HA- Final Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/212
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
213 Terms
1
New cards
Digitalis (Digoxin):
- usually given to patients with congestive heart failure
- bradycardia possible: if the pulse is less than 60 beats/min, hold the meds!
- hypokalemia possible: green/yellow halos and visual disturbances = toxicity
- side effects: decreases weight, edema and HR
- bradycardia possible: if the pulse is less than 60 beats/min, hold the meds!
- hypokalemia possible: green/yellow halos and visual disturbances = toxicity
- side effects: decreases weight, edema and HR
2
New cards
Lasix (furosemide):
- loop diuretic
- patient loses potassium in the urine
- check potassium as both hypo- and hyperkalemia makes patient susceptible to heart arrhythmias
- patient loses potassium in the urine
- check potassium as both hypo- and hyperkalemia makes patient susceptible to heart arrhythmias
3
New cards
Heparin (lovenox):
- anti-coagulant
- given as a S/C injection (or given IV)
- for patient with pulmonary embolus
- improtant to check for side effects of bleeding (gums, IV areas, stools, bruises)
- given as a S/C injection (or given IV)
- for patient with pulmonary embolus
- improtant to check for side effects of bleeding (gums, IV areas, stools, bruises)
4
New cards
- protamine sulphate
Antagonist of heparin (lovenox):
5
New cards
Warfarin (Coumadin):
- often for patinets with atrial fibrilaltion (prevent emboli)
- also for patients after recieving IV heparin after pulmonary embolus
- given by mouth
- educate patient to prevent taking asparin (can increase bleeding)
- also for patients after recieving IV heparin after pulmonary embolus
- given by mouth
- educate patient to prevent taking asparin (can increase bleeding)
6
New cards
- Vitamin K
Antagonist of Warfarin (coumadin):
7
New cards
Nephrotoxic antibiotics:
- Vancomycin and Gentamicin
- can harm the kidneys
- can harm the kidneys
8
New cards
Ototoxic antibiotics:
- Aminoglycosides and Vancomycin
- can cause deafness
- can cause deafness
9
New cards
- beta blocker
What kind of drug is Propranolol?
10
New cards
Beta blockers:
- for patients with hypertension/tachycardia
- can cause severe hypertension and tachy if stopped suddenly
- can lead to bronchospasm and asthma attach in asthmatic patients
- can cause severe hypertension and tachy if stopped suddenly
- can lead to bronchospasm and asthma attach in asthmatic patients
11
New cards
Steroids:
- prednisone/cortisone
- can cause bleeding (ecchymosis) and hyperglycemia with long term use
- striae
- buffalo-hump (or fat deposit on trunk)
- can cause bleeding (ecchymosis) and hyperglycemia with long term use
- striae
- buffalo-hump (or fat deposit on trunk)
12
New cards
Subjective signs:
- perceived by the patient
- feelings, pain, sore throat, etc.
- symptom
- feelings, pain, sore throat, etc.
- symptom
13
New cards
Objective signs:
conditions observed by someone other than the patient
- hyperextension, fever, swelling, etc.
- sign
- hyperextension, fever, swelling, etc.
- sign
14
New cards
Interviewing pit falls:
- be sure nothing is in the way of a patient that can cause harm to them
- i.e. tables, chairs, rugs, etc.
- i.e. tables, chairs, rugs, etc.
15
New cards
Acute pain:
- short-term and self-limiting
- often follows a predictable trajectory, and dissipates after injury heals
- often follows a predictable trajectory, and dissipates after injury heals
16
New cards
Chronic pain:
- 6 months or longer
- Can last 5, 15, or 20 years and beyond
- Can last 5, 15, or 20 years and beyond
17
New cards
Referred pain:
- felt at a particular site but originates from another location
18
New cards
Radiating pain:
- travels from one body part to another
19
New cards
Mental Status Assessment:
- consciousness, language, mood and affect, orientation and attention, memory and abstract reasoning, through process, through content, and perception
20
New cards
Vital Signs:
- interpretation/prioritize
- temp, BP, HR, resp, o2 sat, pain
- temp, BP, HR, resp, o2 sat, pain
21
New cards
Respiratory Assessment:
- effort of respirations
- accessory muscle use
- position of patient
- chest symmetry
- chest wall shape
- auscultate and listen for adventitious sounds
- accessory muscle use
- position of patient
- chest symmetry
- chest wall shape
- auscultate and listen for adventitious sounds
22
New cards
Cardiovascular Assessment:
- auscultate at aortic, pulmonic, erb's point, tricuspid and mitral points
- assess rate and rhythm
- identify extra sounds and murmurs
- assess rate and rhythm
- identify extra sounds and murmurs
23
New cards
Peripheral Vascular System:
- Blood vessels of the body that together with the heart and the lymphatic vessels make up the body's circulatory system.
