CON-317 Safety Management - Midterm Exam
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
NIOSH
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
EMR
Experience Modification Rate - A workers’ compensation multiplier

TRIR
Total Recordable Incident Rate -
The lower the rate, the better the safety performance
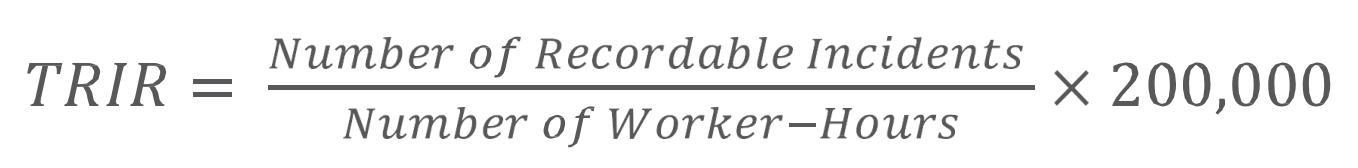
A “recordable” Injury or Illness:
Any work-related fatality
Any work-related injury or illness that results in loss of consciousness, days away from work, restricted work, or transfer to another job
Any work-related injury or illness requiring medical treatment beyond first aid
Any work-related diagnosed case of cancer, chronic irreversible diseases, fractured or cracked bones or teeth, and punctured eardrums (a significant injury or illness diagnosed by a physician or other licensed health care professional)
There are also special recording criteria for work-related cases involving: needlesticks and sharp injuries; medical removal; hearing loss; and tuberculosis
Who is not covered under the OSH Act of 1970?
Self-employed persons
Farms at which only immediate family members of the employer are employed
Working conditions regulated by other federal or state agencies (ex: FAA, DoD)
Safety and Health Regulations for Construction - OSHA Standard
29 CFR 1926
Safety and Health Regulations for General Industry - OSHA Standard
29 CFR 1910
Vertical vs Horizontal Standards
Most OSHA standards are Horizontal (i.e., general safety and health rules) covering hazards that exist in a wide variety of industries.
Vertical standards are very specific safety/health rules and apply solely
to one industry type (ex, construction trench collapse)
Employer’s Duty “General Duty Clause”
“Each employer shall furnish to each of his employees' employment and a place of employment which are free from recognized hazards that are causing or are likely to cause death or serious physical harm to his employees.”
Employer Responsibilities
Notify OSHA Within:
8 hours of workplace fatality
24 hours of hospitalization, amputations, and/or loss of an eye.
Whistleblower Complaint
A complaint alleging that an employer has retaliated against an employee for engaging in protected activity, such as reporting a safety hazard
Safety and Health Complaint
A report about an unsafe or unhealthy condition in the workplace.
OSHA Focus Four Hazards
Falls (35.2%)
Struck-by (16.80%)
Caught-in/between (5.70%)
Electrocution (7.50%)
Fall Hazard
Anything at your worksite that could cause you to lose your
balance or lose bodily support and result in a fall.
OSHA requires fall protection at
6 feet
AND/OR Working over dangerous machinery
Exceptions:
On a scaffold: 10 feet
Steel erection: 15 feet
Fall Protection Standard
29 CFR 1926 Subpart M
Duty for fall protection
An unprotected side or edge which is 6 feet (1.8 m) or more, constructing a leading edge 6 feet (1.8 m) or more, or the inside bottom edge of the wall opening is less than 39 inches requires guardrail systems, safety net systems, or personal fall arrest
Leading Edge: the edge of a floor, roof, or formwork for a floor or other walking/working surface.
Hole (OSHA Definition)
A gap or void 2 inches (5.1 cm) or more in its least dimension, in a floor, roof, or
other walking/working surface;
Guardrail Systems: Top Rail
42 inches (±3 in) above walking/working surface.
Guardrail Systems: Midrail
Installed halfway between top rail and working surface.
Guardrail Systems: Toe Board
At least 3.5 inches high to prevent falling objects.
