Exam Tips/Tricks Pt. 1 - Focus Topics & Exam Strategies
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
In regenerative medicine, how is it a field that applies biological science principles to promote regeneration? What is the main attempt/focus?
What are 3 types of regenerative medicine they use?
promote regeneration by delivering or replacing organs, cells, or tissues in an attempt to restore diseased and damaged tissues and whole organs
1. platelet-rich plasma
2. stem cells
3. viscosupplementation
In platelet-rich plasma (PRP), it releases bioactive proteins which stimulate the body’s ability to heal due to what 3 properties?
It is obtained from where using the centrifugation method, and then injected into where?
platelet rich plasma
stimulate body’s ability to heal due to its regenerative, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory properties
obtained from patient’s blood, then injected into the target site
What are 6 indications for using platelet-rich plasma?
OA
ligament injury
meniscus injury
muscle injury
tendinopathy
spine disorder
In stem cell regenerative medicine, the bone marrow aspirate is collected and centrifuged to harvest stem cells. These cells are capable of doing what into many different cells?
These are also injected where?
stem cells
capable of self-renewal and differentiation into many different cells
injected into the target site
Indications for stem cells:
what potential do they have for treatment?
what are 5 other indications of stem cells?
stem cells have potential for treatment of many malignant and non-malignant diseases
tendinopathies, plantar fasciitis, osteoarthritis, burns, MS, SCI
Viscosupplementation is the injection of what into intra-articular space? It can restore what 2 things of osteoarthritic synovial fluid?
The substance plays an essential role in shock absorption, and what 2 other nature of synovial fluid?
viscosupplementation
injection of hyaluronic acid (HA) into intra-articular space
restores viscosity and elasticity of osteoarthritic synovial fluid
HA plays an essential role in shock absorption, lubrication, and viscoelastic nature of synovial fluid
What is the indiciation for use of viscosupplementation?
FDA approved for knee OA
frozen shoulder
Rehabilitation for post-regenerative medicine pt. 1:
rest for how long but do not do what? avoid what?
avoid what 3 modalities for how long? after what specific regenerative medicine, because it reduces efficacy?
rest for the first 24-48 hours, but do not lie sedentary for healing (avoid WB)
avoid ice/heat and NSAIDs for 14 days before and post PRP and stem cell as it reduces efficacy
How many weeks is initial rehab post regenerative medicine?
What are the main components of rehab?
Avoid what activities?
initial rehab ~4 weeks
protection for healing and gentle range of motion
gentle ROM, isometrics, stationary bike, elliptical
avoid all contact sports as well as jogging, running, or sports that involve impact on that joint
What happens after the early phases ~12 weeks of rehab post regenerative medicine?
strengthening and neuromuscular control exercises emphasized in addition to endurance training
What happens in the final stages of rehab post regenerative medicine over 3 months?
progressive dynamic extremity control and stability during sport specific movements, such as change of direction and rotational movements
Practice Question 1
A patient is two weeks post platelet-rich plasma therapy for meniscal injury of right knee. The physical therapist would want to continue addressing intervention techniques to return the patient to prior level of function and eliminate any discomfort. Which of the following is most likely to be CONTRAINDICATED to include in the plan of care at this point?
A. Stationary bike
B. Quadriceps and hamstring sets
C. Clam shells
D. Proprioceptive training
D. Proprioceptive training
RATIONALE: Proprioceptive training would be not be appropriate to include in the POC in initial 1-4 weeks.
Quadricep/hamstring sets, stationary bike and clam shells are more utilize during weeks 1-4 to prevent muscle atrophy and to increase muscle strength.
foundations for success / exam strategies / follow key rules

What is the rule of opposites?
understand some examples
when 2 options are exactly opposite to each other, there is a very high possibility that the correct answer would be either of them
ex: increase OR decrease in HR
one of those is the correct answer and ignore the rest of the options
think with your brain (NPTE) and not with your heart (PT)
What is the rule of similarities?
when 2 options mean the same thing then both options should be eliminated, as neither of them would be the correct answer