24
New cards
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD):
- blockage of arteries carrying blood to the legs, arms, kidneys and other organs
25
New cards
Peripheral Vascular disease (PVD):
- disease of blood vessels away from central region of body, most typically in legs
- symptoms include pain, numbness, and impaired circulation
- symptoms include pain, numbness, and impaired circulation
26
New cards
Pneumonia:
- infection of lower respiratory tract involving the pulmonary parenchyma
- caused by viruses, fungi, and bacteria
- caused by viruses, fungi, and bacteria
27
New cards
Pneumonia symptoms:
- chest pain when breathing/coughing, confusion or changes in LOC, phlegm with cough, fatigue, fever, sweating, shaking chills, lower than normal body temp, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
28
New cards
Atelectasis:
- alveoli or an entire lung is collapsed, allowing no air movement
- may be post-operatively due to ineffective breathing, anesthesia, pain
- tracheal deviation towards affected side
- may be post-operatively due to ineffective breathing, anesthesia, pain
- tracheal deviation towards affected side
29
New cards
Atelectasis symptoms:
- dyspnea, anxiety, tachypnea, tachycardia, coughing, chest pain, bluish skin/lips
30
New cards
Pneumothorax:
- air enters chest and lung collapses
- needs chest tube to re-inflate the lung
- tracheal deviation away from affected side
- needs chest tube to re-inflate the lung
- tracheal deviation away from affected side
31
New cards
Tracheal Deviation Away from Affected Side:
- pneumothorax, tumor, aortic aneurysm, unilateral thyroid lobe enlargement
32
New cards
Tracheal Deviation Toward Affected Side:
- large atelectasis, pleural adhesions, fibrosis
33
New cards
Incentive Spirometry:
- used to prevent pneumonia
- use 10 times every hour while awake
- use 10 times every hour while awake
34
