exam 1
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
2007 United Nations Treaty
International agreement made in 2007 by the United Nations
Adaptational failure
the failure to master or progress in accomplishing developmental milestones
rarely due to a single cause
differ from children their own age in some aspect of development
Adultomorphism
Attributing adult characteristics to children
Applied Behavioral Analysis (ABA)
examines the relationships between behavior and its antecedents and consequences, which is known as a functional approach to behavior
Positive and negative reinforcement are any actions that increase the target response
extinction and punishment decrease a response
behaviorism (operant + classical conditioning)
ABC’s
Attachment theories and styles
emphasize that the quality of children’s attachment to parents will determine their eventual identification with parental values, beliefs, and standards.
secure,
Atypical development
Development that deviates from the norm
Amygdala
Part of the brain involved in emotion processing
Basal ganglia
Group of structures in the brain involved in movement and reward
Behavioral genetics
a branch of genetics that investigates possible connections between a genetic predisposition and observed behavior, taking into account environmental and genetic influences
Behavioral treatment
Therapeutic approach that focuses on modifying behavior
Behaviorism
Psychological approach that emphasizes observable behavior
skinner
schools of thought: operant and classical conditioning
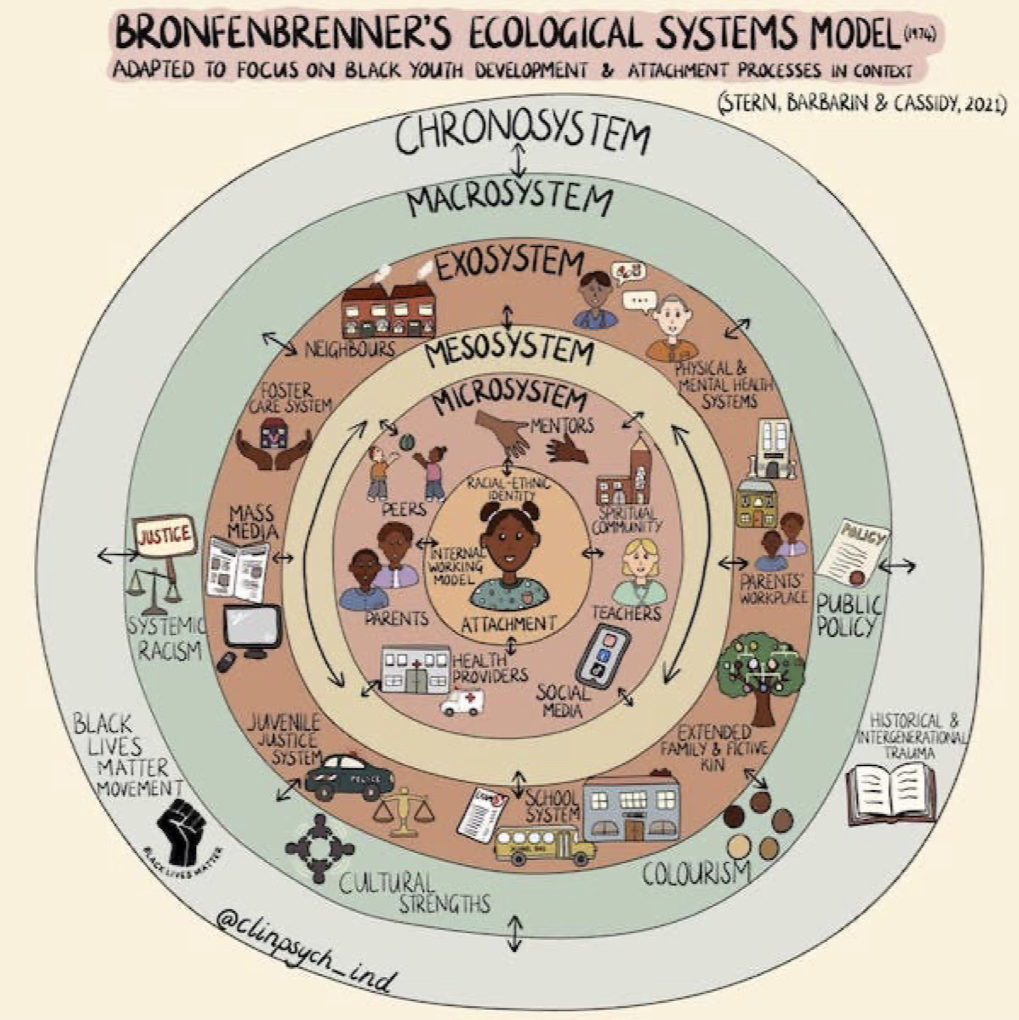
Bronfenbrenner's ecological system theory
Theory that explains development in terms of environmental systems
risks occur at multiple ecological levels
Biological/medical treatment
Therapeutic approach that involves medication or medical procedures
