C4.1-C4.2
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Population
a group of individual organisms of the same species living and interacting in the same area
Random sample
every member of a population has an equal chance of being selected for the sample
Sampling error
difference between the true and estimated value
Quadrat
a frame that is a fixed size and used for random sampling; good for sessile (immobile) organisms; mark the boundary, generate random numbers, stddev indicates the degree of variability
CMRR
Capture, Mark, Release, Recapture; used for counting motile organisms
Lincoln index
M*N/R; M = # of marked, N = # of recaptured, R = # of recaptured with marks (caught twice)
Carrying capacity
maximum population size that an environment can support; b/c limited resources which promotes competition
Negative feedback control
populations might rise and fall periodically, but are relatively stable over time
Density-independent
factors that have the same effect no matter the population size; Ex. natural disaster
Density-dependent
factors that have an increasing effect when the population is bigger; Ex. competition, predation, diseases/parasites
Positive feedback
reproduction causes exponential growth; occurs when density-dependent factors are not effective or movement into a new niche where resources are abundant
Community
several populations living together
Intraspecific relationship
relationship between individuals of the same species
Intraspecific competition
Leads to natural selection because some individuals have traits that help them outcompete others; compete for territory, mates for reproduction, etc.
Intraspecific cooperation
mutually beneficial relationship; group hunting/foraging, defense against predators, parenting, etc.
Interspecific relationship
relationships between different species
Interspecific herbivory
primary consumers eating primary producers; may or may not kill the producer;
Interspecific predation
one species kills and eats another species; predator-prey relationship
Interspecific competition
two different species competing for the same resource
Interspecific mutualism
two different species both benefiting from each other
Interspecific parasitism
a parasite benefits and the host is harmed
Interspecific pathogenecity
a pathogen lives inside a host; causes a disease
Reasons to randomly sample
Time, destructive, feasibility
Random sampling ensures…
Representation, removal of biases, generalization
Natality (N)
the birth rate for a population
Mortality (M)
the death rate for a population
Immigration (I)
the new individuals entering a population
Emigration (E)
individuals leaving a population
Change in population size
(N+I) - (M+E)
Sigmoid Population Growth Curve
describes how a population’s size changes over time in an environment with limited resources; exponential phase → transitional phase → plateau phase
Mutualism
a close relationship between two organisms of different species, where both individuals benefit
Alien species
organisms that have been introduced to an ecosystem, and do not occur there naturally
Invasive species
alien species that cause harm to the natural ecosystem
endemic
native
How may an alien species become an invasive species?
absence of predators in new habitat
absence of diseases in the new habitat
faster rate of reproduction
larger size/more aggressive
outcompeting for food and other resources
Competitive exclusion
states that no two species can occupy the same niche
Positive associations
occur when two species are more likely to be found together in an ecosystem. Species in mutualistic relationships have ____ associations in ecosystems.
Negative associations
occur if two species are not likely to be found together. Species competing for resources tend to have a ___ association as they avoid direct competition by being in different niches in the ecosystem.
Chi-Squared Test
used to distinguish between two distinct possibilities
Null hypothesis (H0)
There is no significant difference between the distribution of two species; accepted if P > 5%
Alternative hypothesis (H1)
There is a significant difference between the distribution of two species; accepted if P < 5%
Degrees of freedom
(# of rows - 1)(# of columns - 1)
Top Down Controls
pressures applied at higher trophic levels to control dynamics in an ecosystem; Predator’s control population of prey
Bottom Up Controls
resources like nutrients available to producers, affecting the growth of producers; Less producers = less resources = less population
Allelopathy
the release of chemicals by one organism which influences the germination, growth, survival, or reproduction of another organism
Root nodules in Fabaceae
____ plants develop __ that protect the bacteria from consumers; also provides carbs for the bacteria to use as an energy source; Rhizobium bacteria fix nitrogen, helping the plant avoid a nitrogen deficiency;
Nitrogen fixing
a process that converts atmospheric nitrogen gas into biologically usable ammonia
Mycorrhizae in orchids
___ provide carbs from photosynthesis for the fungus to use as an energy source; fungus absorbs and supplies nutrients from the soil that the plant needs (water, nitrogen, phosphorus)
Zooxanthellae in hard coral
___ provides a protected environment close to the surface where algae can absorb light, and also carbon dioxide from respiration; the algae provide carbs and oxygen from photosynthesis.