Safety Net Systems Minimum Requirements
No more than 30 feet below where employees work
400-pound drop test
6” maximum mesh
Safety Net Systems - vertical vs. horizontal design
Up to 5 feet from working level = 8 feet horizontal distance
More than 5 ft - 10 ft from working level = 10 feet horizontal distance
10 ft + from working level = 13 feet horizontal distance
Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS) - ABC
Anchorage Connector (Ex: I-Beam)
Body Wear (Ex: full body harness)
Connecting Device (Ex: Shock absorbing lanyard)
Safety Monitoring System
A designated competent person (safety monitor) to monitor the safety of workers and to warn them when their work puts them close to a fall hazard
Must be on the same level as the workers and be able to see them
Competent Person
One who is capable of identifying existing and predictable hazards in the surroundings or working conditions which are unsanitary, hazardous, or dangerous to employees, and who has authorization to take prompt corrective measures to eliminate them
Qualified Person
One who, by possession of a recognized degree, certificate, or professional standing, or who by extensive knowledge, training, and experience, has successfully demonstrated his ability to solve or resolve problems relating to the subject matter, the work, or the project
Is expected to design, specify, or approve systems and equipment
Warning Line System
ALL Sides of permimeter
Flagged with high-vis material
Min. 6’ interval
Types of Struck-by Hazards
Falling object
Flying Object
Swing Object
Rolling Object
Driving Safety
Do not drive a vehicle in reverse gear with an obstructed rear view, unless it has an audible reverse alarm, or another worker signals that it is safe.
Severity of Shock is determined by:
The path of the current through the body
The amount of current flowing through the body
The length of time the body is in the circuit
Pneumonic: BE SAFE
Burns
Electrocution
Shock
Arc Flash/Arc Blast
Fire
Explosions
Electrical Hazards: OSHA Subpart
1926 Subpart K
GFCI
Stands For: Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupters
A fast-acting circuit breaker designed to shut off electric power in the event of a ground-fault
OSHA requires: 120-volt, single-phase, 15- and 20-ampere receptacle outlets
Tools: Use only _____ OR ______. (Electrical)
A proper grounding pin or are designed with double insulated protection
