people with schizophrenia
reduced white matter volume, brain regions are less connected
are these physical symptoms a cause or effect of schizophrenia
we don’t know, we can only study postmortem brains
what do typical antipsychotic drugs look like
D2 receptor antagonist, 70% effective at treating psychosis, side effects, poor compliance
what do side effects of typical antipsychotic drugs look like
weight gain, slowed movement, loss of sex drive
what do atypical antipsychotic drugs look like
D2 plus some other neurotransmitter
do atypical antipsychotic drugs actually have fewer side effects
no, they just marketed them that way, however improved movement
are typical or atypical antipsychotic drugs more common
atypical
do antipsychotic drugs work on overall schizophrenia symptoms
favored antipsychotic drugs by 0.5% (12 year old to 14 year old difference)
do antipsychotic drugs work on positive symptoms
worse than overall symptom management
what does compliance look like in antipsychotic medication
high possibility of relapse, 80% non-compliance
does increasing glutamate help manage symptoms
excitotoxicity with too much but works
does increasing glycine help treat schizophrenia symptoms
no, astrocytes are too good at regulation
why would glycine help improve schizophrenia symptoms
agonist for NMDA receptor (maximum response)
does nicotine help schizophrenia symptoms
90% of schizophrenia patients self medicate with nicotine
what does ECT do
induces a seizure, like restarting a computer
does ECT work as a schizophrenia treatment
yes, especially for catatonic patients
what are side effects of ECT
progressive memory loss the more times you do it (24 hour to 48 to 96)
why is ECT used in depression treatment
instant results that wear off over time, but in time for depression medication to start working
what does trancranial magnetic stimulation do for schizophrenia patients
restores gamma osciliations and increases dopamine activity
does trancranial magnetic stimulation actually work for schizophrenia treatment
meta analysis showed 0% improvement, another one showed improved negative symptoms but results can be biased
do dietary changes help schizophrenia patients
nope
why is it hard to tell if treatment works in schizophrenia patients
subjective assessments and patient self reports
does dopamine activity increase or decrease
increase
does glutamate activate increase or decrease
decrease
what GABA activity increase or decrease
decrease