Ecosystem
all of the organisms and abiotic factors in an area
Open system
both matter and energy can enter and exit
Closed system
energy can enter and exit, but matter cannot
What is the primary energy source for most ecosystems?
Sunlght
Producers (autotrophs)
organism that can synthesize all of the necessary carbon compounds itself using inorganic substances in the environment
Saprotrophs
decomposers that digest things externally
Detritivores
decomposers that digest things internally
Oxidation
the loss of electrons
Reduction
the gain of electrons
Heterotroph
organisms that receive carbon compounds and energy by feeding on other organisms
digestion
chemical breakdown of molecules
Reasons for energy loss between trophic levels
Cell respiration (fewer carbon compounds available for oxidation + heat loss)
Incomplete consumption (not all matter is consumed)
Incomplete digestion (not all matter is digestible)
gross primary production (GPP)
total biomass of carbon compounds made during photosynthesis
net primary production (NPP)
the amount of biomass available to consumers due to the loss of biomass during respiration in plant cells
secondary production
increase in biomass by heterotrophs
Pool
reserve or storage place for certain elements
Flux
transfer of an element from one pool to another
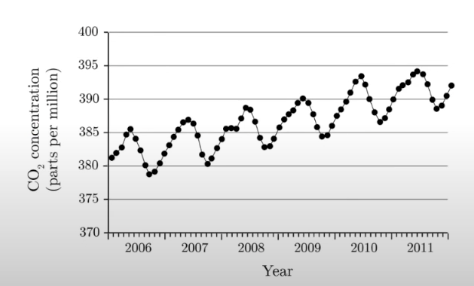
Keeling curve
Photoautotrophs
use light energy to synthesize carbon compounds
Chemoautotrophs
Use the oxidation of inorganic compounds to synthesize carbon compounds
Pyramid of energy
shows the flow of energy through an ecosystem; should be drawn to scale and should be stepped, not triangular
primary productivity
producers synthesizing carbon compounds to increase their biomass
secondary productivity
heterotrophs increasing their biomass by using carbon compounds obtained through feeding
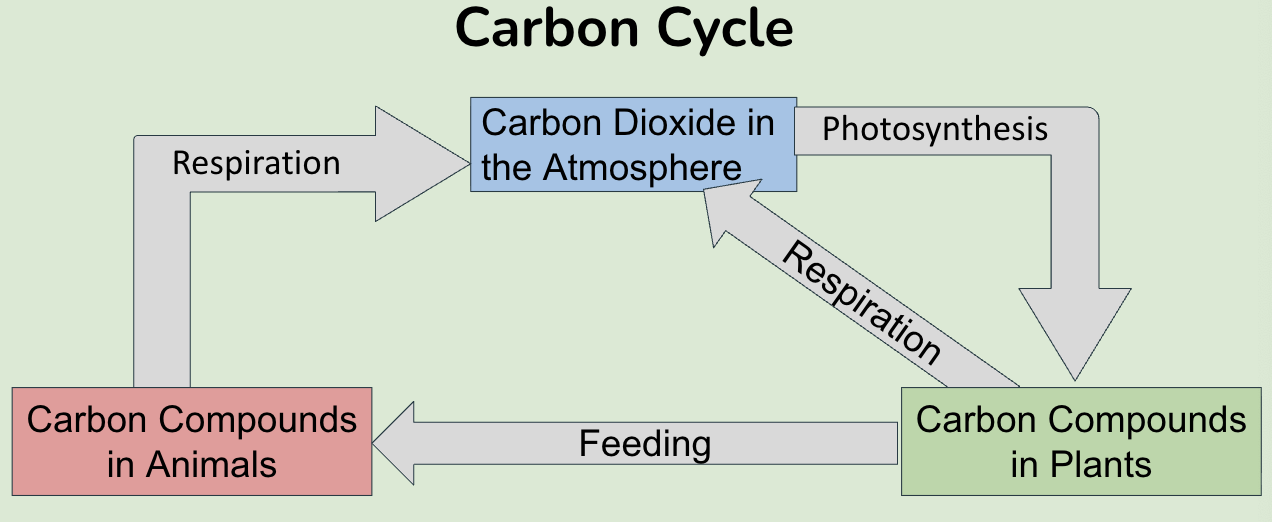
Carbon Cycle