Chapter 23 Redox and Electrode potentials
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
define reducing agent
transfers electrons to the species being reduced
is oxidised
define oxidising agent
accepts electrons from the species being oxidised
is reduced
manganate (VII) titration method
1) standard solution of KMnO4 is added to the burette
2) pipette a measured volume of the solution being analysed to the conical flask. add an excess of dilute H2SO4 to provide the H+ ions needed for the reduction of MnO4- (aq) ions
3) end point judged by first permanent pink colour = indicating excess of MnO4- ions present
4) read the meniscus from the from the top = KMnO4 (aq) is a deep purple colour, very difficult to see bottom of meniscus
what can manganate (VII) titrations be used for the analysis of
Fe2+(aq)
(COOH)2 (aq)
KMnO4 under acidic conditions
oxidising agent reduced to form Mn2+
what are iodine/thiosulfate redox titrations used for
determining content of different oxidising reagents (ClO-, Cu2+)
equation for the reduction of iodine
I2(aq) + 2e- → 2I- (aq)
equation for the oxidation of thiosulfate ions
2S2O32- → S4O62- (aq) + 2e-
overall equation for iodine-thiosulfate titrations
2S2O32-(aq) +I2(aq) → 2I (aq) + S4O62- (aq)
analysis of oxidising agents
1) add a standard solution of Na2S2O3 to the burette
2) prepare a solution of the oxidising agent to be analysed. pipette this solution to a conical flask. add an excess a KI. oxidising agent reacts with I- ions to produce iodine
3) titrate this solution with Na2S2O3 (aq). iodine is reduced back to I- ions, brown colour fades gradually making it difficult to decide on an end point = add starch near to the end point = colour change from pale yellow to blue-black = as more Na2S2O3 is added, blue-black colour fades
define voltaic cell
a type of electrochemical cell which converts chemical energy into electrical energy
can be made by connecting together two different half-cells
define half-cell
contains the chemical species present in a redox equation
describe metal/metal ion half-cells
half-cell made by dipping a metal rod into a solution of its metal ion (aq)
represented using a vertical line for the phase boundary between the (aq) solution and the metal
at the phase boundary, an equilibrium will be set up = forward reaction shows reduction, reverse reaction shows oxidation
the direction of electron flow depends on the relative tendency of each electrode to release electrons
ion/ion half-cells
contains ions of the same element in different oxidation states
inert Pt(s) electrode used
define standard electrode potential
the emf of a half-cell compared with a standard hydrogen half-cell measured at 298K with solution concentration of 1moldm-3 and a gas pressure of 100kPa
what is the standard electrode potential of a standard hydrogen electrode
0V
diagram of a standard hydrogen electrode
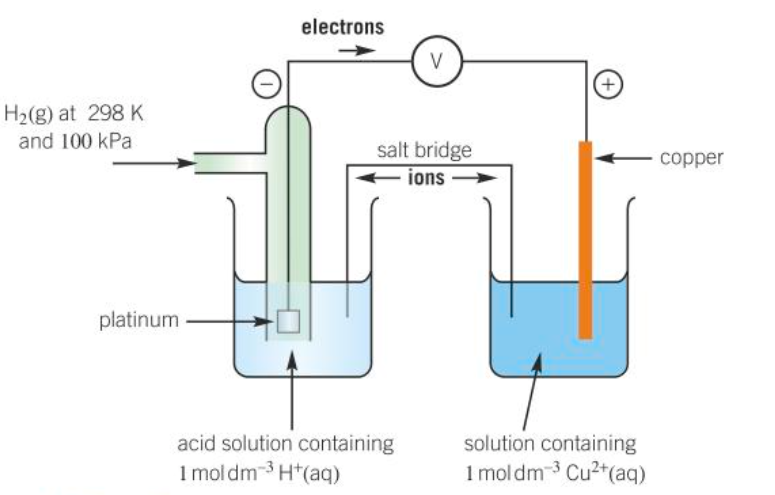
what does a salt bridge contain
a concentrated electrolyte that does not react with either solution
e.g. a strip of filter paper soaked in KNO3 (aq)
the more negative the standard electrode potential…
the greater the tendency to lose electrons and undergo oxidation
the greater the reactivity of a metal in losing electrons
the more positive the standard electrode potential…
the greater the tendency to gain electrons and undergo reduction
the greater tendency of a non-metal in gaining electrons
steps of measuring standard cell potentials
1) prepare 2 standard half-cells
2) connect the metal electrodes of the half-cells to a voltmeter using wires
3) prepare a salt bridge by soaking a strip of filter paper in a saturated solution of KNO3(aq)
4) connect the two solutions of the half-cells with a salt bridge
5) record the standard cell potential from the voltmeter
formula for calculating standard cell potential
standard electrode potential (positive electrode) - standard electrode potential (negative electrode)
the more negative redox system has the greatest tendency to…
be oxidised and lose electrons
reverse reaction
the more positive redox system has the greatest tendency to…
be reduced and gain electrons
forward reaction
how to predict feasibility of a redox reaction
redox system of the oxidising agent has a more positive standard electrode potential value than the redox system of the reducing agent
3 limitations of predictions using standard electrode potential values
1) reaction rate = electrode potentials give no indication on the rate of reaction
2) concentration = if the conc of the sol is not 1moldm-3 the value of the electrode potential will be different from the standard value
3) other factors = standard conditions required, or reactions are not aqueous
what assumption are cells and batteries based on
the two electrodes have different electrode potentials
3 types of cells
primary, secondary, fuel
describe primary cells
non-rechargeable, designed to be used once
provide electrical energy until all the chemicals have reacted
used for low-current, long-storage devices (wall clocks, smoke detectors)
describe secondary cells
rechargeable
when recharging the reactions of the cells can be reversed
used in lead-acid batteries (cars), lithium polymer cells (phones)
describe fuel cells
uses energy from the reaction of a fuel with O2 to create a voltage
operate continuously provided that the fuel and O2 are supplied into the cell
hydrogen fuel cells most common
describe hydrogen fuel cells
produce no CO2 during combustion, H2O only combustion product
a hydrogen fuel cell can have either an alkali or acid electrolyte