MCHE 3920 Week 6 Forging of Metals
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
metal, impact
Forging: Centuries old process of transforming ________ to a desired shape through __________
compressive, plastically
_ in forging: ____________ loads _________ deform material
high forces
Forging is Used for products that need to withstand _____________
knives, hand tools, mining equipment, auto and aerospace
examples of products that are forged
casting, form freedom, mechanical properties
Compared to _________, forging offers less ___________ but better ___________
strength, ductility, hardness
forging offers superior _____, ______, ______
versatile, large, grams, tons, very high, one-offs
Forging is a __________ process with
_________ practical weight range (_____ to _____)
Potential for ____________ production volumes
Can also be made by hand as _____________
improved, deforms, continuous, fibrous, fewer
Forging of metals: The ___________material properties are largely due to the fact that the grain __________ along with the part creating a ___________ and ____________ grain structure with _________ weak spots
billet, work piece, blank, slug, flat dies, decrease, constant, upsetting
Metal forging: In simplest operation a ________, (aka, _________, _________or ________) is compressed between __________ to produce a ____________ in height
Volume stays __________, so diameter increases
Method is called ___________
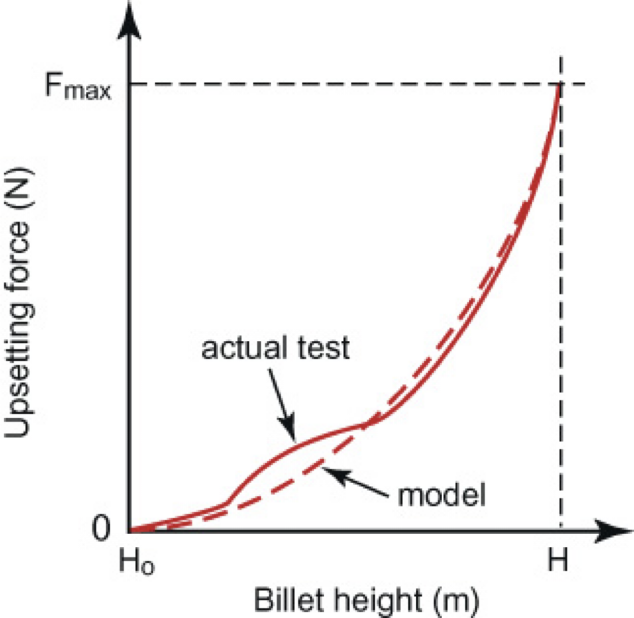
upsetting force, billet heights, exponential, large forces
Plotting _____________ vs. ____________shows an ____________ relationship- large shape changes require ________
increases, force, stress, cold, strain hardening, friction
Three reasons for upsetting relationship
Cross sectional area ____________
More ______ required to produce same amount of __________
In_______ forging, _____________ takes place
__________ between the billet and the die makes the billet more resistant to deformation
upsetting, sigmat=Ket^n
For a given alloy, the s/s relationship in _______ can be fit to a simple model: _________
true, true stress, area, strain hardening, material constant
Simple upsetting model: s/s are _____; _________ is force divided by instantaneous ______, n is ____________ exponent, K is a _________
more difficult, main axis, elastically
In upsetting, it is ____________ to achieve tight tolerances in the ___________ because the dies will also deform ___________ under the compressive load
very large, series of impacts, series of dies, load
Forces involved are __________ , so shaping is often done with a ______________ to gradually change the shape and sometimes with a ______________ to better distribute the ___________ across the changing shape
Cold, 40%, hundreds of
______ forging is generally defined as forging below _________ of melting temperature (in Kelvin)
Can still be at ___________ degrees Celsius
Warm, 40%, 80%
______ forging is between ________ and _________ of melting temp
Hot, 80%
______ forging occurs above ________ of melting temp
solidification range, Tsolidus
in cold, warm, hot forging: Recall that most metals have a ________________ , so the melting temp here refers to the lower end of the range (______)
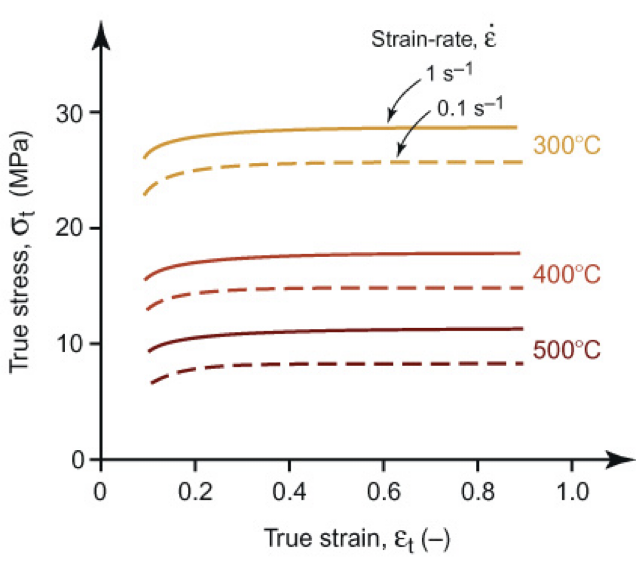
lower, strain rate, Zener-Hollomon
For HOT forging:
At elevated temperature, yield strength is much ________, so requires lower forces to deform metal
However, yield stress becomes a function of ____________, i.e., the how fast the metal is being deformed
Strain-rate and temperature are linked via the “_____________________”
