biology unit 5 - body systems
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
endocrine system
insulin - beta cell of pancreas - decrease blood glucose
glucagon - alpha cell of pancreas - ^ blood glucose
blood glucose regulation
low blood glucose - a-cell secrete glucagon into bloodstream - reach liver. Blood glucose ^ - glycogen hydrolysed into glucose
high blood glucose - bcell secrete insulin into blood - reach liver. Blood glucose lowers - liver stores excess glucose as glycogen
control of blood glucose level - consequence if they arent maintained
a. homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment
b. the pancreas produces hormones that control the levels of glucose
c. if glucose levels in blood are high, beta-cells of pancreas produce insulin
e. liver stores excess glucose as glycogen
f. if glucose levels in blood are low, alpha-cells of the pancreas produce glucagon
g. Glucagon causes the liver to break down glycogen into glucose, increase levels of glucose in the blood
i. negative feedback controls the glucose levels
consequences:
j. if the pancreas produces little/no insulin a person can develop type I diabetes
k. dependent on injections of insulin
l. type II diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin
m. type II diabetes can be controlled by diet and exercise ✔
temperature change detected by
thermoreceptors
thermoregulation
heat &cold
Detected by hypothalamus Thyroid gland secretes less thyroxin Effects: 1. Vasodilation Blood arterioles dilate, more blood pass near skin surface to radiate off heat 2. Sweating - sweat droplets will absorb body heat to evaporate 3. Hair erectile muscles relax, hair lies flat 4. Reduced metabolic rate 5. Reduced cell respiration in brown adipose tissue (BAT) | Detected by hypothalamus Thyroid gland secretes more thyroxin Effects: 1. Vasoconstriction Blood arterioles constrict, blood pass beneath the fat layer to insulate heat 2. Shivering - this causes muscle contraction; cells respire more to produce heat. 3. Hair erectile muscles contract, hair stays upright 4. Increased metabolic rate 5. Increased cell respiration in brownadipose tissue (BAT) |
brown adipose tissue
Cellular respiration normally produces heat as a byproduct.
Mitochondria in brown adipose tissue are able to uncouple cellular respiration from ATP synthesis.
Glucose can be broken down only for heat generation.
kidney function
excretion : removal of body waste from metabolic pathways
osmoregulation : control of water balance of blood , tissue/cytoplasm
nephron structure
glomerulus - site of ultrafilatration - molecules filtered based on size
afferent, efferent arteriole ( afferent wider → increase pressure)
bowsman capsule - ultrafiltration
proximal convoluted tubule - selective reabsorption
loop of henle- establish a salt gradient in mendulla
diastle tubule -final site for reabsorption of water&salt
collecting duct - site of osmoregulation
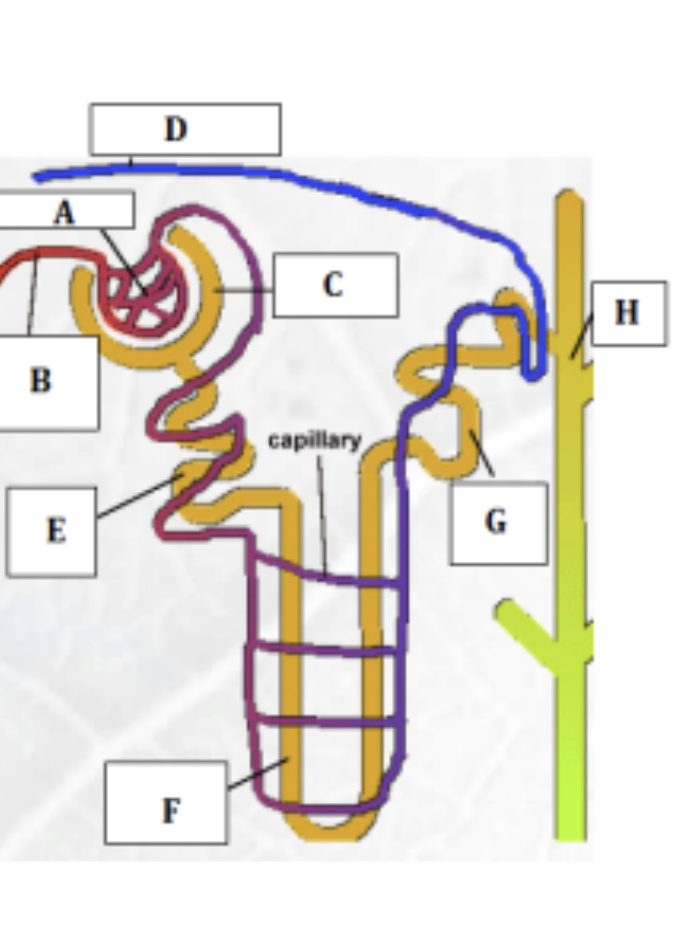
nephon role in kidney
ultrafiltration
reabsorption
excretion
ultrafiltration
Separating substances based on size with the help of blood pressure.
Plasma escapes from blood capillaries in glomerulus into the Bowman’s capsule due to:
1) Very high blood pressure : efferent arterioles are narrower than the afferent arterioles
2) Large pores in the capillary walls
allow any molecules to pass through but there are two filters beyond the pores that only small to medium sized particles can pass through.
