tissues, skeletal frameworks and respiratory subdivisions
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
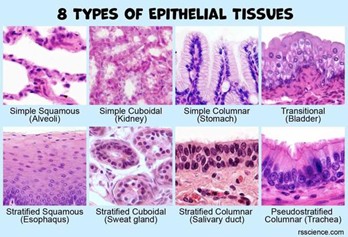
epithelial tissue
body tissue that covers internal and external, lines body cavities and hollow organs and is a major tissue in glands.
connective tissue
vital tissue type in the body that serves as a framework that supports and connects various body structures, maintaining the integrity and function of organ systems.
types: loose (ex. areolar and adipose tissue) dense (ex. tendons and ligaments) specialized (ex. cartilage, blood, lymph)
how many bones in the human body?
206
axial skeleton vs appendicular skeleton
axial = torso, appendicular = limbs
what are the 3 types of joints?
synarthrodial
amphiarthrodial
diarthrodial
synarthrodial joint
no movement ex. skull
amphiarthrodial joint
slight movement - ex. pelvis
diarthrodial joint
lots of movement - ex. larynx, jaw, shoulder
condyloid joint
made of two oval shaped bones that fit together ex. jaw

saddle joint
bone forms a saddle or support for the other bone to rest in ex. sternoclavicular joint
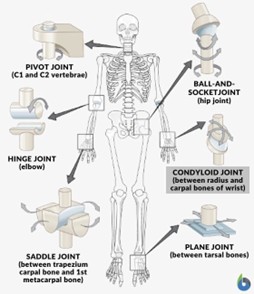
ball and socket joint
ball fits into a socket allow for rotation and gliding motion ex. vocal cord arytenoids
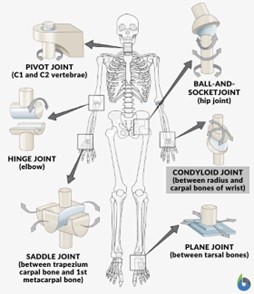
gliding joint (plane joint)
usually flat bones that pass each other ex. the larynx when you swallow moves forward using this type of joint
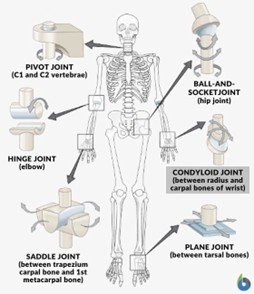
hinge joint
similar to motion of a door hinge ex. temporomandibular joint (TMJ) connecting jaw bone to the head
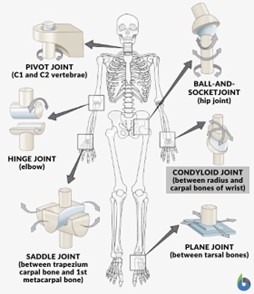
pivot joint
allows for rotation - ex. the head
tendons
dense connective tissue
characterized as tough non elastic
muscle to bone
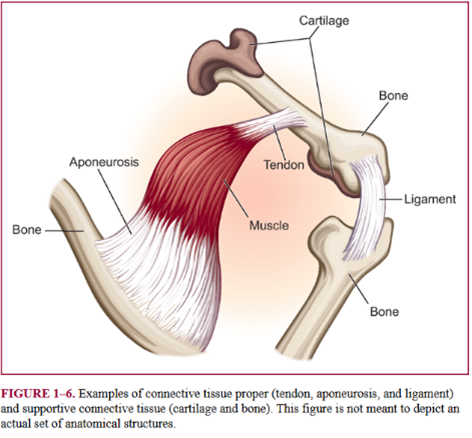
ligaments
elastic
bone to bone
dense connective tissue
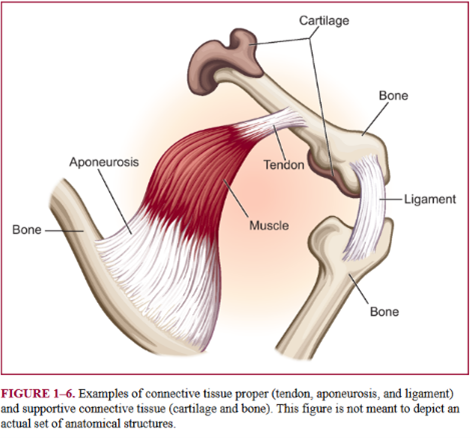
what type of connective tissue is cartilage?
