Introduction to Projection Radiography: X-ray Technology & Applications in Healthcare
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Who discovered X-rays and in what year?
Dr. Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen discovered X-rays in 1895.
What was the first clinical X-ray performed in Ireland?
The first clinical X-ray in Ireland was performed in 1896.
What is the primary aim of the RDGY10090 module?
To provide students with an overview of key technologies used in healthcare, particularly in the Radiology Department.
What are the potential roles of X-ray technologies in healthcare?
X-ray technologies can aid in examinations and play roles in disease diagnosis.
What is ionizing radiation?
Ionizing radiation has enough energy to remove electrons from atoms/molecules, potentially breaking chemical bonds and damaging living cells/DNA.
What is the significance of the year 1896 in the context of X-rays in Ireland?
In 1896, the first clinical X-ray was performed and X-ray equipment was installed in several hospitals.
What is the Crookes Tube?
The Crookes Tube is recognized as the first X-ray tube.
What percentage of the energy supplied during X-ray production is converted into X-radiation?
Less than 1% of the energy supplied is converted into X-radiation.
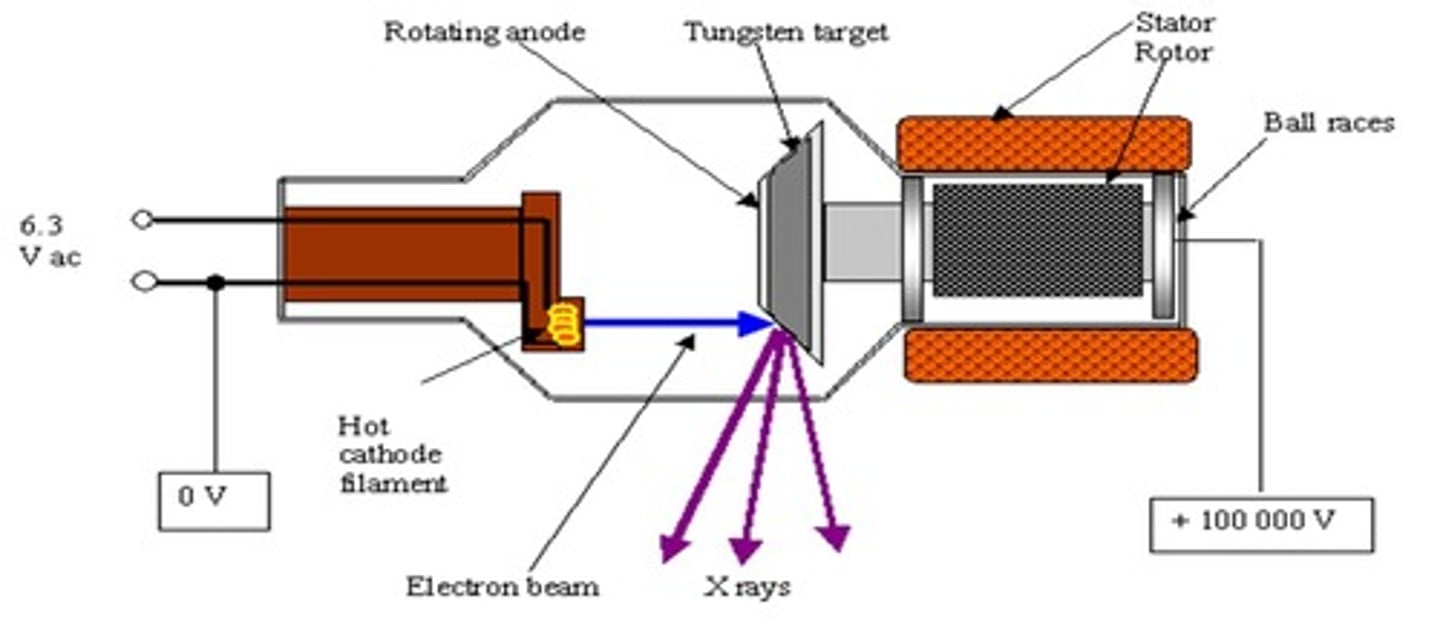
How are X-rays produced?
