2.26 retinal vasculature
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Blood pressure categories?
Normal less than 120 and less than 80
Elevated 120-129 and <80
HTN stage 1 130-139 or 80-89
HTN stage 2 140 or higher or 90+
Hypertensive crisis >180 and/or >120
Risk of CV disease doubles for ...
every increase of 20 points over 115 for systolic and 10 for diastolic over 75
Peripheral vascular disease results in what?
- absence of major pulse in extremities
- claudication (pain in exercising muscle from decreased bloodflow)
Arteriosclerosis
hardening/thickening of artery wall with loss of elasticity
Atherosclerosis definition
progressive inflammation of arterial walls with accumulation of lipids and thickening of wall
- this is a type of arteriosclerosis
Atheroma (Plaque)
develop in sub-endothelial space which expands outward as well as inward
LDL target -- good or bad?
HDL target -- good or bad?
<100 -- bad
>40 -- good
To gauge amount of atherosclerosis, how?
do some inflammatory marker blood tests
Are atheromas seen in retinal vessels?
no but can affect central retinal artery
When it comes to arteriosclerosis, how can hyalinization occur ?
- accumulation of collagen in walls of small arteries/arterioles which is seen in the retina resulting in narrowing of the vessel lumen and ischemia
Retina and optic nerve vascular beds, anterior to lamina cribrosa, are under __________
autoregulation
What is autoregulation?
physiologic mechanism designed to meet metabolic demands (O2/CO2 balance) by maintaining bloodflow and tissue oxygen despite alterations in perfusion/arterial pressure
Are choroidal vascular beds under autoregulation? how do they work?
no, choroidal vessels are fenestrated with no blood-ocular barrier
Perfusion pressure is defined as ...
bloodflow to maintain metabolic/nutritional requirements
What is ocular perfusion pressure? is it constant or variable from day to night?
pressure at which blood enters the eye -- highly variable
In retinal vasculature, what is the initial response to HTN in normal non sclerotic vessels?
arterial-arteriolar vasoconstriction (vasospasm) of smooth muscle in vessel walls (to reduce flow), especially if there is a high O2 percentage b/c that tells the autoregulation that the BP is too high
As a result of hypertensive retinopathy, there eventually is what?
retinal blood barrier breakdown
Sclerotic Phase of HTN in eye? (next after initial effects)
- compensatory structural changes (arteriosclerosis) in arterial walls
- result is thickening of basement membrane, muscle is replaced by collagen with narrowing of lumen resulting (hyalinization)
- as a result, BVs can no longer become narrower or wider
Is the narrowing from sclerotic phase reversible or irreversible in retinal BVs?
irreversible
Sclerotic Phase of HTN -- what are the retinal changes?
- lack of muscle tone
- breakdown of autoregulation
- breakdown of Blood retinal barrier
- flame, dot, blot hemorrhages
- plasma lipoproteins seen as hard exudates
What occurs in the exudative phase of HTN?
- necrosis develops unless BP reduced
- capillary beds are damaged when autoregulation is lost
- impaired flow, ischemia, and CWS
Phases of HTN?
- Initial
- Sclerotic
- Exudative
Retinal vasculature HTN changes?
- attenuation of arterioles
- AV ratio changes
- arteriolar light reflex change
- AV crossing changes
- flame/dot/blot retinal hemorrhages
- CWS
- Exudates
- Vessel sheathing
- ONH swelling
Normal AV ratio?
artery is 2/3 to 3/4 the size of venule
Normal arteriolar light reflex/what happens with increased BP?
- approx 1/5 width of vessel
- reflex is widened and brightened
Sclerosis is related to _______ of systemic HTN?