Type 2/Class II
Double Insulated Electrical Appliances
Double-box emblem
Caught-in or -between hazards
Injuries resulting from a person being caught,
crushed, pinched, or compressed between two
or more objects, or between parts of an object.
Types of caught-in or -between hazards
Machinery that has unguarded moving parts
Buried in or by
Pinned Between
Excavation Safe Work Practices
All excavations and trenches 5 feet deep or more, but less than 20 feet
Protected by: sloping or benching, trench box or shield, or shoring
All excavations is more than 20 feet deep
A professional engineer must design the system
If less than 5 feet deep, a competent person may determine that a protective system is not required
PPE OSHA subpart
1926.28(a) Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
29 CFR 1926 Construction Industry
• Subpart E - Personal Protective Equipment
• Subpart 1910.132(d)(1) and (2)
• Subpart 1910.134 Respiratory Protection incorporated by reference
Head Protection
ANSI Z89.1
Z89.1-2003
Z89.1-1997
Head Protection - 2 Types
Type I - Top Impact ONLY
Type 2 - Top AND side impact
Head Protection - 3 Classes
G (General) – General services limited voltage protection – protect your head up to 2,200 volts
E (Electrical) – Utility service high voltage protection – protect your head up to 20,000 volts
C (Conductive) – Special service – no voltage protection
Hearing Protection Requirements
OSHA requires hearing protection at 90 dBA (PEL, permissible exposure limit)
85 dBA – OSHA’s action level (recommended)
Routes of Entry - Chemical Exposure
Inhalation
Ingestion
Absorption
Injection
Asbestos PEL
OSHA Permissible Exposure Limit:
0.1 fiber/cm3 per 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA)
Silica Dust PEL
PEL for respirable silica dust:
50 mg/m3
Common Health Hazards
Chemical
Physical
Biological
Ergonomic
Effects of Exposure to Ergonomic Hazards
Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)
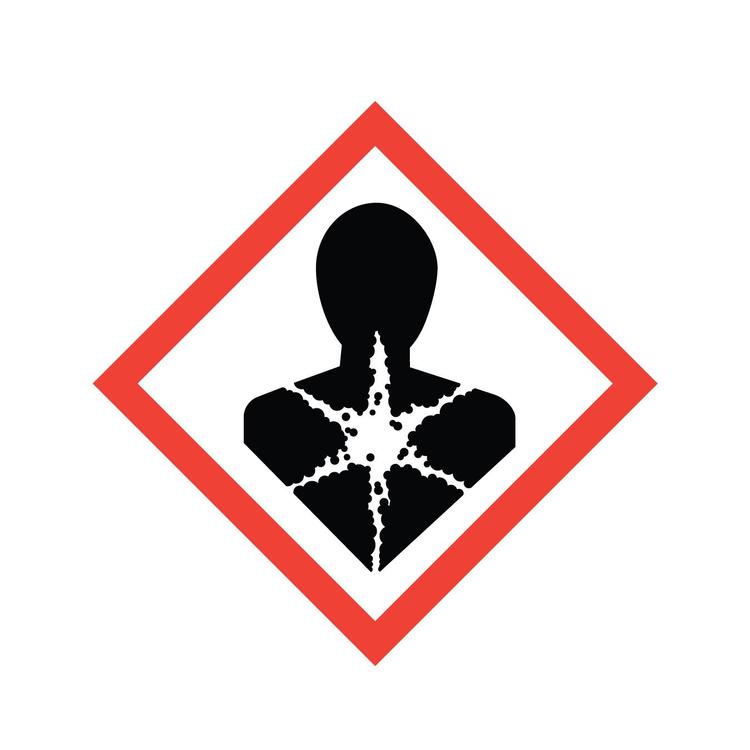
Hazcom: Health Hazard
A cancer-causing agent (carcinogen) or substance with respiratory, reproductive or organ toxicity that causes damage over time (a chronic, or long-term, health hazard).

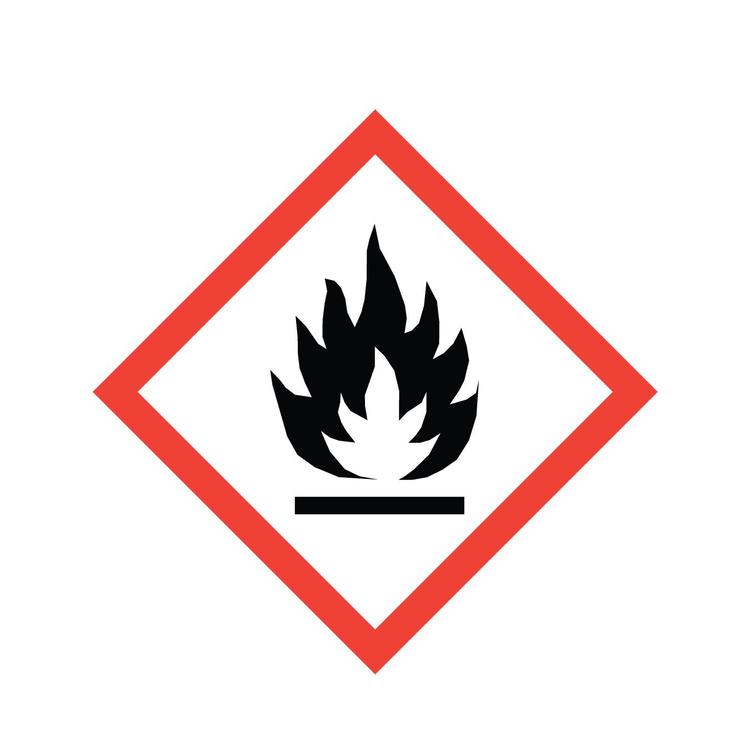
Hazom: Flame
Flammable materials or substances liable to self ignite when exposed to water or air (pyrophoric), or which emit flammable gas.