X-rays are produced when rapidly moving electrons strike a metal target after being accelerated through a potential difference of 1 kV to 1 MV.
What are some safety considerations regarding X-rays?
X-rays are an artificial source of ionizing radiation that must be justified and minimized.
What does the EM spectrum refer to in the context of X-rays?
The EM spectrum refers to the range of electromagnetic radiation, of which X-rays are a part.
What is the role of the filament in X-ray production?
The filament heats up to produce electrons that are then accelerated towards the target anode.
What happens when electrons strike the target anode in X-ray production?
When electrons strike the target anode, they are suddenly decelerated, converting kinetic energy into electromagnetic energy, resulting in X-rays.
What should students do regarding the timetable for the RDGY10090 module?
Students should consult the timetable available on Brightspace, which is subject to change.
What is the significance of the first Nobel Prize for Physics in relation to X-rays?
Dr. Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, who discovered X-rays, was the recipient of the first Nobel Prize for Physics in 1901.
What are the natural sources of background radiation?
Natural sources of background radiation are unavoidable and typically not harmful at low levels.
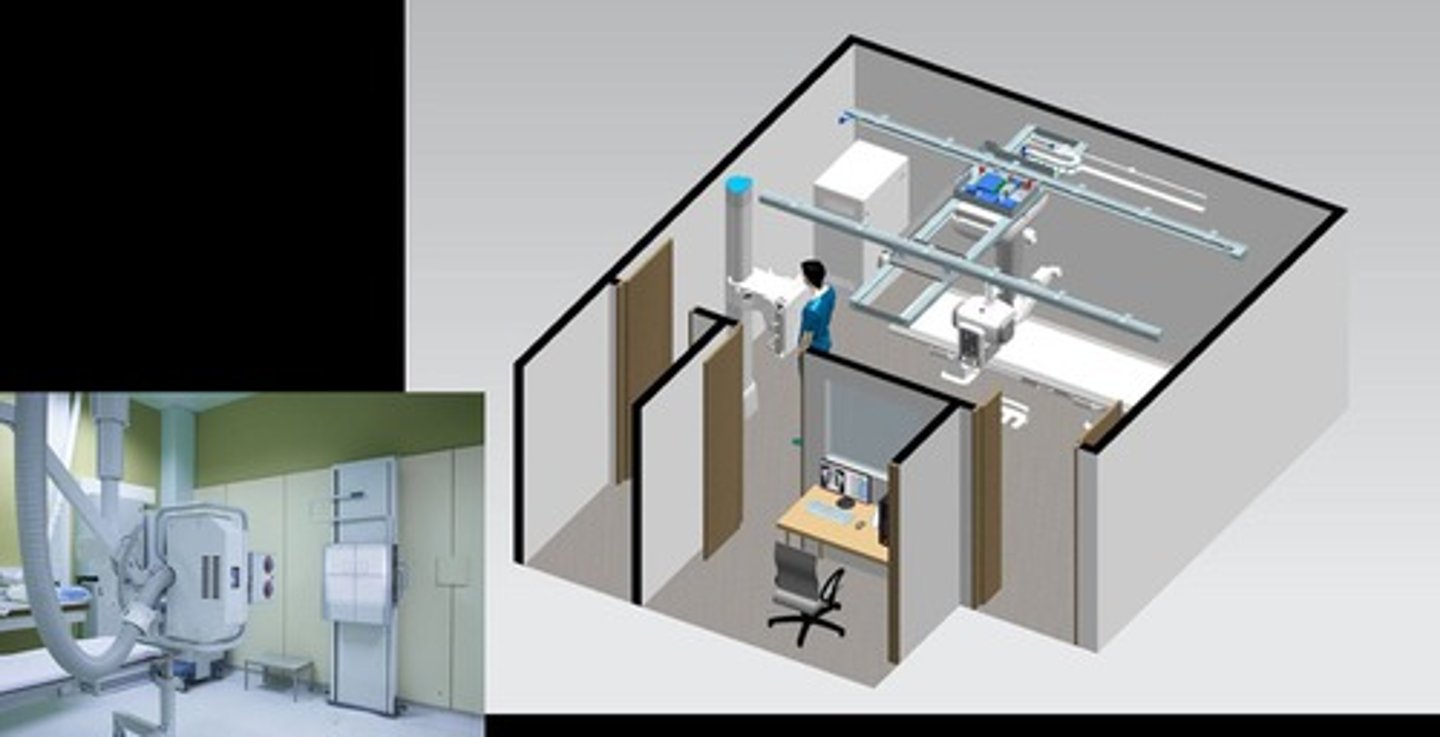
What is the layout of an X-ray room?
