Module 10: Exchange and Transport in Animals & Plants
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
what is an osmoconformer?
isosmotic with its surrounding (osmolarity changes with environment)
less energy expended trying to control osmolarity
what is an osmoregulator?
control internal osmolarity independent of the environment
more energy-intensive to keep osmolarity in a tightly controlled range
how do terrestrial animals deal with lack of water-sweat and urination?
animals have body coverings that prevent water loss and when they do lose water, they drink it or eat; they also make water during respiration and some animals have even adapted to arid environments
how do marine fish osmoregulate?
they lose water and gain solutes because they are in saltwater. they drink a lot of water, save the solutes they need, and excrete most of them to keep a low solute environment inside. they drink extra water, process the solutes out and keep the water
how do freshwater fish osmoregulate?
the gills actively uptake salt from the environment, drink almost no water, and have highly diluted urine; the opposite is true for saltwater fish
characteristics of ammonia waste
less energy, higher toxicity
characteristics of urea waste
more energy, lower toxicity
characteristics of uric acid
most energy, lowest toxicity
what excretes ammonia?
aquatic animals
(they cannot hold their waste for long periods of time, however, water makes the ammonia safe)
what excretes urea?
terrestrial mammals
(since it's not that toxic, animals can hold their waste for long periods and release it in increments)
what excretes uric acid?
birds, reptiles, and insects
(since uric acid is an acid, it helps these organisms conserve water as uric acid is not soluble in water; they are also able to hold their waste for longer periods)
what is involved in osmoregulation and nitrogenous waste disposal?
transport epithelial
what are the four steps of excretion?
1. filtration
2. reabsorption
3. secretion
4. excretion
what occurs during filtration?
driven by blood pressure, water, small solutes, sugars, amino acids, and nitrogenous wastes are filtered out of the blood into the excretory tube
what occurs during reabsorption?
water and useful solutes (sugars, vitamins, amino acids) are returned to the blood via active transport
what occurs during secretion?
nonessential solutes or waste are secreted out the blood via active transport
what occurs during excretion?
filtrate is released from the body (elimination)
where is the tubule in the human body?
kidney
what does the kidney or "nephron" accomplish?
filter, reabsorb, secrete, and excrete liquid waste
based on what the body needs and the environment the water would...
go back and forth that make up the lining of the nephrons and the solute concentration
what is the set point for osmoregulatory homeostasis?
~300 mOsm/L
what does dehydration entail?
more concentrated urine
what does over-hydration entail?
more diluted urine
what is the name of the key hormone for osmoregulation of the mammalian kidney?
ADH
when the hypothalamus detects high blood osmolarity, what occurs?
more aquaporins (water channel proteins) are inserted in the kidney tubule epithelium membrane which helps the body retain water
would you expect there to be more or less reabsorption of water (out of urine & and back into blood) in kidney tubules of desert-adapted animals?
more
would the loop of henle be longer or shorter in desert mammals relative to humans?
longer
the length of the loop is correlated with ____________________________.
water conservation
what animals will have longer loops?
mammals in dessert environments
what cannot concentrate as much urine?
shorter loops of henle
what is the simple body plan?
many or all cells are in direct contact with the environment (small diffusion distance)
what do gastrovascular cavities perform?
digestion and exchange of materials
what is the complex body system?
many cells are not in direct contact with the environment (larger diffusion distance)
what is the function of the circulatory system?
transporting materials throughout the body
what are some basic parts of the circulatory system?
circulatory fluid, interconnecting vessels, and muscular pump (heart)
what is an open system?
circulatory fluid is also interstitial fluid (hemolymph)
what is a close system?
circulatory fluid (blood) is confined to vessels so its compartmentalized
arteries and veins are distinguished by...
wether they carry blood to or from the heart
what are the components of the cardiovascular system?