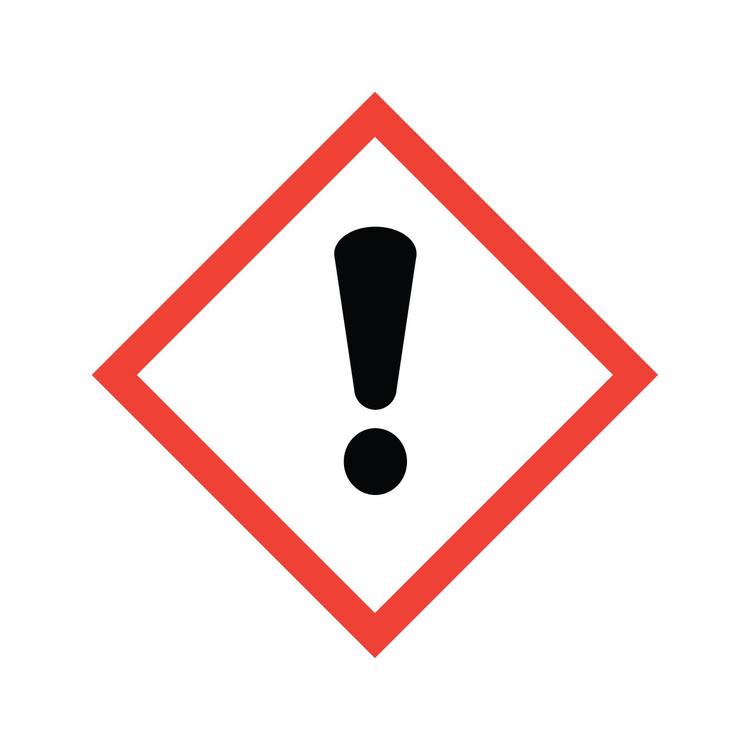
Hazcom: Exclamation Mark
An immediate skin, eye or respiratory tract irritant, or narcotic.

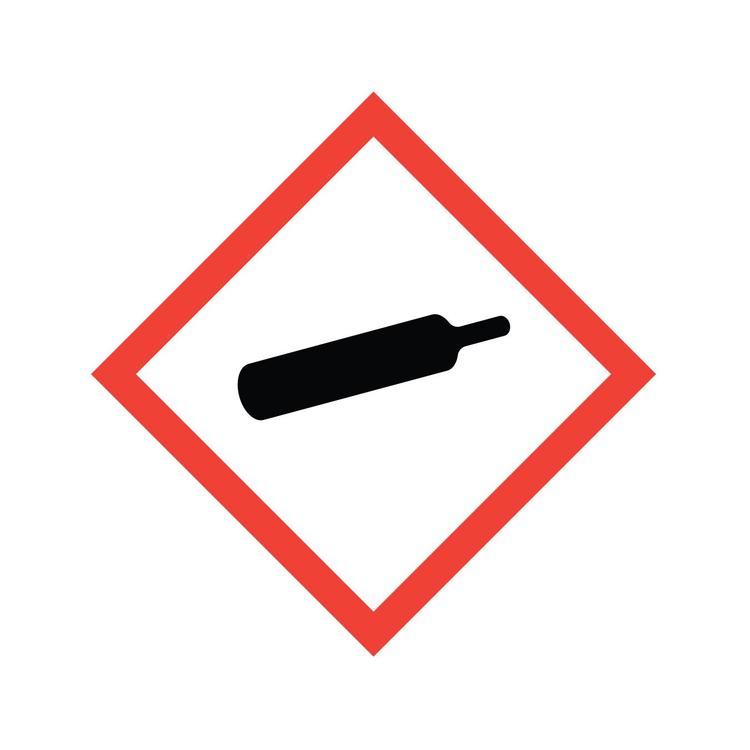
Hazcom: Gas Cylinder
Gases stored under pressure, liquified gases, and dissolved gases; such as ammonia, liquid nitrogen, or acetylene.

