Biochem Lab exam
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Which option is not a recommended technique for dispensing liquid from a micropipette into another solution?
A. Submerge the micropipette tip completely into the solution before dispensing
B. Dispense the liquid along the inside of the glassware
C. Hold the micropipette at a 45 degree angle when dispensing
D. Place the tip slightly below the level of the solution before dispensing
A. Submerge the micropipette tip completely into the solution before dispensing
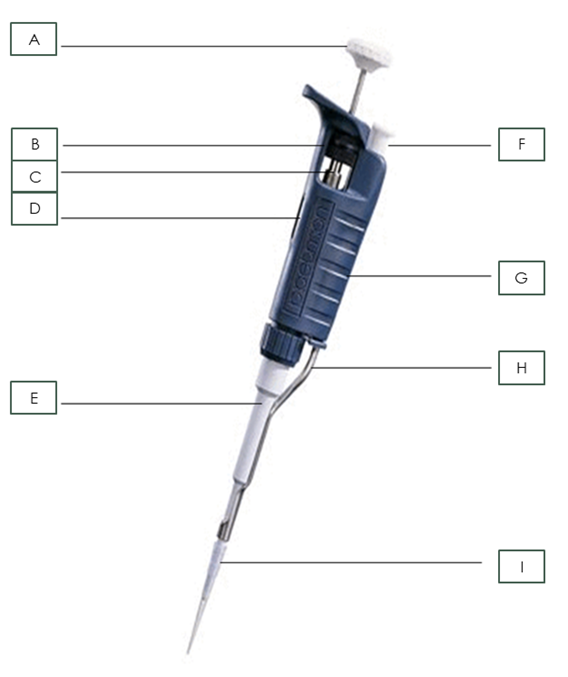
Name each part.
A. Plunger
B. Friction Ring
C. Micrometer
D. Digital volume indicator
E. Shaft
F. Tip ejector button
G. Body
H. Tip ejector
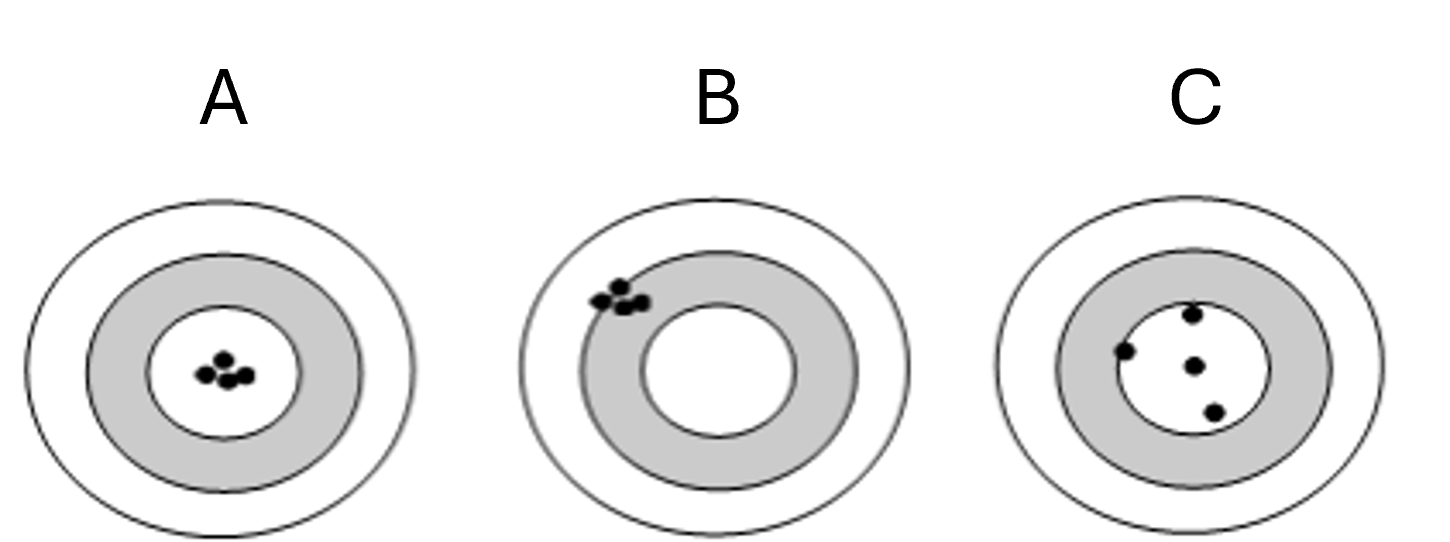
Assign a label to each target image
Precise and Accurate
Precise and Not Accurate
Not precise but Accurate
A. 1
B. 3
C. 2
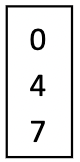
What is the volume pipetted if the dial reads the following for a P1000
470

Determine the volume a P20 micropipette will dispense at the following setting
A. 0.146 microliters
B. 14.6 microliters
C. 146 microliters
D. 146 mililiters
B. 14.6 microliters

Determine the volume a P200 micropipette will dispense at the following setting
A. 72 mililiters
B. 72 microliters
C. 7.2 mililiters
D. 7.2 microliters
B. 72 micoliters

Determine the volume a P1000 micropipette will dispense at the following setting
A. 53 mililiters
B. 53 microliters
C. 5300 microliters
D. 530 microliters
D. 530 microliters
Identify the recommended practice(s) when putting a tip on a micropipette.