The layout of an X-ray room includes the X-ray tube assembly and designated areas for patient positioning.
What are referral pathways in the context of X-ray examinations?
Referral pathways outline the process for patients to receive X-ray examinations based on medical need.
What is the importance of understanding how X-rays interact with the human body?
Understanding how X-rays interact with the human body is crucial for ensuring safety and effectiveness in imaging.
What are some other modalities that use X-rays?
Other modalities that use X-rays include CT scans and fluoroscopy.
What is the significance of the module descriptor for RDGY10090?
The module descriptor provides essential information about the course structure, content, and assessment strategy.
What should students do to stay informed about module announcements?
Students should ensure they are signed up to receive announcements on Brightspace.
What percentage of energy supplied is converted into X-radiation during the X-ray process?
Less than 1%.
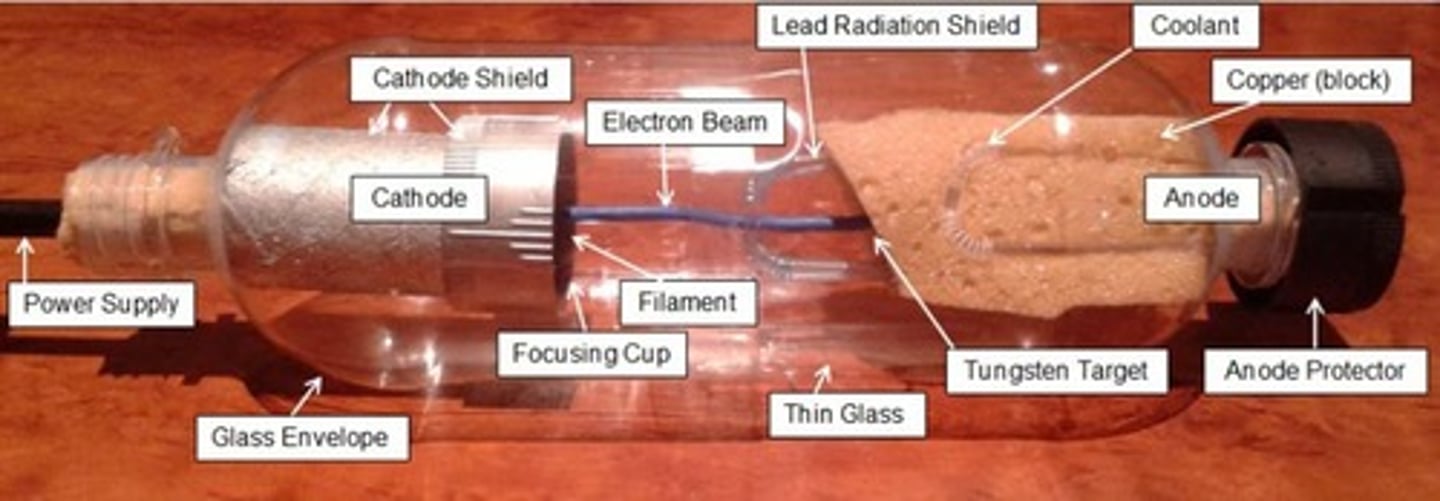
What is the primary material used for the filament in the cathode assembly of an X-ray tube?
