Unit A 17 Phys, Immune System Focus on Innate Immune Response
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Innate immune response
Type of immune response that nonselectively defends against foreign invaders and is inherited as part of the structure of each organism. First line of defense
Adaptive immune response
Type of immune response where an individual acquires or develops the ability to defend against specific pathogens after the body is first attacked by a bacterium, virus, or toxin. Also called acquired immune response.
Innate immune response
Type of immune response that is the first line of defense against pathogens.
Adaptive immune response
Type of immune response that is slower to develop, but with the formation of memory cells allows this response to react more swiftly against specific invaders in the future. Also called acquired immune response.
Innate immune response
Type of immune response that includes external physical and chemical barriers provided by the skin, mucous membranes, acid secretions of stomach and enzyme secretions
Adaptive
Type of immune response mediated by B and T lymphocytes. Also called acquired.
Innate immune response
Type of immune response that includes inflammation, fever, interferons, complement proteins, granulocytes (basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils) mast cells, and macrophages.
Inflammation
Term for the nonspecific response to tissue injury caused by pathogens, trauma, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. The ultimate goal of this process is to bring phagocytes and plasma proteins to injured area to remove cellular debris or in the case of a pathogen, to destroy the invaders.
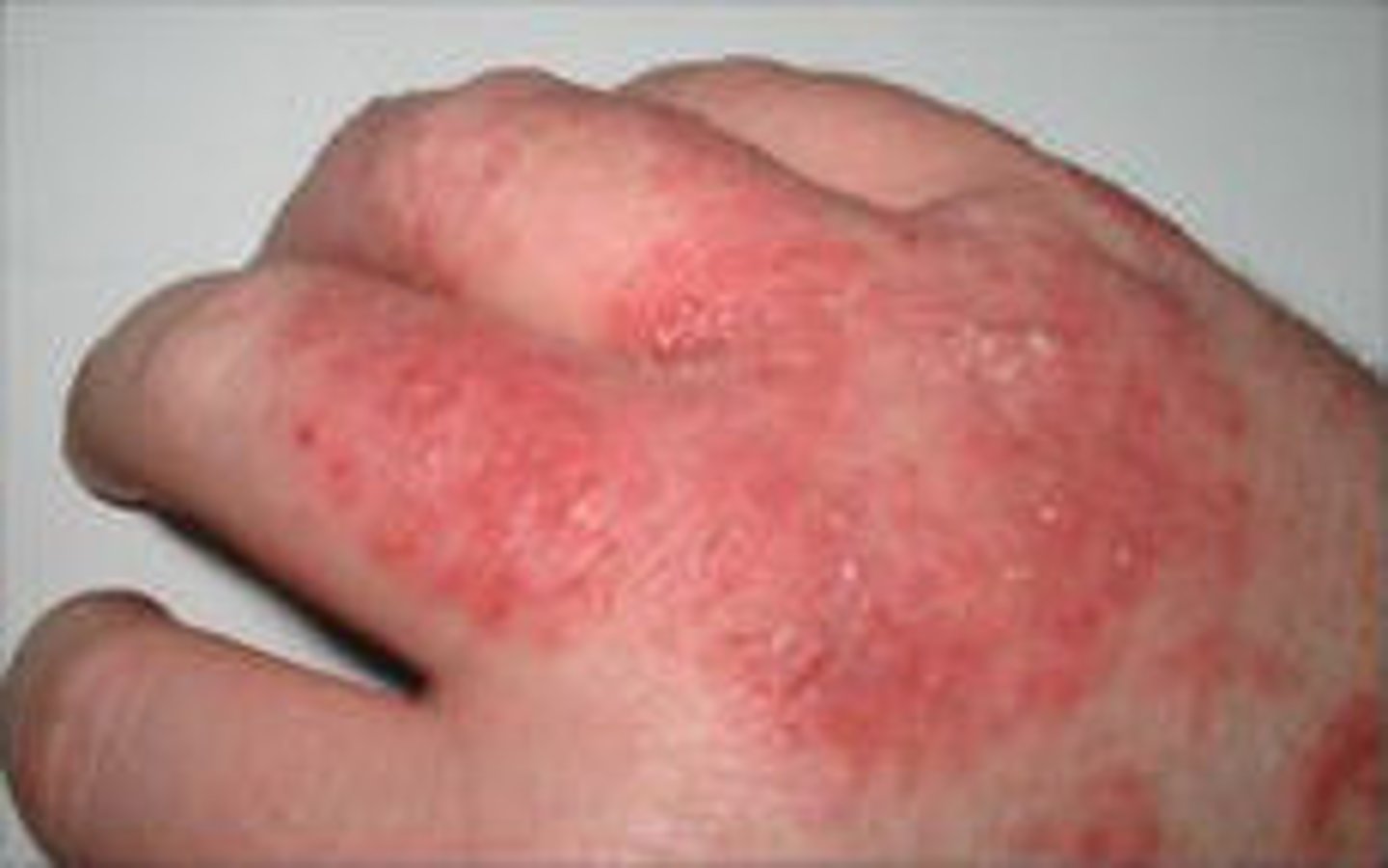
Cytokines
During the inflammatory response, chemicals known as _______________ which include interferon, interleukins, pyrogens and growth factors have an effect on other cells. In this case, they increase capillary permeability, cause a fever, stimulate an increase in acute-phase proteins, and along with chemotaxins, attract other immune cells such as neutrophils and monocytes.