What is the rule of extremes?
answers that present extreme or exaggerated values, or statements that are often incorrect
in contrast, moderate values are more likely to be correct
Practice Question 2
A physical therapist plans to implement a joint mobilization technique to improve a patient’s wrist flexion range of motion following wrist surgery. Which of the following mobilizations is MOST APPROPRIATE to achieve this goal?
A. Dorsal glide of the carpal bones
B. Volar glide of the carpal bones
C. Anterior glide of the carpal bones
D. Radial glide of the carpal bones
A. Dorsal glide of the carpal bones
RATIONALE: Dorsal/ Posterior glide of the carpal bones- Improves wrist flexion
convex on concave - opposite roll and slide
anterior roll, dorsal glide
Volar glide of the carpal bones- improves wrist extension
Anterior glide of the carpal bones – Improves wrist extension
Radial glide of the carpal bones- improves ulnar deviation
What is the rule of elimination?
eliminate known incorrect options to identify the BEST one
commonly used method at most times while solving questions
recall pressure ulcer grades
venous and arterial mnemonic
grades 1, 2, 3, 4
1 = red
2, 3 = fat
4 = bone
unstageable
deep tissue
venous = venmo
arterial = alma
Diabetic ulcer (neuropathic ulcer) is usually seen where?
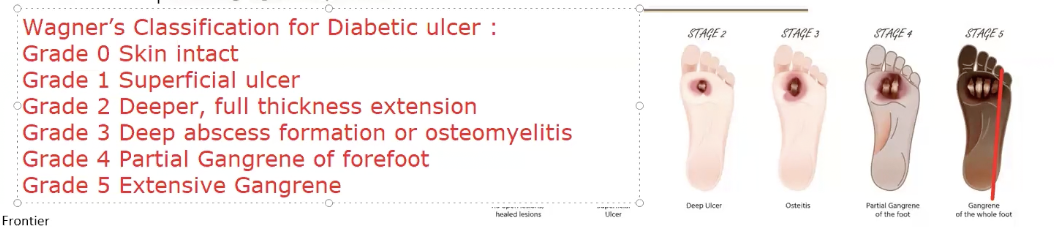
What are the 6 grades of the Wagner scale?
diabetic / neuropathic ulcer
usually seen over the sole of the foot (weight-bearing surface)
Wagner scale
grade 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
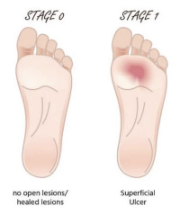
Grade 0 and 1 of the Wagner scale for diabetic ulcer:
ulcerations, deformations, tissues
Grade 0
NO open ulceration, but possible existence of bone deformation of hyperkeratosis
Grade 1
SUPERFICIAL ulceration, but without penetration to deeper tissue
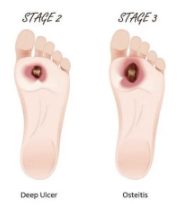
Grade 2 and 3 of Wagner scale for diabetic ulcer:
which tissues exposed or present of what?
Grade 2
deeper extension into tendons, bones or joint capsule, which may be exposed
Grade 3
presence of tendonitis, osteomyelitis, cellulitis or deeper tissue abscess
Grade 4 and 5 of Wagner scale for diabetic ulcer:
gangrene (loss of blood supply —> tissue death) and where, infections?
Grade 4
wet or dry gangrene of toe or dorsum of the foot, often with plantar infection
Grade 5
extensive gangrene of the foot with necrotic lesions and soft tissue infections indicating higher amputation
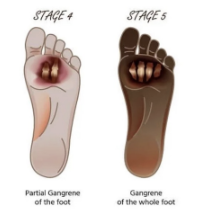
Practice Question 3
Which of the following instruments is MOST APPROPRIATE to assess protective sensation in the feet for a patient with Type 2 diabetes mellitus?
A. Two-point discriminator
B. Cotton ball
C. Skin caliper
D. 5.07 (10 g) monofilament
D. 5.07 (10 g) monofilament
RATIONALE: 5.07 (10 g) monofilament: This instrument is specifically designed to assess protective sensation. It is the gold standard for detecting loss of protective sensation in patients with diabetes mellitus, helping to identify those at risk for neuropathic ulcers and other complications.
Two-point discriminator: Used to assess the ability to distinguish between two points touching the skin simultaneously, which is useful for evaluating fine tactile discrimination but not specifically for protective sensation.
Cotton ball: Used for light touch sensation, which does not adequately assess protective sensation.
Skin caliper: Typically used to measure skin fold thickness, not for sensory assessment.
What assessment is used to assess protective sensation and injury risk?
How many test points are there and where?
Explain the procedure, where you apply it, how strong, what should the patient do, and how many times?
What is a positive test?
What orthotic would be used?
Semmes Weinstein Monofilament (5.07, 10 g)
test points
10 points - 9 on sole, 1 on dorsum - patient’s eyes closed
procedure
apply monofilament perpendicular to the skin
apply enough force to bend the filament for 1-1.5 seconds
ask the patient to respond with “yes” if they feel it
repeat each point 2-3 times
positive test
patient unable to feel the filament, increased risk of ulcers
orthotic
use of total contact cast for walking to offload pressure areas

