8) issues surrounding acute illness
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
possible outcomes of acute disease
recovery
chronic illness
Disability
death
disease
a disorder of structure or function in a human, animal, or plant, especially one that produces specific signs or symptoms or that affects a specific location and is not simply a direct result of physical injury.
illness
an individuals perception of their symptoms and how they and their families respond to symptoms they are experiencing
disability
any impairment, activity limitations, or participation restrictions that result from the health condition or from personal, societal, or environmental factors in the individuals life
illness external factors
impairment
demographic - age, sex
built environment - accessibility, exposure
social environment - support
political environment - policies
illness personal factors
values, culture, beliefs
prior level of function, comorbidities, roles
Personality
education, health literacy, financial resources
coping can be
emotion, appraisal, or problem focused
resilience
internal and external factors
perceived control and roles
appraisal focused adaptive coping
reframing
Spiritually
meditating
painting, dancing, long walks
appraisal focused maladaptive coping
blaming others
harmful beliefs
fanaticism
excessive behavior
problem focused adaptive coping
information gathering
questioning
problem solviing
adherence
problem focused maladaptive coping
Intellectualization
avoidance
excessive behavior
Non-adherence
emotion focused adaptive coping
early denial
emoting
social support
Counseling
companionship
emotion focused maladaptive coping
continuous denial
drinking, drugs, self injury
Promiscuity
isolation
illness affects
the individual and the family
the illness-constellation model incorporates
physical symptoms