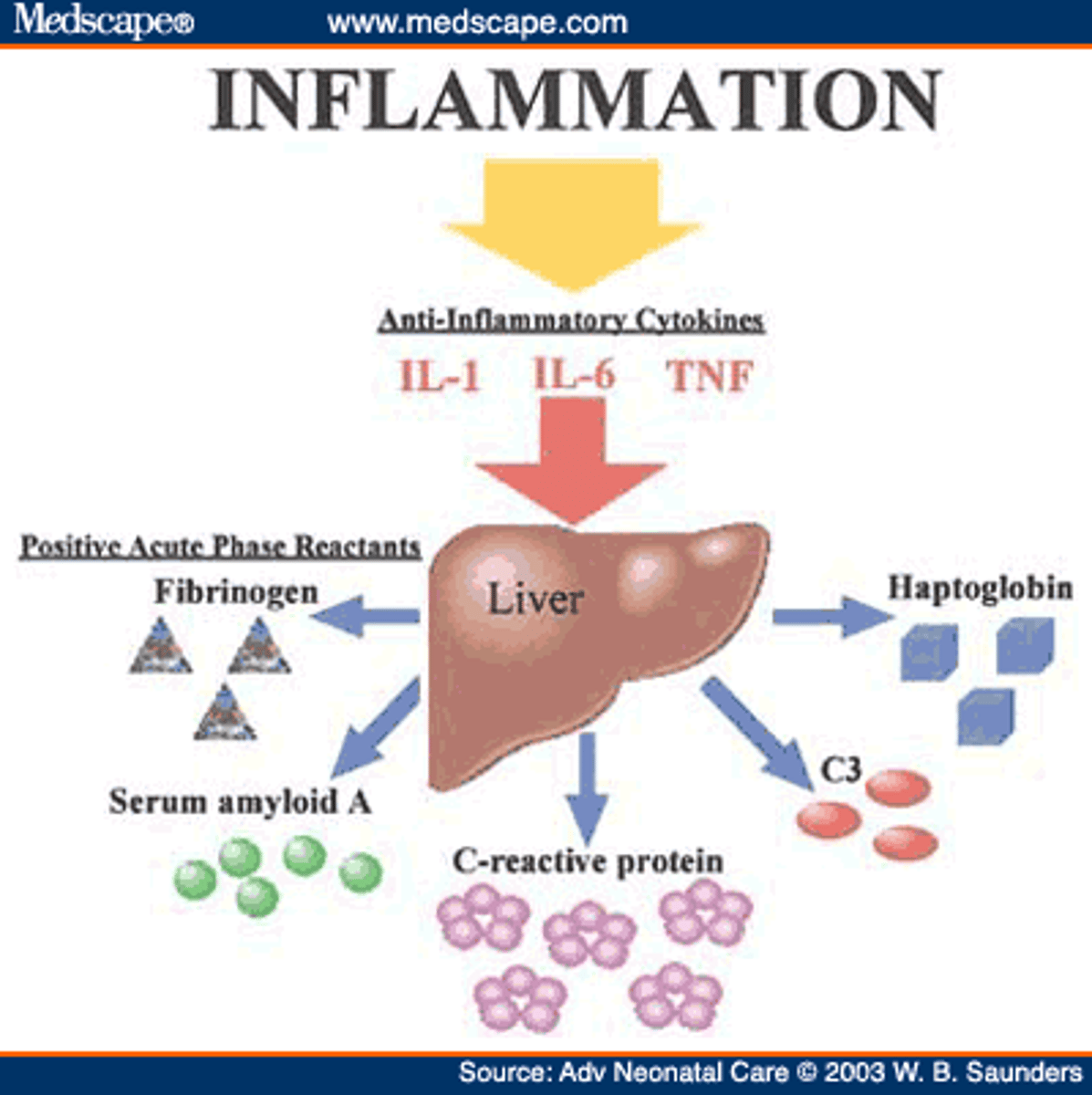
C-reactive protein
Measurement of acute-phase proteins such as ______________________________, is a useful marker of inflammation. Hint: has the initials CRP.
Swelling
The four main signs of inflammation are redness, heat, ___________________, and pain.
Pyrogens
Term for the endogenous chemicals and many bacterial toxins that can induce the development of a fever by resetting the hypothalamus for increased body temperature.
Toll-like receptors (TLRs)
Macrophages and other phagocytic cells detect pathogens by specific receptors on their membranes known as _________. Give name and abbreviation in parentheses.