duration
Attenuation can be _____ or ______
focal or generalized
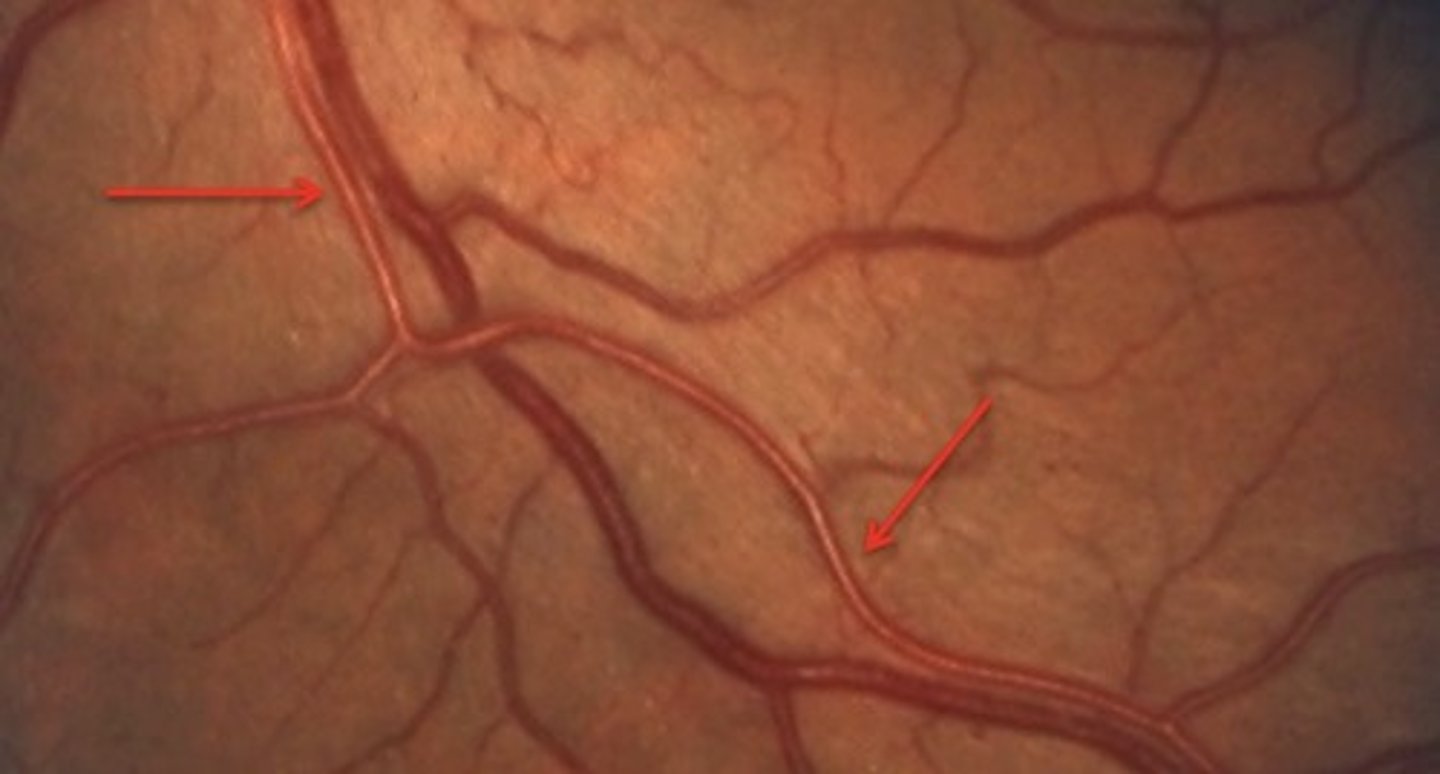
AV crossing changes cause?
thickened arteriole crosses over venule and compresses it
Salus's sign
deflection of retinal vein as it crosses arteriole
Gunn's sign
tapering of retinal vein on either side of AV crossing
CWS disappear in how long?
4-6 weeks
Optic nerve swelling is associated with ...
accelerated (malignant) HTN
What can mimic Hypertensive retinopathy?
- diabetic retinopathy
- retinal venous obstruction
- hyperviscosity syndrome
- ocular ischemic syndrome
- radiation retinopathy
Retinal vein occlusion 2 biggest risk factors
HTN and hyperlipidemia
How does CRVO occur?
- atherosclerosis of adjacent central retinal artery compresses central retinal vein at lamina cribrosa leading to thrombosis in vein (occlusion, endothelial damage, platelet aggregation, venous thrombus formation)
Does CRVO usually present bilaterally or unilaterally?
unilateral
2 types of CRVO
Nonischemic and ischemic
Nonischemic CRVO
- characterized by what?
- avg VA at presentation?
- complications
- mild-moderate retinal capillary perfusion
- 20/50
- cystoid macular edema, venous shunts
is avg age of onset in nonischemic or ischemic CRVO higher?
ischemic CRVO
Ischemic CRVO
- avg VA presentation?
- characterized by...
