1.11 - Electrode Potentials and Electrochemical Cells
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What happens when a rod
of a metal is dipped into a
solution of its own ions?
An equilibrium is set up between the solid metal
and the aqueous metal ions
Write a half-equation for
zinc (s) to zinc (II).
Zn (s) ⇌ Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e
Write a half-equation for
copper (II) to copper (III).
Cu 2+ (aq) ⇌ Cu 3+ (aq) + e
What is the simplest salt
bridge made of?
Filter paper soaked in saturated solution of KNO 3
(potassium nitrate)
Why are salt bridges
necessary?
Complete the circuit, but avoid further metal/ion
potentials as does not perform electrochemistry.
Allows ion movement to balance the charge. Do
not react with electrodes
What symbol is used to
represent a salt bridge in
standard notation?
||
What type of species goes
on the outside (furthest from
the salt bridge) in standard
cell notation?
The most reduced species
What does | indicate?
Phase boundary (solid/liquid/gas)
How would an
Aluminium/Copper cell be
represented?
Al(s) | Al 3+ (aq) || Cu 2+ (aq) | Cu(s)
What happens at the
left-hand electrode?
Left hand electrode is where oxidation occurs.
Left hand electrode is the half cell with the most
negative E o value
What happens at the
right-hand electrode?
right hand electrode is where reduction occurs.
Right hand electrode is the half cell with the most
positive E o value
Which side of the cell has
the most negative E° value?
what happens to the metal
with the most negative E o
value?
Oxidation - left hand electrode
Draw the standard hydrogen
electrode
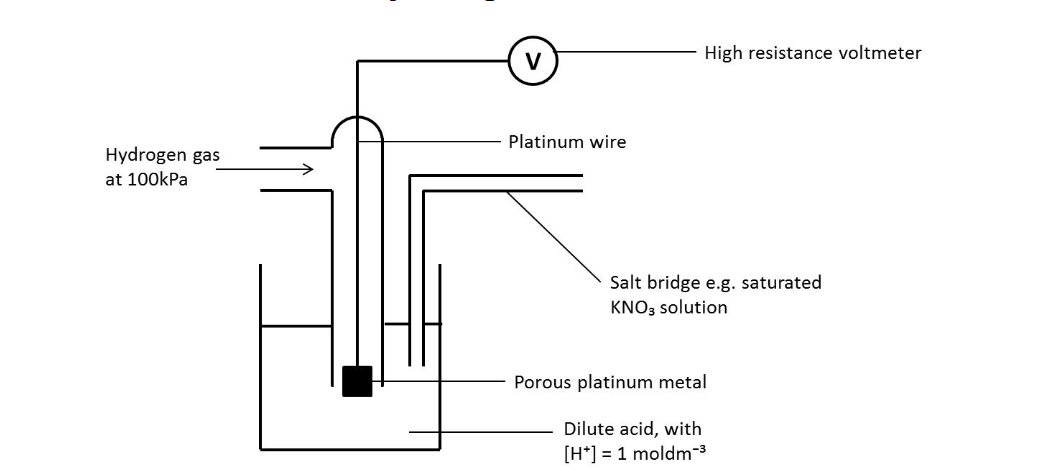
What conditions is the
standard hydrogen
electrode used in?
Temperature = 298 K
Pressure = 100 kPa
[H + ] = 1.00 mol dm -
What is the standard
hydrogen electrode used
for?
Comparing other cells against. E O of SHE is
defined as 0, so all other E o values are compared
against it.
Why might you use other
standard electrodes
occasionally?
They are cheaper/easier/quicker to use and can
provide just as good a reference.
Platinum is expensive
If an E o value is more
negative, what does it mean
in terms of
oxidising/reducing power?
Better reducing agent (easier to oxidise)
If an E o value is more
positive, what does it mean
in terms of
oxidising/reducing power?
Better oxidising agent (easier to reduce)
What factors will change E o
values?
Concentration of ions
Temperature
What happens if you reduce
the concentration of the ions
in the left hand half cell?
Equilibrium moves to the left to oppose the
change of removing ions; this releases more
electrons, the E o of the left hand cell becomes
more negative, so the e.m.f. Of the cell
increases.
How do you calculate the
emf of a cell from E o
values?
E o
cell = E o
right - E o
left
When would you use a
Platinum electrode?
When both the oxidised and reduced
forms of the metal are in aqueous
solution
Why is Platinum chosen?