A. Hold the micropipette at a 45 degree angle to the tip rack
B. Remove the tip from the rack and place it on micropipette by hand
C. Gently push the micropipette into the tip and tap lightly to load the tip
D. Use the tip size designed for the micropipette size in use
C and D
What are the four things you should never do when using a micropipette?
A. Use without a tip
B. Hold the pipette vertically when aspirating liquid
C. Let the plunger snap back after withdrawing or ejecting fluid
D. Rotate the volume adjustor beyond its limits
E. Store the pipette upright on a stand when not in use
F. Press to the first stop to aspirate liquid and the second stop to fully dispense
G. Lay down or turn upside down a pipette with a filled tip
A, C, D, and G
The range of the Std P1000 Tip is
A. 2-20 uL
B. 20-200 uL
C. 100-1000 uL
D. None of the above
C. 100-1000 uL
The range of the Std P200 Tip is
A. 2-20 uL
B. 20-200 uL
C. 100-1000 uL
D. None of the above
B. 20-200 uL
The range of the Electrophoresis tip P20 is
A. 2-20 uL
B. 20-200 uL
C. 100-1000 uL
D. None of the above
A. 2-20 uL
Identify the type of chromatography:
A positively charged bead interacts with the protein to be purified, which carries a negative charge. A high salt buffer is used to elute the protein to be purified.
Ion-exchange chromatography
Identify the type of chromatography:
Beads containing small pores are used to separate biomolecules based on their size. Large biomolecules have little interaction with the beads and elute first, whereas small biomolecules have a lot of interaction with the beads and elute later.
Size exclusion chromatography
Identify the type of chromatography:
Beads are linked to a biomolecule that interacts with the protein to be purified. The protein to be purified is sometimes eluted using a buffer containing a high concentration of salt or acid.
Affinity chromatography
Identify the type of chromatography:
A negatively charged bead interacts with the protein to be purified, which carries a positive charge. A high salt buffer is used to elute the protein to be purified.
Ion-exchange chromatography
Imagine you have a mixture containing two proteins, untagged green fluorescent protein (GFP) and His-tagged GFP (His-GFP). Which type of chromatography would be useful to separate these proteins?
A. Affinity chromatography
B. Size-exclusion chromatography
C. Ion-exchange chromatography
A. Affinity chromatography
What type of chromatography was used in Lab 2?
A. Affinity chromatography
B. Size-exclusion chromatography
C. Ion-exchange chromatography
B. Size exclusion chromatography
If a mix of hemoglobin, myoglobin, and myosin where purified using size exclusion, what molecule would be first, second, and last to appear?
hemoglobin, 65,000 Daltons
myoglobin, 17,000 Daltons
myosin, 180,000 Daltons
First to appear: Myosin
Second to appear: Hemoglobin
Third to appear: Myoglobin
What gives hemoglobin and myoglobin their distinctive colors?
A. Carbon Dioxide
B. Iron-containing heme
C. Oxygen
D. Globin
B. Iron-containing heme
If athletes wanted to increase their endurance by increasing their oxygen-carrying capacity, how might they accomplish this increase?
A. drinking a lot of water
B. training at high altitudes
C. consuming iron-rich foods
D. breathing pure oxygen while training
B. training at high altitudes
How could gene-therapy, where a normal gene is substituted for a defective copy of a gene, help individuals who have vitamin B12 carrier protein disease?
A. by turning on the individual’s working copy of the gene, which has been turned off by mistake
B. by removing all defective copies of the gene
C. by providing a working copy of the gene
C. by providing a working copy of the gene
How does the immune system protect us from disease?