New cards
ABCDE of skin cancer
- asymmetry
- border irregularity
- color variations
- diameter greater than 6mm
- elevation/evolution
- border irregularity
- color variations
- diameter greater than 6mm
- elevation/evolution
35
New cards
A pressure injury may occur if a patient is:
- immobile
- very sick
- can't change positions easily
- have moist skin
- poor circulation
- long term medical devices like O2
- very sick
- can't change positions easily
- have moist skin
- poor circulation
- long term medical devices like O2
36
New cards
Stage 1 pressure ulcer:
- nonblanchable erythema of intact skin
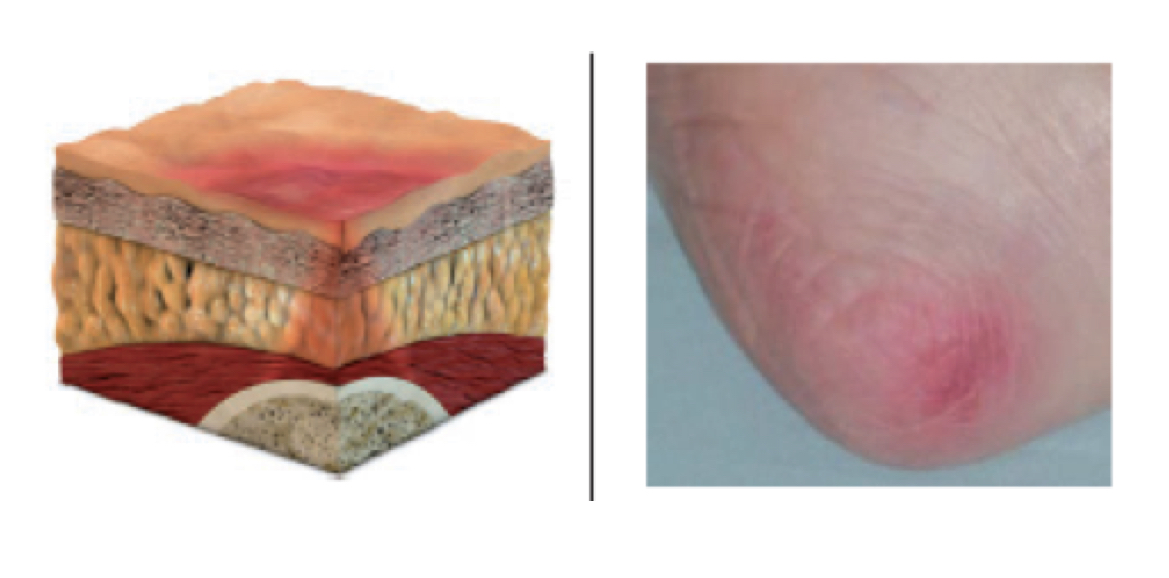
37
New cards
Stage 2 pressure ulcer:
- partial thickness skin loss with exposed dermis
- viable, pink or red, moist, intact or ruptures serum filled blister
- viable, pink or red, moist, intact or ruptures serum filled blister
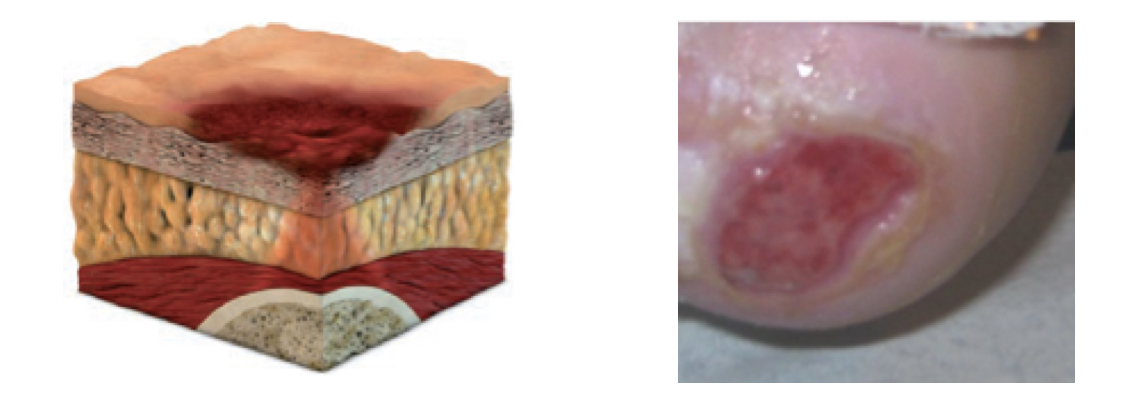
38
New cards
Stage 3 pressure ulcer:
- full thickness skin loss
- eschar may be visible
- eschar may be visible
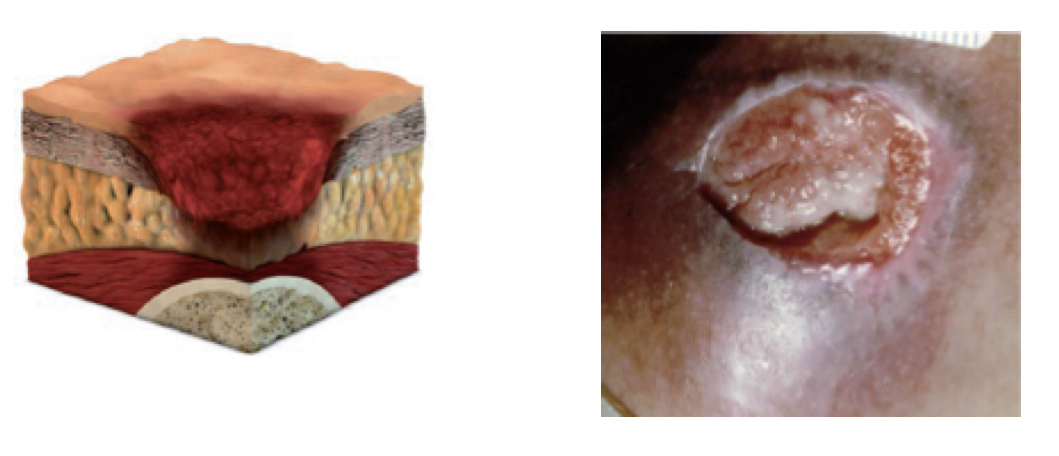
39
New cards
Stage 4 pressure ulcer:
- full thickness skin and tissue loss
- can see bone
- can see bone
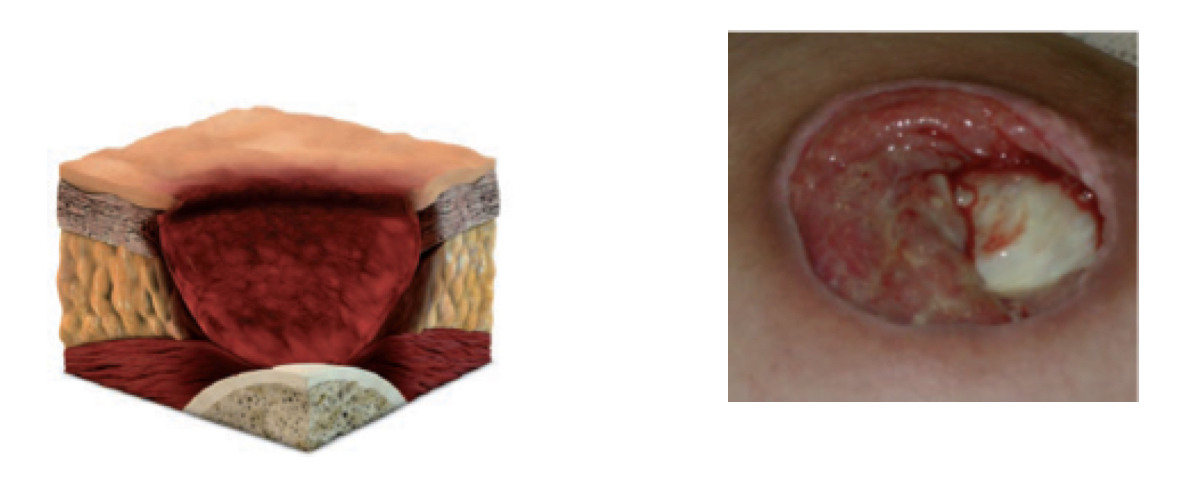
40
New cards
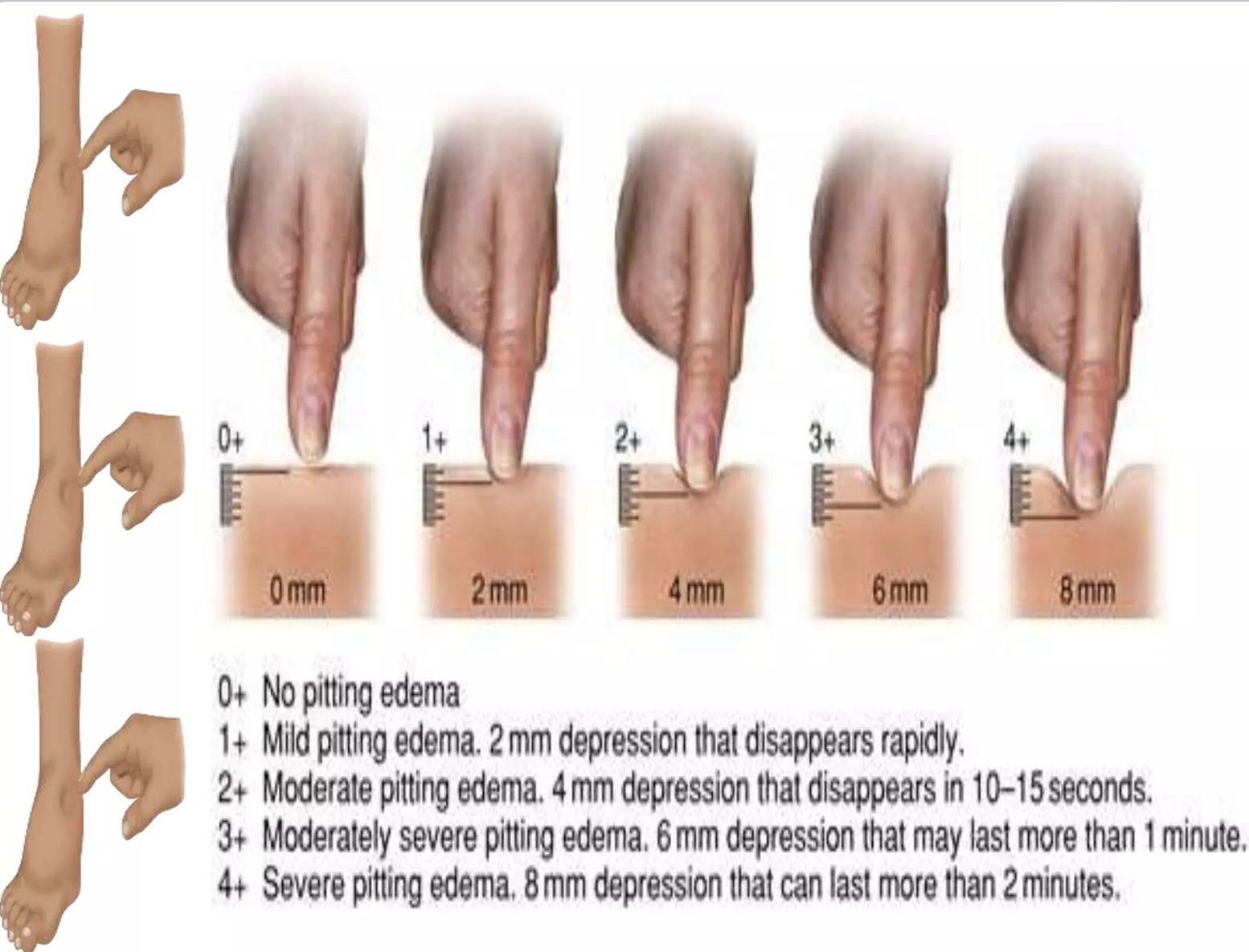
Edema Assessment:
- observe/inspect and palpate for fluid build up in tissues
- press on bony prominences you see edema in for 30 seconds and grade the indent
- scale of 0-4
- press on bony prominences you see edema in for 30 seconds and grade the indent
- scale of 0-4
41
New cards
Dehydration Assessment:
- do the skin turgor test
- slow return = dehydration
- slow return = dehydration
42
New cards
Abdominal Assessment: Inspection
- color
- vascularity
- umbilicus
- symmetry
- contour
- movements
- scars/lesions
- vascularity
- umbilicus
- symmetry
- contour
- movements
- scars/lesions
43
New cards
Abdominal Assessment: Ascultate