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
Phagocytic cells are studded with plasma membrane proteins known as toll-like receptors (TLRs) that recognize _______________________ typically found on viral and bacterial cell walls. Give name and abbreviation in parentheses
Toll-like receptors (TLRs)
Name of the receptor that have been dubbed the "eyes" of the innate immune system. Give name and abbreviation in parentheses.
Phagosome
When macrophages and other phagocytic cells ingest materials it ends up in a cytoplasmic vesicle called a ___________________________. This vesicle with then fuse with intracellular lysosomes which contain enzymes and oxidizing agents that destroy the ingested material
B and T cell receptors
Name of the receptors that have been dubbed the "eyes" of the acquired or adaptive immune system.
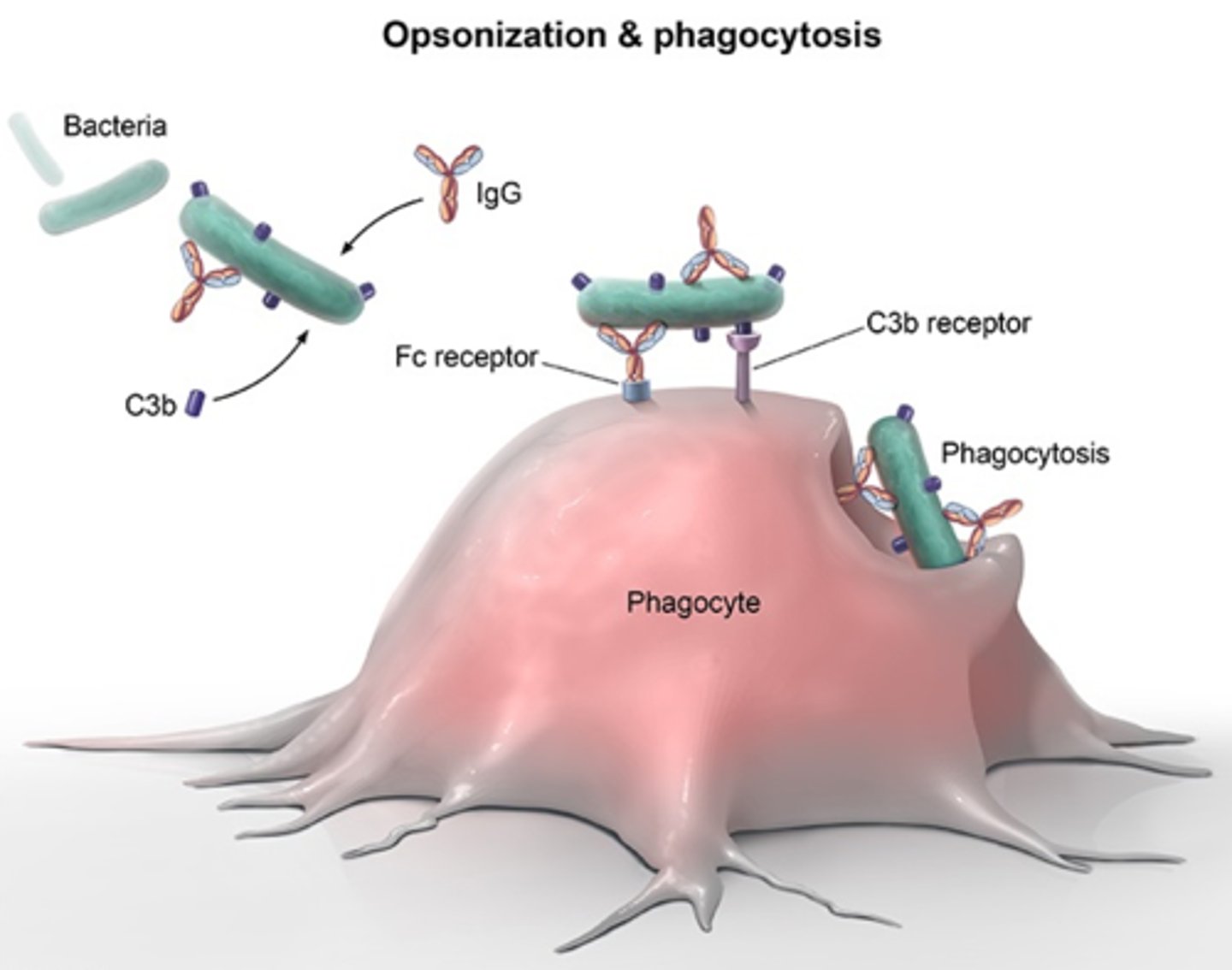
Opsonins
______________________________ are antibodies, complement proteins and other substances that bind to foreign microorganisms or cells, making them more susceptible to phagocytosis.
Histamine
Mast Cells release ______________ which binds to receptors with the same name on the smooth muscle of bronchioles to stimulate bronchiolar constriction (as in asthma), but produces relaxation of the smooth muscles in blood vessels causing localized vasodilation.