Basement membrane – a gel on the outside of the capillary, with small gaps through a mesh of protein fibres
Filtration slits – narrow gaps between the foot, possess of podocyte cells where they wrap around the capillaries
filtrate contains all substances in blood plasma except plasma proteins
selective reabsorption
in proximal convoluted tubules (PCT)
glucose,amino acid, hormones, mineral , water - reabsorpted here
PCT: microvili cell lining - ^ SA for reabsorption of filtrate
mitochondria : reabsorption is active transport
reabsorbed in tubule cell - passive diffusion down the bloodstream
some minerals and vitamin active transport via protein pump/carrier protein
glucose active transported across membrane in symport of sodium
water - osmosis
establish salt concentration in loop of henle
loop of henle
ascending limb: impermeable to water, permeable to salt
desending limb: permeable to water, impermeable to salt
upper region: pumps out Na+ active transport - ^ ion concentration outside. → ^ solute potential, decrease water potential outside
water move out of descending limb by osmosis
movement of water → makes fluid in descending limbmore concentrated as it move down to bottom region → increase concentration of Na and Cl , results in even more Na+ moving out of bottom of ascending limb
salt concentration greater in bottom region
→maintains a hypertonic environment
osmoregulation - ADH ( dehydration)
hypertonic medulla- draws water from osmosis
ADH hormone released by posterior pituitary gland in response to dehydration
ADH ^ permeability of collecting duct to water , allowing more water reabsorbed by osmosis via aquaporin
less water remain in filtrate - urine more concentrated
individual is rehydrated, ADH level decrease, less water absorb in collecting duct
emergent property- cheetah
flexible spine : spring during running - increase stride length
longer hind limb : enable longer stride
cerebrum
biggest part in the brain , two halves - cerebrum hemispheres
→ advance mental activity
consist of of 5 idiffernet part
corpus callosum ( band connect two cerebrum hemisphere)
frontal(learning) , temporal( auditory) , parietal (sensory) and occuptal (visual) lobes
spinal cord responsible for
unconscious processing
input of CNS
input
Changes in the external or internal environment → detected by receptors, sensory neuron convey signal → CNS
swallowing of good, Egestion - CNS
role of cerebellum
receive information from cerebrum, spinal cord, brainstem
cerebrum motor cortex receive movement
movement begins, cerebellum receive feedback impluses from various area of body - sent out impluse to coordinate movement and time
walking, hand movement…
hypothamus and pituitary gland
hypothamuls maintain homeostasis -. lining endocrine system to nervous system
respond to signal by inhibit/stimulate pituitary gland
nuclei in hypothalamus - control release of hormones in pituitary gland
melatonin
circadian rhythm ( 24hr of physical, behavioural and mental) → set by SCN cells in hypothalamus → controls secretion of serotonin in pineal glands
light inhibit secretion, night secretion ^ , decreases by age
→adjusted by exposure of light
cell in retina detect light - send neural impluse to SCN - adjust timing of release of metatonin
epinephrine
flight or fight response
Prepare body for vigorous, immediate response with intense muscle contractions.
secreted by adrenal glands
peristalsis control
wavelike contractions of smooth muscle → peristalsis
Swallowing and egestion are voluntary actions controlled under the CNS.
Peristalsis is an involuntary action controlled by the (ENS)
ensure material through gut is coordinated
stretch receptors in gut - detect position + direction of movement of bolus
various excitatory& inhibitory neurotransmitter - released on longitudinal+circular muscle around bolus - coordinate contraction
trophic
the turning of all or part of an organism in a particular direction in response to an external stimulus.
ex. shoot grows towards light - positive phototrophism
root bend away from light - negative phototropism
Phytochromes
plant hormones that regulate physiological processes in plants.
phytochromes example
auxin
growth hormone
produced in shoot apical meristem
cell elongation for tropic movements + inhibit growth of lateral buds- vertical elongation
cytokinins
promote cell division
abundant in growing tissue
produced in root , pass to leaves and fruits
promote cell division, differentiation of meristem
auxin
produced in tip of stem, promote cell elongation
tropic movement in plants - auxin uneven distribution
move away from light stimulus
sun on top
diffuse evenly - all cell grow at same rate
shoot grow vertically upwards
sun on side
auxin molecules move towards shaded side of shoot , away from light
^ concentration on auxin - rapid cell elongation + growth on that side
uneven growth , cause stem bend towards light source
phototrophism
the turning of plant in one direction in response to external stimuli
phototrophism in auxin - auxin gradient
Auxin is produced at the apex (tips) of the shoot.
When light in the shoot is detected → trigger movements of auxins by active transport by auxin efflux pumps
Efflux pump pumps auxin from cytoplasm→ cell wall, diffused to the next cell.
enters the cell→ auxin is trapped inside the cytoplasm until the efflux pump pumps it out again.
Auxin efflux pumps→ move in response to differences in light intensity→ creating a concentration gradient of auxin from lower on the lighted side and higher in the shaded side.
phototrophism in auxin - elongation of cell
Plant cells contain auxin receptor. Auxin binds→ transcription of the genes for proton pump
Expression of these genes → the secretion of hydrogen ions into the cell wall.
hydrogen bonds between cellulose , weakened, loosens the cell wall.
expansion of cell due the increase water uptake and higher turgor pressure.
auxin and cytokinin work together
Auxin is produced in the shoot and cytokinin is produced in the root.
Both areas are growing regions of the plant.
Auxin is responsible for cell elongation, cytokinin is responsible for cell division.
Both phytochromes needs to be transported to the opposing growth regions → regulate the growth of all parts of the plant and integrate both signals.
Cytokinin is transported through xylem up the plant and auxin is transported through phloem down the plant.
Together, the phytohormones work on meristems to integrate cell growth
The ratio of the two determines whether it results in:
Synergism - work together to stimulate a process
Antagonism - have opposing effects to regulate a process
fruit ripening - feedback control
Positive feedback: the amplification of response to a stimulus
Ethylene (Ethene) is produced in ripping fruits.