- begin in RLQ going clockwise listening to all 4 quadrants
- note sounds
- note sounds
44
New cards
Normal bowel sounds:
- high-pitched, gurgling, cascading, irregular
- 5-30 per minute
- 5-30 per minute
45
New cards
Borborygmus bowel sounds:
- loud, gurgling sounds made by the movement of gas through the intestines
46
New cards
Hyperactive bowel sounds:
- loud, high-pitched, rushing, tinkling sounds that signal increased motility
47
New cards
Hypoactive bowel sounds:
- slow, decreased sounds
48
New cards
Absent bowel sounds:
- no sounds in 3-5 minutes
49
New cards
Abdominal Assessment: Percussion
- Percuss lightly over each of the four quadrants
- Normal finding: tympany
- Abnormal: dullness
- Normal finding: tympany
- Abnormal: dullness
50
New cards
Tympany in abdomen
- indicates air
51
New cards
Dullness in abdomen:
- occurs over a distended bladder, adipose tissue, fluid, or a mass
52
New cards
Hyperresonance in abdomen:
- after severe diarrhea
- gaseous distention
- gaseous distention
53
New cards
Abdominal Assessment: palpitation
- light 1cm
- deep 5-8cm
- deep 5-8cm
54
New cards
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD):
- Painful burning feeling in the middle of chest behind breastbone towards throat
- Regurgitation or stomach contents coming back up through esophagus into throat and mouth
- Regurgitation or stomach contents coming back up through esophagus into throat and mouth
55
New cards
GERD symptoms:
- chest pain
- nausea
- problems swallowing
- pain when swallowing
- heart burn
- regurgitation
- nausea
- problems swallowing
- pain when swallowing
- heart burn
- regurgitation
56
New cards
Peptic Ulcer:
- open sore in the lining of the stomach or duodenum
- casued by helicobacter pylori and longterm use of NSAIDS
- can result in bleeding which is life threatening
- casued by helicobacter pylori and longterm use of NSAIDS
