Test 1
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapters 1-10 if you're in my class and using this... you're so welcome
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
three main approaches of studying anatomy
regional (trunk; thorax, abdomen, back, plevis) and surface anatomy ( anatomy beneath the skin)
system anatomy (mbodys organ system working together to carrie out complex functions)
clinical ‘applied’ (focused on body structures and function important to the practice of medicne)
anatomicomedial terminology
terms provide info on structure,shape,size,location and function
anatomical position
body standing upright, eyes/head facing forward, arms by side and palms facing anteriorly, feet parallel
median plane
divides body into left and right halves
sagittal plane
parallel to median plane, left and right sections
frontal plane
divides body into anterior and posterior
transverse plane
divides body into superior and inferior parts
longitudinal sections
parallel to long partaxis of body. median and (sagittal) and frontal planes. 180 degree range of possible sections
transverse sections
cross sections, horizontally
oblique sections
non right cuts
palmur vs dorsal
palmar is palm of hand and dorsal is top of hand
plantar vs dorsal
plantar issole of foot and dorsal (dorsum) top of foot
superficial vs deep
superficial is closer to the skins surface, deep is farther away from skins surface
inferomedial
closer to feet and median plane
superolateral
closer to head and further from median plane
external vs internal
outside or further vs closer to center
bilateral
left and right members. ex kidneys
unilateral
only on one side. ex spine
contralateral
occuring on oppisite side
ipsilateral
occuring on same side as another part. ex acl tear?
flexion vs extension
decreasing angle between bones vs increasing angle
abdcution vs adduction
away from median vs ADDing to median
medial rotation vs lateral
anterior surface towards midline vs anterior surface away from median plane
opposition vs reposistion
thumb (1st diget) to another diget vs reposition of thumb back to orginal position
supination vs pronation
sup radius brings arm up (back to anterior position) vs pro turns radius down
protraction vs retraction
scapula on thoraic wall moves anteriorly vs retraction moves scapula prosteriorly
elevation vs depression
raises part superiorly vs lowers part inferiorly
dorsiflexion vs plantarflexion
flex at ankle lift foot up to sky vs bending feet towards ground
curcumduction
abd,add,flexion,extenstion,flexion
rotation
turning around longitudal axis
lateral bending
side to side
protrusion vs retrusion
movement anteriorly vs movment prosteriorly
joints are… and 3 types of movment
unions or junctions between 2 or more bones or rigid parts of skeleton: no movement, slight movement, freely movable
fibrous joints
united by fibrous tissue, movment depends on length of fibers (syndesmosis type- unites boin with sheet of fibrous tissues)
cartilaginous joints
united by hyline cartilage/fibrocartilage
two types of cartilaginous joints
primary (sychondroses) secondary(sympyses)
-light bend in early life -stong and provides
-growth in length of bone shock absorption and ex. head of femur flexability ex. vertebra
synovial joint
unitad by joint capsile made of fiberous layer, lined by serous synovial membrane, articular cartilage covers ends of bones
6 types of synovial joints
plane,hinge,saddle,conyloid,ball and socket,pivot,
plane
sliding and gliding, opposed bone surfaces are flat, limited movement from tight joint capsules
hinge
flexion/extension, uniaxial joint, bones joined by strong laterally collateral ligaments
saddle joint
abduction/adduction flexion/extension, biacial joint movment in two planes, some circumduction
condyloid
abd/adduction,flexion/extention, biaxial joint in one plane, not much circumduction.