1. arteries
2. veins
3. capillaries
4. atria
5. ventricles
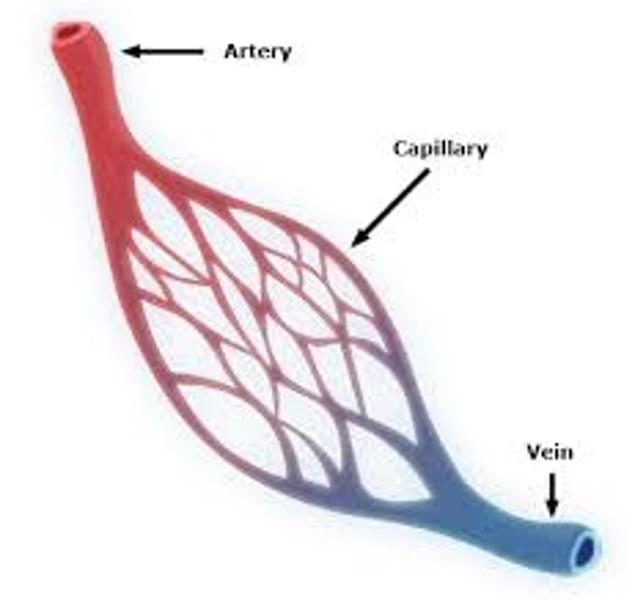
what is the function of the arteries?
carry blood from the heart to the organs (away from the heart)
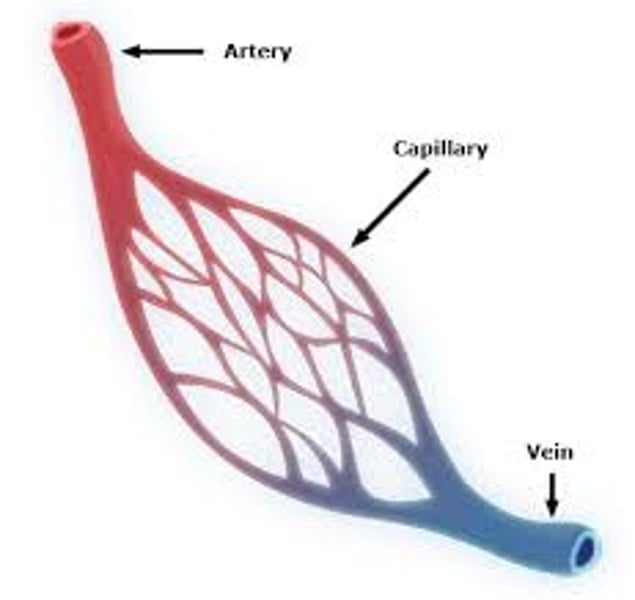
what is the function of the veins?
carry blood from the organs to the heart (toward the heart)
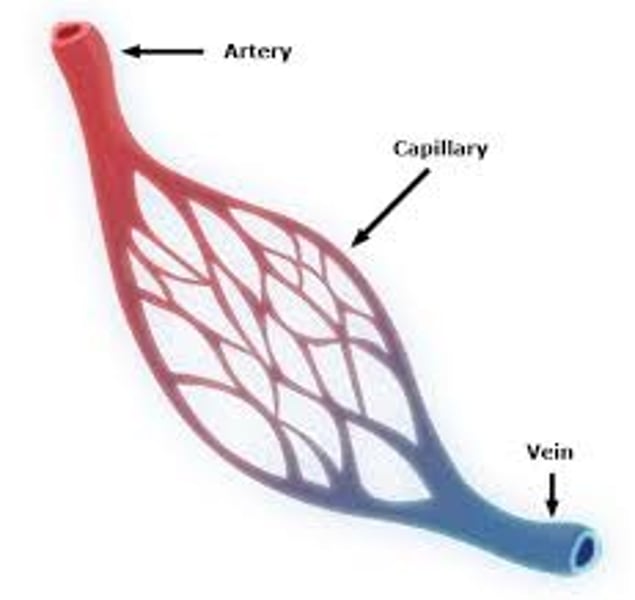
what is the function of capillaries?
thin-walled vessels that infiltrate each organ and are involved in exchange
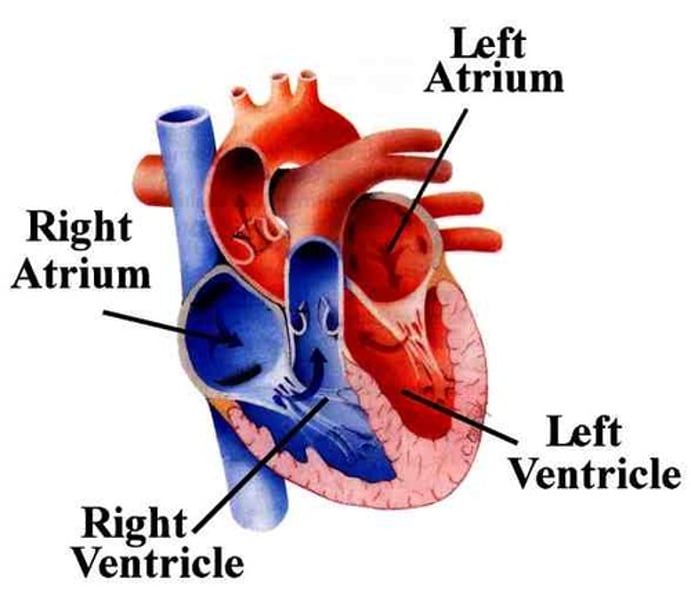
what is the function of the atria?