Once the ripening process starts, fruit produces more ethene.
one fruit started to produce ethen → cause surrounding fruit to ripen and produce even more ethene.
This helps fruits to become more attractive to herbivores→ increasing the seed dispersal rate
skeleton (2)
exoskeleton ( chitin )
endoskeleton ( bones)
joint (2)
hinge joint ( elbow and knee)
one plant of movement
bend & straight
ball and socket joint ( hips, shoulder)
large range of movement
protraction, retraction , abduction, adduction , rotation
measure joint
goniometer
most allowing movement joint
synovial joint - human hip joint
Bone (Femur & Pelvis) | Cartilage | Synovial fluid | Ligaments | Muscles | Tendons |
function
bone- anchorage for muscle & ligants, guide movement
muscle - provide force for movemet
cartilage - smooth connective tissuet that covers the end of bone to reduce friction
synovial fluid - lubricate joint reduce friction
ligaments - slight elastic tissue - attaches bones to bones
tendons - non elastic tissue - attaches muscle to bone
skeletal muscle
attacth bones - cause movement of animal body
It consists of large multinucleated cells called muscle fibers.
There are also mitochondria between the myofibrils.
level of organisation
muscle fibres → myofibris → microfillaments → sacromere
wra around myofibrils
sacroplamatic reticulum
skeletal muscle & electrical impluse
Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles that requires electrical impulse from the brain.
Electrical impulse sent from brain through motor neuron → neuromuscular junction.
Each motor neuron has a set number of muscle fibers that it control called a motor unit.
motor unit + function
contraction of skeletal muscle
include single motor neuron & muscle fibres
muscle fibre contract when stimulated by motor neuron
stimulus pass through neuron , through synapse- neuromuscular junction to muscle fibre
require neurotransmitter : acetylcholine ( basically just the normal neurotransmitter process)
sacromere
two protein filaments
subunit of myofibrils
between two Z-lines
myosin
thick , dark bands
head that forms cross bridge by binding to actin
actin
thin, light bands
lengthening and shortening of sarcomere
attach at the end of Z lines
crose bridge cycle
When a nerve impulse arrives at the neuromuscular junction,calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
calcium bind with troponin, change shape, move tropomyosin to expose the myosin-binding site on actin
Myosin heads bind to actin, forming crossbridges
Myosin releases ADP and Pi, causing the power stroke - pulls the actin filament towards the centre of the sarcomere
ATP binds to myosin, breaking the crossbridges
ATP is hydrolysed to ADP and Pi, provide energy that “cock” the myosin head away from the center
Myosin heads bind to actin at a new binding site further along the sarcomere
The cycle continues until Calcium is pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, or there is no ATP available
titin
contraction of antagonistic muscle → creates energy → needed to lengthen a muscle, which stretches titin. titin recoils → release energy → adds to the force of contraction in that muscle (provide supplemental force)
prevent overstretching of sacromere
holds myosin filaments in place
Explain how a skeletal muscle contracts

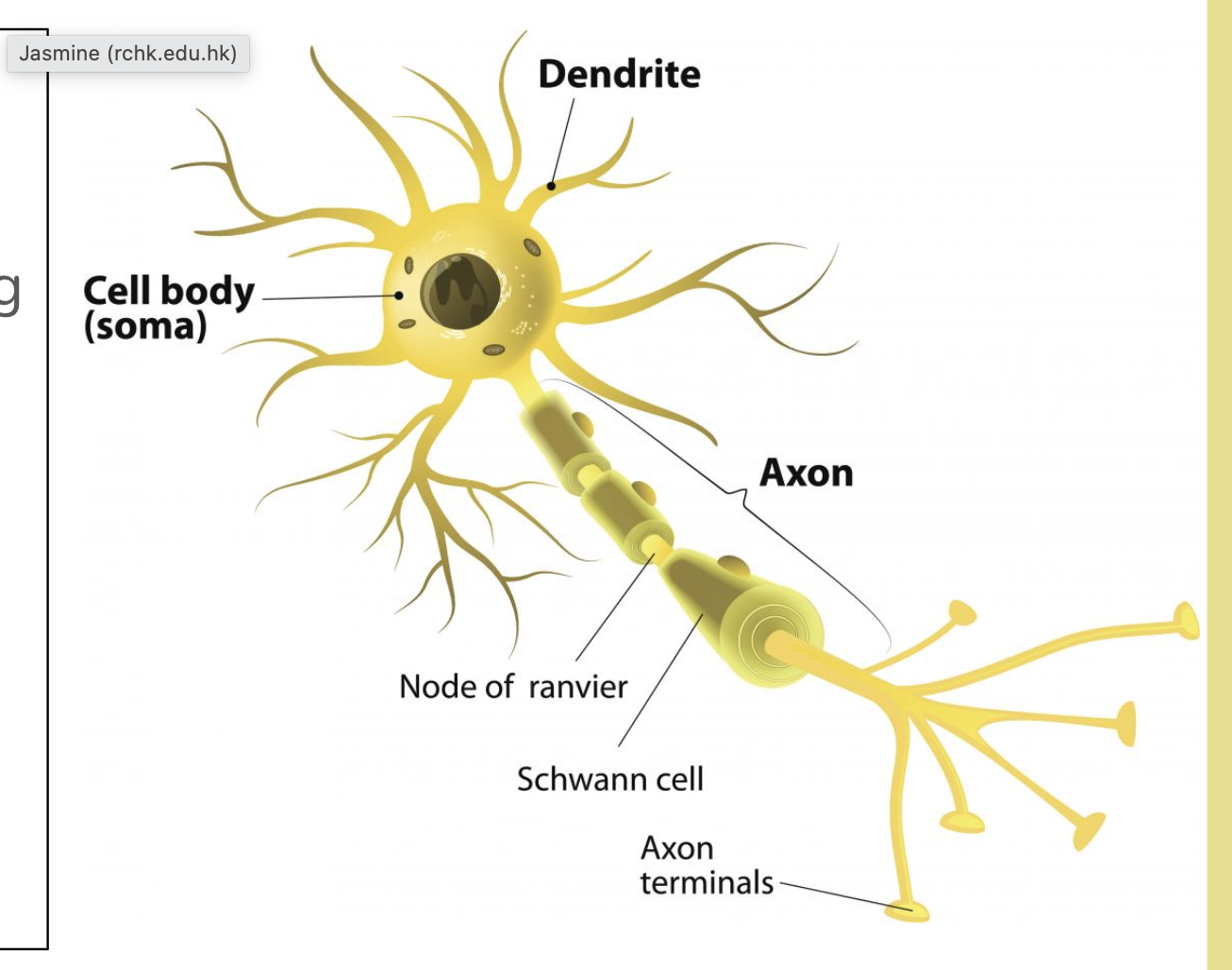
neuron
cell body - cytoplasm&nucleus , elongated nerve fibre- conduct electrical impluse
dendrities - shorter fibres, projecting from cell body
nucleus
schwann cell
node of ranvier
axon terminal
sodium potassium pump