ball and socket
movment in mulitiple axis, flex/extension,abd/adduction, medial/lateral rotation, circumduction, Highly moveable joint
pivot
rotation around central axis (uniaxial), rounded process of bone rotates within a sleveve or ring. ex. radio-unlar joint
axial skeleton
bones of head,neck, and trunk
long bones
humerus,femur
short bones
found in ankle (tarsus) and Carpus (wrist)
flat bones
cranium,scapula, for protection and increse muscle attachment
Irregular bones
bones of face
sesamoid bones
protect tendons from lots of wear and tear. ex. patella, medial sesamoid of foot
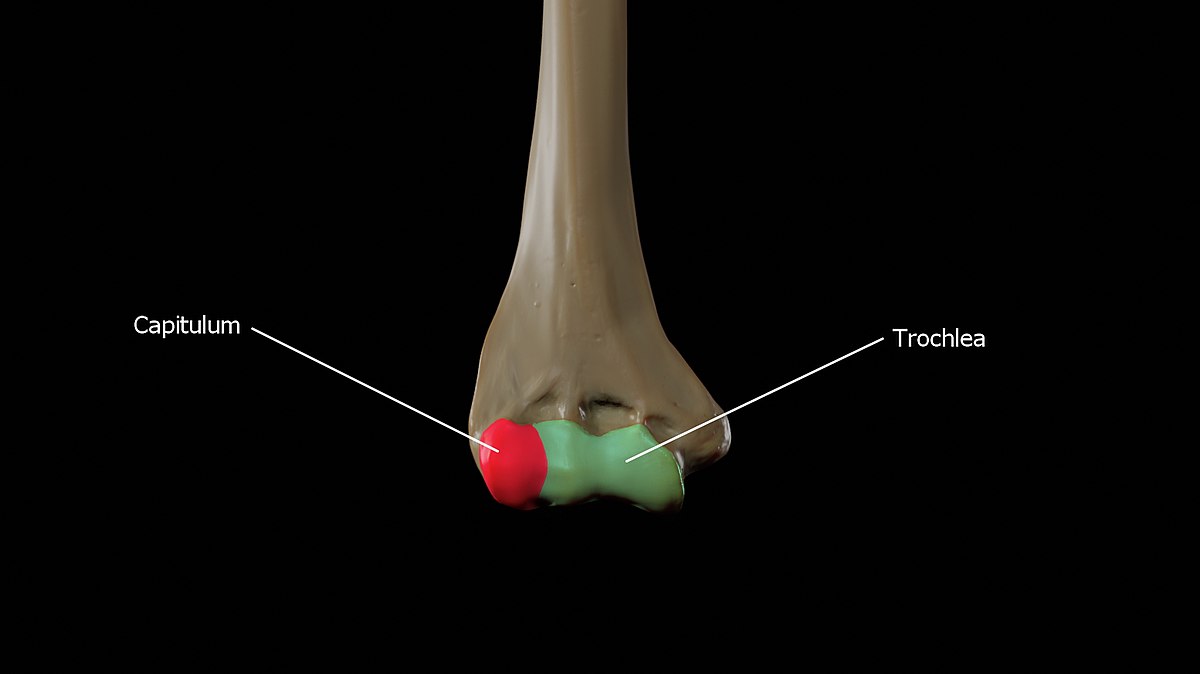
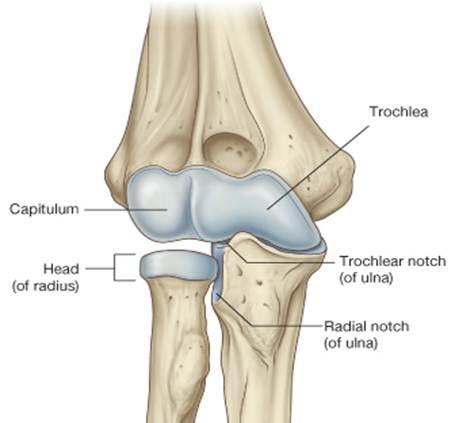
capitulum
small, round, articular head (lateral bottom part of humerus)
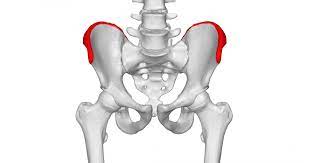
crest