human response to those symptoms
illness experience
illness-constellation model stages
Uncertainty
Disruption
regain self
wellness
stage of uncertainty
- The individual detects or suspects signs of illness
- The individual attempts to make sense of the symptoms
- Family members may or may not be aware
stage of disruption
- acknowledgment of need for medical intervention
- relinquished control to others
- family begins to accept responsibility
striving to regain self
- examines the past for why the illness occurred
- attempts to make sense
- individual strives to preserve a sense of self
- focus on future - goal setting
- family may become protective
- role renegotiation
regaining wellness
- The individual takes charge
- attains mastery
- seeks closure
- revalues experience
- accepts consequences
- views life beyond one's self
- family monitors
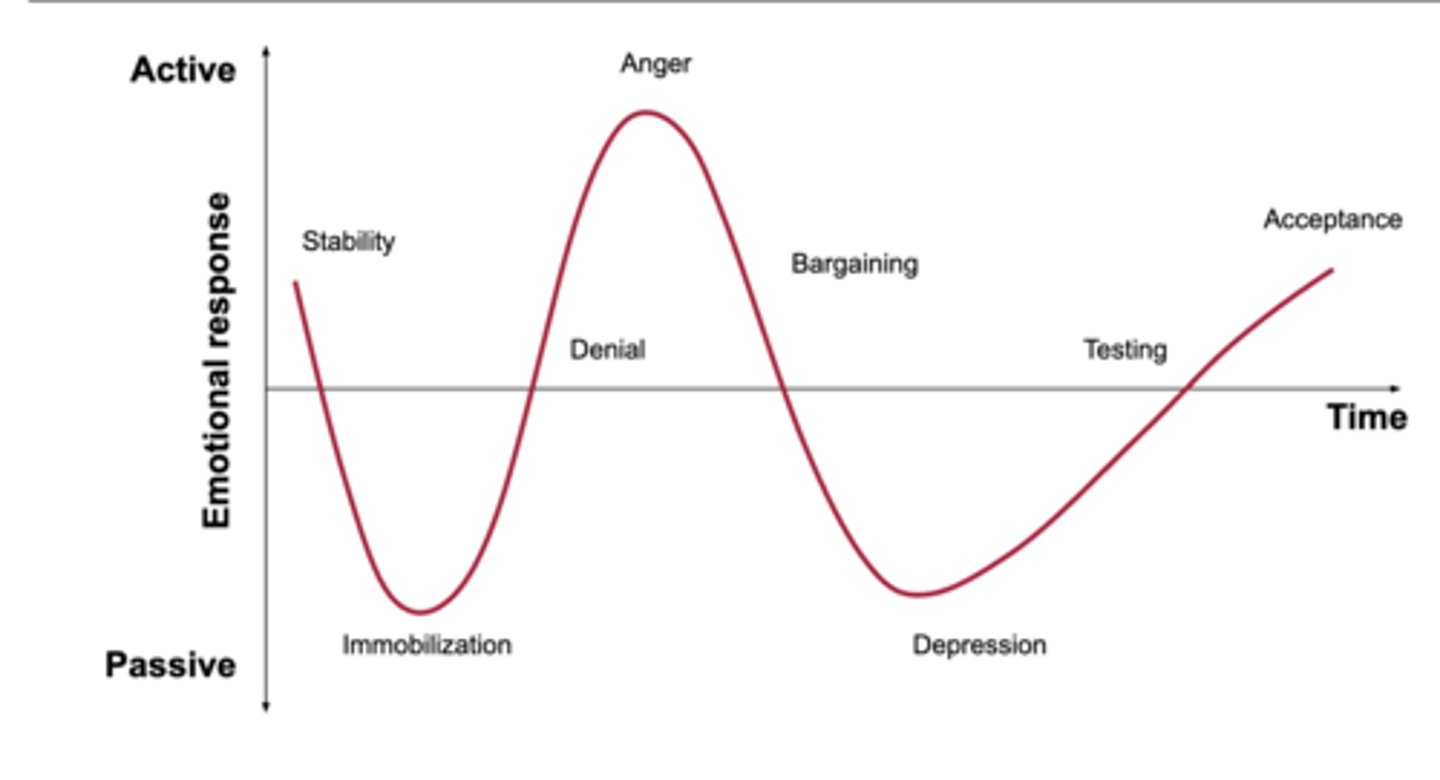
5 stages of grief