- can result in bleeding which is life threatening
57
New cards
Gastric Ulcer:
- pain occurs on an empty stomach
58
New cards
Duodenal Ulcer:
- pain occurs every 2-3 hours after a meal
- may be relieved by eating more food
- may be relieved by eating more food
59
New cards
Ascites:
- accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity
- fluid wave test
- decreased albumin production -> less osmotic pressure
- fluid wave test
- decreased albumin production -> less osmotic pressure
60
New cards
- once a month 3-5 days after menses
When to do a self breast exam?
61
New cards
- size, shape, contour and symmetry
What to note during a self breast exam?
62
New cards
During a breast examination, we inspect the skin for:
- color, pigmentation, vascularity, surface characteristics and lesions
63
New cards
During a breast examination, we inspect the areolae for:
- color and surface characteristics
64
New cards
During a breast examination, we inspect the nipples for:
- position, symmetry, surface characteristics, lesions, bleeding, and discharfe
65
New cards
Confrontation Test:
- Client sits facing examiner 2ft away, eyes should be at the same level, both cover eyes directly opposite of each other and stare at each other's uncovered eye; bring small object into peripheral visual field and test the superior, temporal, inferior and nasal field; have client state when they see object
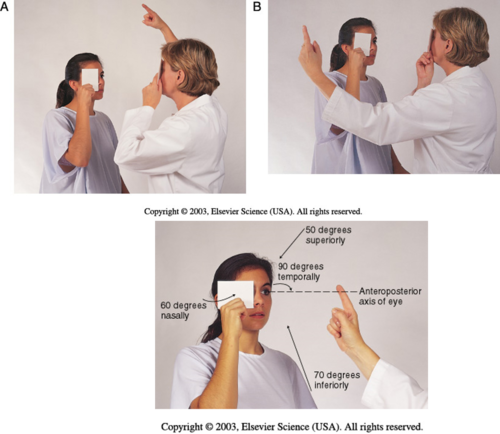
66
New cards
6 cardinal fields of gaze:
- Use finger through 6 positions of gaze to assess for eye movement related to cranial nerves III, IV, and VI
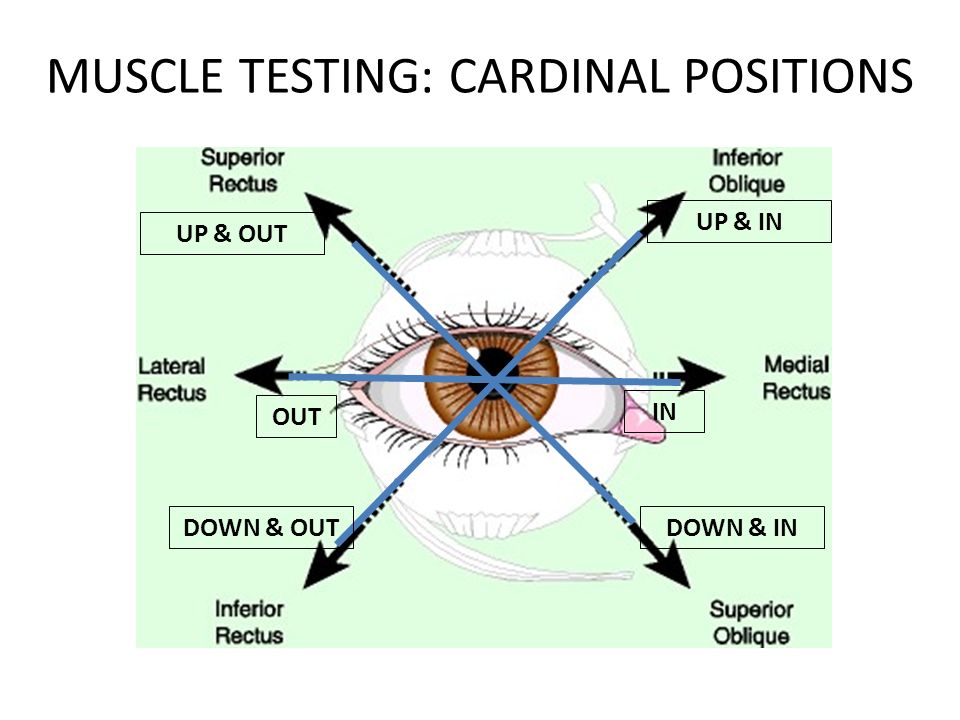
67
New cards
Snellen test:
- Tests for visual activity and if cranial nerve II is intact
- Test with glasses first then without
- Start with right eye, then left, then both
- Test with glasses first then without
- Start with right eye, then left, then both
68
