A&P unit 4 flashcards
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is epithelial tissue?
Filteraton
Absoprtion
Protection
Secretion
A type of tissue that lines/forms a divider between our body and our environment
What three structures to all epithelial tissues share?
free surface
basal layer
basement membrane
→ All of these tissues are avascular
How do simple and stratified epithelial tissues differ?
Simple has one layer of cells, while stratified has multiple
What are the 3 types of simple epithelial tissue?
simple squamous
simple cuboidal
simple columnar
What are the characteristics of simple squamous tissue?
single, flat layer of cells that is thin and permeable.
location: blood vessels and lung tissues
function: rapid diffusion of materials
“simple squamous spreads (diffuses)”.
What are the characteristics of simple cuboidal tissue?
A single layer of cube-shaped cells
function: secretion and absorption
location: kidney tissues
“A Rubik’s cube absorbs your thoughts.”
What are the characteristics of simple columnar tissue?
single layer of tall, closely packed cells
^ may have cilia or goblet cells (secretes mucus)
function: secretion of mucus for protection & absorption of substances
location: lining of digestive tract
“when you cough (columnar) mucus comes up”.
What are the three types of stratified epithelial tissue?
stratified squamous
stratified cuboidal
stratified columnar
Describe stratified squamous tissue:
Thick layers protect the underlying layers
location: epidermal layers of the skin
Describe stratified cuboidal tissue:
more than one layer of cuboidal cells
very rare in body
location: salivary and mammary glands
Describe stratified columnar tissue:
free surface is lined with columnar cells
rare in the body
location: larynx and male urethra
what is pseudo-stratified epithelium?
Cell nuclei are found at different levels, so it appears stratified, but it is not.
Function: secretion and absorption
Location: upper respiratory tract
What is transitional epithelium?
the free surface cells vary in appearance based on the stretching of the tissue
location: found in the urinary bladder lining
What is the glandular epithelium?
a group of cells that secrete a fluid substance
^ classified in two ways:
1. complexity
2. exocrine/endocrine
exocrine gland:
secretes substances outward through a duct (ex: sweat glands)
endocrine gland:
ductless glands that secrete hormones through the bloodstream (ex: thyroid gland), they are packed tightly together with capillaries running through glandular tissue
→ cells use exocytosis
What are the types of exocrine glands?
Holocrine: cell rupture and spills products into a duct
Apocrine: a portion of the cell pinches off with the secreted products
Merocrine: cells excrete the products
What are the types of connective tissues?
connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and blood.
What are the functions/characteristics of connective tissues?
provide support and bind other tissues together
provide insulation and protection for other tissue
Some can transport substances
All are formed from one stem cell
vary in their degree of vascularity
All are mostly composed of extracellular matrix
What are the 3 types of loose connective tissue?
Reticular: contains reticular fibers, which create a stiff framework to support other cells
Areolar: mostly open space, holds water and salts, found in the epithelium under other organs
Adipose: composed of fat cells, large vacuoles that contain fat/oil, insulates and warms the body, and provides nutrients to other cells
What are the 3 types of dense connective tissue (DERMIS):
Regular: collagen fibers arranged in one direction, providing tensile strength like a rope found in tendons and ligaments.
Irregular: collagen fibers are arranged in many directions, providing strength in those directions, found in capsules around organs
Elastic: provides flexible cushioning, found between vertebrae and arteries
What are the 3 types of cartilage?
Hyaline: glassy looking, firm ground substance with lacuna, few collagen fibers, found in the larynx, bridge of nose, and ribs
Fibrocartilage: contains lots of collagen, mostly running parallel, found in intervertebral spaces
Elastic: highly flexible, more elastic fibers, found in outer ear and tip of nose
What are the characteristics of bone tissue?
Osteocytes: secrete ground substances, fibers, collagen, and fluids.
The ground substance eventually becomes calcified and hard
2 types are spongy and compact
What are the types of vascular tissue?
mast cells: detects foreign substances, contains granules that secrete inflammatory chemicals
macrophages: blob-like cells that engulf invading substances or organisms
blood cells
What are the layers of the epidermis:
stratum corneum: layer of dead cells, 20-30 thick. keratinized cells protect the deeper layers (shed regularly)
stratum lucidum: a thin layer of translucent cells only found in the palms and soles
stratum granulosum: cells here begin to flatten and disintegrate
stratum spinosum: “spiny layer” named for the irregular shape of cells.
stratum basale: diving and pushing cells up into the next layer
How melanocytes protect the body?
Melanin protects the skin from harmful UV rays
When UV radiation mutates a cell’s DNA, it starts to divide uncontrollably.