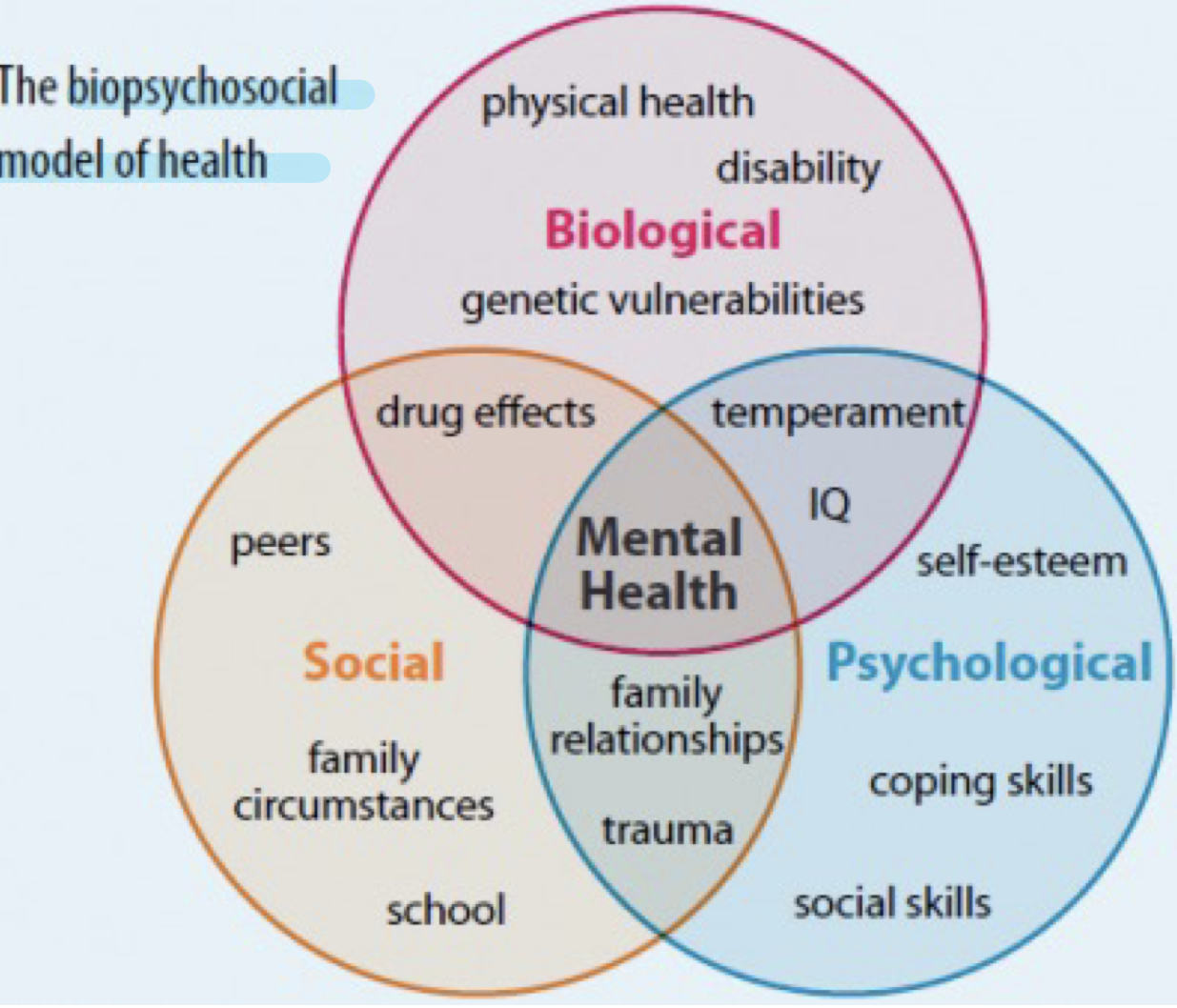
Biopsychosocial model
Brain structure and function
Classical conditioning
pavlov
dog + bell, bell rings —> food
paired associations with a neutral stimulus
Comorbidity
Presence of multiple disorders or conditions in an individual
Competence
The ability to use internal and external resources to adapt to one’s environment.
Children’s competence involves their performance relative to their same-age peers as well as their individual course of development.
Continuity
Concept that development is a gradual and continuous process
Cultural beliefs and values
Ideas and principles that are shared by a particular group
Defining psychological disorder
Process of determining what constitutes abnormal behavior
Developmental norms
Typical patterns of development at different ages
Developmental pathways
Different routes or trajectories of development
Developmental psychopathology
abnormal development is determined by comparing and contracting symptoms and behaviors with typical development and normal developmental processes
emphasizes developmental processes, context, influence of multiple and interacting events
Developmental tasks
developmental challenges that must be mastered by children in different age groups
Developmental continuity
Concept that development is a cumulative process
Discontinuity
Concept that development occurs in distinct stages
Distress
Emotional or psychological discomfort
Emotion reactivity
Individual differences in emotional response to stimuli
Emotion regulation
Ability to control and manage one's emotions
Epigenetics
Study of how gene expression is influenced by environmental factors
changes in gene expression result from alterations in gene structure linked to environmental influences
Equifinality