Margination
Blood-borne leukocytes like neutrophils and monocytes stick to the endothelial lining of capillaries of affected tissues by a process called ____________
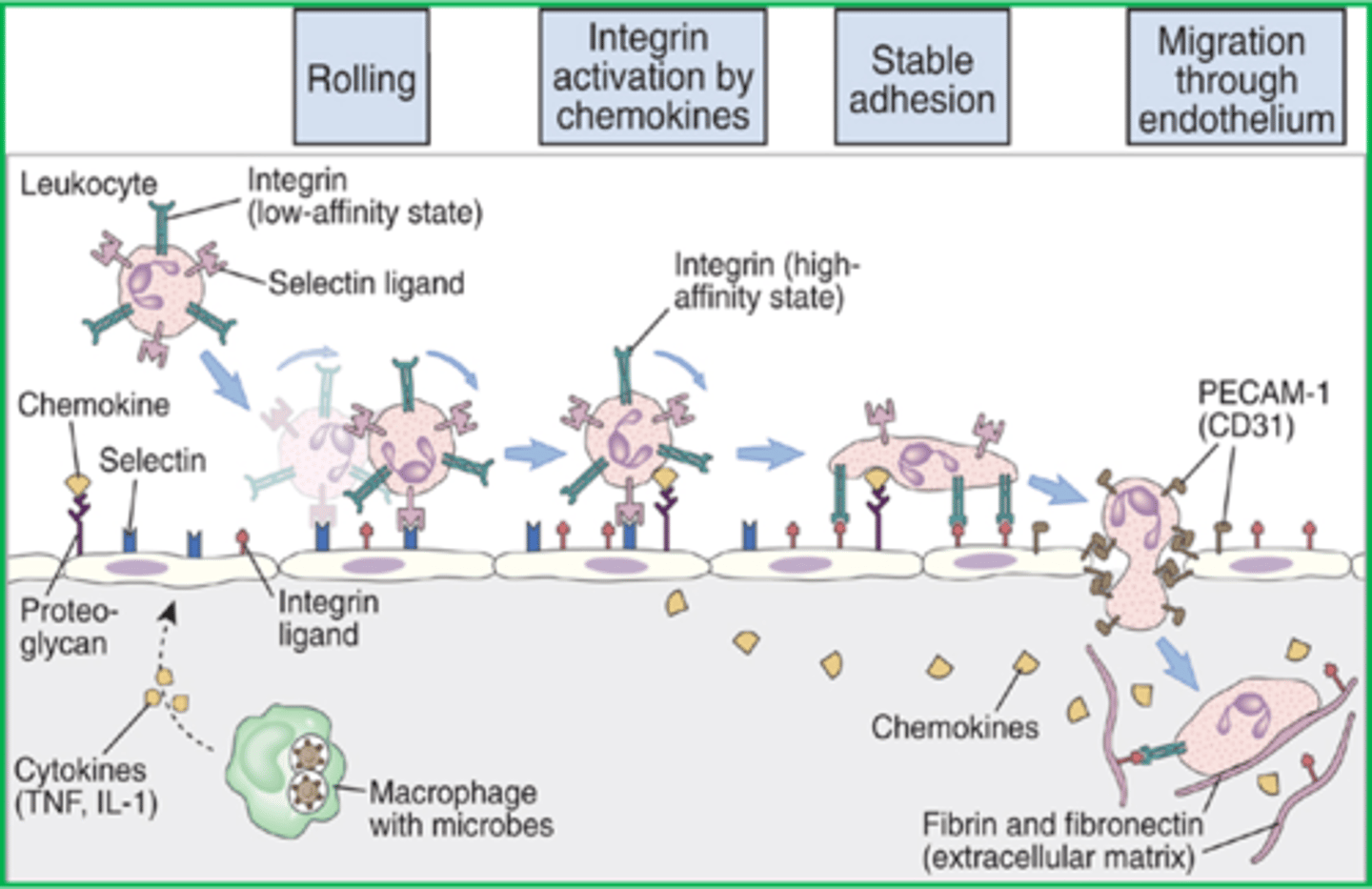
Cell adhesion molecules (CAM)
General term for the proteins that protrude from the endothelial lining and cause leukocytes and monocytes flowing through the blood to slow down and roll along the interior of the vessel. This allows for diapedesis to occur. An example of such a protein is selectin. Give term and abbreviation in parentheses.