20/400
more than 50% capillary nonperfusion and nerve edema
Ischemic CRVO
- retinal findings
- complications
- marked venous engorgement, venous tortuosity, hemorrhages, CWS
- cystoid macular edema, optociliary shunts, neovascularization
In CRVO, neovascular glaucoma is more likely the greater the ...
degree of retinal capillary nonperfusion
Risk factors for CRVO
- HTN, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, hyperviscosity of blood
In 40-70% of CRVO patients, what is seen?
primary open angle glaucoma or ocular HTN
Branch retinal vein occlusion is most common in what part of retina?
superior temporal retina
BRVO symptoms
many are asymptomatic
BRVO management
observation, laser for macular edema
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO)
- mainly caused by what?
- form of what?
- thromboembolism or local thrombus formation of Central retinal artery at lamina cribrosa (narrowest part of CRA)
- acute ischemic stroke
CRAO is associated with ...
life threatening stroke and CV diseases
emboli from the heart
Main risk factors for CRAO
Obesity, HTN, smoking, hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol)
CRAO
- symptoms?
- sudden painless loss of vision
- RAPD
- evidence of retinal hypofusion
95% of CRAO are classified as what?
5% of CRAO are classified as what?
nonarteritic
arteritic (disorder of giant cell arteritis)
CRAO what are the main sources of emboli?
- carotid artery disease
- emboli from heart
Inner 2/3 of retina supplied by _____
Outer 1/3 of retina (RPE and photoreceptors) supplied by ______
CRA
choroid
Main clinical observations of retina of CRAO
- retinal pallor
- cherry red spot on fovea
- arteriole attenuation
- boxcarring (slow segmental bloodflow)
In majority of CRAO how does ONH look?
normal
Why would acuity be nearly normal in CRAO case?
in presence of a cilioretinal artery (which occur in 20-32% of eyes--congenital)
What is the retinal ischemic tolerance time?
4 hours