denial, anger, bargaining, depression, acceptance
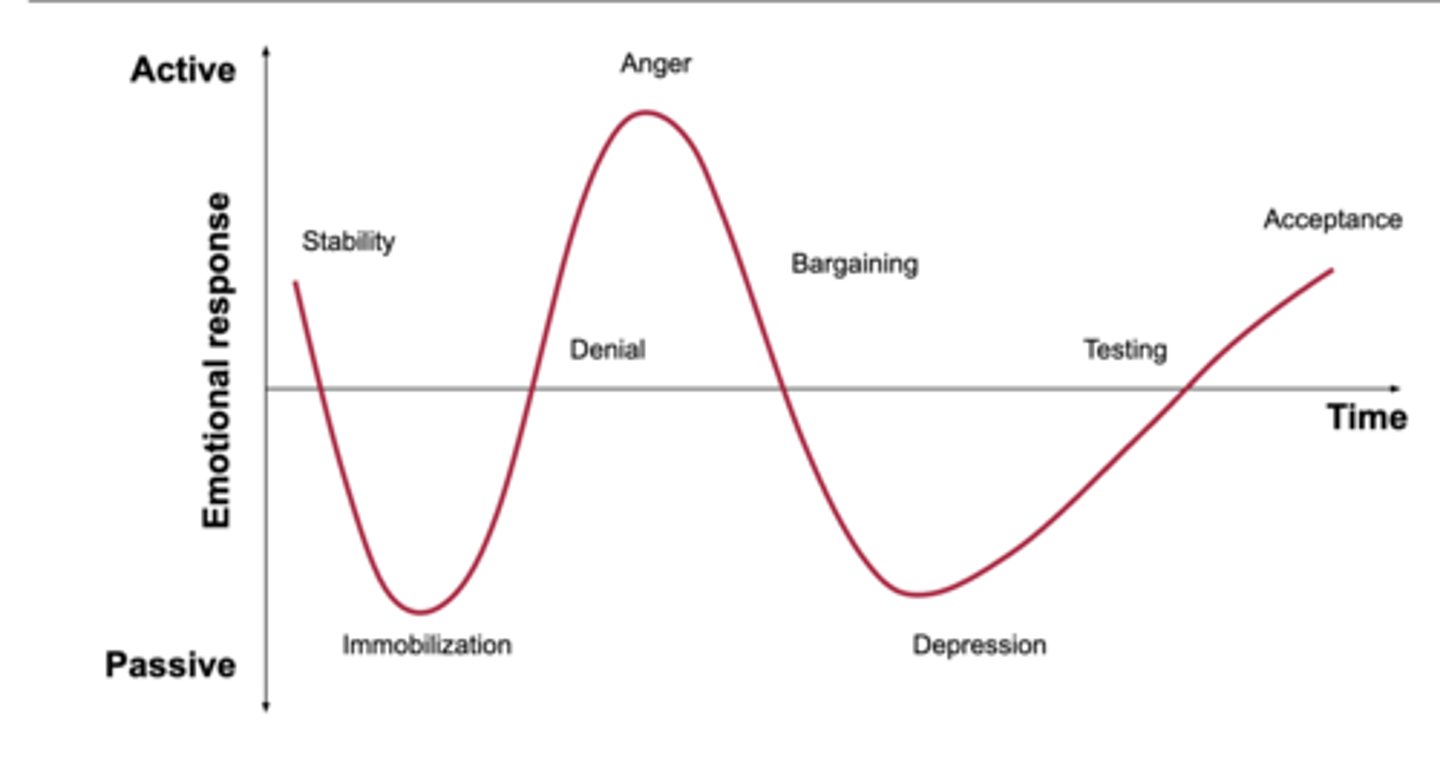
denial
protective response
believe the diagnosis is a mistake
avoidance
refusal of the truth
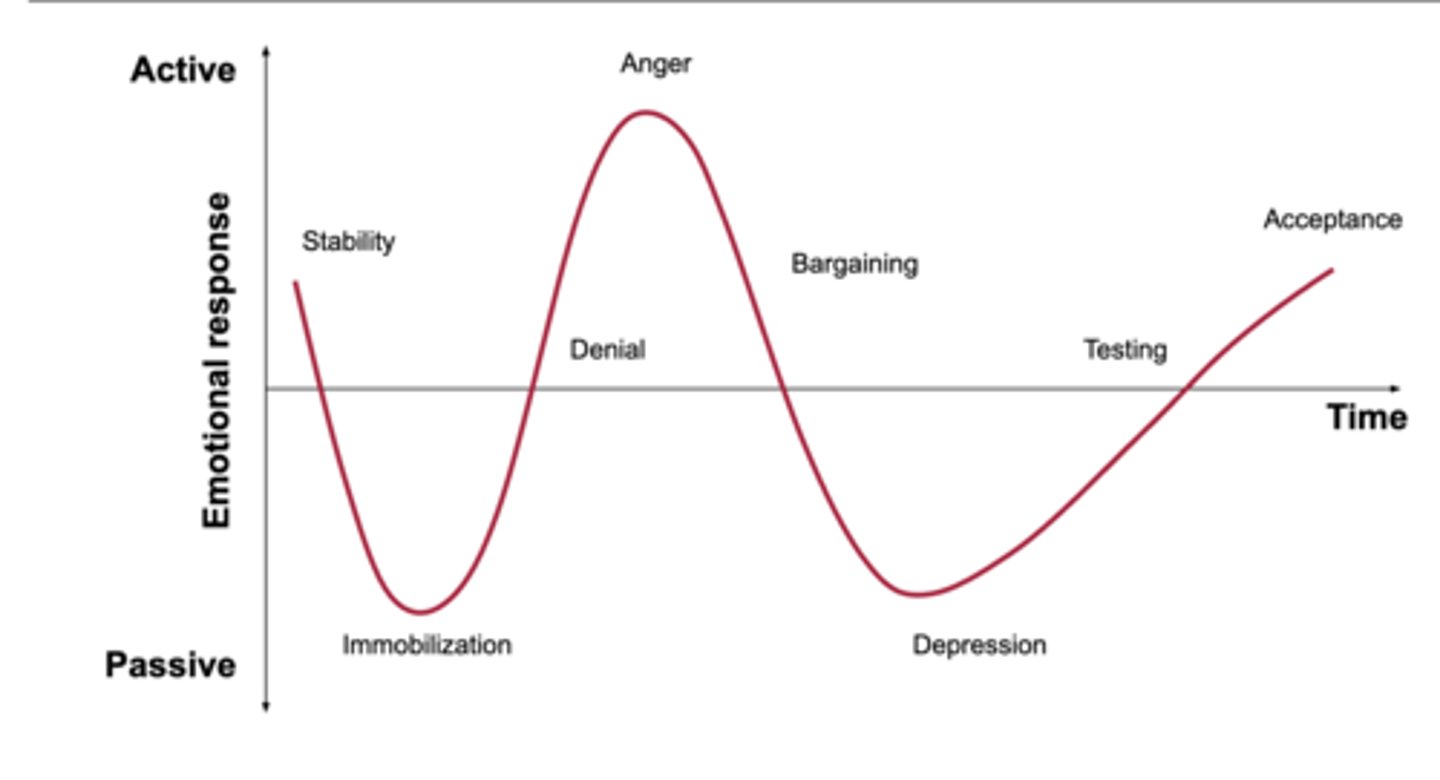
anger
victim "why me"
attempts to place blame
frustration
lack of trust with physician
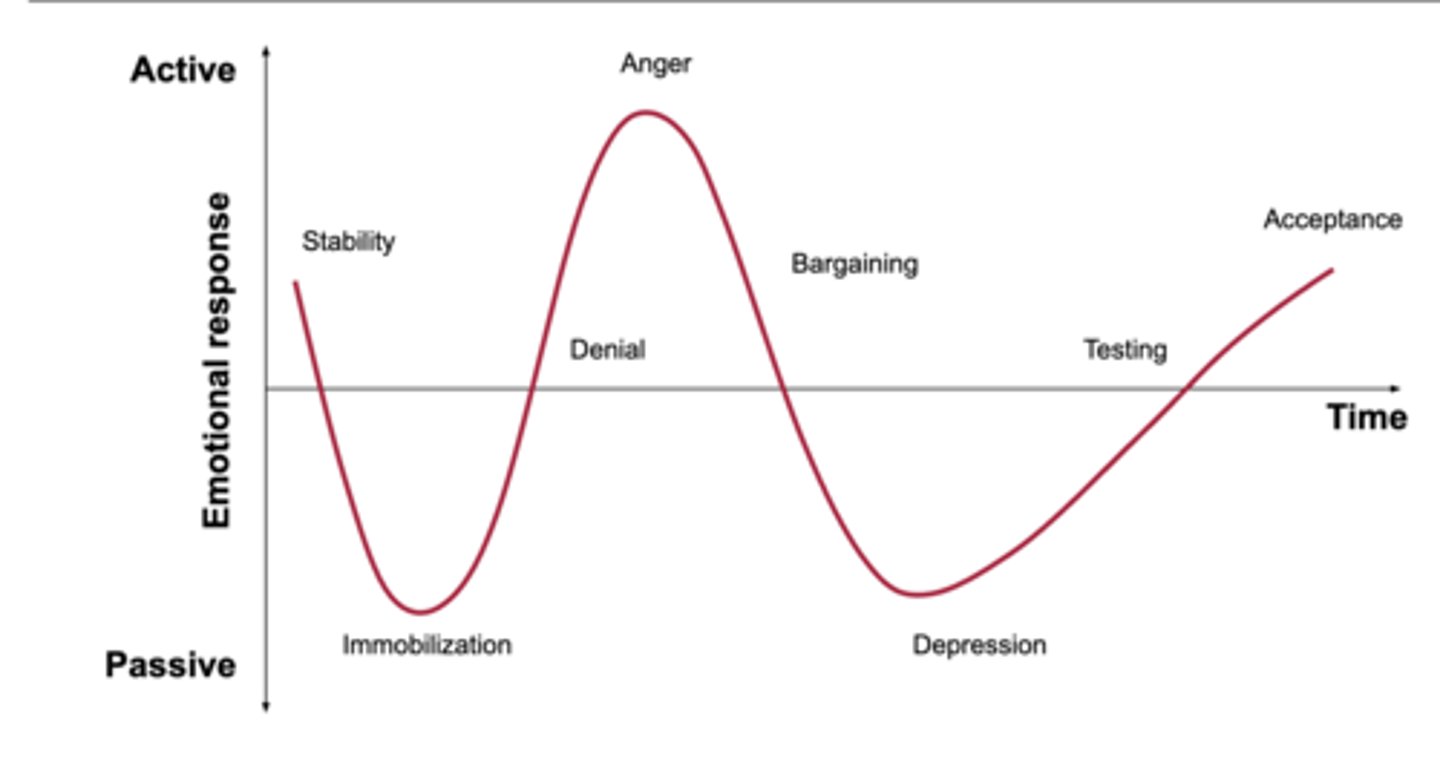
barganing
postpone or distance from the reality of the situation
exhibits good behavior, makes up for perceived wrong doings, engages in behaviors to please
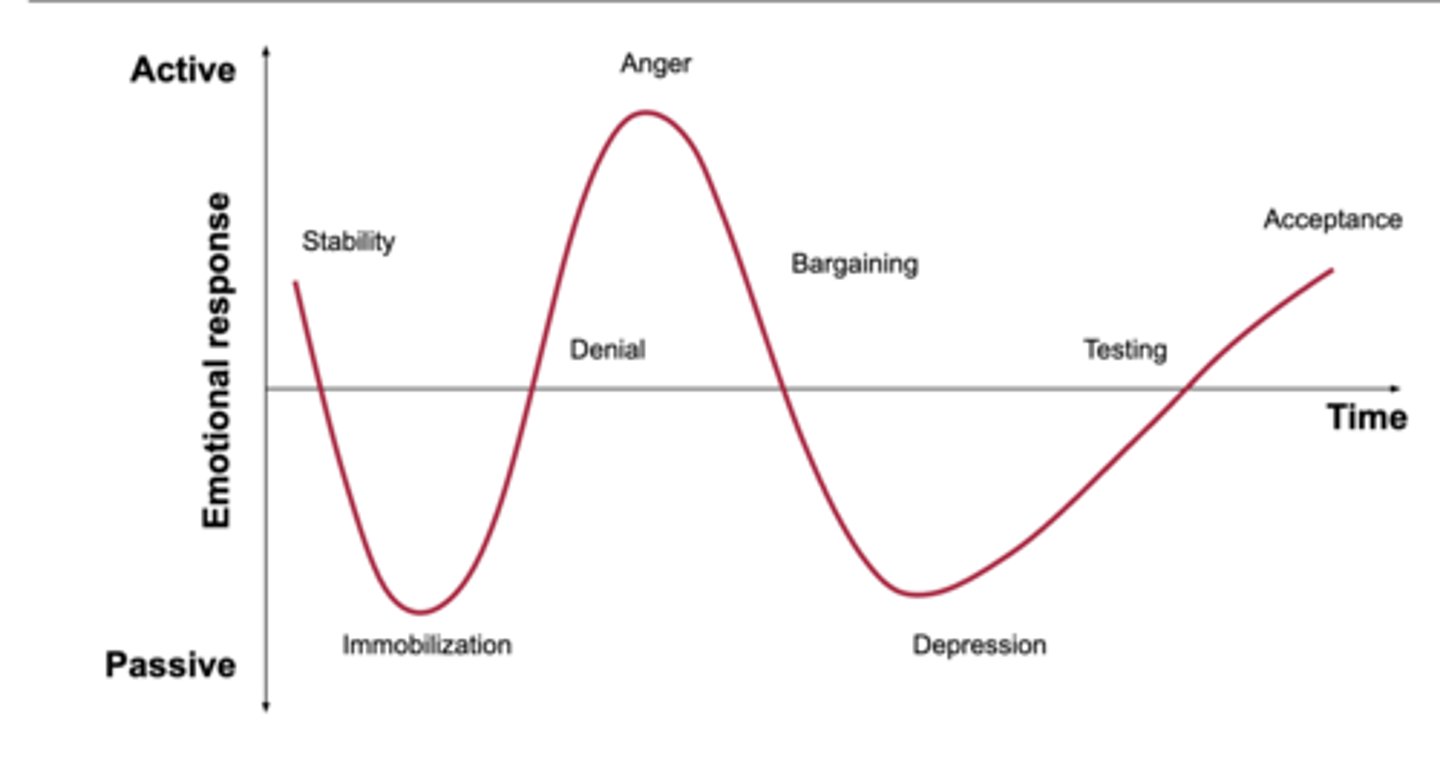
depression
feeling of loss of control or helplessness
withdrawn, no energy
makes few demands
when the situation can no longer be ignored
person grieves for themselves
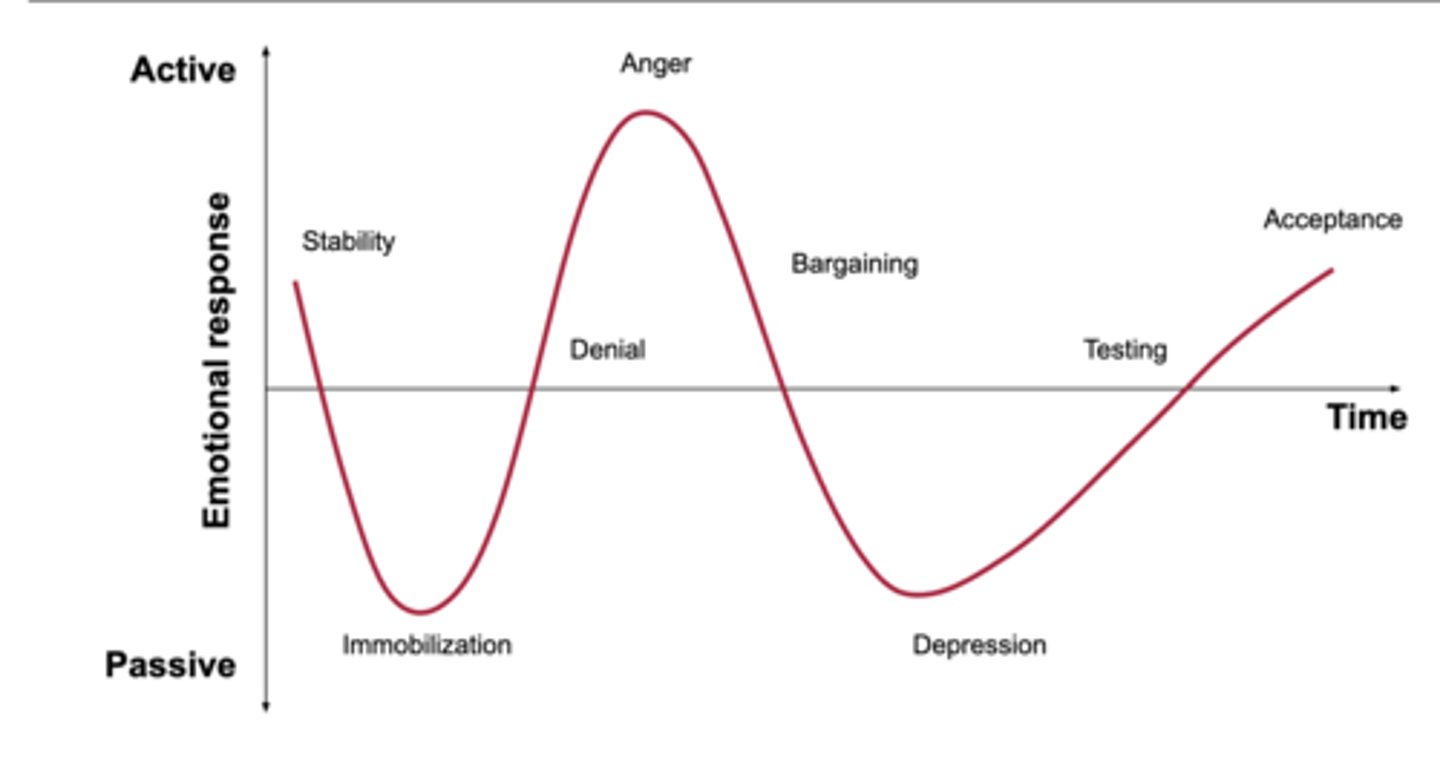
Accpetance
a feeling of ability or resignation
makes realistic expectations
Individual becomes an active participant in their lives
"yes, i am ready"