What are the characteristics of the dermis?
contains: nerves, blood vessels, sweat glands, and hair follicles
papillary layer: loose connective tissue
reticular layer: made of bundles of collagen fibers → arrangement causes lines of cleavage/tension
Why are lines of cleavage important?
for surgeons
cuts should be made parallel to the lines of cleavage for quicker healing + less formation of scar tissue
What are the characteristics of the hypodermis?
subcutaneous layer
composed of loose, fatty, connective tissue
insulates and stores nutrients
What are the characteristics of the Sudoriferous glands?
sudoriferous: sweat glands
Eccrine sweat glands are long tubes that open into pores on the surface of the skin
Apocrine sweat glands contain all the original components of sweat
sebaceous: oil glands
holocrine glands
lubricates skin and hair + kills bacteria
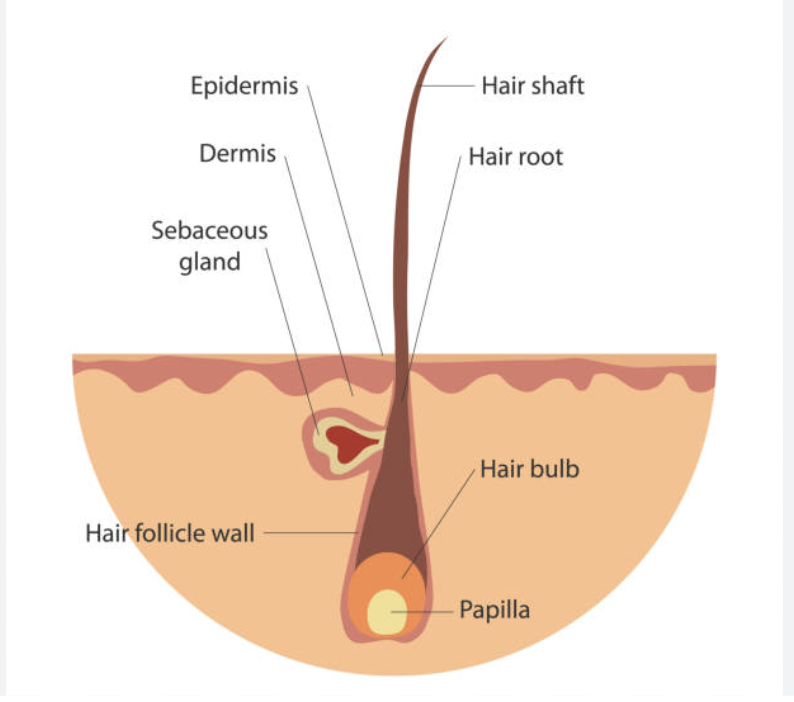
Hair follicle parts:
← know parts
the hair follicle is located in the dermis
cells divide within a region of the follicle called the hair bulb
^ these are filled with keratin and pigments
tiny arrector pili muscles attach to the hair shaft to make it stand
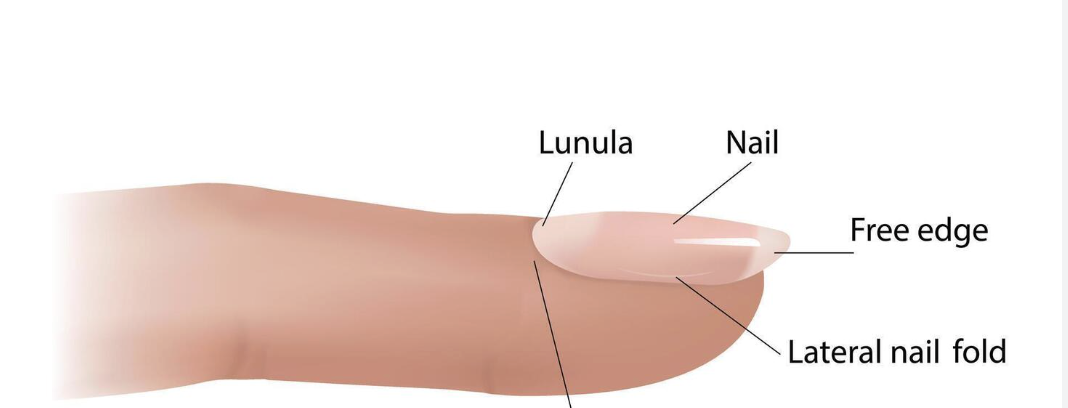
Nail parts:
Know + label ( proximal is underneath)
protective and a good tool
The nail matrix produces heavily keratinized cells
protected on 3 sides from folds
lunula: “little white moon”
cuticle: a seal for the nail matrix
Shallow cut vs. Deep cut
shallow: affects only the epidermis, results in these cells to divide more rapidly to fill the gap
deep: reaching dermis or subcutaneous layer, blood vessels break → forming a clot
identify burns from first degree → third degree
1st: injures only the epidermis; redness, heat, inflammation, heals in 2 days
2nd: destroys epidermis and some dermis; blister, stem cells help regenerate, usually recovering completely with no scarring
3rd: destroys epidermis and dermis + extra structures; minimal healing from margins, often requires a skin graft (replacement)
What is the rule of nines?
estimates the extent of the injured body surface
divides the body’s surface into 9% or multiples of 9
^ to estimate plans to replaces fluids, electrolytes, and skin can be figured.