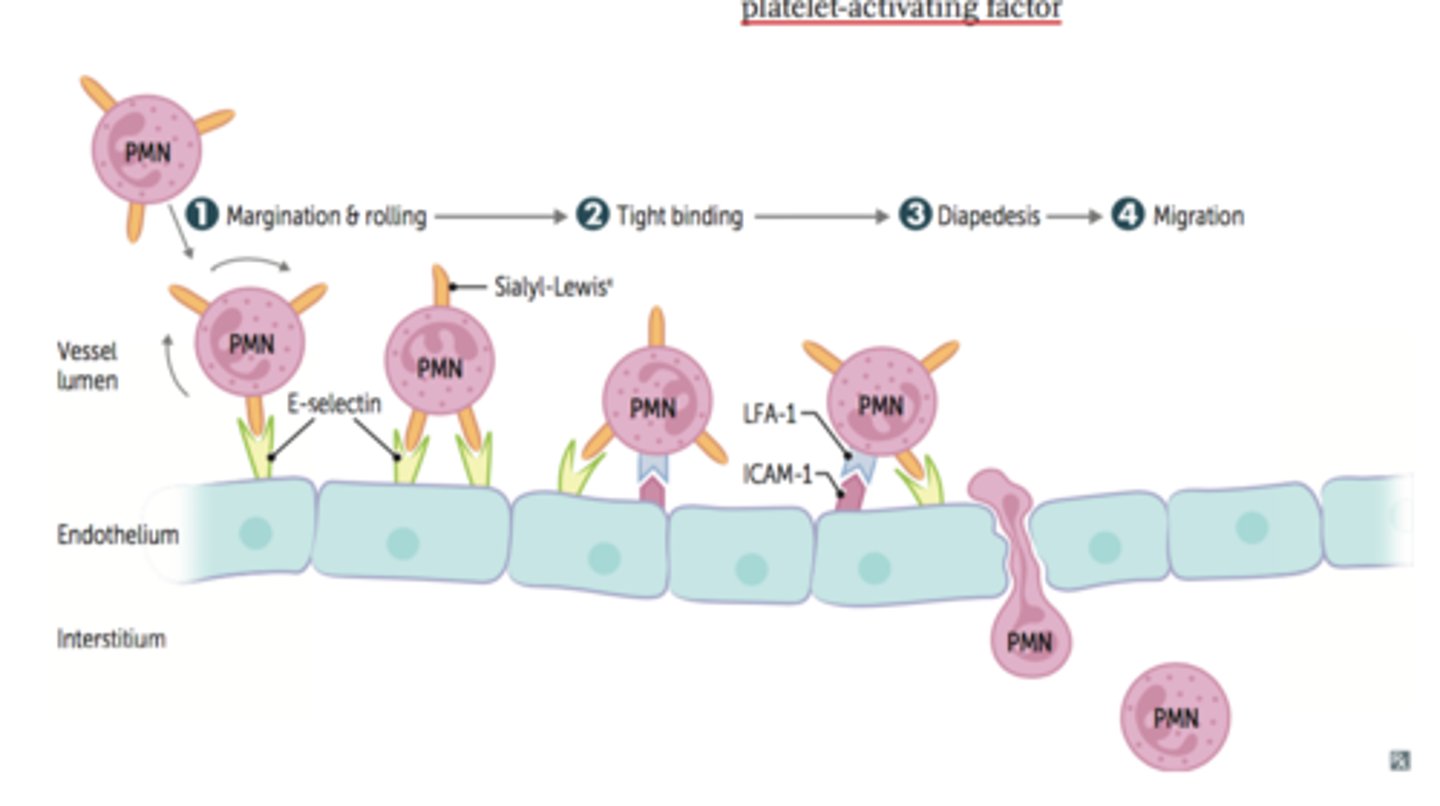
Selectin
Name a type of Cell Adhesion Molecules (CAM) discussed in class that protrudes from the endothelial lining. These proteins cause leukocytes and monocytes flowing through the blood to slow down and roll along the interior of the vessel - allows for diapedesis to occur.
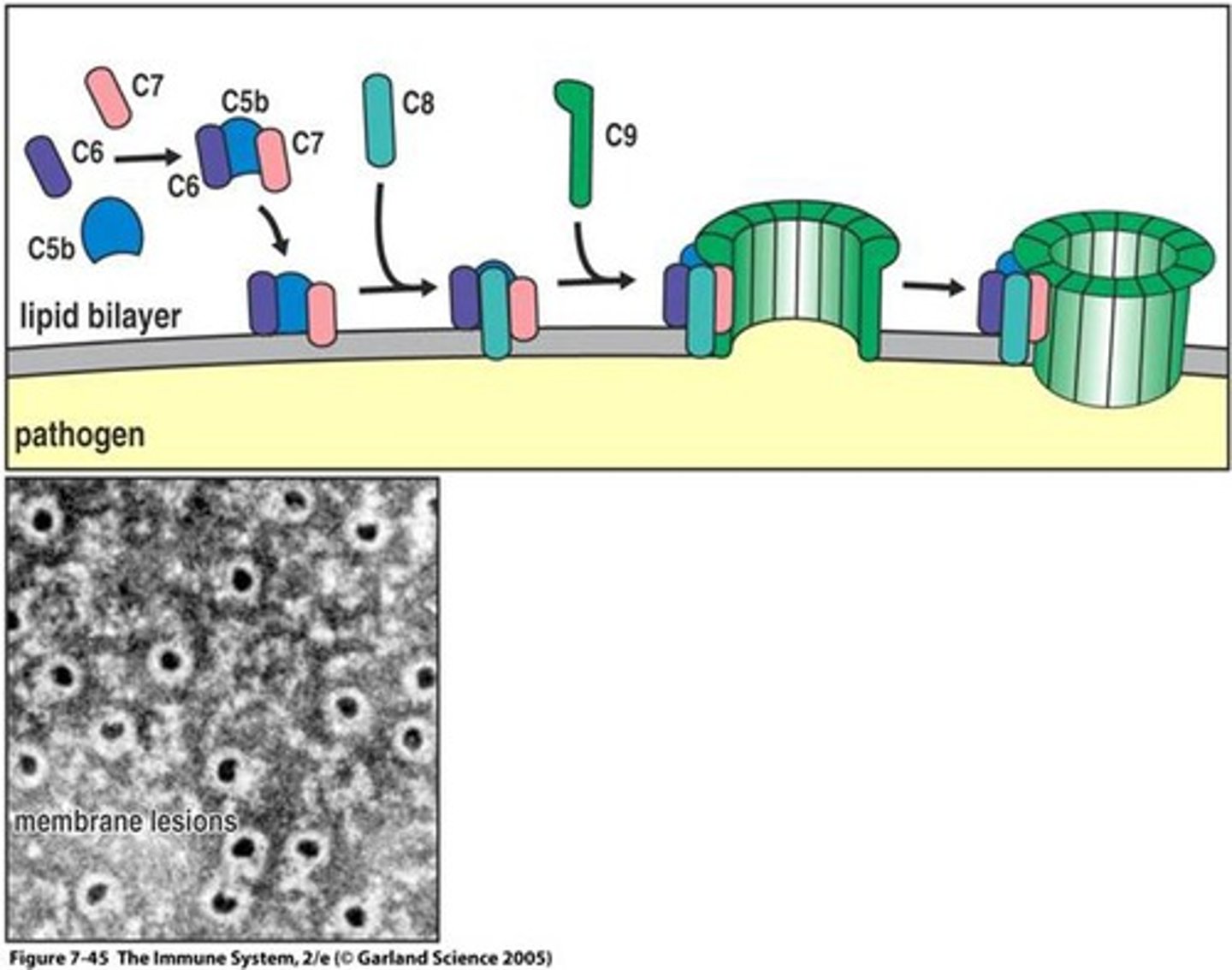
Classical complement
In the _____________________ pathway antibodies are used to start the complement cascade which eventually destroy bacteria by forming a pore-like channel
Alternate complement
