Chapter 20, Lesson 1: General Anatomy of the Blood Vessels
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 20, Lesson 1 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Blood vessel categories
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
Arteries
Blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart
Capillaries
Blood vessel that connects small arteries to veins, forming a circuit
Tunics
Vessel wall layers; there are three in total:
Tunica interna
Tunica media
Tunica externa
Tunica interna
The innermost tunic that lines the blood vessel with a selectively permeable barrier and chemical secretions for constriction and dilation
Tunica media
The middle tunic consisting of smooth muscle, collagen, and elastic tissue for strength
Tunica externa
The outermost tunic made of loose connective tissue to connect with other organs as an anchor
Artery classes
Three classes:
Conducting (elastic or large)
Distributing (muscular or medium)
Resistance (small)
Conducting (elastic or large) arteries
The biggest arteries (such as the aorta or common carotid) that expand and recoil with the systole and diastole to regulate pressure
Distributing (muscular or medium) arteries
The arteries that distribute blood to specific organs (such as the brachial, femoral, renal, or spenic)
Resistance (small) arteries
Smaller arteries to smaller areas
Arterioles
The smallest of the resistance arteries with a 200mm diameter
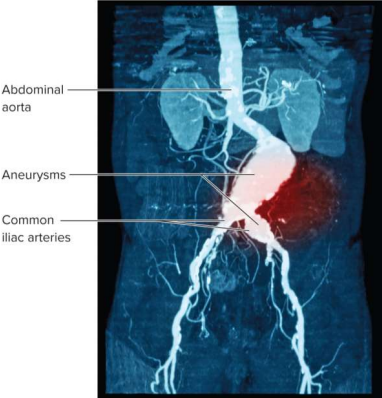
Aneurysm
A weak point in an artery or heart wall that forms a thin-walled, bulging sac that pulses and can rupture or cause pressure
Carotid sinuses
Baroreceptors (blood pressure sensors) in the walls of the internal carotid artery
Carotid bodies
Oval bodies near the branch of common carotids that function as chemoreceptors (chemistry montors) for O2 and CO2 respiration rates
Aortic bodies
The one to three chemoreceptors in the aortic arch
Capillaries
The smaller exchange vessels to allow gasses, nutrients, wastes, and hormones pass between blood and tissue fluid
Capillary types
Three types:
Continuous capillaries
Fenestrated capillaries
Sinusoids
Continuous capillaries
The most common capillaries that allow smaller solutes (like glucose) to pass while blocking large molecules (proteins, blood cells, platelets)
Fenestrated capillaries
Capillaries found in organs needing rapid absorption or filtration (kidneys, small intestine) with filtration pores (fenestrations)
Fenestrations
Filtration pores in fenestrated capillaries that only allow very small molecules to pass
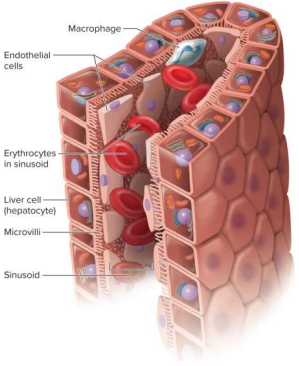
Sinusoids
A type of capillary found in the liver, bone marrow, and spleen for irregularly shaped spaces filled with blood, allowing particles to enter circulation
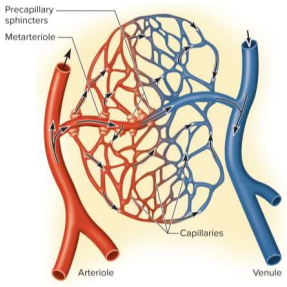
Capilalary beds
Networks of 10 to 100 capillaries - not all are used; 75% of all capillaries are shut down by precapillary sphincters
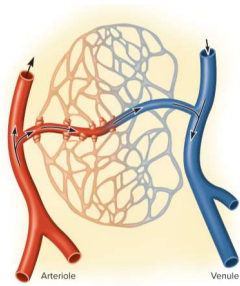
Precapillary sphincters
Controls flow in capillary beds supplied with blood; relaxation allows flow and contraction constricts entry
Veins
The thin-walled, flaccid vessels that collapse when empty and expand easily for steady, low pressure flow back to the heart
Postcapillary venules
The smallest veins with just a tunica interna, some fibroblasts, and pores for fluid exchange
Muscular venules
Veins that recieve blood from the post-capillary venules up to 1mm in diameter with one to 2 layers of smooth muscle
Medium veins
Veins up to 10mm in diameter with thick tunica media, externa, and interna as a result of venous valves while pumped by skeleta muscles
Varicose veins
The failure of venous valves in the merium veins as a result of blood pooling and distended veins; can happen as a result of hereditary weakness, obesity, and pregnancy
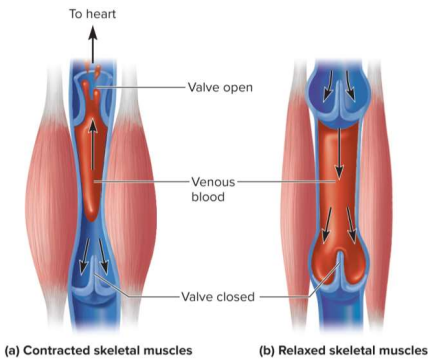
Skeletal muscle pump
Pump that propels venous blood back to the heart using skeletal muscles; found in the gastrocnemius (calves)
Large veins
Veins with a diameter greater than 10 mm with smooth muscle in all three tunics; thick tunica externa - includes the IVC/SVC, pulmonary veins, and internal jugular veins
Hemorrhoids
Varicrose veins of the anal canal