na+ binds - stimulate phosphorylation by ATP- protein change shape , release NA+
k+ binds, trigger release of phosphate group - protein returns original shape - k+ out, NA+ site receptive

oscilloscope trace (3)
resting potential - 70mV- neuron not stimuated
na+ pump out, K+ diffuse in
action potential +40mV
stimulus reaches threshold, activate neuron
na+ k+ pump turn off, sodium ion channel opens → influx of sodium → +40
refractory period - more negative than -70
Na+K+ pump on
potassium ion channel opens- k+ diffuse out - axon membrane impermeable to potassium, none diffuse in
more negative than 70
X new electrical impluse can pass through befoe neuron return to resting potential
ensure electrical impluse pass through 1 direction
depolarization & repolarization
During depolarization Na+ diffuses into the cell
making the membrane potential positive
During repolarization K+ diffuses out of the cell
restoring a negative membrane potential
saltatory conduction
schwann cell wrap axon with myelin sheath containing fatty substance
insulate electrical impluse
as only node of ranvier is site of depolarization - electrical impluse jump from node to node
speeds up the electrical conduction
speed of impluse factors affecting it
temperature - hotter, quicker
axon diameter - larger, faster
schwann cell
synapse - neurotransmitter
electrical impluse arrive at the end of postsynaptic neuron. calcium ion channel opens - influx of calcium
vesivle containing neurotransmitter migrates to presynaptic knob
neurotransmitter release synapse via exocytosis
diffuses down the synaptic cleft
releases & binds to postsynaptic receptor
sodium channel opens - generate electrical impluse in postsynaptic neuron
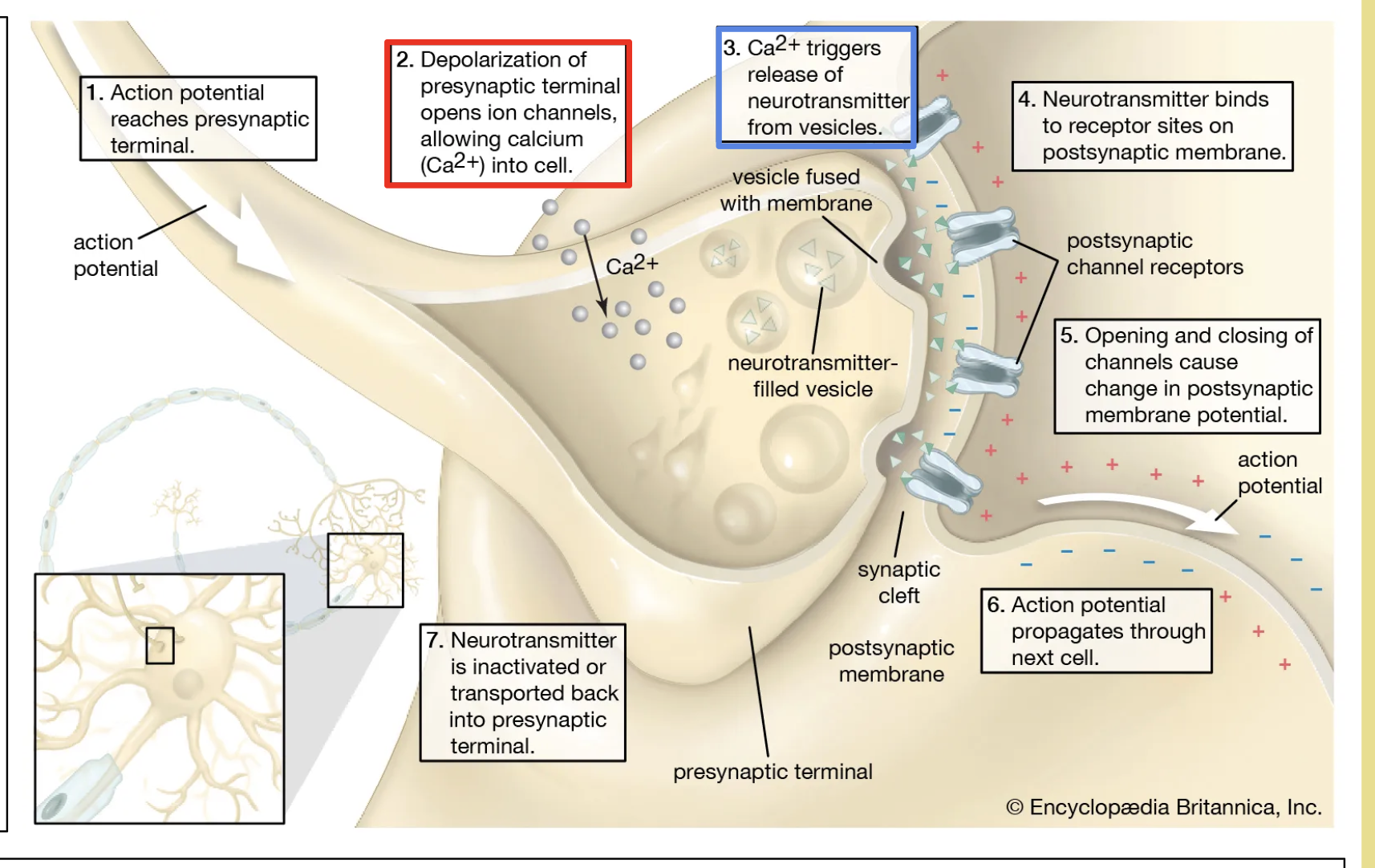
excitatory and inhibitory channels
excitatory:
neuroreceptors that are sodium (Na+) channels
channels open, positive ions diffuse in, causing a depolarization
excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) -stimulate an action potential
acetylcholine, glutamate.
inhibitory
neurotransmitter that are chloride(Cl-) chanels
channel open - negative ion diffuse in - hyperpolarization
inhibitory postsynaptic potential - supress action potential
impluse in one neuron inhibit the impluse in the next
GABA
acetylcholine - neurotransmitter
exist in many synapse - inculding neuromusular junctions
break down ACh in synaptic cleft
Ch ( choline) - absorb in presynaptic neuron - regenerate ACh

propagation of nerve impulses
action potential of one part triggers action potential in another part
Na+ diffuse from a region with action potential to next region in resting potential
diffusion of NA+ - causes local current - change voltage from resting (-70) to threshold ( -50) - voltage gated sodium channel opens - causes action potential
exogenous chemical
chemical substance that alter the physiological state of organism
block synaptic transmission:neonicotinoids
promote synaptic transmission:cocaine ( excitatory)
drugs affect body in 3 ways
Mimic the neurotransmitter - acts as competitive inhibitor
Prevent the breakdown / re-uptake of neurotransmitter, constantly activate the receptor
Prevent the release of neurotransmitter
how neonicotinoids kill honey bees
normal
AChE break donw ACH - prevent overstimulation & blockage of acetylcholine receptor
wiht neonicotinoids
bind to acetylcholine receptor- AChE , cannot break down neonicotinoids → lead to paralysis ( blockage of acetylcholine receptor)
Neonicotinoid pesticides bind to aceylcholine receptors at post-synaptic membrane of cholinergic synapse of insects