top ridge of part of pelvis bone, Lliac cest. purpose is for muscle attachment
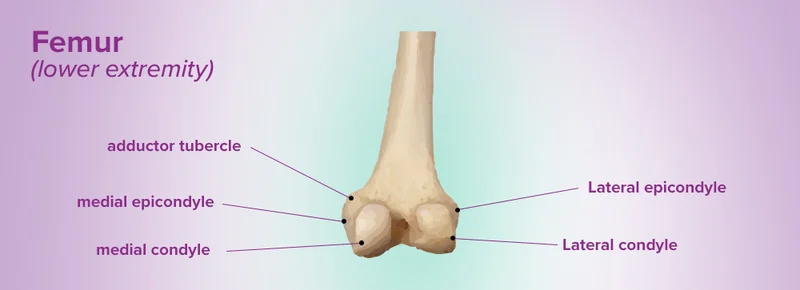
condyle
in pairs medial and lateral femoral condyle
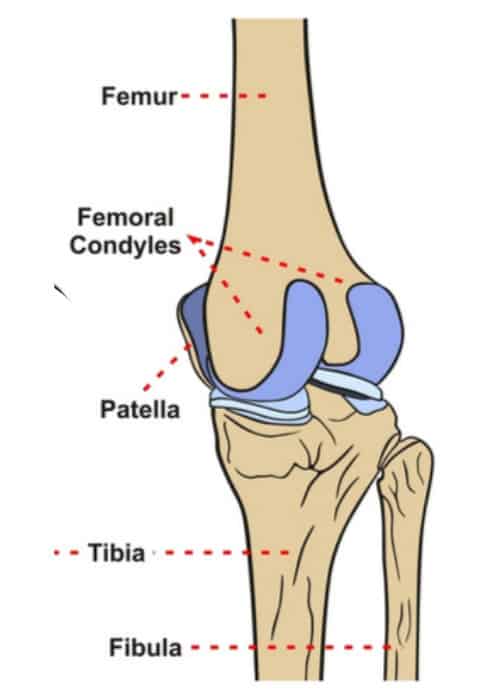
epicondyle
superior to condyle, small lateral stuck out part. point of attachment for ligaments to attach
facet
smooth flat area, bone articulates with another bone, covered in cartlige
foramen
passage through a bone, nerves arteries pass though. (lower pelvis) obturator
fossa
hollow or depressed area. allows muscle attachment. ex. infraspinous fossa
groove
long depressed area for tendons to pass through. ex. bicipital groove
head
large round articular head. ex head of femur
line
slightly elevated. ex. soleal line of tibia
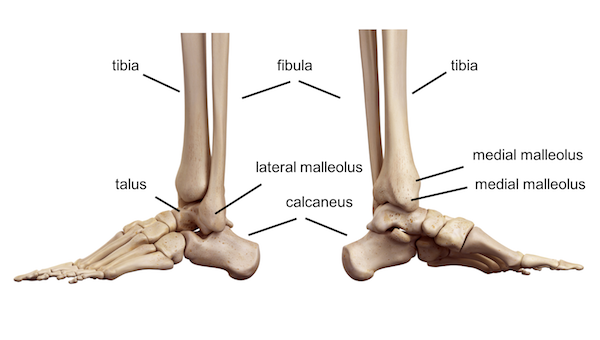
malleolus
rounded process. ex lateral malleolus fibula
notch