the same clinical disorder may reflect different developmental pathways
similar outcomes stem from different early experiences and developmental pathways
multiple factors can lead to one outcome
Etiology
the causes of psychopathology or disorders of any sort
Family systems
Approach that views the family as a complex system
Gender differences in disorders
male
neurodevelopmental impairment + externalizing problems
ASD
ADHD
childhood-onset schizophrenia
conduct problems
females
emotional disorders + internalizing problems
depression
eating disorders
History of mental health views and key historical figures
Study of the evolution of ideas about mental health and influential individuals
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
Neuroendocrine system involved in stress response
Hypothalamus
Part of the brain involved in regulating basic functions
Internalizing and externalizing problems
Categories of behavioral and emotional difficulties
Irritability
Tendency to become easily annoyed or angered
Behavioral Inhibition/Fearful
Temperamental trait characterized by shyness and avoidance
Key factors that affect rates and expression of mental disorders
Factors that influence the occurrence and manifestation of mental disorders
Language development
Acquisition and use of language skills
Limbic system
affective processing
hippocampus, cingulate gyrus, amygdala
emotion processing + regulation
memory
fear extinction
learning
impulse control
hunger, sleep, sexual drive
Medical model
Approach that views mental disorders as medical conditions
Molecular genetics
Study of the role of specific genes in behavior and development
Multifinality
diverse clinical disorders may reflect many common risk factors
various outcomes may stem from similar beginnings (in this case, child maltreatment)