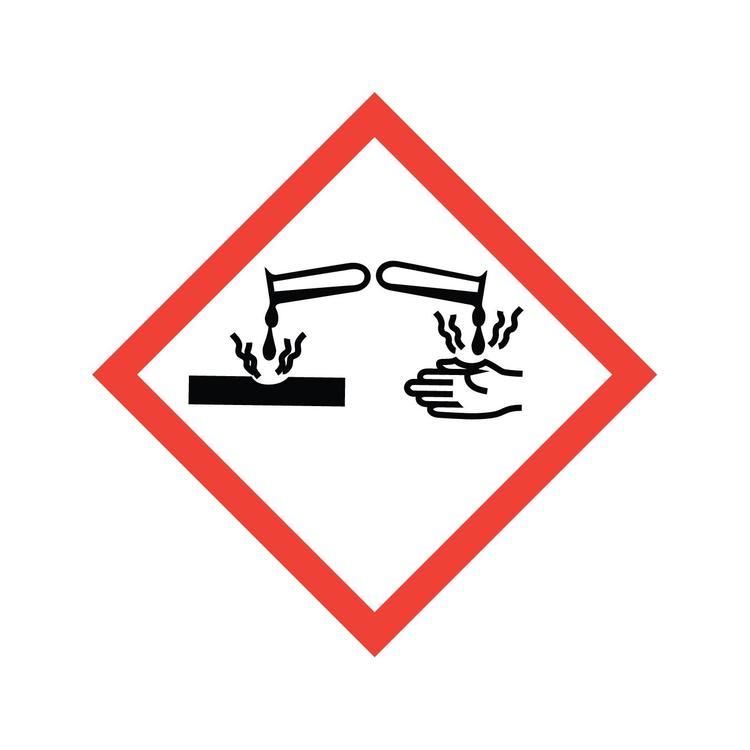
Hazcom: Corrosion
Materials causing skin corrosion/burns or eye damage on contact, or that are corrosive to metals.
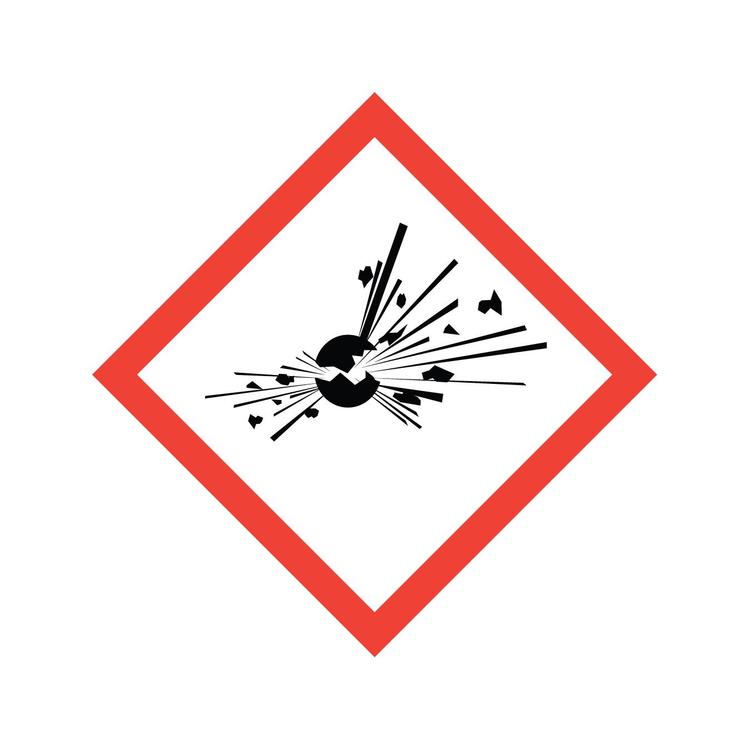
Hazcom: Exploding Bomb
Explosives, including organic peroxides and highly unstable material at risk of exploding even without exposure to air (self-reactives).

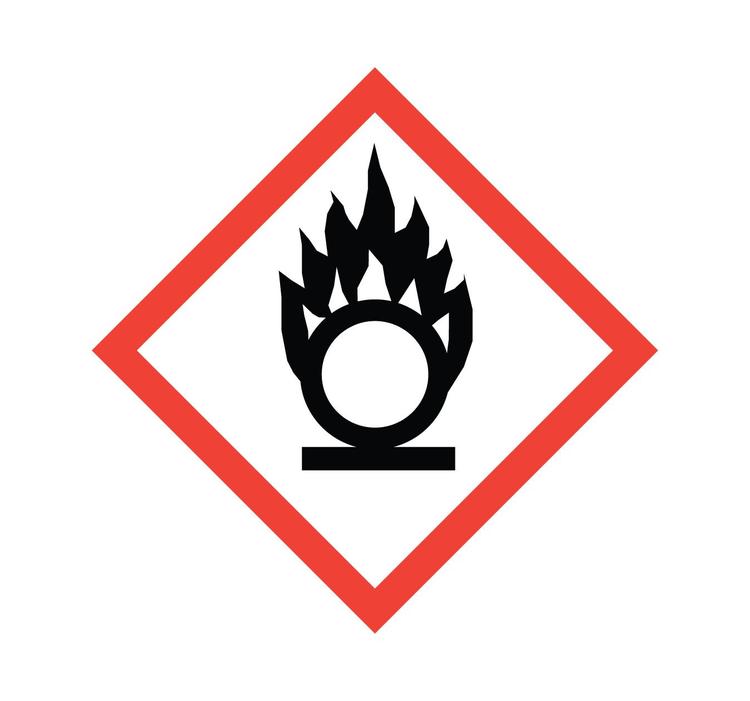
Hazcom: Flame over Circle
Identifies oxidizers. Oxidizers are chemicals that facilitate burning or make fires burn hotter and longer.