receives blood entering the heart
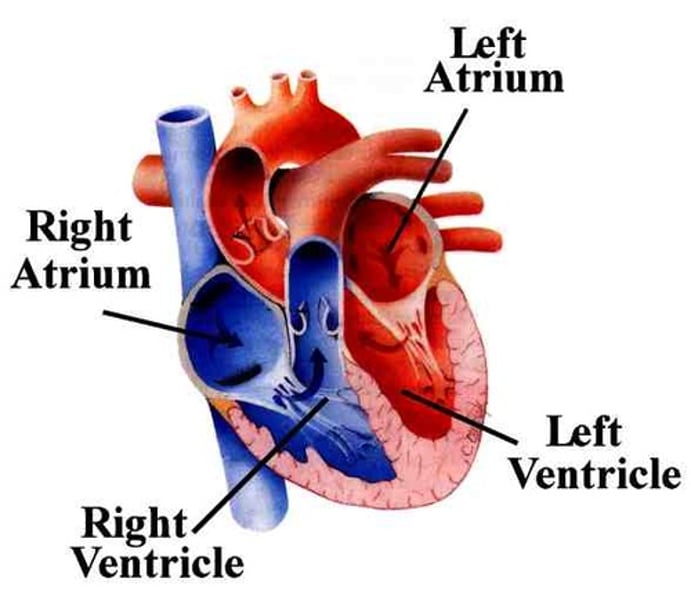
what is the function of the ventricles?
pumps blood out of the heart
O2 comes in as...
oxygenated blood
CO2 leaves as...
de-oxygenated blood
what is aerobic respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 à 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (ATP, heat)
where does respiratory occur in aquatic organisms?
counter-current exchange in gills
where does respiratory occur in terrestrial organisms?
ventilation of lungs
what is partial pressure?
the pressure exerted by a particular gas in a mixture of gases
gases cross respiratory surfaces via
diffusion (passive transport)
where is it easiest to obtain oxygen: from the air or from the water?
air
what are gills?
out-foldings of the body surface suspended in water
what is ventilation?
movement of the respiratory medium over the respiratory surface
(i.e., water over gills)
what is countercurrent exchange?
the exchange of a substance or heat between water and blood flowing in opposite directions
describe how an aquatic organism breathes
1. fish swim and move water over the gills and blood goes going the opposite direction.
2. water flows in one direction through the mouth over the gills but the blood flows in the other.
3. oxygen goes from the water to the blood and CO2 from the blood to the water.
4. blood always has less oxygen than water so oxygen diffuses in (look at the box on the bottom right)
5. the higher oxygen-saturated water is always flowing over the area. oxygen is always getting extracted so the partial pressure gradient favors diffusion of oxygen from water to the blood along the length of the capillary.
what are lungs?
in-foldings of the body surface exposed to air
what are the epithelial cells lining the trachea and bronchioles
cilia and a thin film of mucus
where does the gas exchange occur in the lungs?
between the alveoli and capillaries
(O2 dissolves in the film of liquid lining the alveoli
and diffuses into capillary beds)
plants vs animals: energy acquisition
animals: digestive system/cellular respiration
plants: photosynthesis/cellular respiration
plants vs animals: osmoregulation
animals: excretory system
plants: water potential
plants vs animals: transport
animals: circulatory system
plants: transpiration/translocation
plants vs animals: gas exchange
animals: respiratory system
plants: stomata
where do plants exchange specific substances with air and soil?
within the leaves
what are mesophyll cells?
leaf cells that contain the main structures for photosynthesis.