post-stroke depression (PSD)
occurs in 25-50% of stroke survivors
peaks in the first 3 months post-stroke
PSD risk factors
psychological factors - pre-stroke history of depression, personality and coping, inadequate social support
level of disability
age <68 years
PSD symptoms
- persistent sad/empty mood
- hopelessness
- guilt, worthlessness, helplessness
- loss of interest/pleasure of doing things
- decreased energy
- thoughts of death/suicide
- weight changes
why PSD matters in PT practice
reduced adherence to exercise/therapy plans
lower functional recovery
increased caregiver burden and stress
poorer QOL and community reintegration
higher risk of mortality
elements of motivation
Attitude towards attending therapy
level of understanding
Acknowledgment of the need for treatment
increased engagement is correlated with
greater functional gain
decreased LOS
improved outcomes at 3 months
when screening for PSD, the PT role is
recognize red flags and refer
acute myocardial infarction (acute heart attack), depression preveleance
about 15-30%
impacts adherence to exercise and cardiac rehab
key partners we can work with
psychology/psychiatrist
nursing
medicine
OT/SLP
pharmacologic treatment
mirtazapine (remeron)
Sertraline (zoloft)
Non-pharmacological interventions
counseling and psychotherapy
group therapy
shorter and more intensive rehab for stroke survivors can lead to
improved long-term recovery
if we give intense rehab too soon it could lead to
higher medical instability
when thinking about when to start therapy for a stroke patient we need to consider
balance timing and safety
strategies to increase engagement
goal setting
problem-solving
behavioral contracts
diaries, logs, journals
promoting adjustment
social support from family and friends in early stages
education in problem-solving or practical caregiving skills