Tungsten.
Why is tungsten used for the filament in X-ray tubes?
1. High melting point (~3422°C). 2. Excellent thermionic emitter. 3. Durable and can be shaped into fine wire.
What is thermionic emission?
The emission of charged particles (electrons) from a heated material due to thermal energy.
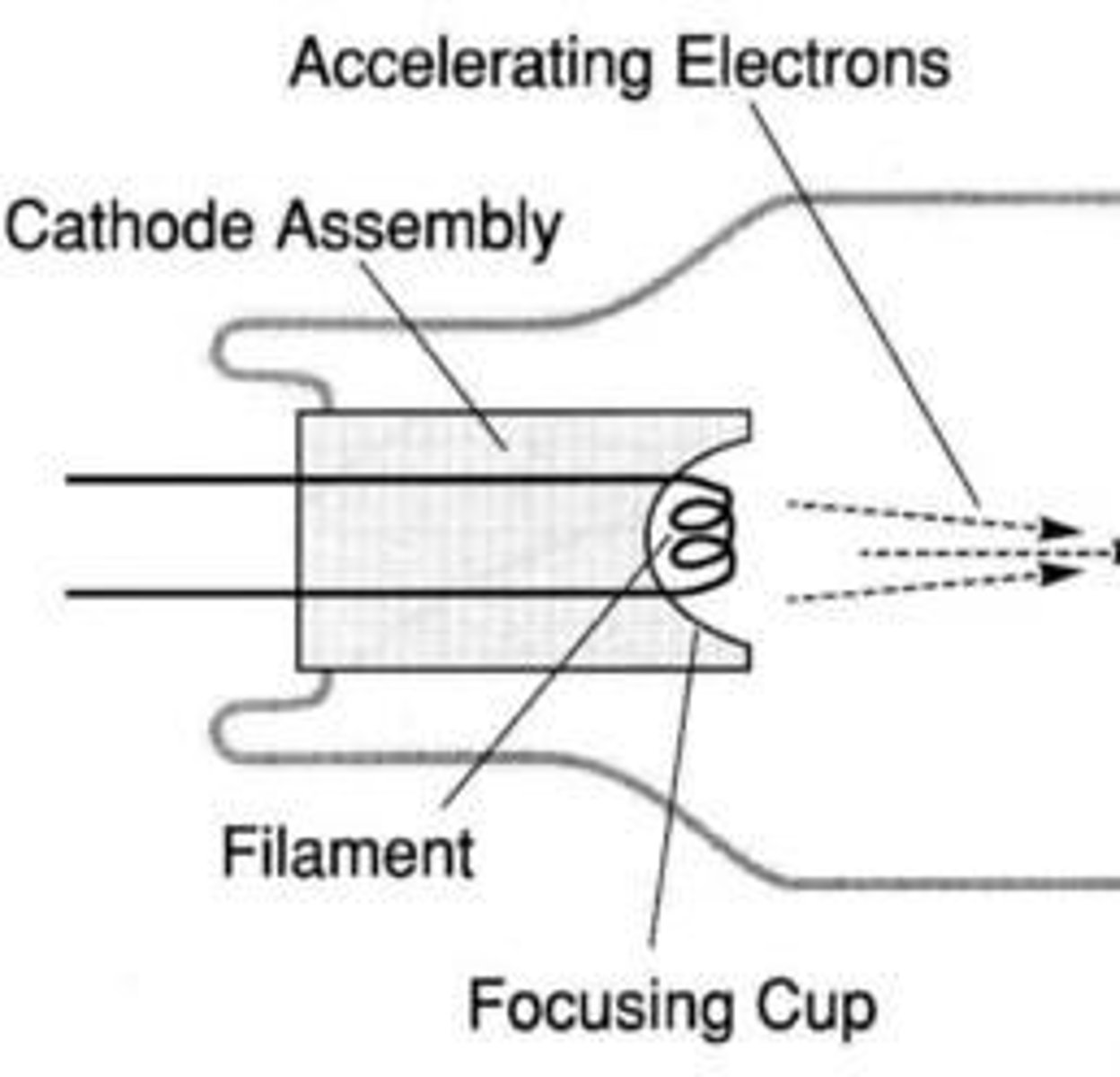
What is the purpose of the focusing cup in the cathode assembly?