In the ______________________ pathway no antibodies are used. Complement proteins bind directly to an invader and activate the complement cascade forming a pore-like channel
Membrane attack complex (MAC)
In either the classical or alternate complement pathways the end product is a cylinder called a _______________________ that punctures the target cell membrane and allows fluids to flow into the cell by osmosis causing lysis of the invader. Give the name and abbreviation in parentheses.
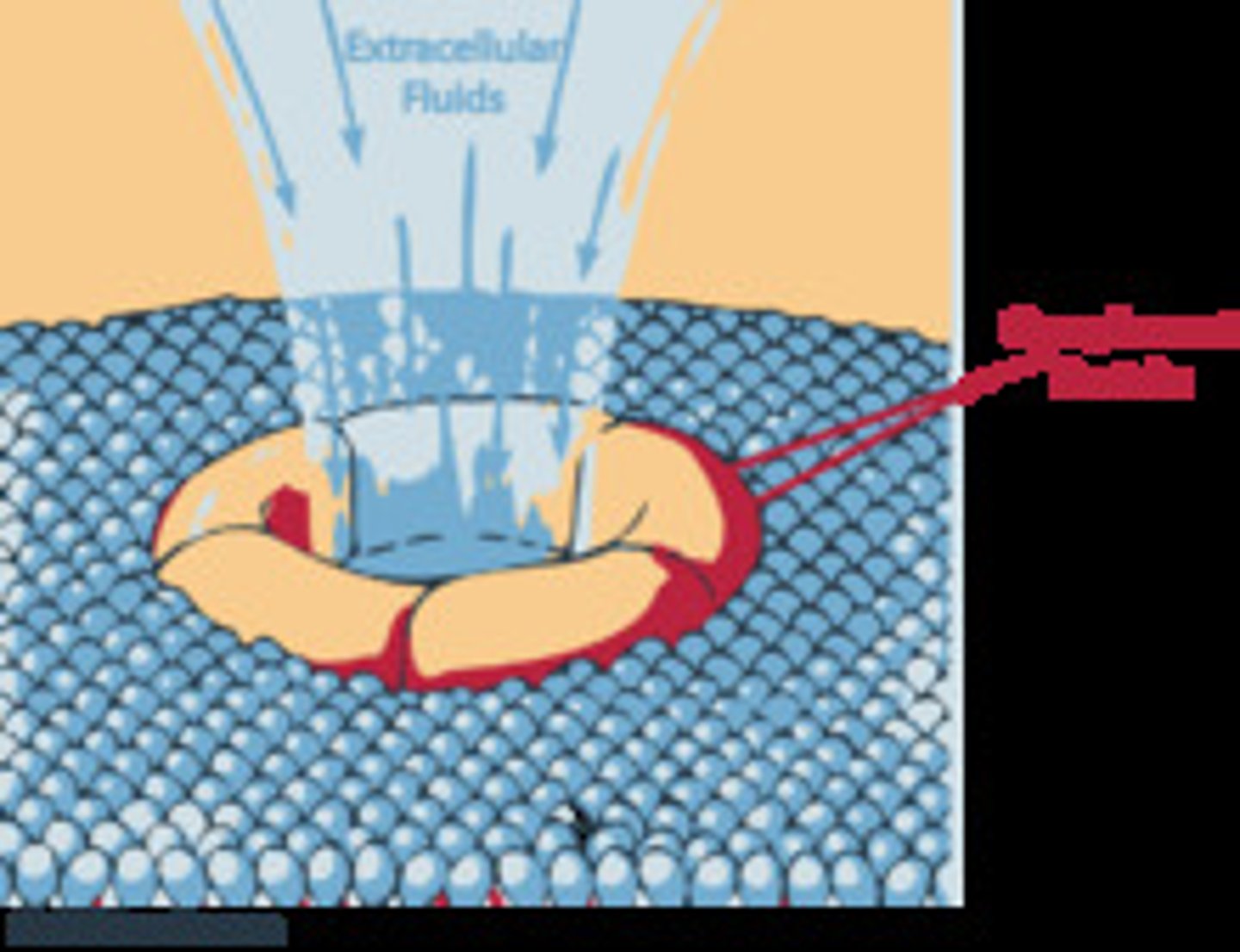
Opsonins