specialized
subtypes of cartilage
fibrous (tough) found in some joints, vertebral discs
hyaline (semi-rigid) mostly collagen, lines joint surfaces and connects ribs
elastic (flexible) - found in ear epiglottis and small cartilages of larynx
3 types of muscle tissue
striated skeletal - found on skeleton, fibers are bundled, voluntary control
striated cardiac - found in heart, fibers are separate cellular units, involuntary
smooth - found in organs, long spindle shaped cells, involuntary control
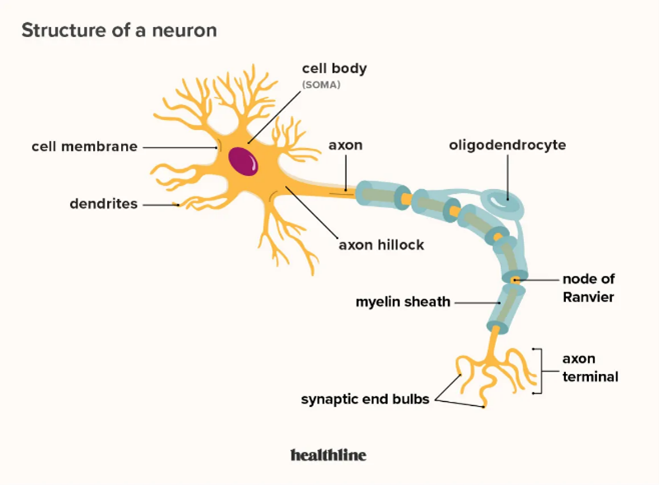
label the neuron
cell membrane
dendrites
cell body
axon
oligodendrocyte
axon hillock
myelin sheath
node of Ranvier
axon terminal
synaptic clefts
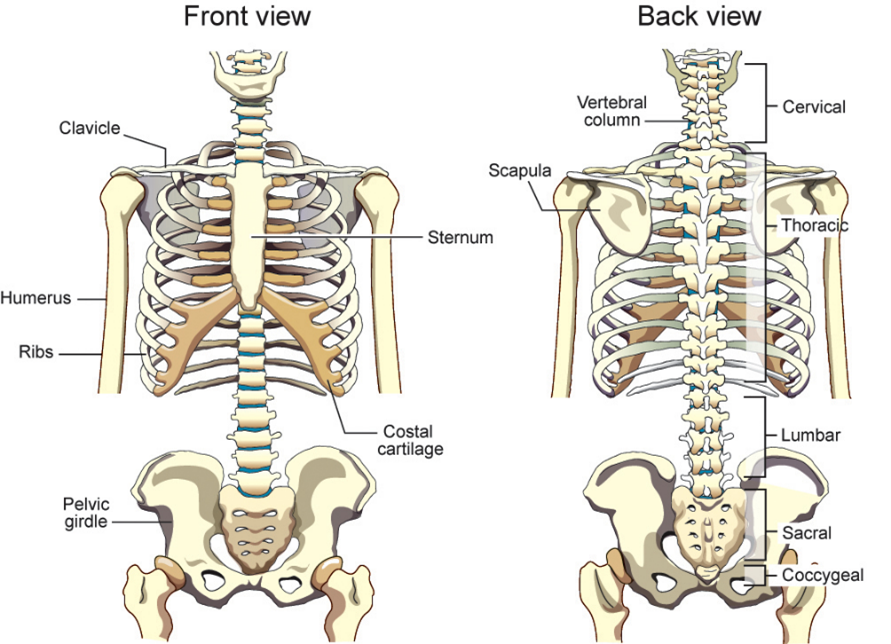
breakdown the vertebrae into its section including how many in each
7 cervical vertebrae (neck)
12 thoracic vertebrae (chest)
5 lumbar
5 sacral
5 coccygeal
what are the 3 sections of the sternum?