(they lie below the epidermis cells; they are stacked tall in layers near the top and are loosely packed near the bottom)
where does the green color of the plants come from?
chlorophyll
(plants cannot absorb the green wavelength and so they reflect it)
what enters, leaves and evaporated in the stomata?
enters: CO2
leaves: O2
evaporates: H2O
what is the stomata?
tiny pores in leaves where carbon dioxide enters and oxygen exits
what is the function of a plant's root hairs?
extra surface area for absorption, proton pumps, ion channels, and co-transporters for uptake
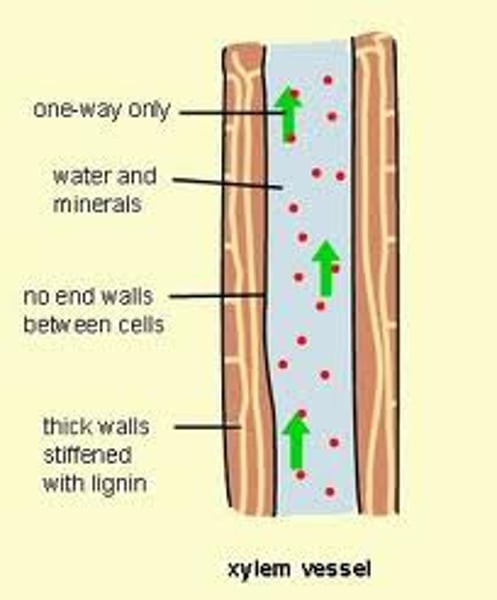
what is the function of the xylem?
transports water and minerals upward from the roots through transpiration, adhesion, cohesion, and root pressure
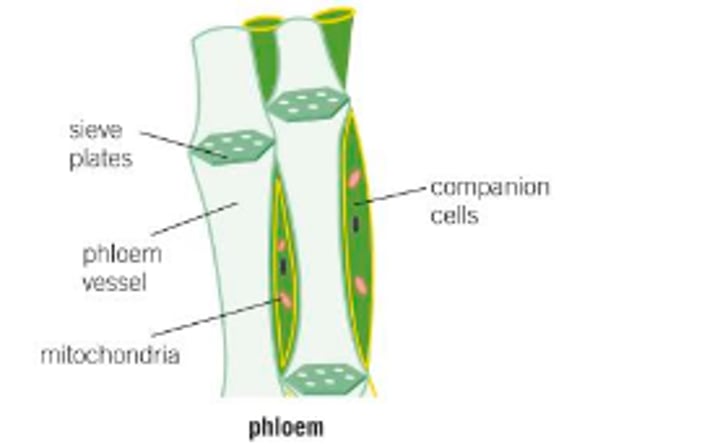
what is the function of the phloem?
transports sugar solutions from source (where they are made or stored) to sink (where they are used)
what is osmosis?
the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
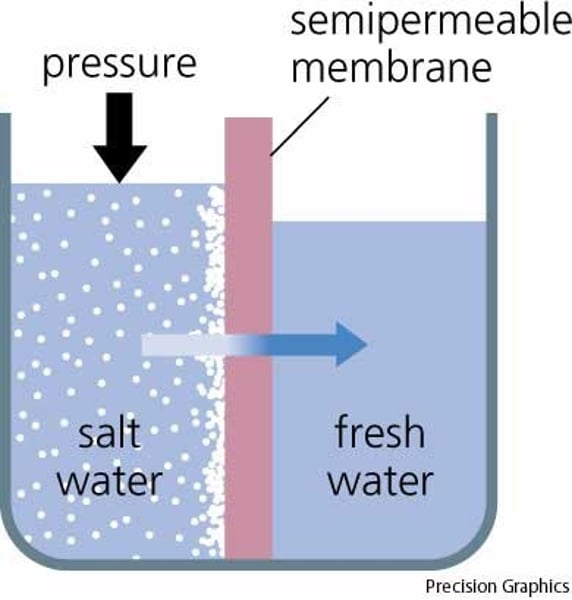
what is turgor pressure?
the force of water against a cell wall due to osmotic uptake of water in the plant cell
what are guard cells?
cells that balance water conservation with gas exchange for photosynthesis
turgid guard cells...