indentation at edge of bone. ex greater sciatic notch
protuberance
projection of bone. ex. external occipital protuberance
spine
thorn like process. ex spine of scapula
spinous process
projecting spine like part, ligament and muscle attachment, protects nerves, ex. spinous process of vertebra
trochanter
larger blunt elevation of bone, ex. greater trochanter of femur
trochlea
articular process or process that acts like a pulley, hinge joint/flex & extend, ex. trochlea of humerus
tubercle
greater and lesser tuercle of humerus
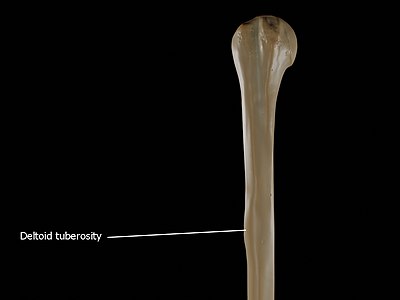
tuberosity
larger rounded elevation, ex. deltoid tuberosity
movements of scapula
retractin, protraction, elevation, depression, dowanward and upward rotation
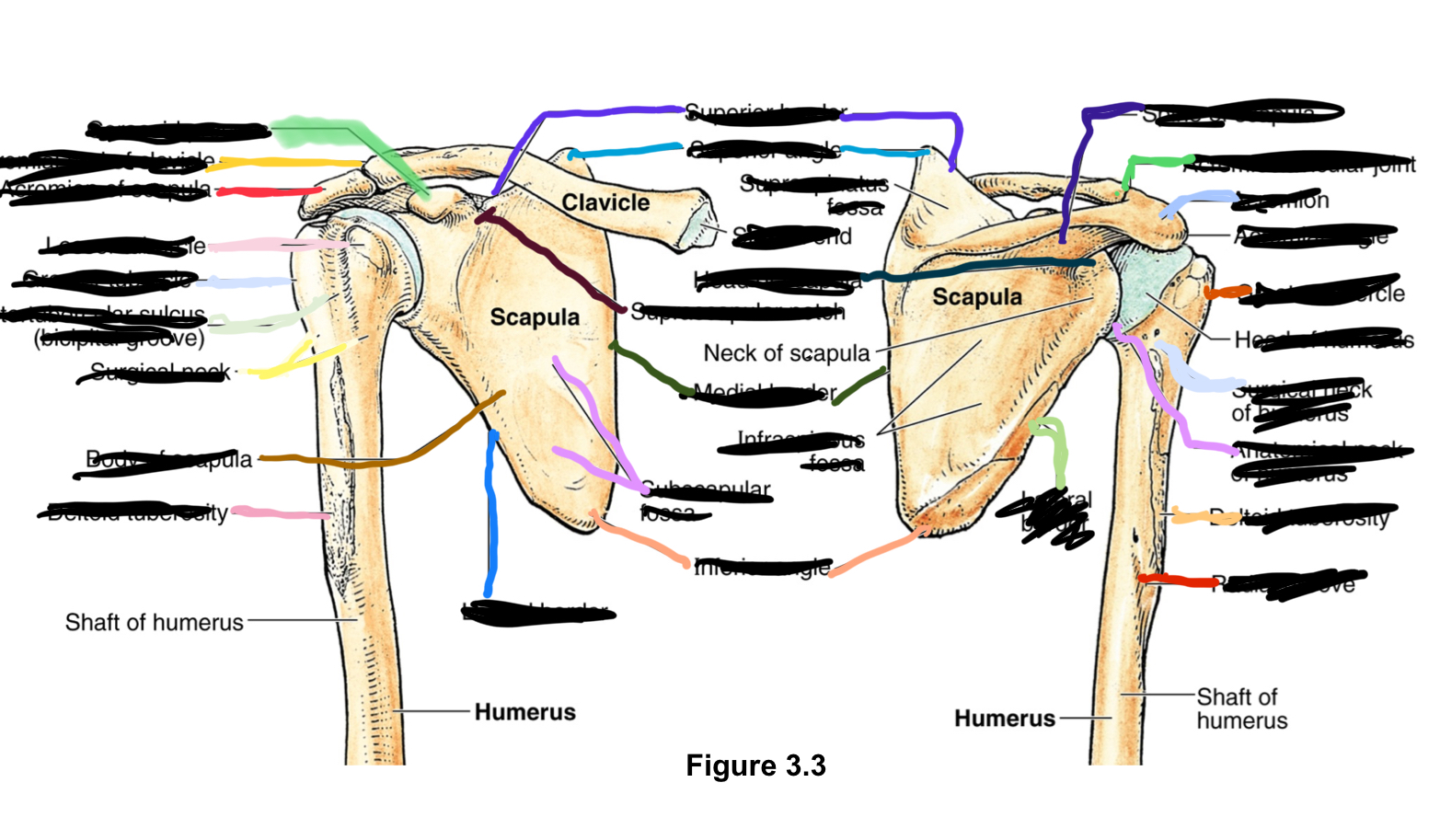
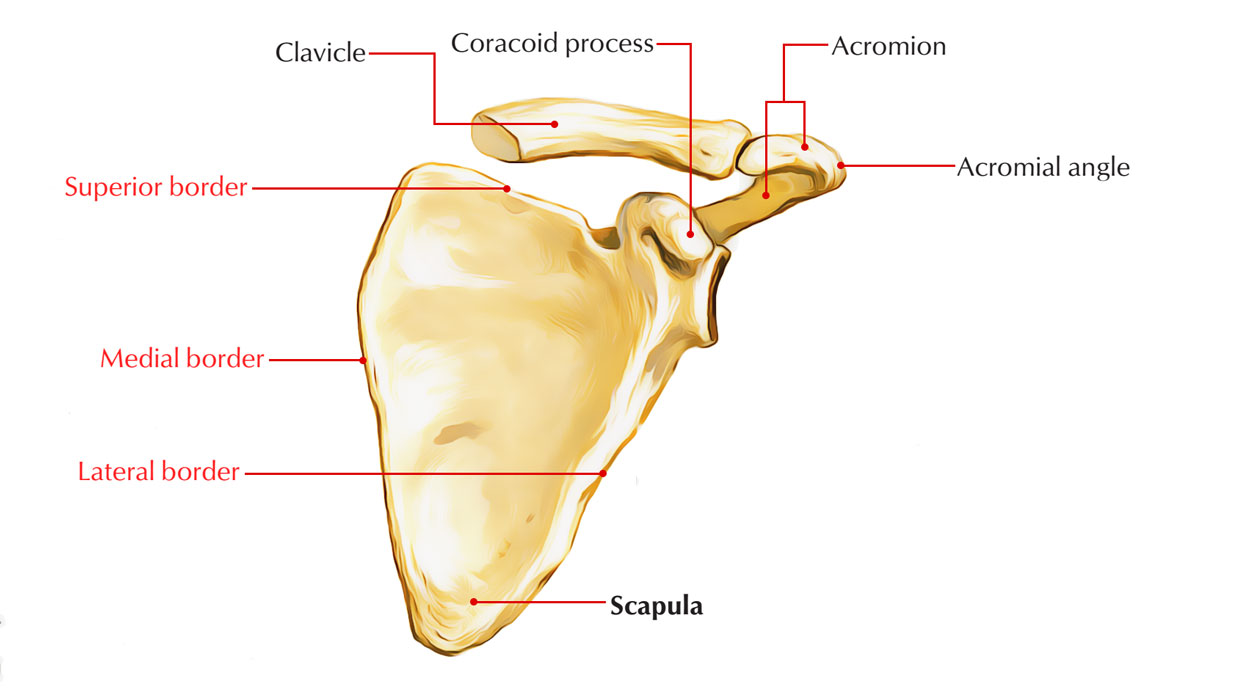
coracoid process?