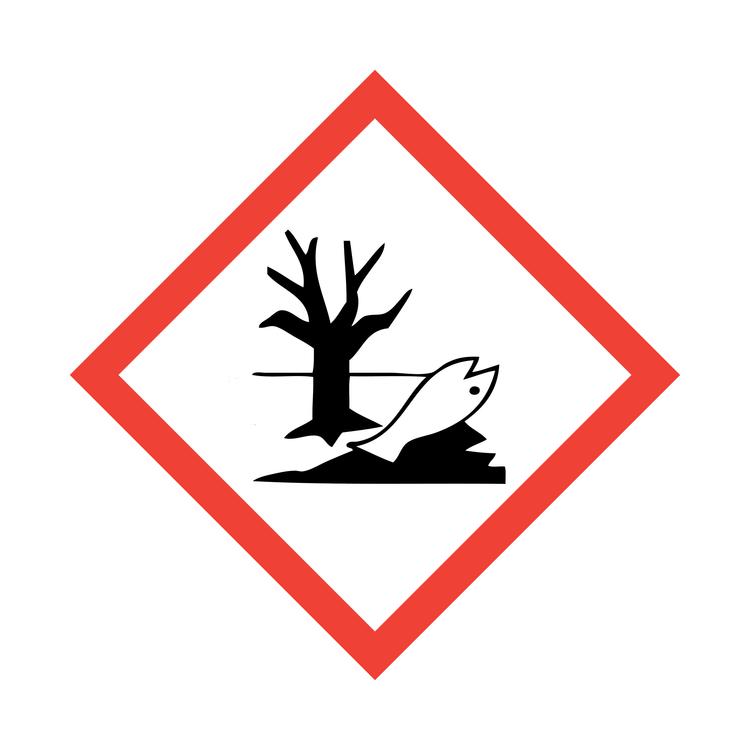
Hazcom: Environmental
Chemicals toxic to aquatic wildlife. (Non-Mandatory)

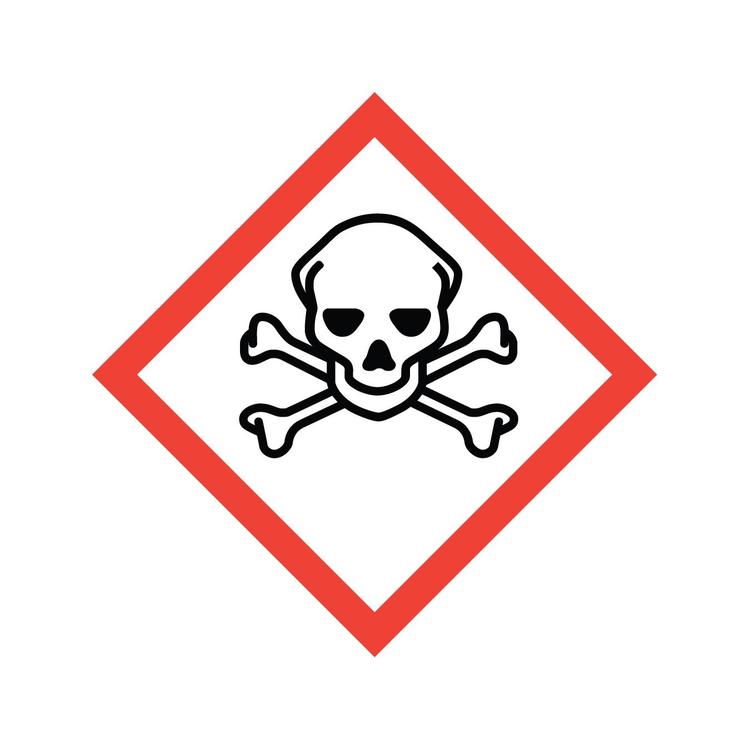
Hazcom: Scull and Crossbones
Substances, such as poisons and highly concentrated acids, which have an immediate and severe toxic effect (acute toxicity).