Cholinesterase does not break down pesticides - remain bound to receptor - prevent acetylcholine from binding
block synapse transmission - kill honey bees
how cocaine works
bind to dopamine reuptake receptor - inhibit reuptake of dopamine
dopamine accumulation in synaptic cleft
^ likelihood of parkinson disease, dopamine receptor loses sensitivity to dopamine ( also why cocaine users increase dosage)
inhibitory neurotransmitter - GABA
gaba bind on ligand gated Cl- channels
makes postsynaptic membrane negative - hyperpolarization
harder for postsynaptic neuron to reach threshold , inhibiting nerve impulse
ligand function + process
binds to protein receptor, causes a change in metabolism within the cell
sending cell release signal molecules-ligand → transport to target cell → binds on ligand binding site on receptor → stimulates response in target cell
whole process of chemical signalling is called
single transduction pathways
quorum sensing
bacteria regulate behaviour based on population density
coordinate communications between bacteria
autoinducter(ligand) - concentration reaches a threshold - gene expression of bacteria will be altered
bioluminscent
V. fisheri bacteria - only bioluminescent in large enough numbers
mutualistic/symbiotic relationship with Bobtail squid
luminscent its underside- camoflage to matches mooonlight - hidefrom predators+sneak up on prey
V.fischeri in return for homw and nutrient
quorum sensing in V.Fischeri
v. fischeri releases signal molecules called autoinducer in a low rate
autoinducer passes to external environment , ^ number of bacteria ^ autoinducer concentration
reaches a threshold - move back into bacteria cell - bind to LuxR receptors
activated LuxR - bind to DNA binding site : Lux Box
Binding activated genes responsible for production of luciferase ( luminescent protein)
ligand - Hormone & neurotransmitter
hormone
endocrine system glands release hormone into bloodstream to elicit response w target cell
long lasting & widespread - slow (LH from brain to ovary)
ex. amine(epinephrine) , protein(FSH) , steriods (progesterone)
neurotransmitter
nervous system transmit signals through synapse
short lived & local effect - fast
ex. amino acid (GABA - inhibitory, glutamate - excitatory) , acetylcholine
ligand - cytokinesis & calcium ions
cytokinesis - immune system
calcium ion - secondary messanger in muscle + nervous system
difference between transmembranbe & intracellular receptors
transmembrane( embedded in cell membrane )
signals affect permeability
bind to receptor - activate transporter ( substance can enter and leave the cell)
calcium gated ion channel - insulin increase uptake of glucose
signals release secondary messenger
bind to receptor - activate enzyme (affect various aspects of cell)
GPCR - adrenaline stimulates glycogen breakdown
intracellular ( within cytoplasm)
hydrophobic signals go through membrane , diffuse to nucleus - bind to receptor which forms transcriptional factor → activates protein synthesis
estrogen stimulated growth in uterus
ligand gated ion channel & acetyloine
multi pass protein - thread back and forth across the cell membrane - center is a pore, allows sodium ions to pass through
pore opens when acetylcholine binds to receptors
influx of sodium ion - new action potential on post synaptic knob / muscle contraction at neuromuscular junction
GPCR
multi transmembrane protein receptor
acts indirectly on enzyme/ion channel with G-protein
ligand binds to extracellular receptor- activated receptor → allow g-rpotein to bind to nucleotide GTP