The monofilament (10 g or 5.07) means the thickness of the brush.
What are the values for sensation?
if you are unable to feel a 4.17, then you have superficial sensation loss
5.07 = protective
6.1 = all is gone

Keywords when reading the question

Practice Question 4.1
Which of the following is the BEST interpretation based on the grade on Modified Ashworth Scale?
A. More marked increase in muscle tone through most of ROM however affected parts difficulty to move
B. More marked increase in muscle tone through part of ROM however affected parts easily moved
C. Considerable increase in muscle tone as it difficult to perform passive movements
D. More marked increase in muscle tone through most of ROM however affected parts easily moved
D. More marked increase in muscle tone through most of ROM however affected parts easily moved
RATIONALE: More marked increase in muscle tone through most of ROM however affected parts easily moved. According to Modified Ashworth Scale: Score 0- no increase in muscle tone,
score 1 Slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch and release or by minimal resistance at the end of the range of motion when the affected part(s) is moved in flexion or extension,
score 1+ - Slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch, followed by minimal resistance throughout the remainder (less than half) of the ROM,
score 2 - More marked increase in muscle tone through most of the ROM, but affected part(s) easily moved,
score 3 - Considerable increase in muscle tone, passive movement difficult.
Modified Ashworth Scale is used for testing what?
What are the number grades?
0 —> best
1 —> at end of ROM, catch and release
1+ —> part ROM, sustained catch
2 —> throughout ROM, passive movement possible
3 —> throughout ROM, passive movement difficult
4 —> fixed
TIP:
remember 2, 3, 4 are throughout ROM, 1+ is part


Practice Question 4.2
Based on the lab values, what condition is the patient MOST LIKELY to have?
A. Liver failure
B. Hypoglycemia
C. Heart arrhythmias
D. Anemia
C. Heart arrhythmias
RATIONALE: All of the following lab values are within normal limits beside potassium. The normal value for potassium = 3.5-5.0mEq/L. Electrical conduction of the heart is controlled by electrolyte levels (potassium, calcium, and magnesium).
BUN (10-20) and creatinine (0.5-1.2mg/dL) are important for kidney function.
Glucose (70-110mg/dL) is closely observed in patients with diabetes.
Low potassium produces heart arrhythmias and lower extremity cramping.
If hemoglobin (adult female = 12-16g/dL, adult male = 13-18g/dL) is low then it is termed anemia.
Lab values:
sodium
potassium
chloride
calcium
BUN
creatinine
carbon dioxide
magnesium
hemoglobin
hematocrit
MNEMONIC:
I go to 7/11 for sugar drinks - 70-110 glucose
Call 911 when you break your hip - 9-11 calcium
Little MAGgie is 1.5-2.5 years old - magnesium
She ate 3.5-5 bananas - potassium
and drank 9-11 oz of milk - calcium
she had a 135-145 minute nap - 135-145 Na - sodium
After swimming in the ocean we cook our buns in the over for 10-20 minutes - 10-20 BUN


Practice Question 4.3
Which of the following is MOST APPROPRIATE recommendation for a wheelchair accessible plan for the patient's home?
A. Ramp slope 6:1
B. Ramp width of 36 inches
C. Carpet floors
D. Door width of 22 inches
B. Ramp width of 36 inches
RATIONALE: For wheelchair accessibility, the door width must be at least 32in, wooden floors, ramp slope of 1:12.
Other guidelines for wheelchair accessibility include:
Open floor plan
•Wheelchair access to bathroom
•Toilet seat height same as wheelchair seat height
•Adequate clearance under sinks
•Insulated pipes
•Roll-in shower
•Ramp landings every 30 ft (9.1 m)
•No thresholds through doorways
• Lever-type door handles.
Slopes and Ramps:
How wide is the hallway when turning is not required?
What is the minimum ramp grade for a wheelchair?
Example: 2 steps, each step 7 inches
hallway
36 inches in width, when turning is not required
ramp for wheelchair
minimum ramp grade for a wheelchair ramp = for every inch of threshold height, there is a corresponding 12 inches of ramp length
running slope of 1:12
example
2 steps needed, one step = 7 inches (standard step height), running slope 1:12
7 × 12 = 84 inches
84 × 2 = 168 inches