open the stomata
(K+ is taken up by the guard cell, H2O follows by osmosis)
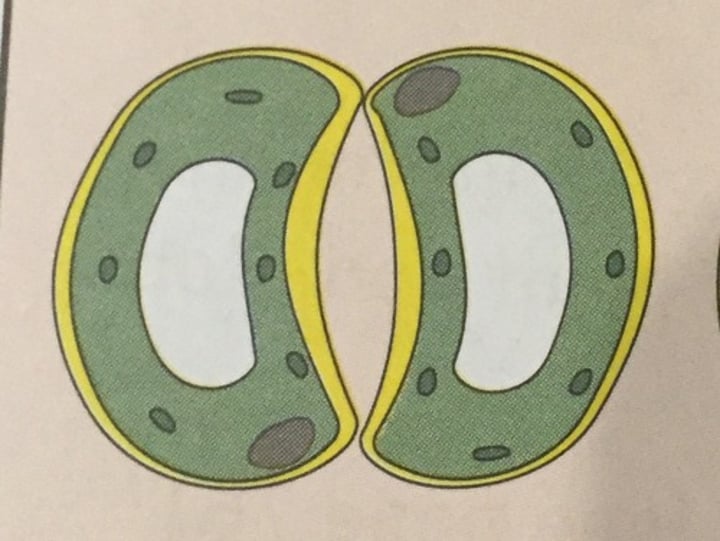
relaxed guard cell...
closes the stomata
(K+ pumped out of the guard cell, H2O follows by osmosis)
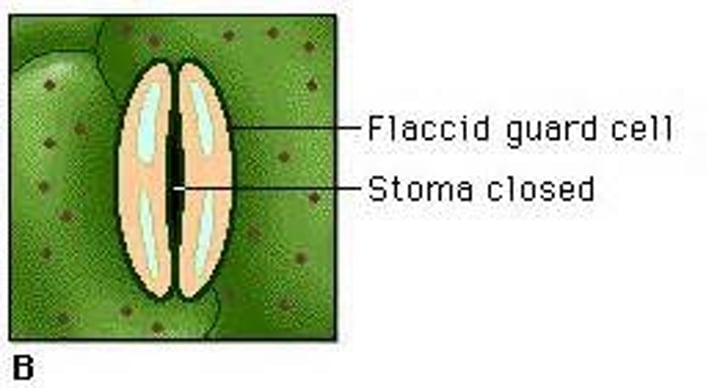
what is a factor that would cause for the stomata to open/close?
1. light/dark
2. amount of CO2 in the leaf
3. circadian rhythm
4. environmental stressors such as droughts, temperature, etc
what happens when the stomata are opened?
CO2 intake increases; transpiration increases
what is transpiration?
the loss of water vapor from leaves and other aerial parts of the plant
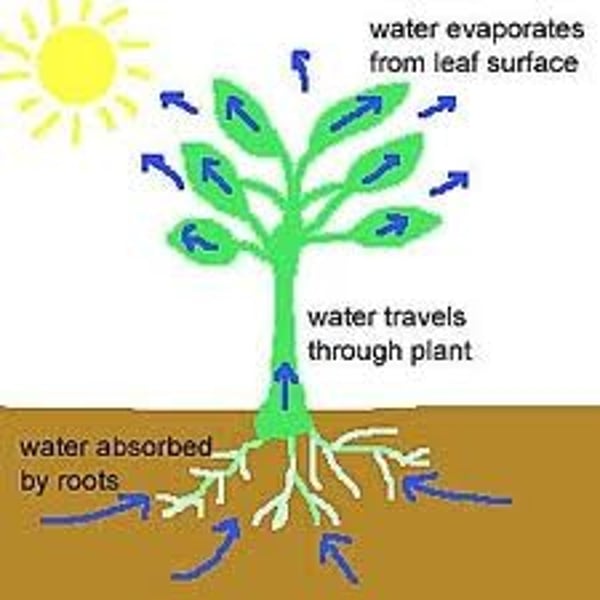
what is the process of transpiration?
water and solutes absorbed into roots --> water and solutes move up plant --> water evaporates through stomata (transpiration).
what is the cohesion-tension hypothesis?
transpiration provides the pull for the ascent; cohesion/adhesion transmits this pull along the entire length of the xylem
what would would cause water to enter a plant cell?
increased solute concentration inside the cell and lower fluid pressure inside the cell than outside
when sucrose is loaded into the phloem near the source, water moves...
into phloem there, increasing its fluid pressure
when sucrose is moved out of phloem into a sink cell, water moves...
out of phloem there, decreasing its fluid pressure
water solutions move down their pressure gradient, from...
higher fluid pressure to lower fluid pressure
how do freshwater fish osmoregulate?
Collecting salt with gills and then drinking very little water and excreted super dilute urine. Hyperosmotic