To focus the stream of electrons with a negative charge.
What is the target anode in an X-ray tube?
The part of the anode struck by the stream of electrons from the cathode.
Why is tungsten used for the target anode in X-ray tubes?
1. High melting point. 2. High atomic number (Z = 74) for increased X-ray production efficiency. 3. Efficient heat conductor.
What is the function of the glass/metal envelope in an X-ray tube?
To create a vacuum that allows the efficient flow of electrons.
What is the purpose of the lead lining in the X-ray tube housing?
To absorb most unwanted X-rays and provide radiation shielding/safety.
What is leakage radiation in the context of X-ray tubes?
Unwanted X-rays that could spread into the environment, causing unnecessary ionizing radiation.
What are the components of an X-ray room?
1. Tube (source of X-rays). 2. Image receptor/detector. 3. Erect and supine positions for patients.
What types of image receptors are used in X-ray imaging?
1. Radiographic film (old). 2. CR cassettes (old). 3. Digital image receptors.
What must occur before a patient receives an X-ray?
A clinical examination by a designated referrer and evaluation of signs and symptoms.
Who can be a designated referrer for an X-ray?
A doctor, dentist, radiographer, or nurse in certain instances.
What is the role of the image receptor in X-ray imaging?
To detect X-rays.
What is the significance of the angle of the target anode?
It facilitates X-ray photons exiting the tube.
What is the purpose of insulating oil in an X-ray tube?
To provide insulation and cooling.
What is a common precaution for mobile X-ray procedures?
Not undertaken in the X-ray room.
What types of X-ray positions are mentioned for patients?
Erect (standing CXR) and supine (supine AXR).
What is the function of the cathode assembly in an X-ray tube?
To emit electrons that will be directed towards the anode.
What is the purpose of the vacuum in the X-ray tube?
To allow for efficient electron flow and prevent scattering.
What is the primary purpose of considering an X-ray before diagnosis and treatment?
To justify the value of the X-ray in aiding diagnosis and commencing treatment.
What must a letter of referral for an X-ray include?
The referrer's signature, reasons for referral, and sufficient medical information to justify the examination.
What are the steps a patient goes through upon arrival at the radiology department?
Check-in to confirm ID, wait to be called, possibly change in a cubicle, and have clinical information checked before the X-ray.
What are the two main processes by which X-ray radiation is attenuated?
Absorption and scattering.
How does absorption affect X-ray photons?
It results in the transfer of energy from the X-ray photon to atoms of the material.
What is the effect of scattering on X-ray photons?
It involves deflection of photons from their original course.
What factors affect the attenuation of X-ray beams?
Density of the tissue, atomic number of the tissue, thickness of the tissue, and energy of the X-ray beam.
What is the atomic number of air, and how does it compare to fat and muscle?
Air has an atomic number of 7.78, which is slightly higher than fat or muscle but has much lower density.
What effect does air have on X-ray imaging?
Air absorbs fewer photons, allowing more to reach the image receptor, resulting in a darker appearance on the X-ray.
What is the atomic number and density of bone, and how does it affect X-ray imaging?
Bone has an atomic number of 12.31 and a density of 1650, making it the greatest absorber of photons, resulting in a brighter appearance on the X-ray.
What role does calcium content play in the attenuation of X-rays by bone?
Calcium contributes to the high atomic number and density of bone, enhancing its ability to absorb X-rays.
What information is typically included in a referral request for an X-ray?
Patient details, referrer details and signature, examination requested, clinical information, and any relevant mobility or learning difficulties.
What happens if an X-ray examination is justified?
The X-ray examination is performed.
What should patients be informed about after their X-ray examination?
They should be informed about the availability of the results.