one factor thing leads to multiple things
Multiply determined
Result of multiple factors influencing a particular outcome
Neural plasticity and development
Ability of the brain to change and adapt over time
Negative affect
Tendency to experience negative emotions
Neurotransmitters implicated in psychological disorders
Chemicals in the brain that are involved in the development of disorders
Operant conditioning
b.f skinner
box + mice
reward and punishment
Organization of development
Patterns and structures that shape the course of development
Protective factors
any attributes of individuals, environments, or events that temper predictions of psychopathologies based on exposure to risk
operate only in context of risk
Pruning
Process of eliminating unused neural connections
Psychoanalytic theory
Psychological approach that emphasizes the role of unconscious processes
Poverty
Lack of material resources and opportunities
Resilience
individuals display adequate competence despite exposure to adversity or trauma
a dynamic process
the individual, family, and school and community can contribute to resilience
ex) mn doctor
Risk factors
any preexisting factor that increases the chance that a child will develop behavior/emotional problems
biological
dispositional/psychological
learning
social/ecological
biological risk factors
genetic influence
prenatal influence (teratogens)
neurobiological influence (ab. in brain structure)
perinatal insults (LBW, anoxia, preterm)
sleep (deprivation)
dispositional risk factors
“difficult” temperament
negative self-evaluation
poor self-regulation
deficient or deviant social cognition
low intelligence
learning risk factors
behavioral
classic conditioning
instrumental (operant) conditioning
social learning
social/ecological risk factors
maltreatmnet