bent finger lookin, provides inferior attachment
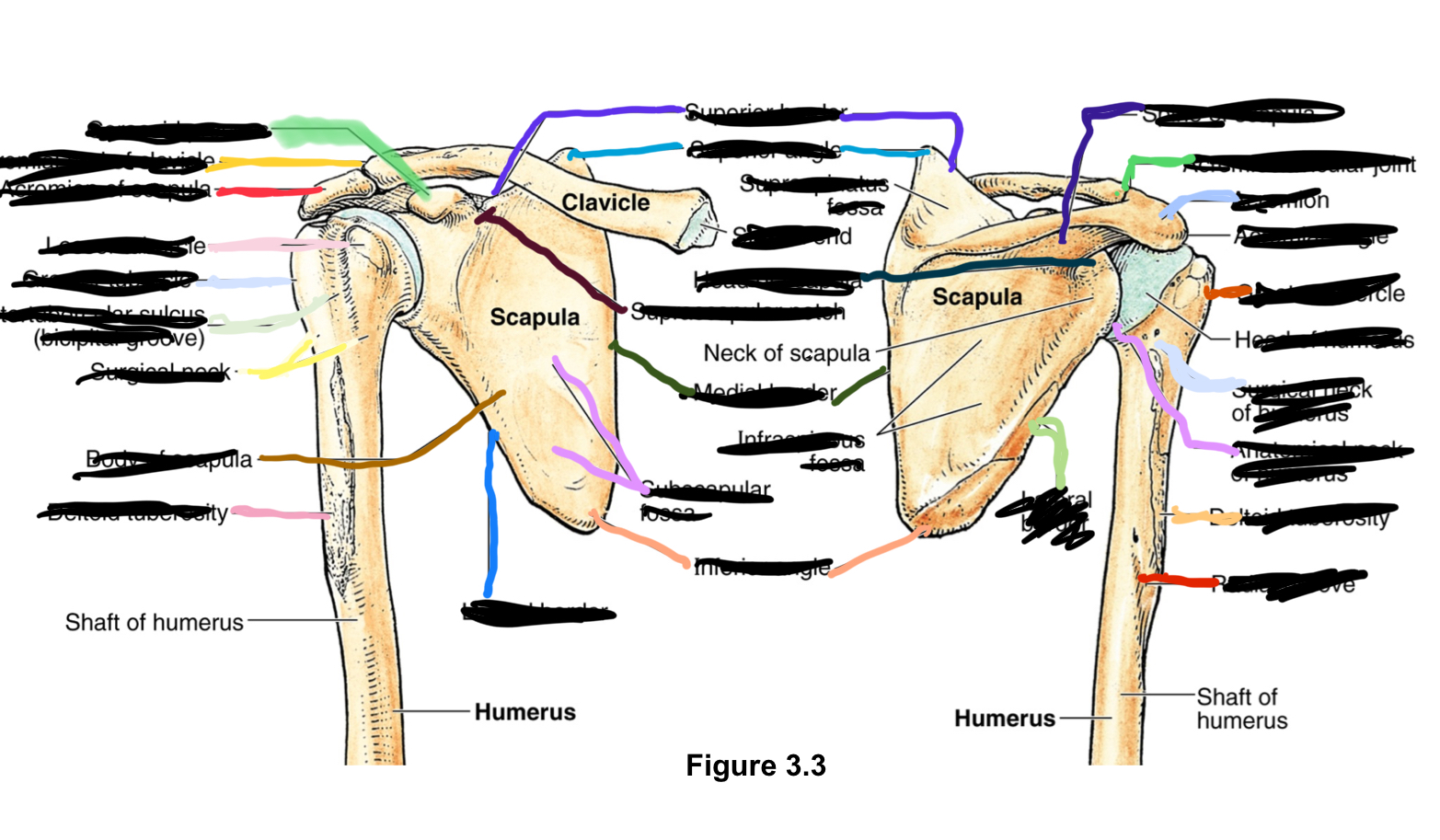
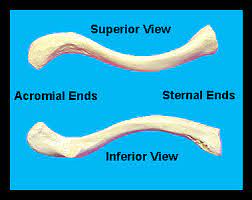
acrominal end of clavicle?