New cards
PEERLA:
- pupils equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation
69
New cards
Glaucoma:
- increased intraocular pressure leading to loss of peripheral vision

70
New cards
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD):
- loss of central vision

71
New cards
Diabetic Retinopathy:
- damage to blood vessels in retina
- causes blindness and black spots in vision
- causes blindness and black spots in vision

72
New cards
- pull the pinna up and back
How to place an otoscope in an adult?
73
New cards
- pull the auricle down and back
How to place an otoscope in a child?
74
New cards
Normal tympanic membrane:
- pearly gray, shiny, translucent
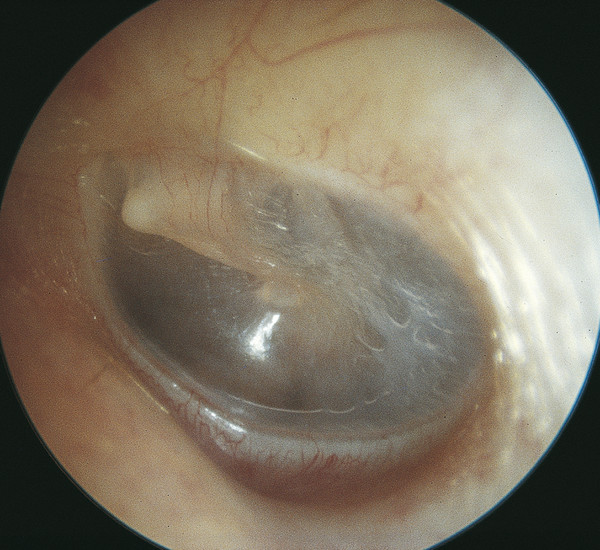
75
New cards
Abnormal tympanic membrane:
- lesions, edema, erythema, tenderness, blue/pink-red
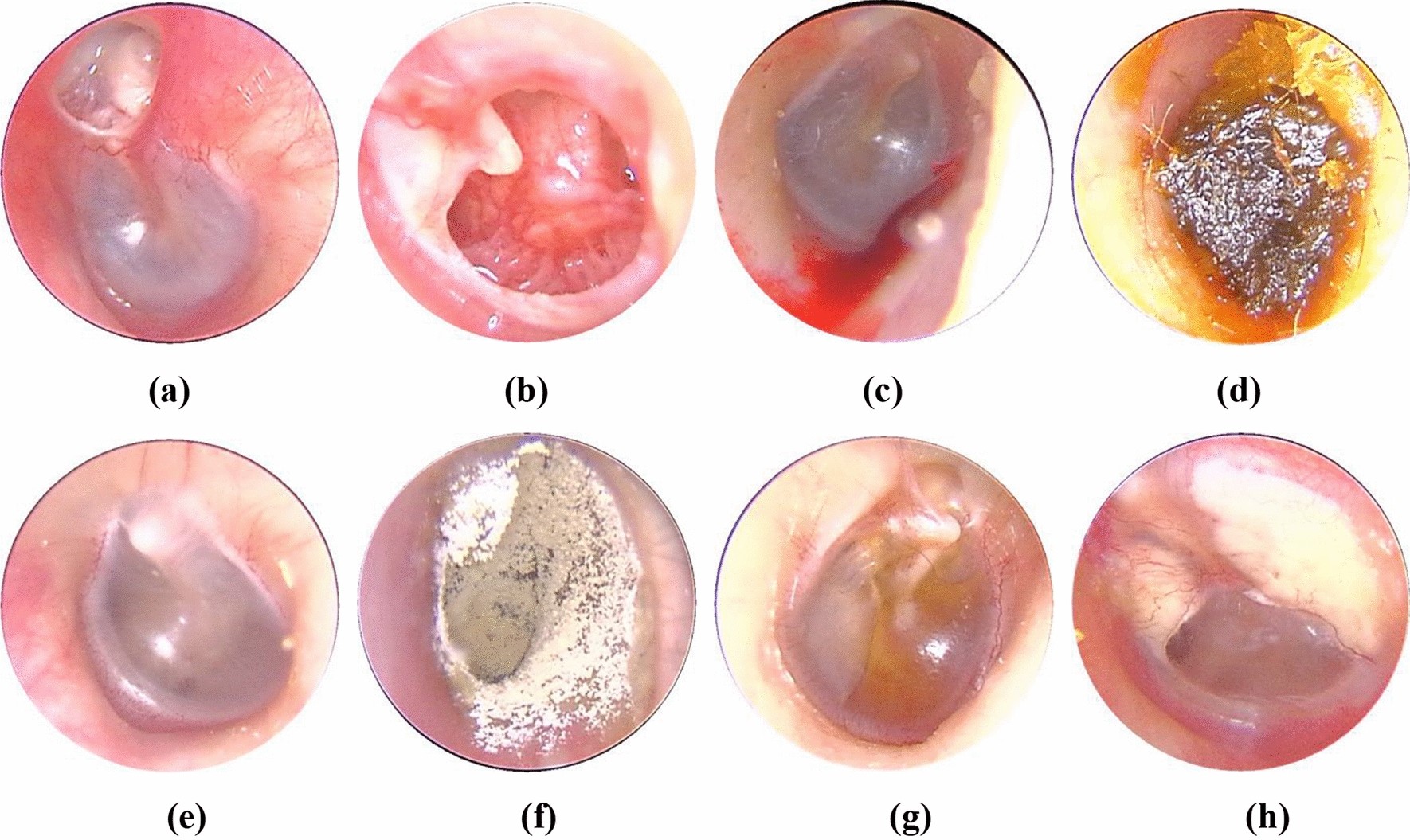
76
New cards
Hearing loss can be caused by:
- age
- antibiotic use
- trauma
- obstruction
- prolonged exposure to loud sounds
- antibiotic use
- trauma
- obstruction
- prolonged exposure to loud sounds
77
New cards
Whisper test (CN VIII)
- stand 1-2 feet away from client; ask them to block 1 external ear canal; whisper a statement and ask client to repeat it
78
New cards
The Central Nervous System consists of:
- the brain and spinal cord
79
New cards
The Peripheral Nervous System consists of:
- the cranial nerves and spinal nerves
80
New cards
- frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital
What are the lobes of the cerebrum?
81
New cards
What does the frontal lobe control?
- smell
- speech
- concentration
- planning
- problem solving
- motor control
- speech
- concentration
- planning
- problem solving
- motor control
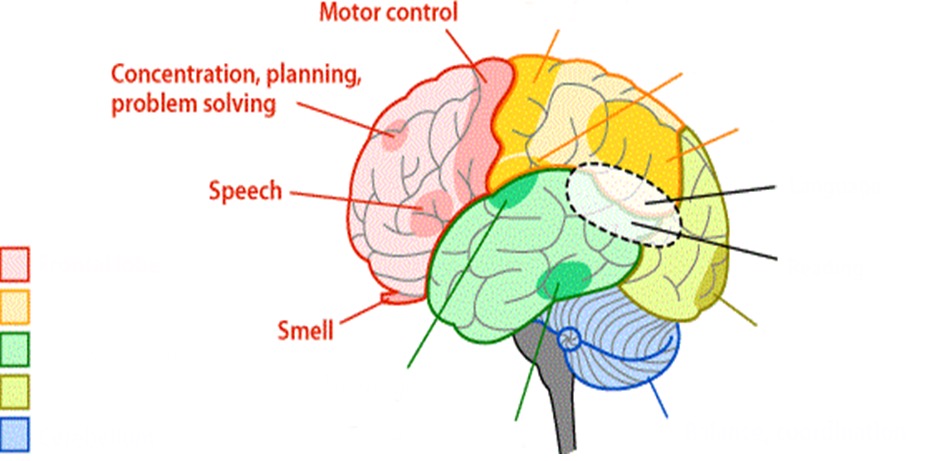
82
New cards
What does the occipital lobe control?
- vision
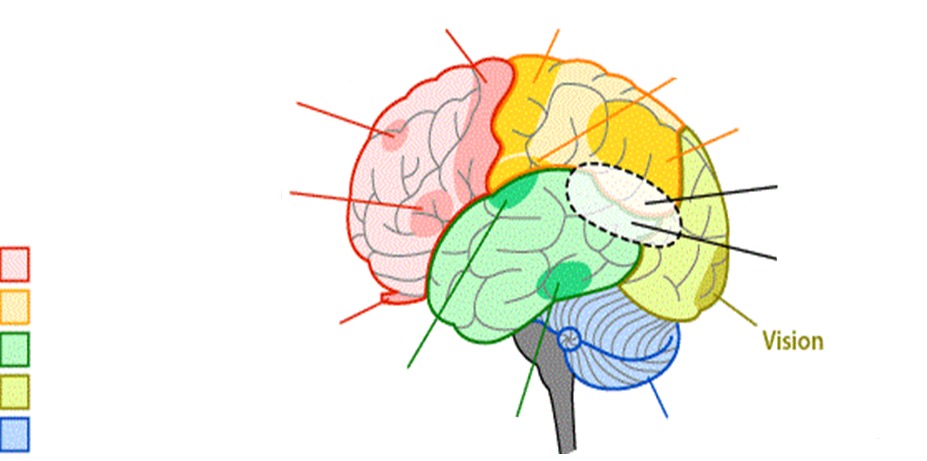
83
New cards
What does the parietal lobe control?
