61 Lesson 1: The Cash Flow Statement: Components and Format
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What are the three main categories of the Cash Flow Statement?
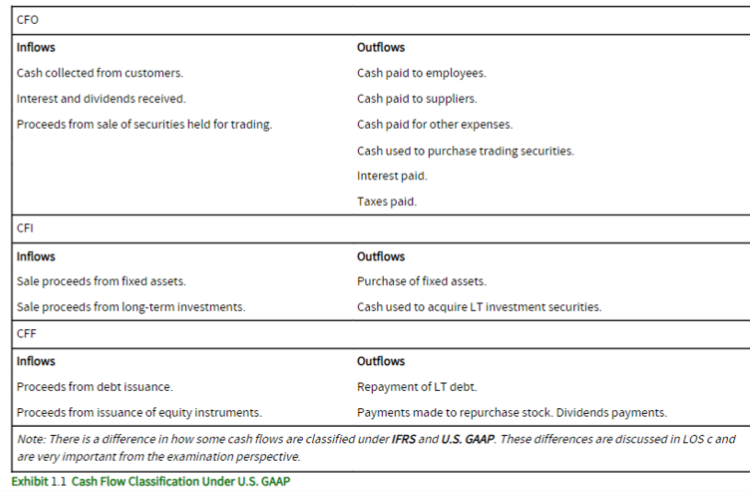
Cash Flow from Operating Activities (CFO)
Cash Flow from Investing Activities (CFI)
Cash Flow from Financing Activities (CFF)
What does Cash Flow from Operating Activities (CFO) represent?
CFO represents the inflows and outflows of cash related to daily business operations, representing the core operations of a company.
What does Cash Flow from Investing Activities (CFI) include and exclude?
CFI includes cash flows associated with long-term investments, such as purchases and disposals of plant, machinery, equipment, intangible assets, and nontrading debt and equity securities. It excludes highly liquid investments (cash equivalents) and securities held for trading.
What does Cash Flow from Financing Activities (CFF) encompass?
CFF includes cash inflows and outflows from the issuance and repayment of capital, including interest-bearing debt and equity. It reflects a company's financing and capital structure.
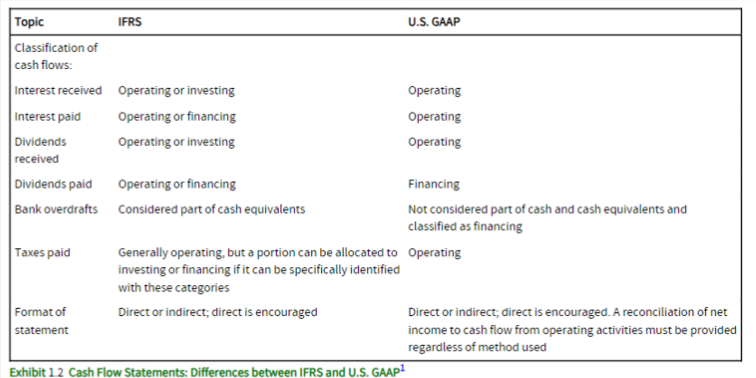
How does IFRS 16 impact the Cash Flow Statement?
Under IFRS 16, operating leases are treated similarly to finance leases. The interest component of lease payments can be reflected in either the operating or financing section, while the principal component of lease payments is included in the financing section. This impacts how lease-related cash flows are presented in the statement.
What items are excluded from investing activities and considered operating activities in the Cash Flow Statement?
Highly liquid cash equivalents and securities for trading purposes are excluded from investing activities.
Cash flows related to short-term borrowings from suppliers (classified as accounts payable) and changes in receivables from customers are considered operating activities.
Under both IFRS and U.S. GAAP, cash flows are classified into the following categories:
What are non-cash investing and financing activities in accounting?
Non-cash investing and financing activities are transactions that do not involve actual cash receipts or payments and are therefore not reported on the cash flow statement.
Can you provide examples of non-cash investing and financing activities?
Examples of non-cash investing and financing activities include barter transactions where nonmonetary assets are exchanged, the issuance of common stock for dividends, and the conversion of convertible bonds or convertible preferred stock into ordinary shares. It can also include the acquisition of real estate with financing provided by the seller.
How are significant non-cash investing and financing activities disclosed?
Companies are required to disclose significant non-cash investing and financing activities in a separate note or supplementary schedule alongside the cash flow statement.
What are the main differences of the Cash Flow Statement under IFRS and U.S. GAAP?
Classification of cash flows: Certain cash flows are classified differently under IFRS and U.S. GAAP. IFRS offers more flexibility regarding the classification of certain cash flows.
Presentation format: There is a difference in the presentation requirements for cash flow from operating activities.
What are the two formats for presenting the cash flow statement?
The two formats for presenting the cash flow statement are the direct method and the indirect method.
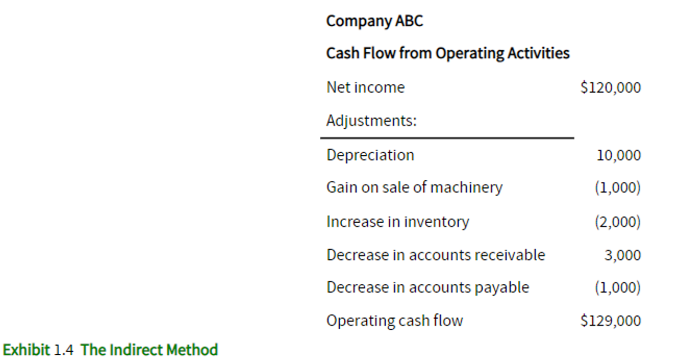
What is the key difference between the direct and indirect methods in the cash flow statement?
The key difference is in the presentation of the Cash Flow from Operating Activities (CFO) section. The direct method directly reports cash receipts and cash payments, while the indirect method calculates CFO by adjusting net income for specific items.
Do the direct and indirect methods result in different values for CFO?
No, both methods result in the same value for CFO. The choice of method affects the presentation but not the final CFO value.
Provide an example of the direct method

Provide an example of the indirect method
What is a benefit of the direct method for the cash flow statement?
The direct method provides a detailed breakdown of cash flows, making it useful for evaluating past performance and projecting future cash flows.
How does the indirect method help with forecasting future cash flows?
The indirect method simplifies forecasting by adjusting future net income for changes in balance sheet accounts due to accrual and cash accounting differences, facilitating more accurate projections.