acromioclavicular joint sits vetween this and acromion end of scapula
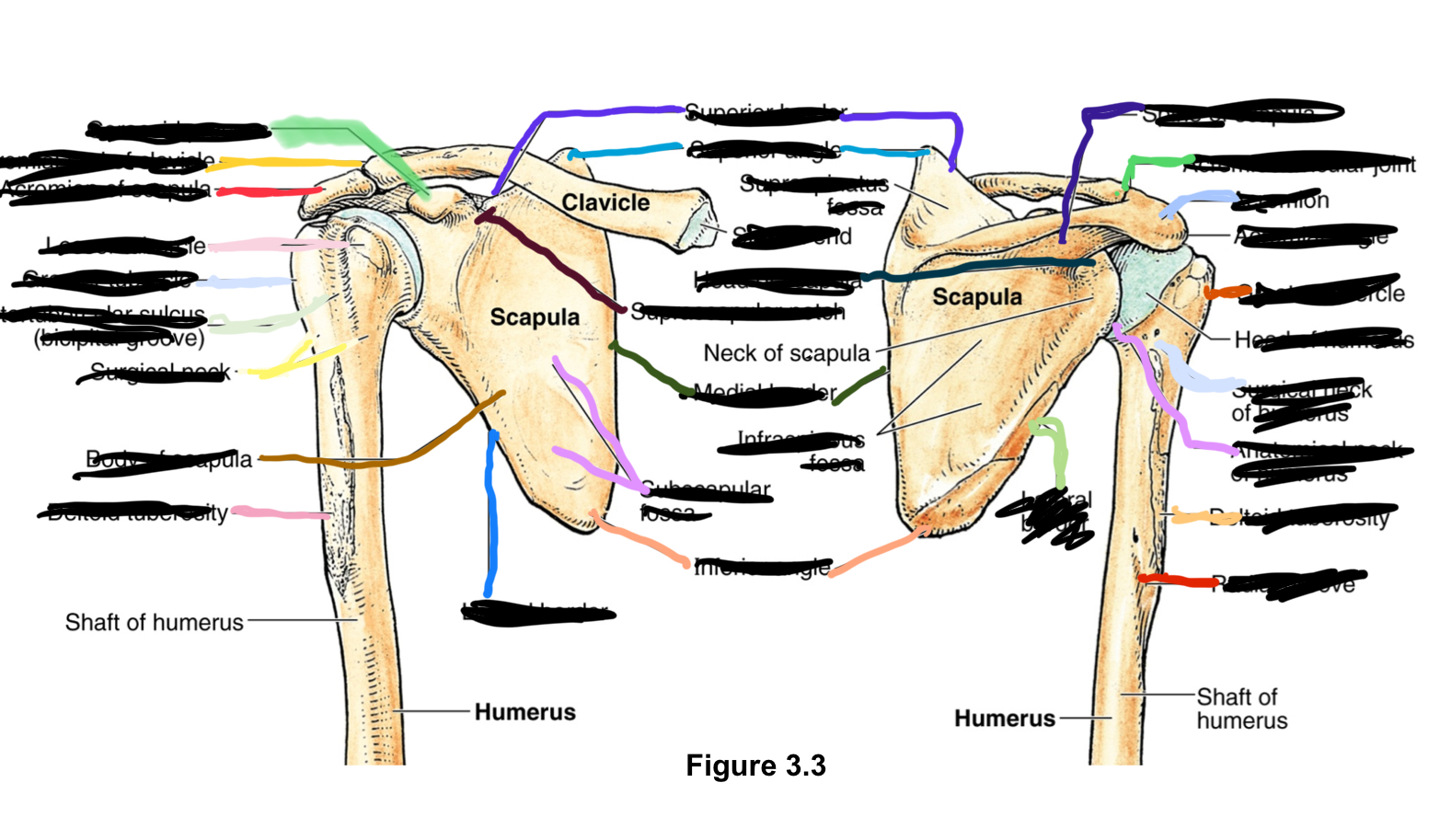
acromion of scapula?
lateral end of scapula
lesser and greater tubercle?