A. by physically blocking pathogens from entering the body
B. by developing molecules and cells that recognize specific pathogens
C. by producing molecules like penicillin to kill bacteria
B. by developing molecules and cells that recognize specific pathogens
How do doctors use the immune response to protect you from disease?
A. by intentionally infecting you with a pathogen that could make you sick
B. by exposing the immune system to a weak or inactive pathogen that cannot make you sick
C. by helping to stop pathogens from entering the body
D. by providing pharmaceuticals that help stop an active infection
B. by exposing the immune system to a weak or inactive pathogen that cannot make you sick
What are some ways that diseases spread? Select all that apply.
A. vector transfer
B. inhalation
C. ingestion of contaminated food or water
D. exchange of body fluids
A, B, C, and D
What is an example of a disease that attacks the human immune system?
A. E. coli
B. HIV
C. Lupus
D. Influenza
B and C
Which are problems that can prevent the immune system from working properly?
A. production of antibodies after exposure to influenza virus
B. affliction with an autoimmune disorder such as multiple sclerosis
C. overreaction to an antigen
D. infection with a pathogen that attacks the immune system
E. a genetic disorder that affects the immune system
F. treatment with immunosuppressive medications
B, C, D, E, and F
Why are immunosuppressant drugs necessary when someone has an organ transplant?
A. to get the immune system to attack the transplanted tissue
B. to prevent the immune system from attacking tissues that were not transplanted
C. to prevent infection after the transplant surgery
D. to stop the immune system from damaging the transplanted tissue
D. To stop the immune system from damaging the transplanted tissue
Why is rapid detection of disease exposure important? Pick all that apply.
A. for minimizing or preventing exposure to others
B. for identifying who should receive treatment
C. for identifying who is at fault for spreading an infection
A and B
What does ELISA stand for?
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Why are enzymes used in the immunoassay from lab 3?
A. to convert the substrate into a colored compound
B. to mark the primary antibody
C. to mark the secondary antibody
D. to degrade the antigen if it is present
A. to convert the substrate into a colored compound
Why do you need to assay positive and negative control samples as well as your experimental samples?
Positive control is to show when the antigen is present
Negative control is to show when the antigen is absent
What are four different ways light can interact with biomolecules?
A. Transmission
B. Absorption
C. Polarization
D. Light scattering
E. Reflection
F. Luminescence
A, B, D, and E
In the Bradford assay, the protein-dye complex at 595 nm makes the protein-dye complex blue, while the dye alone (without protein) absorbs blue light at 470 nm making the dye _______________ color.
A. Bright blue
B. Yellow-Green
C. Reddish-Brown
D. Pale Yellow
C. Reddish-Brown
In the Bradford assay, the peak absorbance of unprotonated _______ is at 595 nm, and the spectrophotometer is set to read at 595 nm.
A. Bradford Reagent
B. Milk
C. Coomassie G-250 dye
D. Protein
C. Coomassie G-250 dye
There are several colorimetric methods for determining the total protein content of a sample. What are three of them?
A. Biuret
B. Lowry
C. Gel electrophoresis
D. Western Blot
E. Bradford
A, B, and E
The Bradford assay is easy to perform and involves four main steps. List them in order.
A. Binding of dye to protein, resulting in a color change, and reading of the absorption at A595 in a spec
B. Addition of Bradford dye and incubation for >5 minutes
C. Preparation of a dilution series of known protein standards and preparation of unknowns
D. Compilation of the data into a standard curve and unknown protein concentration determination
C, B, A, D
What is the primary interaction that occurs between Coomassie G-250 dye and proteins in the Bradford assay?
A. Electrostatic interactions between arginine and sulfate groups
B. Hydrogen bonding with polar amino acids
C. Electron stacking interactions with aromatic amino acids
D. Hydrophobic interactions with non-polar amino acids
A. Electrostatic interactions between arginine and sulfate groups
Why is it important to use a fresh tip for each standard and sample when adding them to the cuvettes in the Bradford Assay?
A. Tips degrade protein samples
B. To avoid cross-contamination and ensure accurate readings
C. To save on the amount of tips used
D. Protein samples degrade tips
B. To avoid cross-contamination and ensure accurate readings
The DeNovix spectrophotometer uses a standard curve to calculate the concentration of an unknown sample. The closer the correlation coefficient (R²) is to ________, the better the fit of the standard curve.
A. 0.5
B. 1
C. -1
D. 0
B. 1