NFPA Diamond

Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
Identification
Hazard(s) identification
Composition/Information on Ingredients
First-Aid Measures
Fire-Fighting Measures
Accidental Release Measures
Handling and Storage
Exposure Controls/Personal Protection
Physical and Chemical Properties
Stability and Reactivity
Toxicological Information
Ecological Information (non-mandatory)
Disposal Considerations (non-mandatory)
Transport Information (non-mandatory)
Regulatory Information (non-mandatory)
Other Information
Concrete and Masonry - OSHA Subpart
29 CFR 1926.700 (Subpart Q)
Masonry Hazards - Common Mistake
Common mistake to guard vertical rebar and forget the horizontal rebar.
Post-Tensioning Operations: Safety Measures
No employee (except those essential to the post-tensioning operations) shall be permitted to be behind jacks or end anchorages during post-tensioning operations.
Signs and barriers shall be erected to limit employee access to the post-tensioning area during tensioning operations.
Concrete Pumping Systems Design Requirements
Designed For 100% overload
Concrete Bucket Requirements
Hydraulic or Pneumatic gates shall have positive safety latches
Formwork must be capable of supporting both ______ and ______ loads.
vertical, lateral
Precast Concrete Requirements
Lifting inserts capable of supporting 2X the intended load
Lifting inserts in other than tilt-up members 4X the intended load
Lifting Hardware… 5X intended load
Limited Access Zone Requirements
Height of wall + 4 feet
Excavations vs. Trenches
EXCAVATION: Any man-made cut, cavity, trench, or depression in an earth surface, formed by earth removal
TRENCH: A narrow excavation (in relation to its length) made below the surface of the ground
Depth > Width
Width (at the bottom) ≤ 15 feet
“The First Line of Defense from Cave-ins” - OSHA Subpart
1926 Subpart P
Access/Egress: Trenches
Stairway, ladder, ramp, or other safe means required for excavations over 4’, 25’ access from person at all times
Ladder should extend 3’ from T.O excavation
Confined Space - OSHA Subpart
1926 Subpart AA
Confined Space - 3 requirements:
The space must be “large enough and so configured that an employee can bodily enter it” AND
The space must “have limited or restricted means for entry or exit” AND
The space must not be “designed for continuous employee occupancy”
Permit Required Confined Space (PRCS)
Contains or has the potential to contain a hazardous atmosphere;
Contains a material that has the potential for engulfing an entrant;
Has an internal configuration such that an entrant could be trapped or asphyxiated by inwardly converging walls or by a floor which slopes downward and tapers to a smaller cross-section; or
Contains any other recognized serious safety or health hazard.
Hazardous Atmospheres:
Too little oxygen – under 19.5%
Too much oxygen – over 23.5%
Carbons Monoxide, Sulfide
Which part of the Code of Federal Regulations applies to construction?
CFR Part 1926 Title 29
Whistleblower Complaints can be filed anonymously (T/F)
False
Subpart M does not apply for Steel Erection (Subpart R) (T/F)
True
Approximately what percentage of fatal injuries in construction are due to electrocution?
7.5%
For proper eye protection, safety glasses and goggles must be marked:
ANSI Z87.1
Which respirator is NOT NIOSH-approved?
Single-strap dust mask
Type __ soil is the strongest, while type __ soil is the least strongest
A, C
Engulfment hazards typically involve:
Flowable materials such as sand or liquids
A scaffold must be capable of supporting:
Its own weight and four times the maximum intended load.
Supported scaffolds with a height-to-base ratio greater than 4:1 must be reinforced with extra planks. (T/F)
False
The OSHA Subpart covering scaffolds is:
Subpart L