Complement proteins can also act as _________________, which are chemicals that bind to foreign microorganisms or cells, making them more susceptible to phagocytosis.
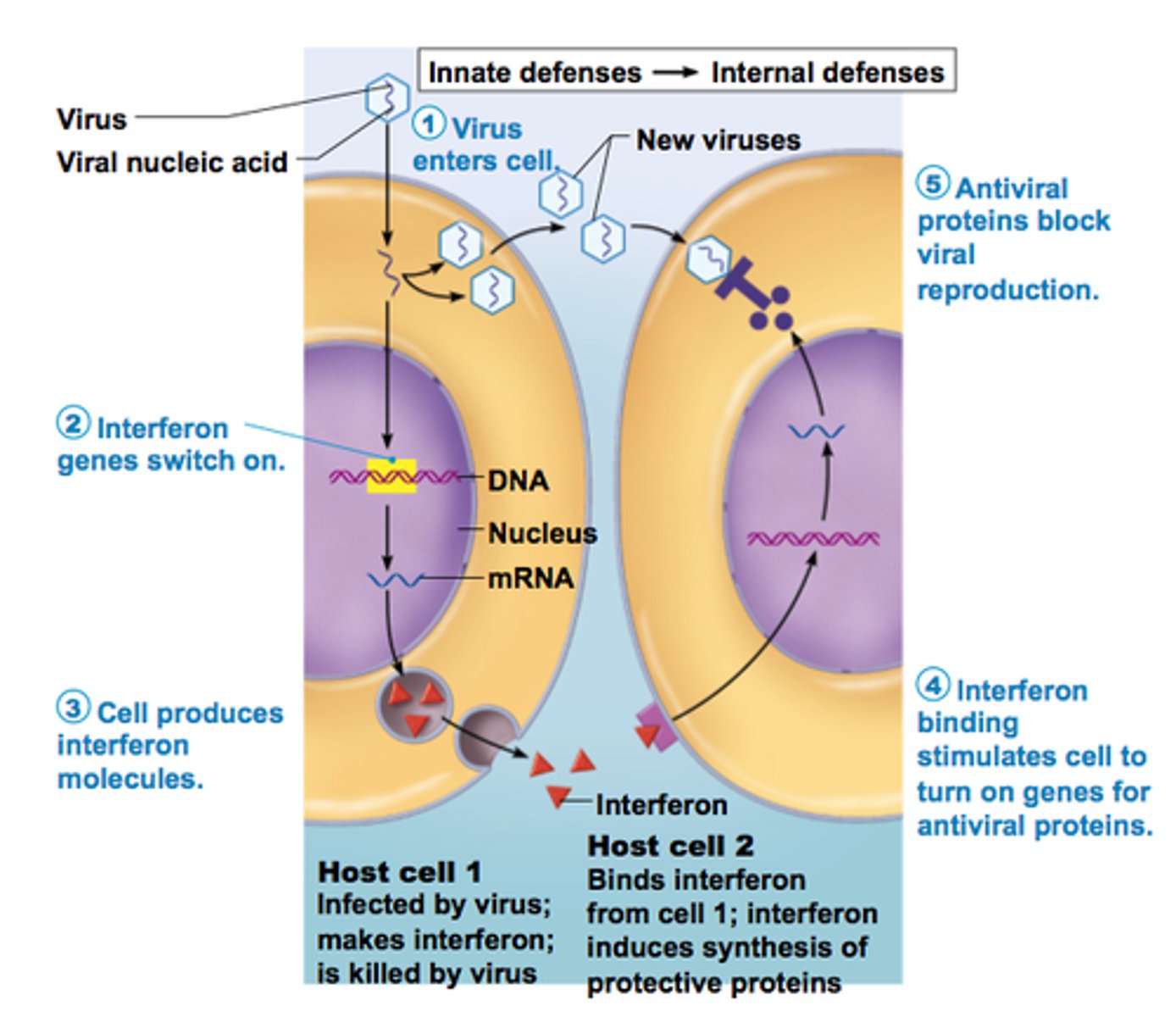
Interferon
When a virus enters a cell it can trigger the production and release of _____________________
This chemical binds with receptors on uninvaded nearby cells and stimulates them to produce enzymes capable of breaking down viral mRNA. If virus enters previously-uninvaded cell, now with antiviral enzymes, the virus will not be able to replicate.