binding of GTP - activate g protein : carry signal into cell , activate other protein and carry out response
removal : hydrolysis of GTP - GDP , G- protein can be deactivated and reuse
GPCR and secondary messager ( & advantages)
use seconary messager to produce and amplify a response - cAMP
cAMP produced when enzyme adenylyl cyclase activated by ATP
continues a cascade of multiple activations of phosphorylation until final effect is reached
ex. human liver convery glycogen - glucose in response to adrenaline and glucagon
advantages -
one hormone - differnet effects in a celldifferent
two hormone - same affect in a cell
each hormone - different effects - different cells
epiphrine receptors + break down of glycogen
g-protein coupled receptors which uses secondary messager of cAMP
g-protein activate adenylyl cyclase - convert ATP - cAMP
cAMP activates PKA → PKA phosphorylates + activate protein ( enzyme)
ex. liver - oxidation of glycogen to glucose
what is kinase
enzymes that uses atp to phosphorylate molecules
tyrosine kinase with insulin receptor
receptors work/link as a enzyme
a pair of single pass protein with 3 domains
1. extrcellular: receptor for ligand (eg. insulin)
2. transmembrane : pass through cell membrane once
3. intracellular : acts as kinase- autophoryates after binding with insulin
insulin binds to transmembrane receptor
tyrosine kinase enzyme tail on cytoplasm side - phosphorylates each other
trigger signal transduction → glucose transporters inserted in the plasma membrane
glucose uptake into cells
intracellular receptor on gene expression + examples( function of examples) ( steriod hormones)
steriod hormones - hydrophobuc - pass through cell membrane
bind to receptors inside cell - hormone-receptor complex - diffuse into nucleus - directyl affect gene transcription
ex. progesterone, oestradiol
progresterone: thickens, maintain endometrium - implantation
oestradiol : hypothalamous, ^ transcripton of GnRH - increase of LH&FSH.
positive and negative feedback on signalling pathway
positive
amplfy cell signalling - enhance response
end product amplify start point - more product
blood clot , oestradiol stimulation, labour duirng birth
negative
dampen cell signalling - inibit response
end product inhibit start point
gluvose regulation with insulin+ glucagon
gas exchange function
obtain gases for metabolism
release waste products
gas exchange occurs
diffusion - gases travel from high to low concentration to reach diffusion
structure to facilitate gas exchange (4)
large SA:V (branches+foldings)
permeability of O2 and CO2
thin tissue layer minimise diffusion distance
moist layer for gases to dissolve
how is concentration gradient maintained (3)
Dense capillary network around gas exchange surfaces
Continuous blood flow
Ventilation
With air for lungs
With water for gills
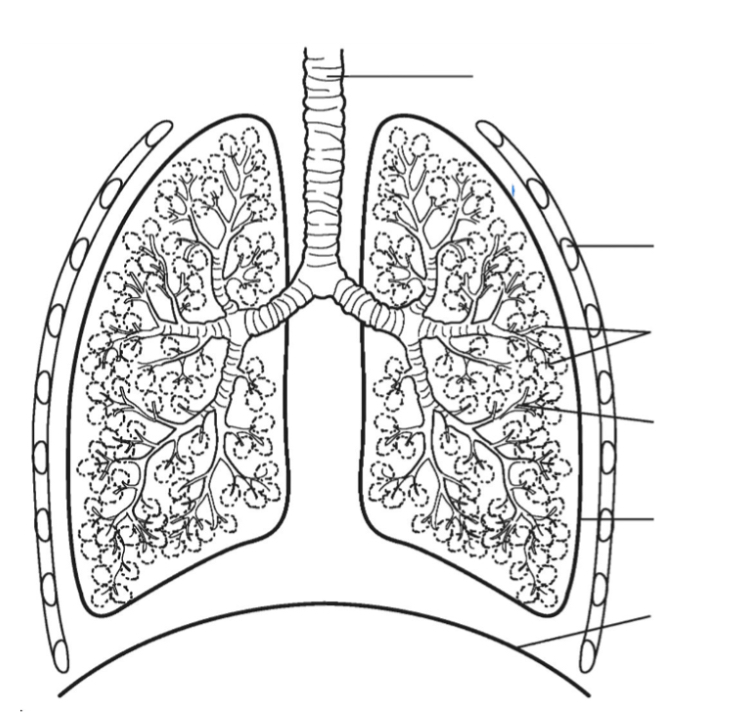
Lungs
trachea
bronchus
bronchiole
alveoli
lungs
ribs
intercostal muscle
diaphragm
definition for ventilation + gas exchange + cellular respiration
Ventilation : exchange of air between atmosphere and lungs - breathing
Gas exchange : exchange of O2 and CO2 between alveoli and bloodstream - passive diffusion
Cellular Respiration : release of ATP from organic molecules
exchange on ventilation rate
increase rate exercise > increase cellular respiration > increases uptake of oxygen > increase ATP - breath in faster
By product of cellular respiration increases: Co2 > blood gets acidified > proteins like RBC denatures > dont carry oxygen > dies.