poverty
family adversity
exposure to community/political violence
poor peer relations
racial/ethnic discrimination
Sensitive periods
Periods of time when the brain is particularly responsive to certain experiences
Shared and non-shared environmental influences
Effects of the environment that are shared or unique to individuals
Stage of development
Period of life characterized by certain tasks and challenges
Social cognition
Thought processes and understanding of social situations
Social learning
Learning through observing and imitating others
Temperament
Innate behavioral and emotional characteristics
Teratogens
Substances or factors that can cause birth defects
Transactional model
Concept that development is influenced by ongoing interactions between individuals and their environment
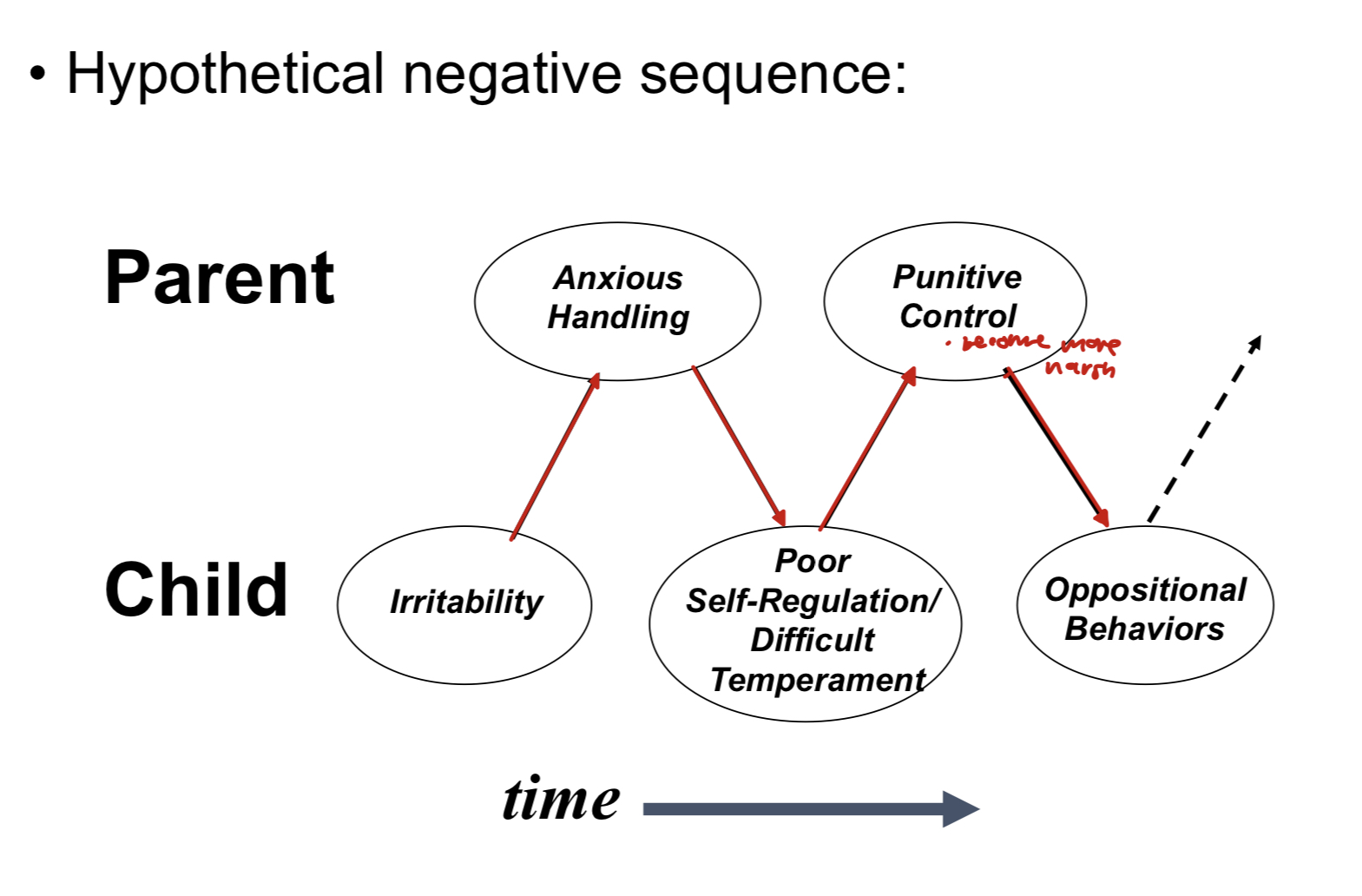
Vulnerability
Susceptibility to developing a disorder
any factor that intensifies the effects of risk
operate only in context of risk
Analogue research
Research method that simulates real-world situations in a controlled setting
Behavior analysis or functional analysis of behavior
Approach that examines the relationship between behavior and its consequences
Behavioral assessment (ABC's)
Process of observing and recording behavior in specific situations
Case studies
In-depth examination of a single individual or group
Checklist and rating scales
Tools used to assess and measure behavior or symptoms
Consent/Assent
Permission given by an individual or their legal guardian to participate in research or treatment
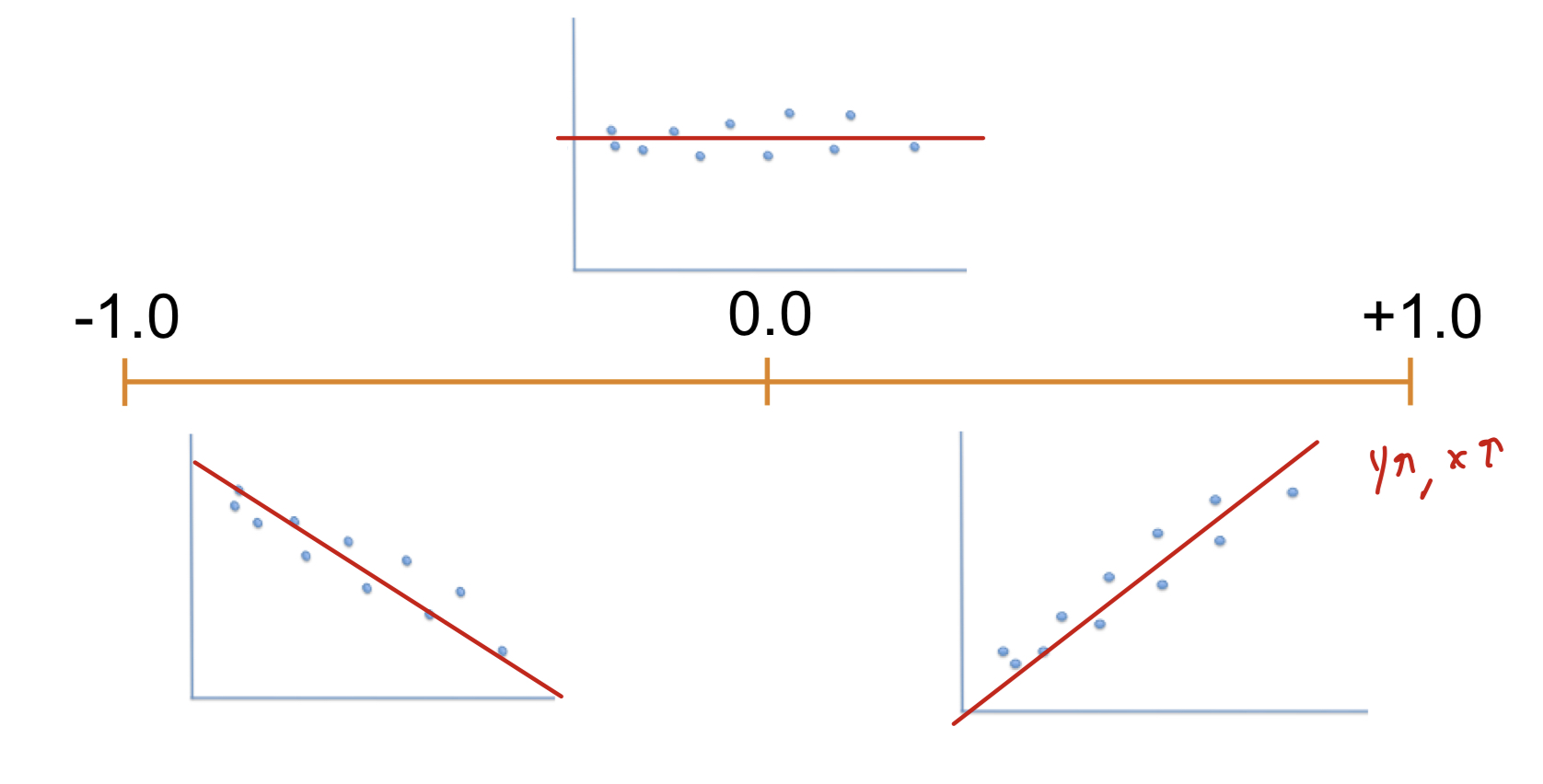
Correlation coefficient
a statistical value that describes how strongly variables (events/characteristics) are related
Cohort effect
Impact of being born in a particular time period or generation
Correlational studies
Research method that examines the relationship between two or more variables
Cross-sectional research
Research method that compares different groups at the same point in time
Epidemiological research
Study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states or events
Experimental studies
Research method that involves manipulating variables to determine cause and effect
Ethical issues
Concerns related to the moral principles and conduct of research or treatment
Hypotheses
statement or proposition that is an effort to explain, predict, or explore something
Longitudinal research
Research method that follows individuals over an extended period of time
Mediating variables
Variables that explain the relationship between two other variables
Moderating variables
Variables that influence the strength or direction of a relationship
Multiple-baseline design
Research design that involves staggered introduction of an intervention
Natural experiment
Research method that takes advantage of naturally occurring events or conditions
Naturalistic observation
Observation of behavior in natural settings without intervention
Neuroimaging
Techniques used to visualize and study the brain
Operational definition
Clear and specific definition of a variable or behavior
Prevalence vs incidence rates
Measures of the frequency of a disorder in a population
Prospective design
Research design that follows individuals over time to observe outcomes
Reliability
Consistency or dependability of a measure
Qualitative research
Research method that focuses on understanding experiences and meanings
Random assignment
Process of assigning participants to different groups by chance
Randomized controlled trials
Research method that involves randomly assigning participants to different treatment conditions