- touch and pressure
- taste
- body awareness
- taste
- body awareness
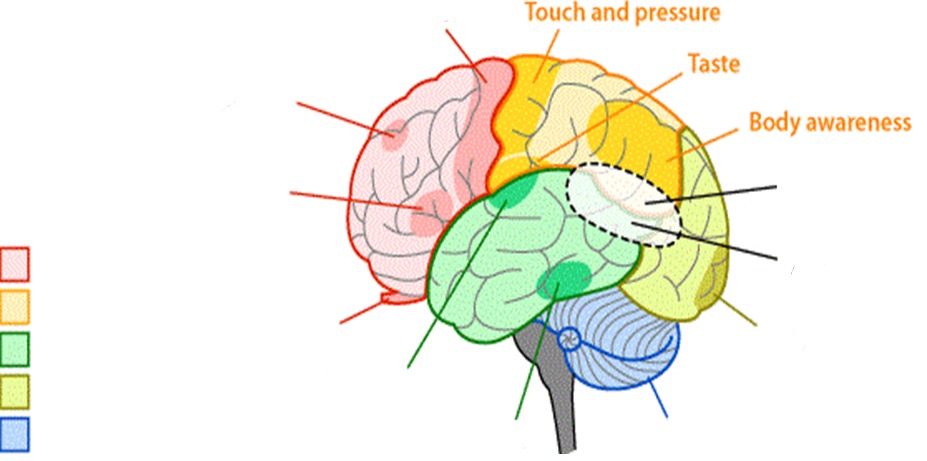
84
New cards
What does the temporal lobe control?
- hearing
- facial recognition
- facial recognition
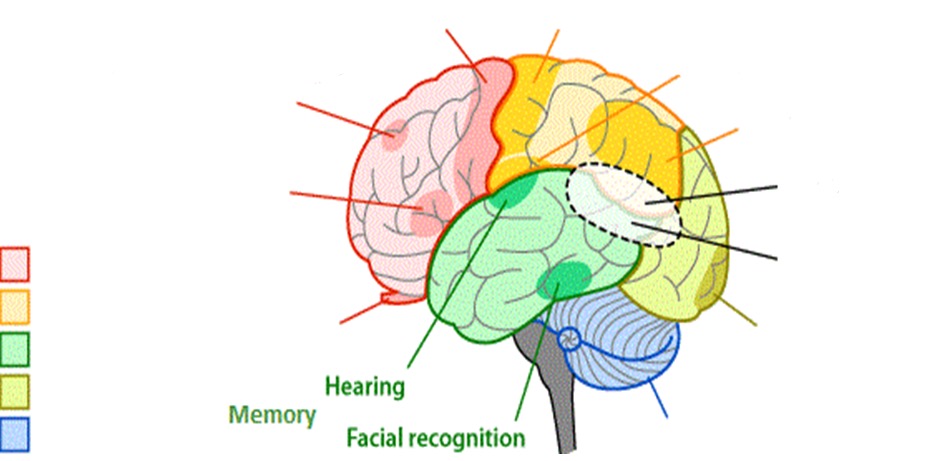
85
New cards
What does the cerebellum control?
- balance and coordination
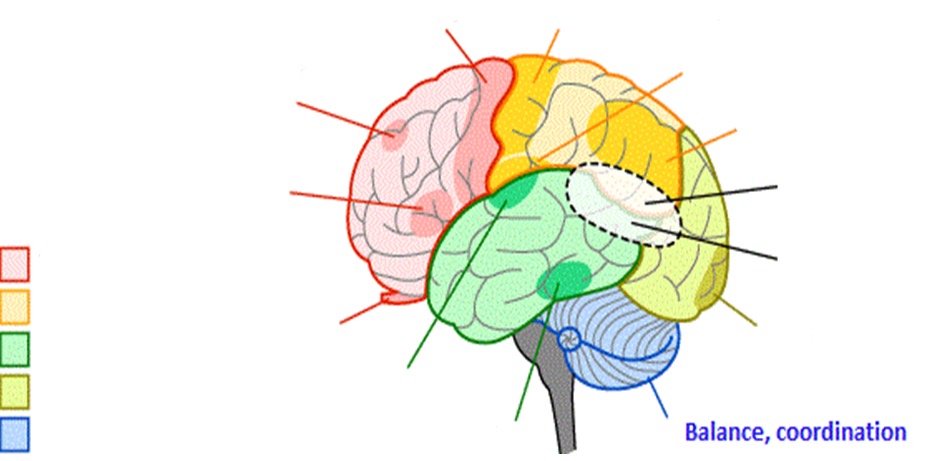
86
New cards
- the left frontal lobe
Where is Broca's area located?
87
New cards
- the left temporal lobe
Where is Wernicke's area located?
88
New cards
Broca's aphasia:
- inability to produce speech
- Broken words, Motor, Frontal lobe (Bad Mother F*****)
- Broken words, Motor, Frontal lobe (Bad Mother F*****)

89
New cards
Wernicke's aphasia:
- inability to comprehend speech
- Wacky words, Sensory, Temporal lobe (Want Some Tea?)
- Wacky words, Sensory, Temporal lobe (Want Some Tea?)

90
New cards
Proprioception:
- the sense of body position
91
New cards
- Ask patient with eyes closed while you move a thumb or toe and ask patient what way its going
How do we assess proprioception?
92
New cards
Lethargic:
- in a state of sluggishness or apathy
93
New cards
Obtunded:
- state in which the patient has a lessened interest in the environment, slowed responses to stimulation, and tends to sleep more than normal with drowsiness in between sleep states.