Inert so does not take part in the electrochemistry
Good conductor to complete circuit
How would you predict if a
reaction would occur?
Take the 2 half equations.
Find the species that is being reduced (this is effectively the
right hand electrode)
Calculate its E o value minus the E o value of the species that
is being oxidised (effectively the left hand cell).
If E o overall > 0, reaction will occur.
What was the first
commercial cell made from
(Daniell cell)?
Zinc/copper (II)
What are zinc/carbon cells
more commonly known as?
Disposable batteries
What are the two reactions
that take place in
zinc/carbon cells?
Zn oxidised to Zn 2+
NH 4
+ reduced to NH 3 at carbon electrode
What are the reactions that
occur in a lead/acid battery
(car batteries)?
Pb + SO 4
2- → PbSO 4 (s) + 2e -
PbO 2 + 4H + + SO 4
2- + 2e - → PbSO 4 + 2H 2
O
How are cells recharged (if
they are rechargeable)?
Reactions are reversible and are reversed by
running a higher voltage through the cell than the
cell’s E o
Nickel/cadmium cells are
rechargeable AA batteries
etc. What reactions occur at
the electrodes?
Cd(OH) 2 (s) + 2e - → Cd(s) + 2OH -
NiO(OH) (s) + H 2
O + e - → Ni(OH) 2 (s) + OH
Where are lithium-ion cells
used?
Mobile phones
Laptops
What reactions occur on
discharge in lithium-ion
cells?
Li + + CoO 2 + e - → Li + [CoO 2 ] -
Li → Li + + e -
What is a fuel cell?
A cell that is used to generate electric current;
does not require electrical recharging
What are the reactions that
take place at the two
electrons in an alkaline
hydrogen fuel cell?
2H 2 + 4OH - → 4H 2 O + 4e -
O 2 + 2H 2 O + 4e - → 4OH
Draw a diagram of a
hydrogen fuel cell.
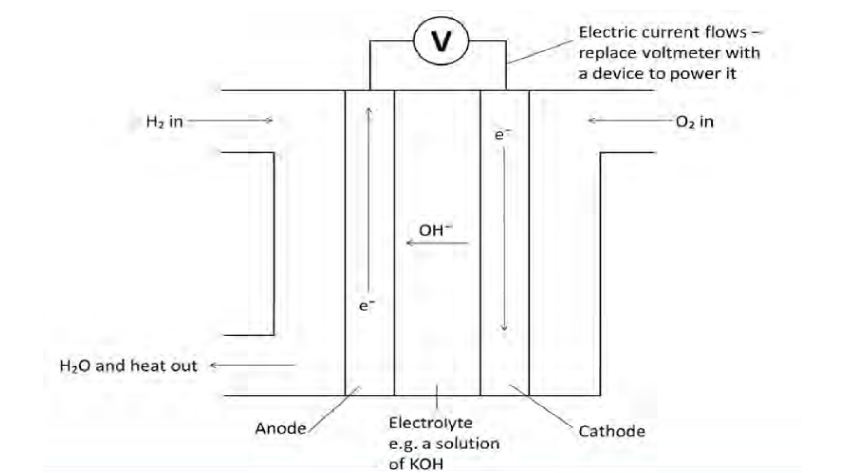
Why is it better to use a fuel
cell than to burn H 2 in air,
even though the same
overall reaction occurs?
In combustion, sulfur containing compounds (SO 2 , SO 3 ) and
nitrogen containing compounds (NO 2 , NO x
) are produced due
to the high temperatures and the S and N in air. These are
bad for the environment.
This does not occur in a fuel cell; the only product is water.
More efficient
Disadvantages of fuel cells?
Hydrogen is a flammable gas with a low b.p. → hard and
dangerous to store and transport → expensive to buy
Fuel cells have a limited lifetime and use toxic chemicals in
their manufacture
How do you find the
weakest reducing agent
from a table of electrode
potential data?
Most positive E θ value. Then it is the PRODUCT
of the reduction equation i.e. imagine equation
going from right to left
What is the reason that
some cells cannot be
recharged?
Reaction of the cell is not reversible - a product is
produced that either dissipates or cannot be
converted back into the reactants
Why might the e.m.f. Of a
cell change after a period of
time?
Concentrations of the ions change - the reagents
are used up
How can the e.m.f. Of a cell
be kept constant?
Reagents are supplied constantly, so the
concentrations of the ions are constant; E o
remains constant