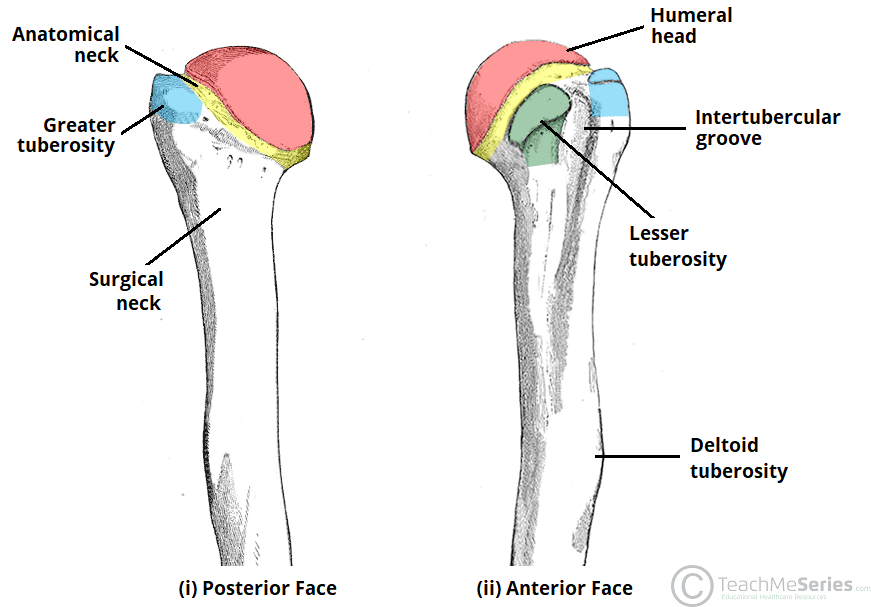
intertubercular groove (bicipital groove)?
surgical neck?
deltoid tuberosity?
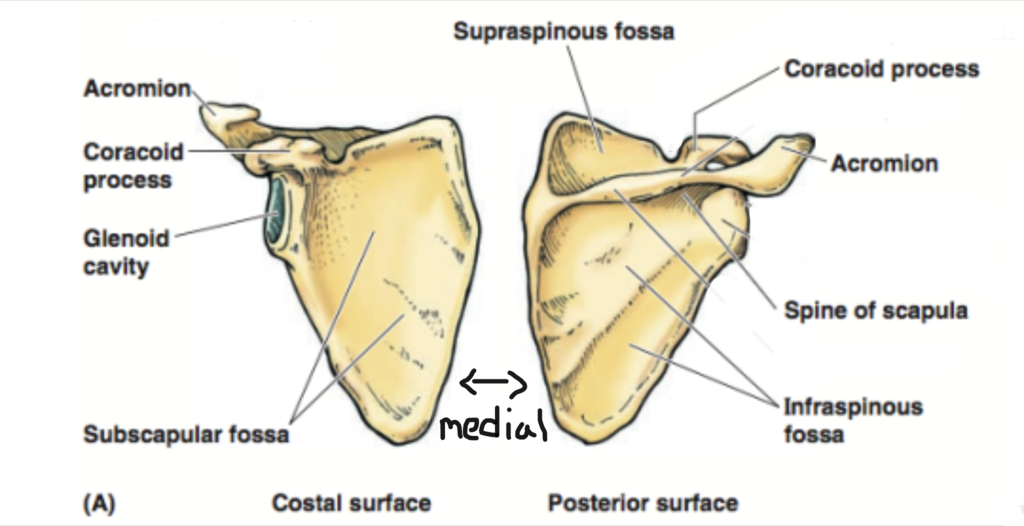
superior border?
superior angle?
supraspinatus fossa?
superior to spine
sternal end?
sternoclavicular joint superior and attaches sternal end of clavicle and sternum
supraspcapular notch?
nerves go in through here
medial border?
side of scapula closest to midline
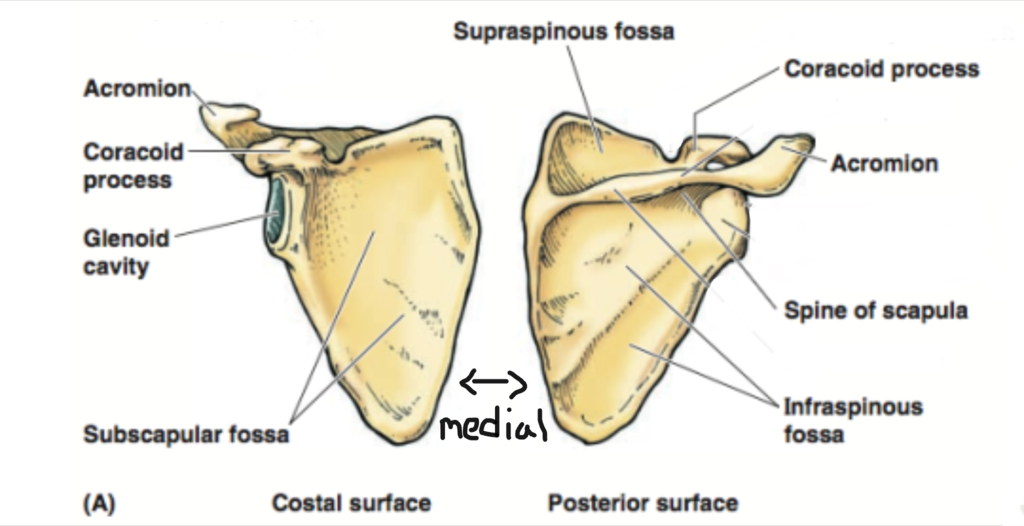
inferior angle?