manubrium
body
xiphoid process
respiratory system subdivision?
pulmonary apparatus - lungs and airways
chest wall - rib cage wall, abdominal wall, diaphragm
parts of the lower airway in order that air travels
trachea (windpipe)
main stem bronchi (to left and right lungs)
lobar bronchi - to each lobe (5 lobes, 2 on left 3 on right)
20 generations of divisions (like a tree)
alveoli - site of gas exchange
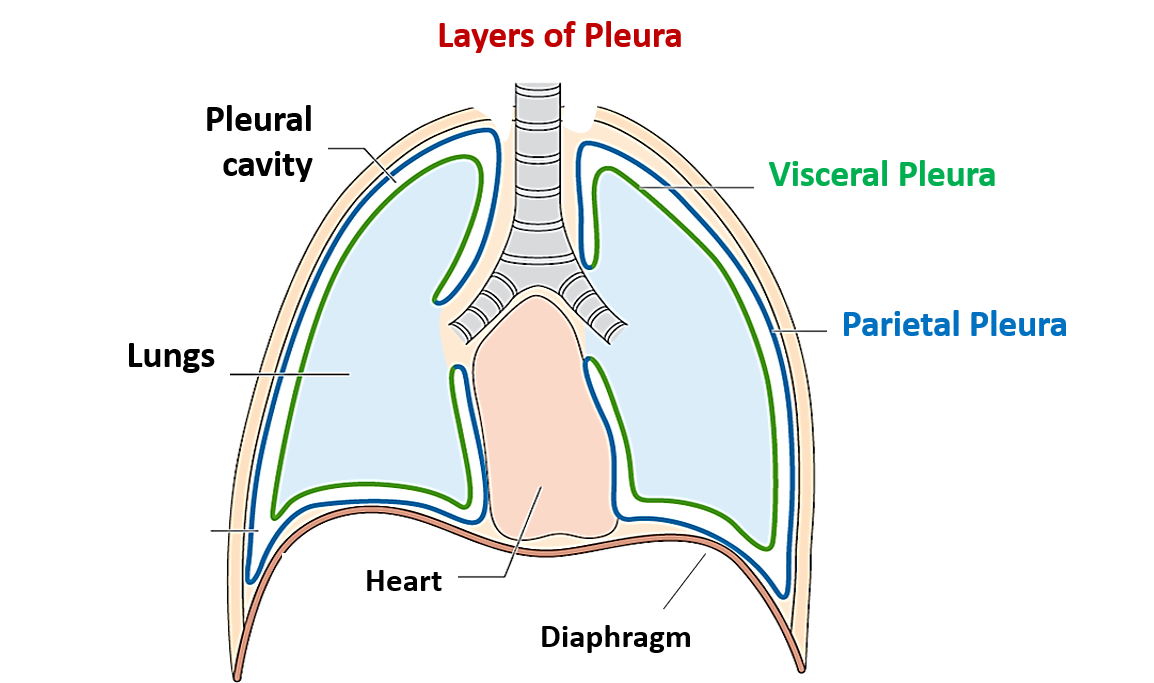
visceral pleura vs parietal pleura
visceral pleura is the thin membrane covering the lungs
parietal pleura is the thin membrane lining the inner chest wall
what is pleural linkage?
connection between lungs and chest wall by the visceral and parietal membranes. surface tension of the fluid on these membranes links the lungs and thoracic cavity together - allows lung and thorax to operate together as a unit.