94
New cards
Stupor:
- state of near-unconsciousness or insensibility
95
New cards
Coma:
- state of profound unconsciousness
96
New cards
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
- a scale used to assess the consciousness of a patient upon physical examination, typically in patients with neurological concerns or complaints
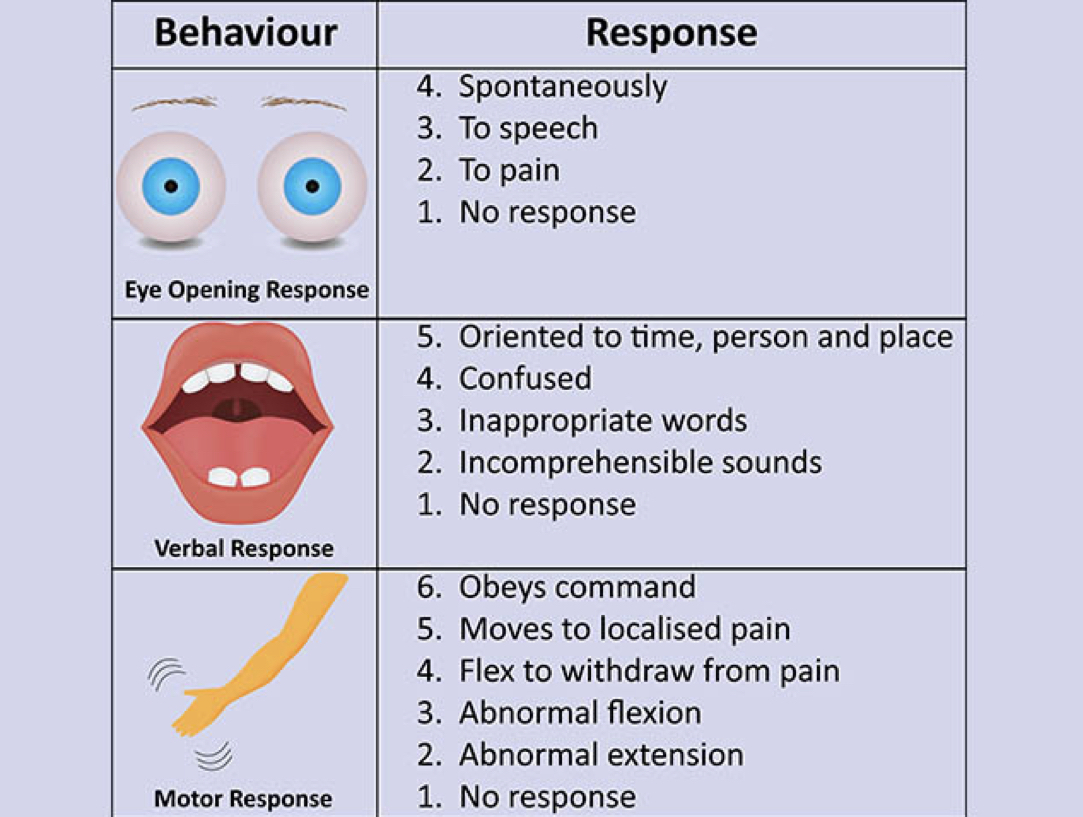
97
New cards
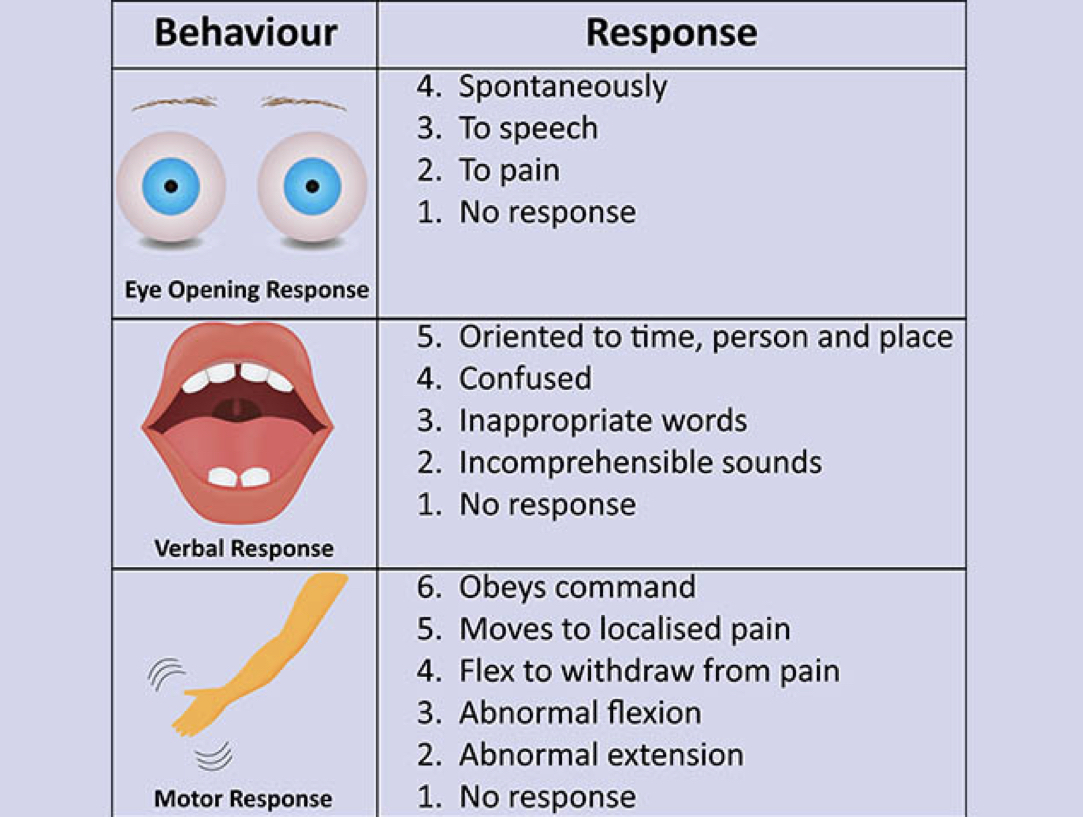
- 15 possible points
- GCS of 3-8 = severe
- GCS of 9-12 = moderate
- GCS of 13-15 = mild
- GCS of 3-8 = severe
- GCS of 9-12 = moderate
- GCS of 13-15 = mild
How to use the Glasgow Coma Scale
98
New cards
Sympathetic response:
- fight, flight, fright
99
New cards
Parasympathetic response:
- rest and digest
100
New cards
If sympathetic dominant, what would be the pulse rate, BP, and pupil size?
- increased pulse
- increased BP
- dilated pupils
- increased BP
- dilated pupils