To avoid Co2 accumulation - breath out faster > ventilation rate faster
respiratory system (5)
air travels from nose&mouth - pharynx - trachea
air divides into two bronchi
right : 2 lobes, left : 3 lobes
bronchi - many bronchiole ( increases SA)
bronchiole - airsacs: alveoli ( gas exchange w bloodstream occurs)
structure of alveolus
thin epithelial layer ( one cell thick ) > minimuze diffusion distances
surrounded by rich capillaries layer > increase capacity for ge with blood
spherical in shape > maximize SA for ge
internal surface - covered with surfactant > dissolved gas better able to diffuse in bloodstream + reduce surface tention
where is pneumocytes
(alveolar cells) - line the alveoli , comprise the majority of inner surface of lungs
what is alveoli made out of
type 1 + type 2 pneumocytes
type 2 pneumocytes
secrete alveolar fluid → contain surfactant
how surfactant works
both alveoli have equal surface tension
left one - smaller radius - higher pressure - hard to inflate, more likely to collapse
with surfactant: less surface tension, able to have same pressure - wont collapse
adaptations for lungs(4)
surfactant - decrease pressure
short diameter of bronchiole - slow air flow increases efficiency
many alveoli attached at the end - increase SA for gas exchange
extensive capillaries around alveoli - short diffusion distance
ventilation in antagonistic muscle
Inhalation
external intercostal muscle - contracts → ribcage move out and up
diaphagram - contracts → move down and flattens
volume increase in thorax