How does the atomic number of a substance relate to its ability to attenuate X-rays?
A higher atomic number generally results in more attenuation of X-rays.
What is the significance of tissue density in X-ray attenuation?
Higher density tissues absorb more X-rays, leading to less exposure on the image receptor.
What is the typical order of patient preparation for an X-ray examination?
Check-in, confirmation of ID, possible changing in a cubicle, and clinical information check.
What is the effect of muscle on X-ray imaging compared to fat?
Muscle has a higher atomic number and density than fat, leading to different attenuation characteristics.
What is the role of previous imaging in the referral process for an X-ray?
It provides relevant information that may influence the current examination request.
What is the significance of the triple ID check in the X-ray process?
It ensures patient safety and correct identification before the examination.
What are the implications of having air in the bowel or lungs for X-ray imaging?
Air allows more photons to reach the image receptor, resulting in a darker appearance on the X-ray.
What is attenuation in the context of X-ray imaging?
Attenuation is the reduction in the intensity of an X-ray beam as it passes through matter.
What are the two main types of interactions that cause attenuation at diagnostic X-ray energies?
1. Photoelectric Absorption 2. Compton Scattering
Describe the process of Photoelectric Absorption.
An incident photon interacts with an inner shell electron, is completely absorbed, ejects the electron (photoelectron), ionizes the atom, and an outer-shell electron fills the vacancy, emitting an X-ray.
What occurs during Compton Scattering?
An incident photon interacts with an outer shell electron, ejects the electron, and causes a change in direction or scatter of the photon.
What is the significance of high atomic numbers in fluoroscopy contrast agents?
High atomic numbers provide excellent attenuation for imaging.
Name two contrast agents used in fluoroscopy and their solubility.
Barium Sulfate (not water soluble) and Gastrografin (iodine-based, water soluble).
What is the primary use of DEXA scans?
To measure bone mineral density (BMD) and assess fracture risk.
What is the gold standard for diagnosing osteoporosis?
DEXA (Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) scans.
What type of imaging technique is mammography?
A low dose X-ray technique focusing on soft tissues to detect or investigate masses and calcifications.
What are some applications of forensics in medical imaging?
Forensics utilizes radiological techniques for suspicious death investigations, child abuse cases, drug trafficking, body identification, bullet location, and body part orientation.
What is the role of the abdominal psoas muscle in X-ray imaging?
It is easy to distinguish from surrounding soft tissue/fat due to its higher atomic number and density, making it a greater attenuator of the beam.
What terminology is used to describe radiolucent and radiopaque substances?
"Dark/Black" is radiolucent, while "Light/White" is radiopaque.
What is the purpose of radiation protection devices in X-ray rooms?
To protect against the effects of Compton Scattering, which causes scatter radiation.
What are some common theatre procedures that utilize X-ray imaging?
Femoral nailing, tibial nailing, hip pinning, dynamic hip screw, and Open Reduction Internal Fixation (ORIF).
What is the focus of mammography screenings?
To conduct breast checks for both symptomatic and non-symptomatic individuals.
What is the primary benefit of using DEXA for body composition analysis?
It provides low radiation doses while accurately measuring bone mineral density.
What is the significance of the atomic number in differentiating between fat and muscle in X-ray imaging?
Muscle has a higher atomic number and density compared to fat, making it a better attenuator of X-rays.
What does the term 'photoelectron' refer to in the context of Photoelectric Absorption?
The electron that is ejected from the atom when an incident photon is absorbed.
Why is it important to understand beam attenuation in medical imaging?
It helps in interpreting images and understanding how different tissues interact with X-ray beams.
What is the purpose of using contrast agents in fluoroscopy?
To enhance the visibility of structures within the body during imaging.
How does the DEXA scan contribute to athletic performance settings?
It is less commonly used for body composition analysis but can provide insights into bone health and fracture risk.
What are the implications of using X-ray imaging in forensic investigations?
It assists in legal matters by providing evidence related to suspicious deaths, abuse, and other criminal activities.