ėe(Q/(RT)), ė, Q, R, yield stress
Zener-Hollomon Parameter is given by: Z=______, where _____ = strain rate, _____ = Activation energy, _____ = Universal gas constant
For a given material, the same Z value indicates the same ___________
tolerances, warpage, distortion, oxidation, cracks, surface faults, strain hardening, weaker, softening
Hot forging drawbacks:
Reduced control over _____________
_________ and ___________ can occur during cooling
_____________ can be severe at higher temperatures leading to __________ and ____________
At elevated temps, there is no _______________, so parts made by hard forging are ___________ than cold-forged parts
High temperatures can lead to recrystallization and grain growth, effectively ____________the material
dies, material, dead metal zone, impeded, radially, barreling
Effects of friction in forging: Friction between the __________and the _________ inhibits the material from the ends from deforming outward
Creates a _____________in which material does not deform
Away from ends, material is not _________ by friction and deforms __________
Called “___________”
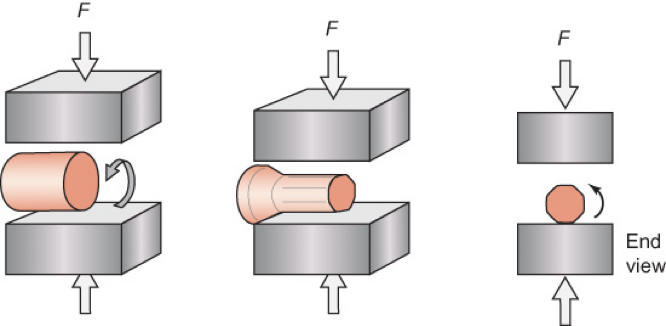
open die forging, manipulated, two, blacksmith’s hammer, smith forging, slow, low, no
In __________: A metal block or rod is ____________ between ________ dies that move up and down in a fixed rhythm
Essentially a mechanized version of a _________________ , so it is sometimes called “______________”
Relatively ___________ process, so __________ production volumes, but __________ product specific investment
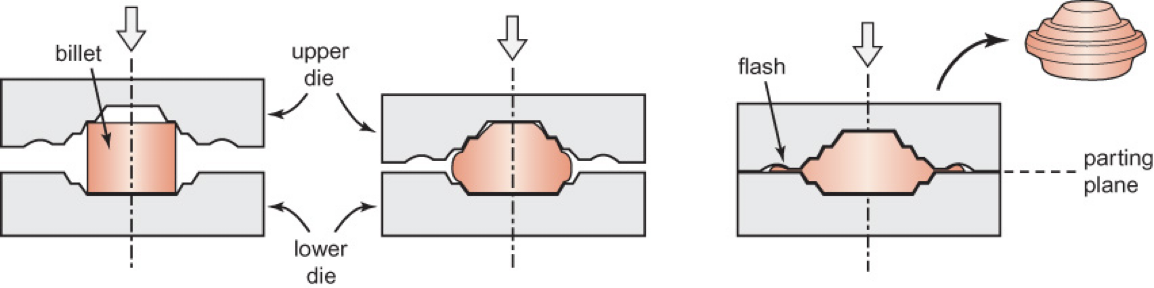
completely, 10%, 20%, flash, critical, corners, flash
In _________:
Uses profiled dies with goal being to fill the die __________
Often performed in steps
Usually uses ________ to __________ extra material that is squeezed between the dies
Known as “___________”
Makes billet size less __________
Material would rather flow into the ________ of the die than into the ___________ region
press forging, low, force, displacement, strain rate, flash, cool, reheated
In _______: Uses two dies brought together at ________ speed by hydraulics
Allows control over ________ and _________ (and thus __________)
Also generates __________
Because it is slower, the billet may _______during forging and need to be __________ during the process
Net-shape forging, impression die forming, eliminate, finishing, expensive, titanium
__________:
Essentially ____________________, but with very tight tolerances and control
Goal is to _________ waste and need for __________
Beneficial for ___________ materials (e.g., __________) or when the functional and/or quality requirements demand a tightly controlled process
Cold heading, fasteners, bolts, screws, at room temperature, impacting dies, grooved plates, strain hardening exponent (n)
_________:
Used exclusively for ___________ (e.g., ________ and __________)
Usually done _____________________
Head is formed by passing a thick metal wire through a series of ________________
Threads are made by rolling the parts between ______________
Only feasible with metals that have a low _______________________
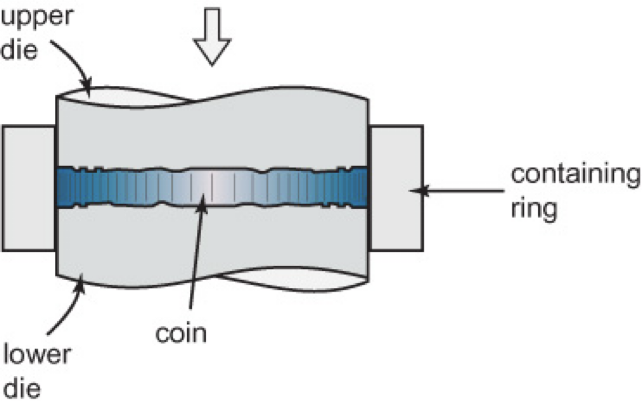
Coining, flash, convex, wouldn’t deform, positive imprints, negative pattern
__________: Used with thin disk-like billlets
Closed die process (i.e., no __________ is produced)
Dies are made to be slightly ________so contact and deformation starts in the center
Otherwise center _________
Coins have _________ imprints (i.e., ____________ on the die which is much more durable)