decrease of pressure in lungs compare to atmospheric pressure - air flows into the lungs
exhalation
internal intercostal muscle - contracts → ribcage move in and down
abdominal - contracts → pushes diaphragm into dome shape
volume decrease in thorax
increase of pressure in lungs compare to atmospheric pressure - air flows out the lungs
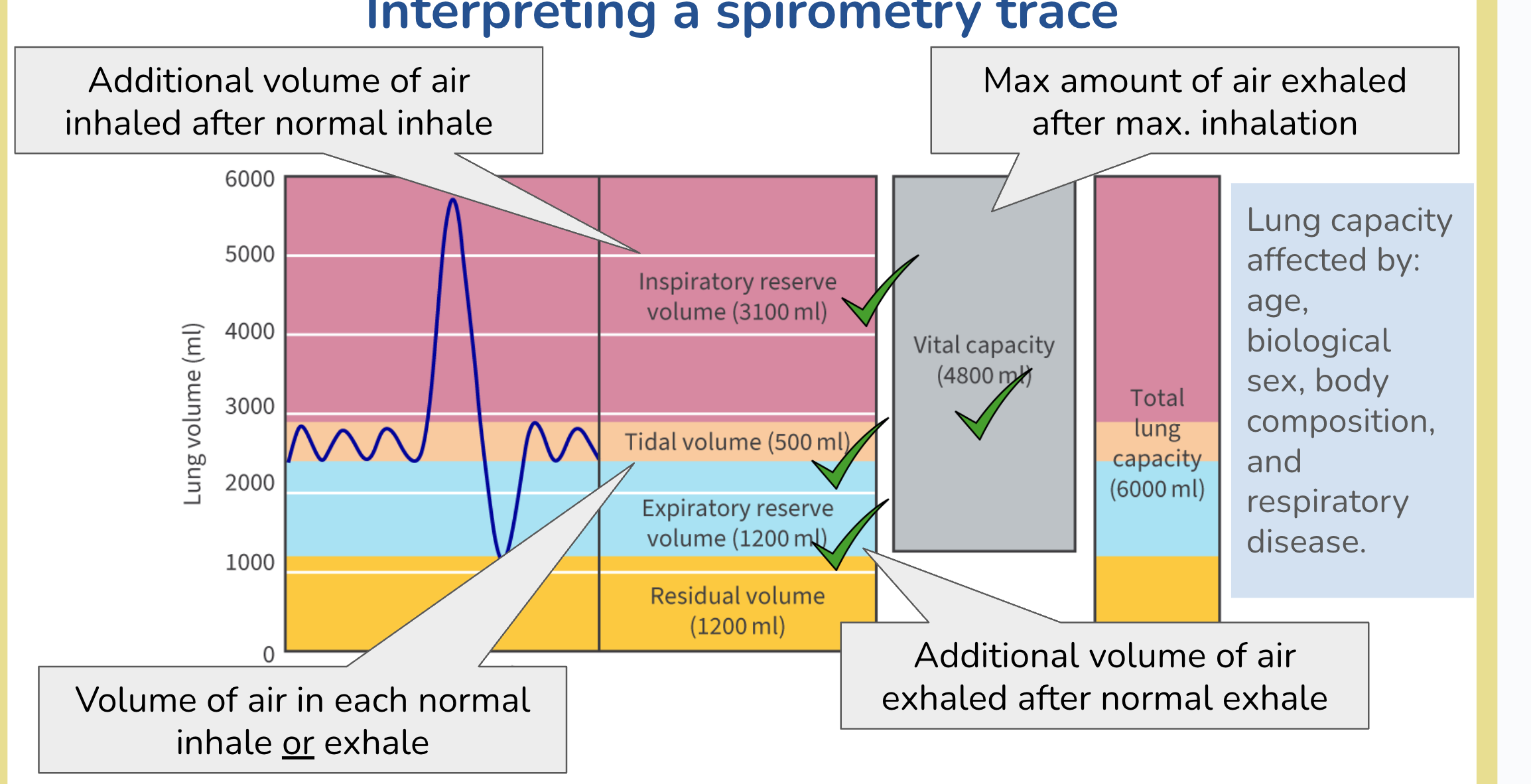
measure lung volume
spirometry
spirometry trace
gas exchange in leaf
stomata
guard cells control opening and closing of stomata
adaptations of leaf
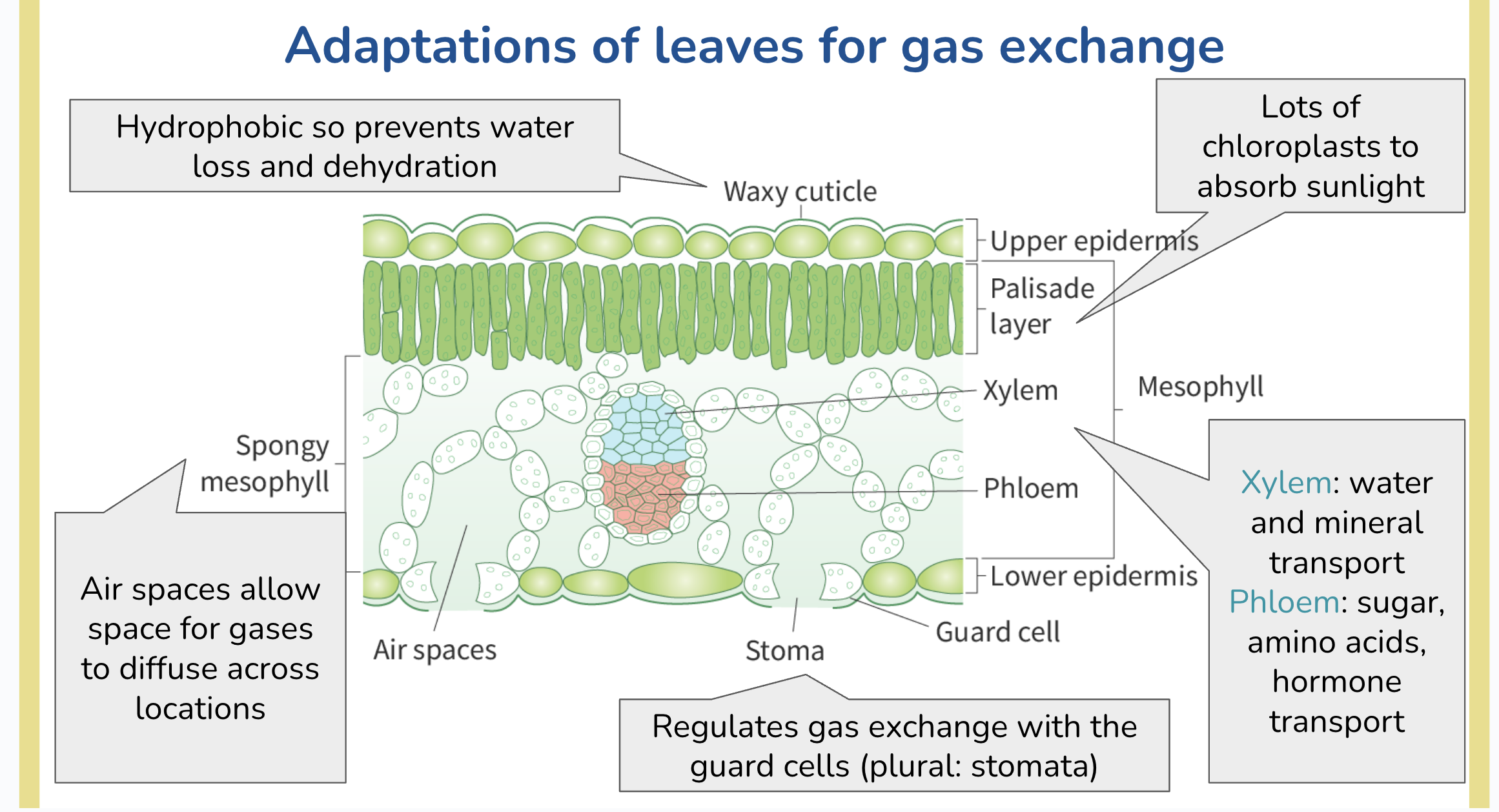
waxy cuticle
palisade layer
spongy mesophyill
xylem&pholem
stoma & guard cells
transpiration
water lost by stomata
Water vapour is lost via the stomata
Diffuses down its concentration gradient into the atmosphere → creating negative pressure in the xylem
Creates tension that further draws water up the xylem from the roots to the leaves.
Transpiration facilitates:
Temperature regulation
Absorption of water and minerals from soil
factors affecting transpiraton
increase transpiration
wind: ^water concentration gradient
temperature : ^ saturation point of air
light : ^ photosynthesis
decrease transpiration
humidity : decrease water concentration gradient
hemoglobin (location, function , structure)
Location: RBC
Function : transport O2 to respiring tissue, transport byproduct Co2 to lungs
Structure : quaternary , conjucated protein - 4 polypetide with heme group
hemoglobin and oxygen
coorporative binding
structure changes - affinity for oxygen ^