lowest angle
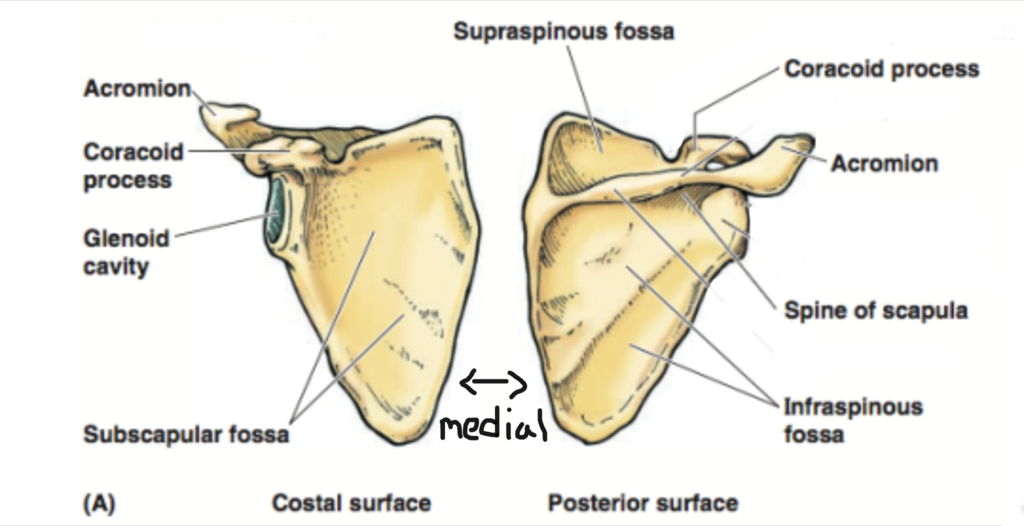
lateral border?
away from midline
spine of scapula?
acromion?
lateral extension of scapula
sternoclavicular joint (sc)
very strong, articulates with sternal end of clavicle and sternum. acts as a shock absorber/ full elevation of limb (clavicle 60 degrees)
acromioclavicular joint (ac)
articulates with clavicle aromaial end and acromion of scapula, plane synovial joint,
articular disc of sc joint
inferior part of clavicle
coracoclavicular
inferoir part of clavicle, strong, united concoid process of sacpula to the clavicle
glenohumeral joint
ball and socket, unstable but moves alot, outside lining is glenoid labrum
transverse humeral ligament
bridging lesser and greater tubercle, over laying the bicep tendon
costoclavicular
oval area for attachment to the first joint
coracoacromial
aromion end of sacpula to coracoid process
coracohumeral
coracoid process to greater and lesser tubercle
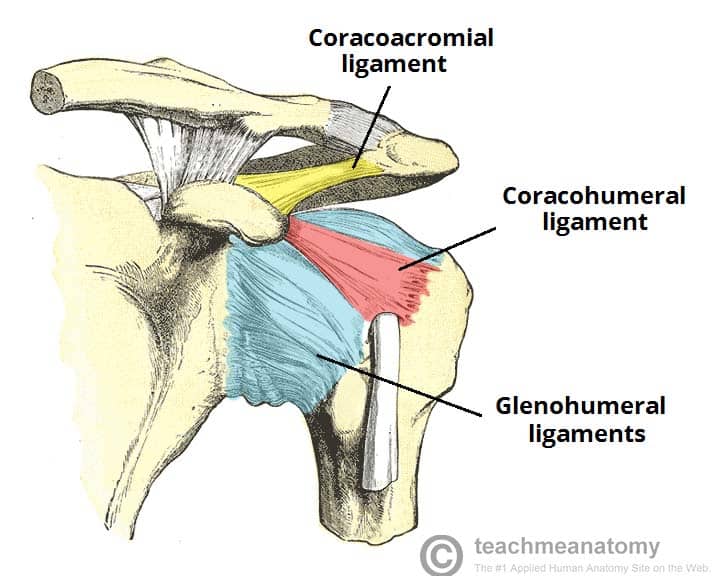
capsular
connects humerus to the glenoid, sac that surrounds a joint