CRAO risk factors
HTN, DM, high cholesterol, smoking, giant cell arteritis
When you see optic disc edema in CRAO, suspect what?
arteritic CRAO
CRAO management
- immediate referral to ER
- ant chamber paracentesis (aqueous release of ant chamber to raise and lower IOP quickly--attempts to dislodge emobli)
- ocular massage
- CO2/O2 combo
CO2 results in _______
O2 results in _______
vasodilation
vasoconstriction
Carotid artery disease
- what is usually the main symptom?
- transient monocular loss of vision (amaurosis fugax) TIA
Hollenhorst plaques (cholesterol emoblis) in retina can indicate what?
carotid artery disease
Cholesterol emobli in retina
- describe typical presentation
temporary with emboli moving downstream
asymptomatic, transient, or permanent vision loss
retinal circulation often not obstructed
Calcium emboli
- describe typical presentation
- large pearly white nonmobile opacity
- observed within arteries or optic nerve
- originate from calcified aortic. valves
Platelet-fibrin emboli
- describe these
- long, dull white slowly moving opacities within arterioles
- originate from ulcerating carotid atheromas
- result in amaurosis fugax and retinal infarction
Fat and air emboli
- describe these
- cause controversial
- called purtscher's retinopathy
what is bruit
sound indicating blood flow turbulence secondary to plaque, stenosis, occlusion
it's not heard if stenosis is less than 80 or 100%
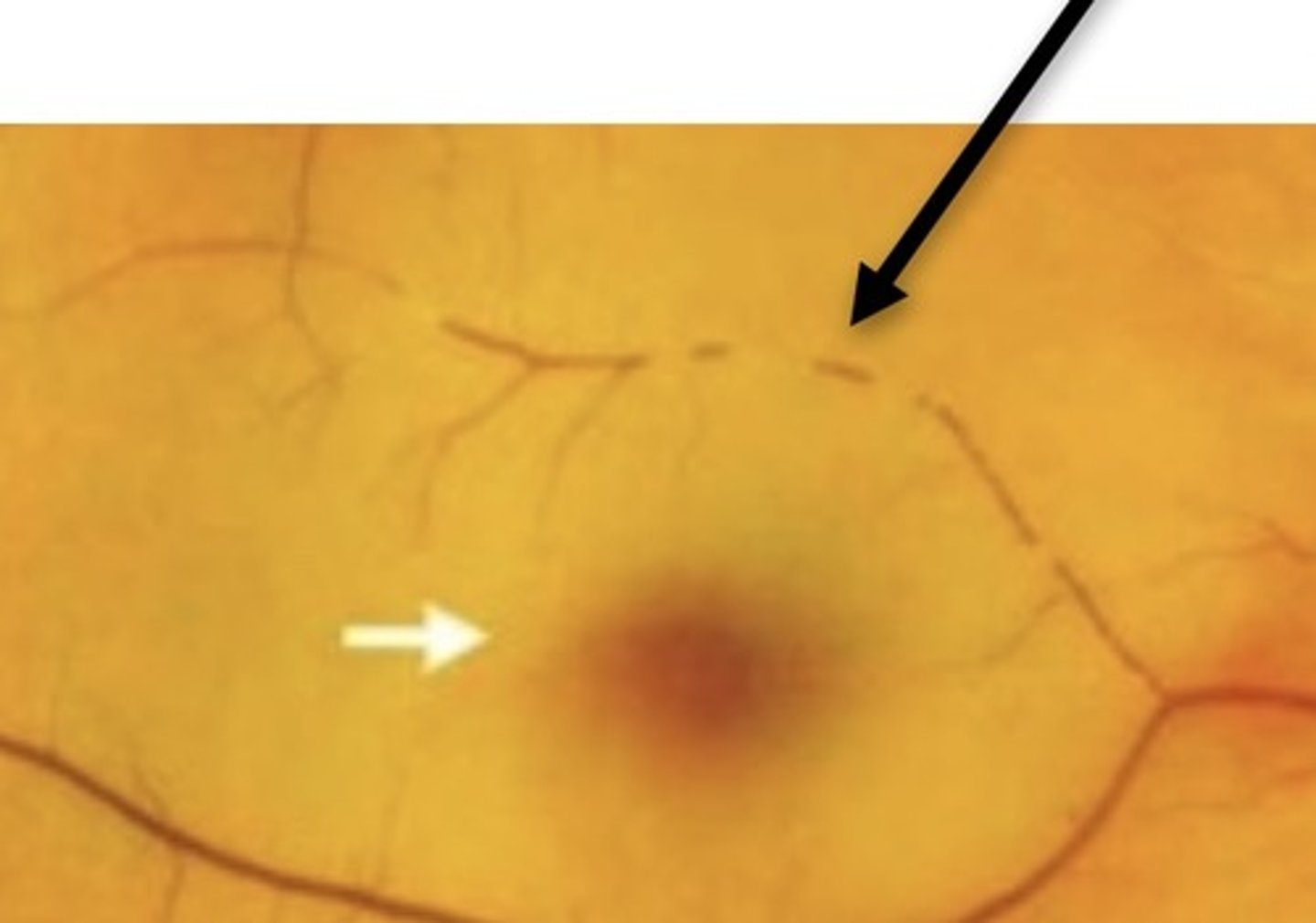
focal attenuation of arterioles
widening of venule light reflex
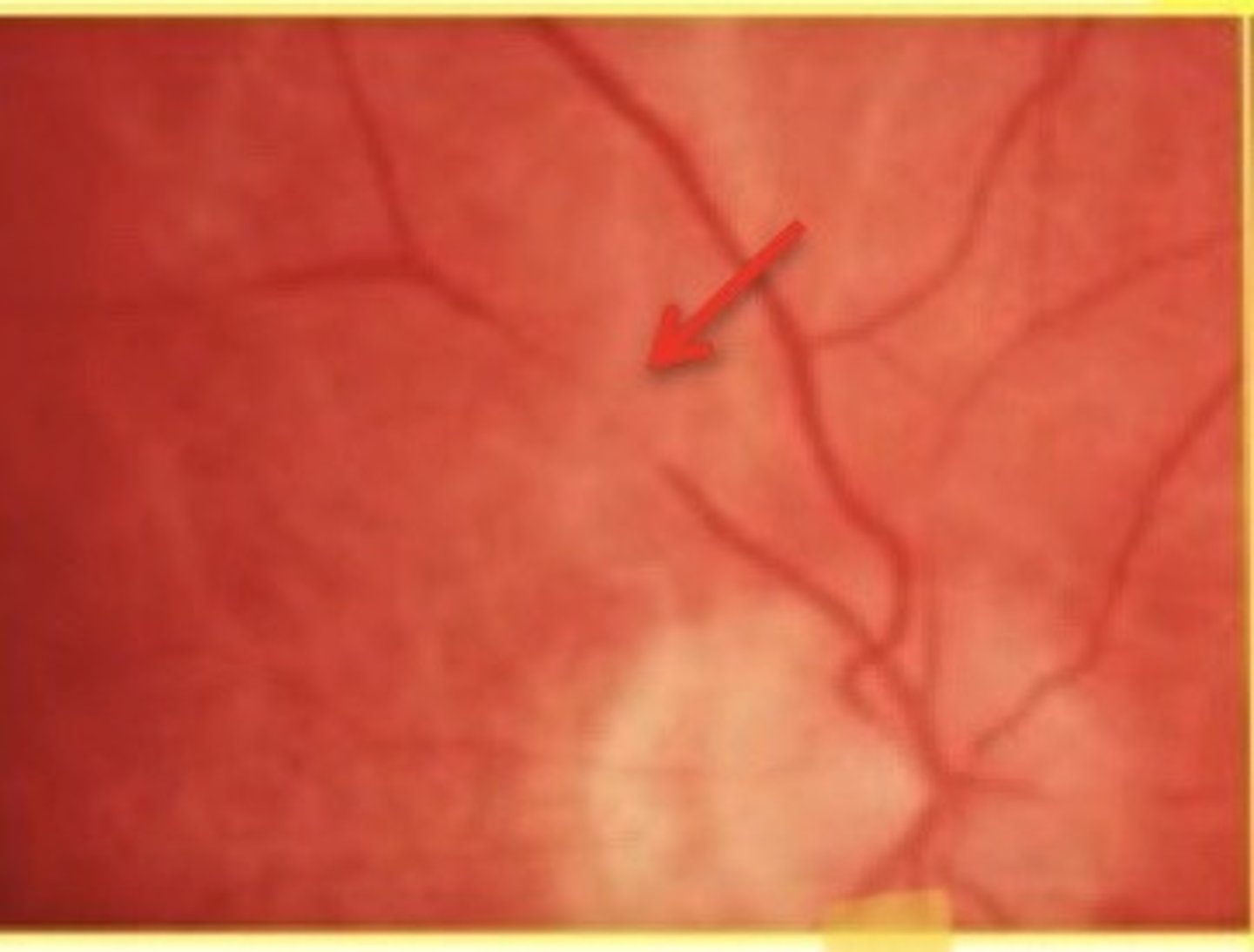
Which is more seveere copper wire light reflex or silver light reflex?
silver light reflex
nonischemic CRVO and ischemic CRVO
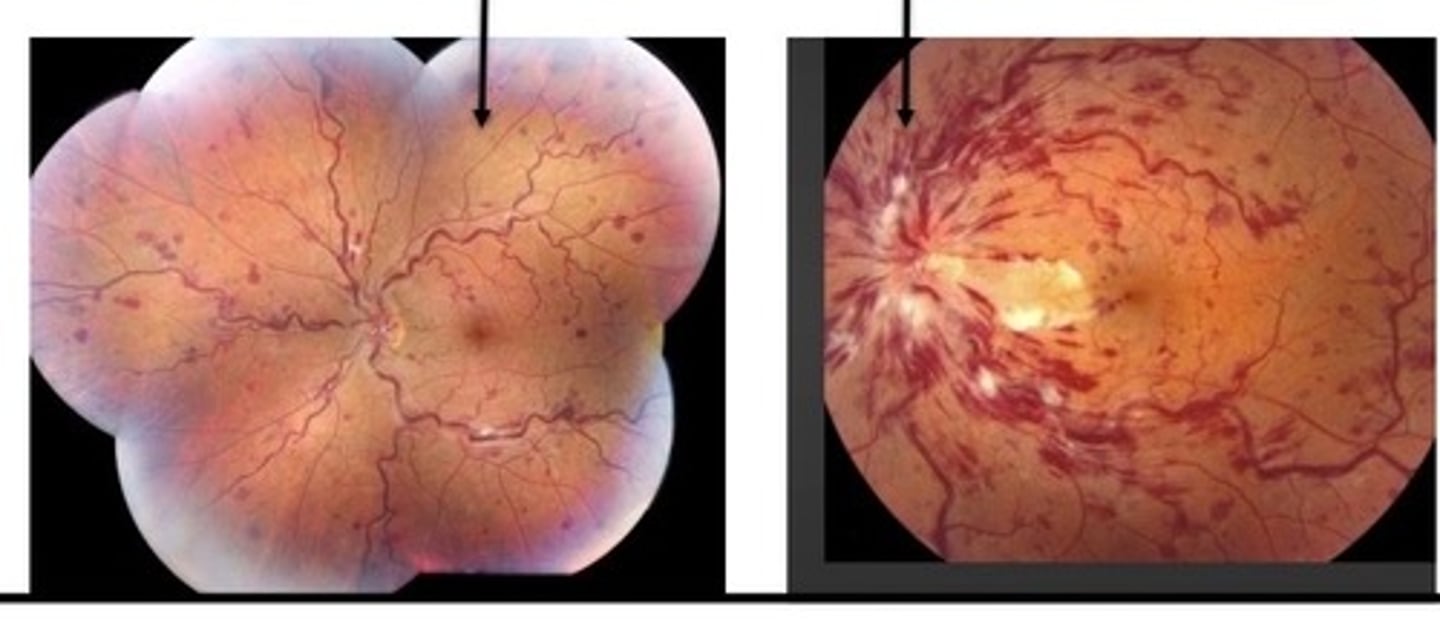
hemiretinal vein occlusion (HRVO)
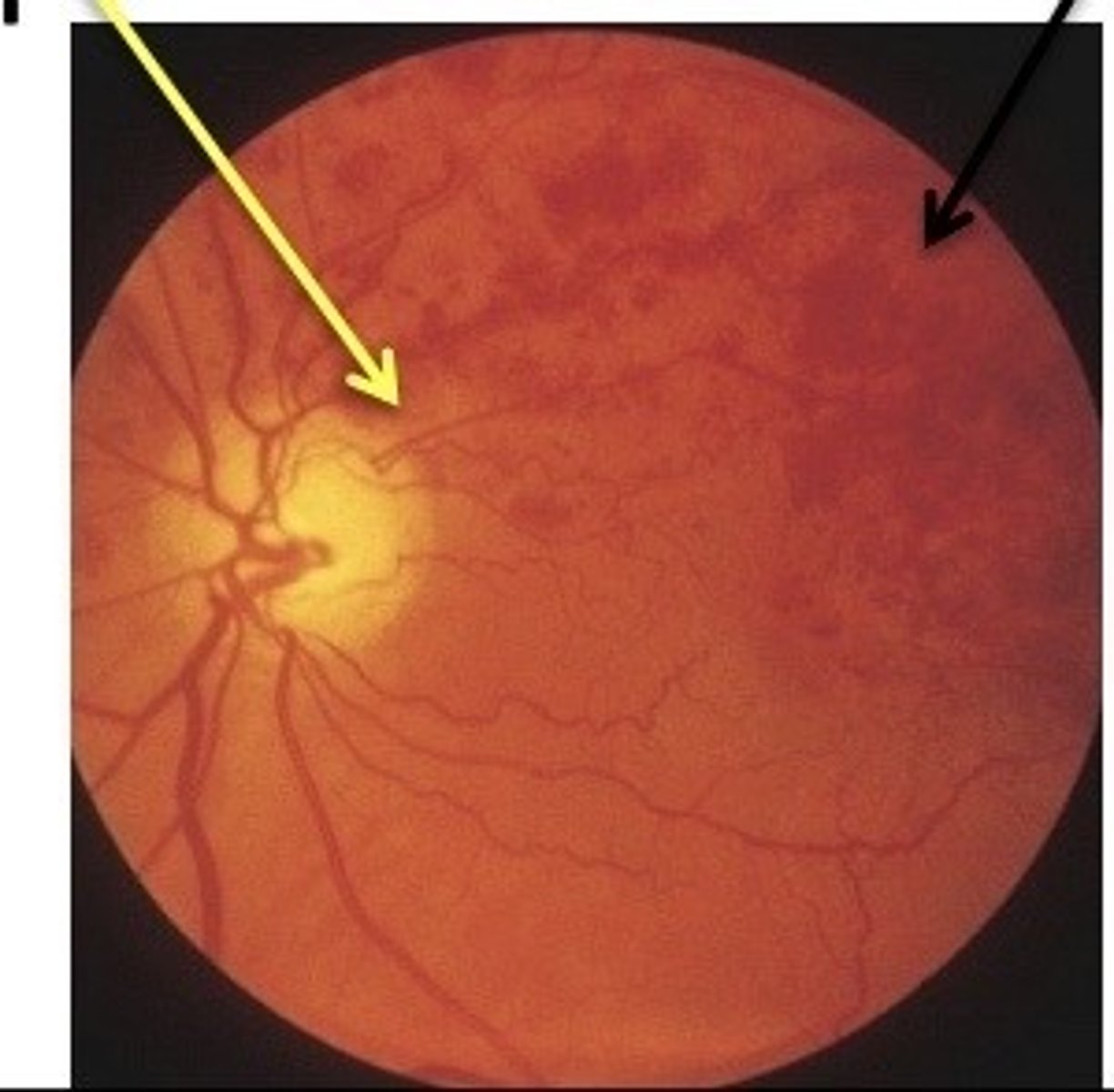
branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO)
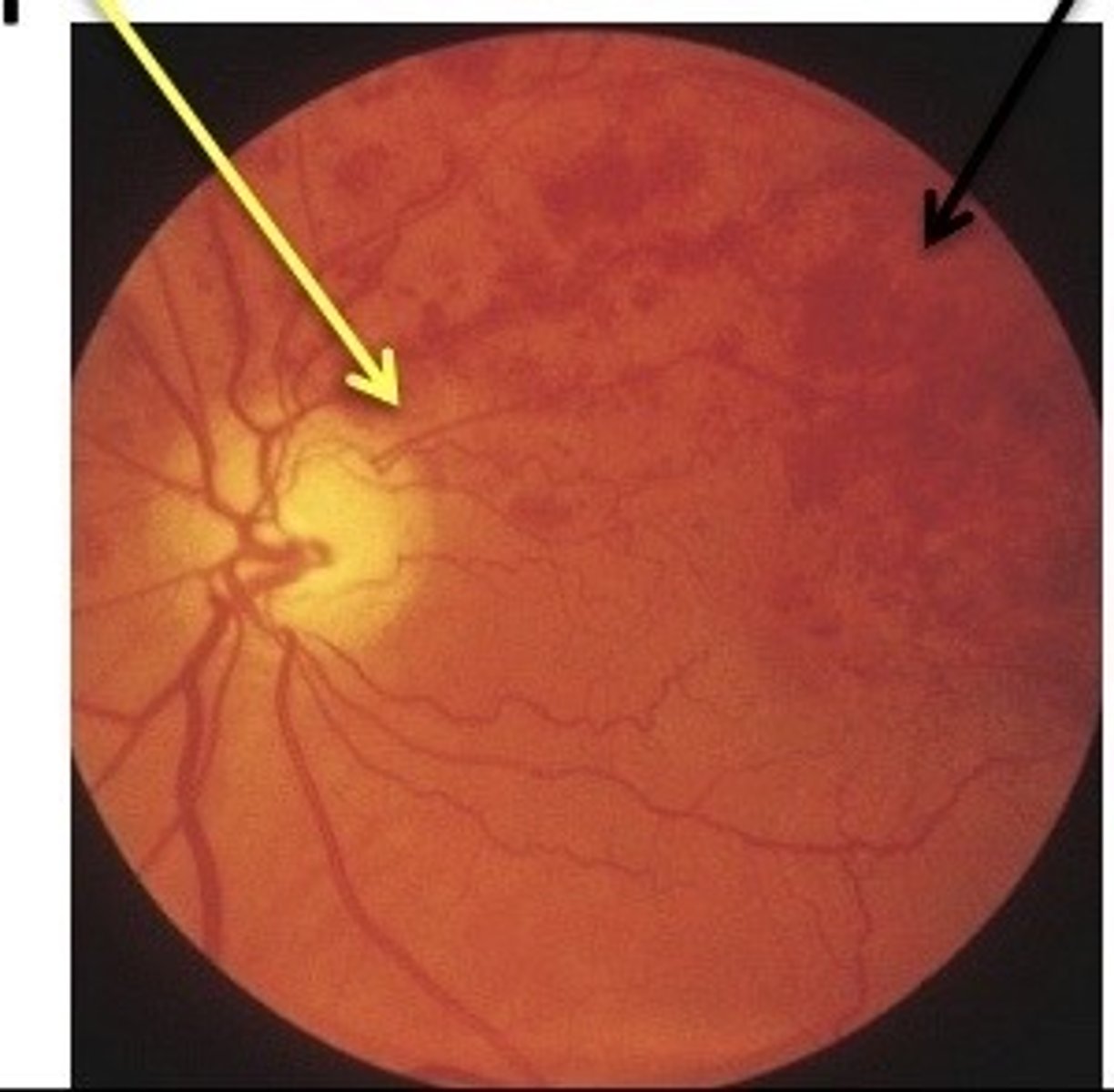
CRAO
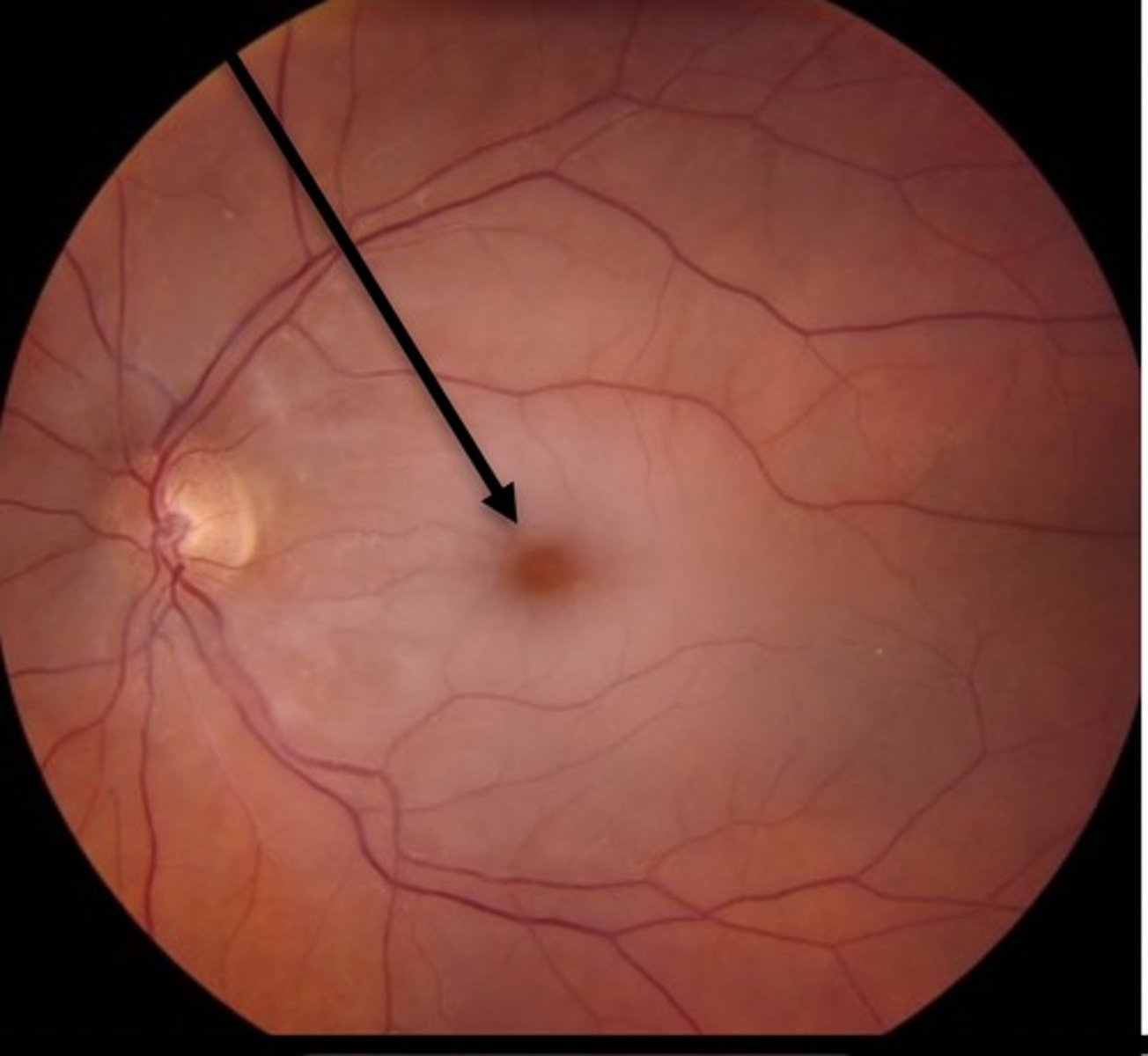
boxcarring