Lactoferrin
Neutrophils phagocytose pathogens/cellular debris and secrete the protein called _____________________ , which binds with iron, making it unavailable for use by invading bacteria
Interferon
Name of a substance that inhibits multiplication of viruses in most cells. Its production and release is stimulated when a virus enters a cell. This substance binds with receptors on uninvaded nearby cells stimulating them to produce enzymes capable of breaking down viral mRNA. If virus enters previously-uninvaded cell, now with antiviral enzymes, the virus will not be able to replicate.
Membrane attack complex (MAC)
The complement cascade is set off when the first complement molecule, C1, encounters an antigen or antibody bound to antigen in an antigen-antibody complex. The end result is a ___________________________ that punctures the target cell membrane and allows fluids to flow into the cell by osmosis causing lysis. Give the name and abbreviation in parenthesis.
Natural killer cells
Name of the type of cells that are part of the innate immune system and nonspecifically destroy cancer cells and virus infected cells. They are similar to cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in that they destroy cancer cells and virus infected cells with perforin proteins and granzymes, but unlike CTLs, do not require antigens to be presented on MHC class I molecules
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Natural killer cells are part of the innate immune system and nonspecifically destroy cancer cells and virus infected cells. They are similar to ____________________________ (CTLs) in that they destroy cancer cells and virus infected cells with perforin proteins and granzymes, but unlike CTLs, do not require antigens to be presented on MHC class I molecules
Perforin proteins
Natural Killer (NK) cells are part of the innate immune system and nonspecifically destroy cancer cells and virus infected cells. They are similar to cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in that they destroy cancer cells and virus infected cells with _______________________ and granzymes, but unlike CTLs, do not require antigens to be presented on MHC class I molecules
MHC class I
Natural Killer (NK) cells are part of the innate immune system and nonspecifically destroy cancer cells and virus infected cells. They are similar to cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in that they destroy cancer cells and virus infected cells with perforin proteins and granzymes, but unlike CTLs, do not require antigens to be presented on ___________________ molecules
Apoptosis
Granzymes, which are enzymes that enter through the perforin channels and cause the cell to self-destruct through a process known as ______________________
MHC class I
Normal healthy cells express ____________________________ molecules on their surface that contribute to self-tolerance. The molecules are recognized by inhibitory receptors of NK cells and prevent their activation so they do not destroy normal cells.
MHC class I
Activation of NK cells results from cells that have little to no ___________________________ molecules due to their down regulation coupled with membrane activation signals. The cell surface expression of these molecules is often down-regulated in tumor and virus-infected cells, enabling these cells to escape being killed by cytotoxic T cells. However, NK cells can recognize and kill cells that have down-regulated these molecules from their cell surface.
Cytotoxic T cells
Activation of NK cells results from cells that have little to no MHC I molecules due to their down regulation coupled with membrane activation signals. The cell surface expression of MHC class I is often down-regulated in tumor and virus-infected cells, enabling these cells to escape being killed by ____________________________. However, NK cells can recognize and kill cells that have down-regulated MHC class I molecules from their cell surface.
Ligands
Tumor cells and virus infected cells can acquire stress-associated molecules which act as ___________________ for activating NK receptors. Thus, the lack of MHC I inhibitory signaling coupled with induction of activating signaling results in NK cell activation.
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Natural Killer (NK) cells can also be activated by bound antibodies (opsonization) in _________________________________ (give the complete name and abbreviation in parenthesis. Cancer cells and virus infected cells can produce antigens on their cell surface that activate B cells to become plasma cells and produce antibodies.
ADCC
What is the abbreviation for antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity?
Natural killer cells (NK)
Name the type of cells that can be activated by bound antibodies (opsonization) in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). Give the cell name and its abbreviation in parenthesis.