A1.1: Water
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Is water polar or non-polar? What is the significance of this?
Polar: this makes it an excellent solvent and allows the formation of hydrogen bonds.
Why is it important to have intra- and extra- cellular water?
All chemical communication in and out of cells require water environments.
Properties of water
Polar (pro)
Provides buoyancy (pro)
Provides stable thermal properties - high specific heat capacity (pro)
Higher viscosity than air (con)
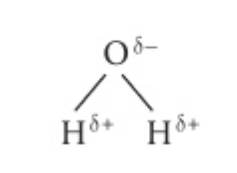
Polarity of molecules depends on:
Equal or unequal sharing of electrons
Covalent bonds
Two atoms share electrons
Water molecule polarity diagram
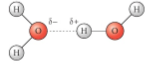
Hydrogen bonds
Ephemeral (short-lived) attraction between water molecules. The oxygen bonds to one of the hydrogens.
Cohesion
Molecules of the same type are attracted to each other
Hydrogen bonds below freezing point
Molecular motion slows until it stops, hydrogen bonds become locked into place, ice crystal forms
Surface tension cause
Water molecules at the surface face have stronger cohesion with the molecules below them, causing inward tension. This is what allows water surface to be a habitat for some organisms.
Water column (cohesion)
Evaporation and cohesion (hydrogen bonds) in water molecules causes tension which pulls on water molecules further down in the xylem where water is evaporating from, and cohesion causes all the water molecules to move upwards in a “water column.” Water is replaced in the xylem within the roots.
Adhesion
Attraction and hydrogen bonding between two different types of molecule. Found in: water column in the xylem, capillary action in soil
Water column (adhesion)
When the water column is not actually being “pulled up,” adhesion between water molecules and cellulose in the plant cell wall allows the column to not fall back down again.
Cuticle (plant)
Wax layer preotecting the leaf from excessive evaporation
Capillary action
Water entering small spaces resisting gravity (for example moving up through soil and into plants) due to adhesion
Cytoplasm soluble molecule examples
Cytoplasmic enzymes
Glucose
Ions
Amino acids
Proteins
Cytoplasm insoluble molecules examples
Steroid hormones
Membrane-bound proteins (can stay attatched to membrane and still interact with other molecules.
Fats/lipids
Cholesterol
The first cells originated in water: true or false?
True
Water importance to living organisms:
Makes up the cytoplasm
Makes up intracellular/tissue fluid
Makes up fluid found in all organelles
Facilitates transport in and out of the cell
Is essential to blood and other fluids
Is the medium for life in bodies of water
Polar covalent bonds:
Electrons are unequally shared. This is what causes hydrogen bonds in water.
Non-polar covalent bonds
Electrons are equally shared
Hydrophobic/insoluble molecules exp.
Steroid hormones
Membrane-bound proteins
Epidermal cells (cuticle)