Zygotic patterning
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
L13
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Where is there a low gradient of nuclear localisation of the dorsal protein?
on the dorsal side
By which protein are dorsoventral genes activated? How is different gene expression moderated?
dorsal protein
different activation thresholds/concentration gradients
Does snail have low or high affinity for dorsal binding sites? What gradient concentration is therefore required for snail expression?
low
high levels of nuclear dorsal protein
What do regions expressing snail give rise to?
mesoderm
Does rhomboid have low or high affinity for dorsal binding sites? What gradient concentration is therefore required for snail expression?
high
low levels of dorsal protein are sufficient for rhomboid expression
Why is rhomboid not expressed in high concentrations of dorsal protein?
in high levels, snail is expressed - the latter inhibits rhomboids expression by interfering with its promoter
What does a promoter region promote?
transcription of the gene
Where is rhomboid expressed? What does it give rise to?
laterally on both sides of mesoderm
neuroectoderm
What sets up a second signalling centre in the dorsal ectoderm? On which side of the embryo is it set up?
Decapentaplegic (Dpp)
dorsal side
What is Decapentaplegic (Dpp) signalling known as in vertebrates?
Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signal.
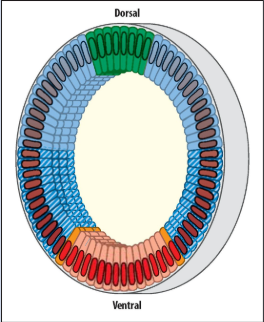
Place the mesoderm, ectoderm, dorsal ectoderm and amnioserosa. What are they refered to?
domains (formed during this dorsoventral patterning)

How do different levels of nuclear Dorsal lead to different gene expression?
more dorsal transcription factor = high affinity binding gene called snail is expressed - this inhibits rhomboid, and gives rise to the mesoderm
less dorsal = low affinity binding gene rhomboid is expressed and gives rise to neuroectoderm
Name a highly conserved signal that acts on the dorsal side, also the vertebrate equivalent
Dpp (decapentaplegic) and BMP (bone morphogenetic protein)
Once bicoid, nanos and hunchback have set up an initial polarity and triggered the expression of gap genes, how are different regions of the embryo defined? Give an example
gap genes expressed create a combinatory code = specific region ie at very anterior both hunchback and knirps are expressed, in a portion of abdomen only knirps
What causes striped pair-rule expression? What was assumed was causing it?
each stripe is driven by a specific gap gene combination
periodic wave-like process
What explains how stripes are set up by gap genes?
different gap gene combinations activate different gene expressions eg promoter of the eve gene is thought to contain an element that is activated by hunchback but blocked by giant or kruppel.
What are pair rule gene expression stripes known as?
para segments
Do stripes of gene expression correspond to the visible segments formed during segmentation?
no - slightly shifted like anterior part of eve becomes posterior of the visible segment
What do high levels of ftz or eve switch on?
engrailed gene
What do segmentation genes pattern the pair rule pattern into?
segmental pattern - 14 stripes formed, 1 in each 1 segment
What drives the formation of denticles or stripy pattern on larvae?
14 striped expression of engrailed
What do engrailed positive cells form in each segment?
posterior boundary of the segment
What type of role does engrailed have on other genes?
transcription regulation
How is the expression of Wg, Hh and En maintained? What is this therefore called?
Wg by Hh
En and Hh by Wg
feedback loop
Once intra segment patterning occurs, what is the cellular structure of the embryo? What does this imply?
cellularised
cell-cell signalling across cell membranes
Which gene does Hh maintain?
Wg
How do wingless and hedgehog communicate within the embryo? What do they cause?
through protein signals acting across cell boundaries
changes in gene expression
What do reduced or aberrant activity levels of wingless and hedgehog cause?
congenital defects
What does inappropriate activation of wingless and hedgehog cause in humans?
many types of cancer like
wnt (wg in vertebrates) - colon cancer
Hh -basal cell carcinoma
What are homeotic mutations?
mutations where one structure is replaced by another structure like two sets of thoraxes (bithorax) or legs instead of antenna (antennapedia)
In what types of organisms are hox genes found?
present in most if not all multicellular organisms
What is the hox complex? Is this found in drosophila?
single complex made up of hox genes - found in most organisms
complex broken down into 2 in drosophila
In what direction are hox genes expressed? (5’ to 3’ or 3’ to 5’) How is this reflected in the structure of the hox complex?
3’ first and anterior to 5’ last and posterior (opposite of usual DNA)
timing and spatial expression corresponds with the order of their expression (lab is closed to 3’ and expressed first etc)
How many hox complexes do humans have? What explains this?
4
genome duplication - deuterostomes like drosophila have the OG genome, vertebrates like humans have double
What types of genes are hedgehog, wingless and engrailed?
segmentation genes
Which of all signals are cell-cell?
wingless
hedgehog
wnt
dpp (decapentaplegic) triggers transcription
bmp (bone morphogenetic protein) triggers transcription
Which of all signals are transcription factors?
dorsal protein
dpp
bmp
bicoid
hunchback
The signalling genes are conserved in other organisms and high activity is linked to…?
cancer
Homeotic genes are in a (1), in an (2) order, mammals have (3) of these complexes
complex
A/P
4
What is the bithorax complex responsible for? What genes is it made up of?
diversification/specification of the posterior segments (thoracic and abdominal segmental identity depending on different hox gene combinations)
Ubx, abd-A and Abd-B (3’ to 5’)
What happens when all three genes of the bithorax complex are knocked out?
What happens if only some are knocked out and what does this suggest?
most segments take on a T2 fate which is a default state so undifferentiated
some segments are formed = sort of combinatorial code
Who received a Nobel prize for understanding the logic of patterning and homeotic mutations?
ed lewis
What do Abd-A, Abd-B and Ubx define respectively?
all create a combinatory code but:
abd-A can be expressed from A2 to A8
Abd-B can be from A4 to A8
Ubx across T3 to A8
Where does the name bithorax complex come from?
If Ubx is mutated, T3 can turn into another T2—so the fly gets two pairs of wings instead of wings + halteres