Student RDH Pharmacology 2024
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
Brand name vs. Generic name
Brand Name: Manufacturers name, capitalized. ie. Tylenol
Generic Name: chemical name for drug, lowercase, Ie, acetaminophen
pc/ac means
pc- after meals
ac- before meals
hs means
at bedtime
Safest route of drug administration is
GI tract- SAFEST
slowest, most variable route.
If taken orally, may cause GI upset.
What is enteral absorption of drugs associated with?
First pass effect
What is the first pass effect?
When the GI or liver metabolizes the drug BEFORE it reaches systemic circulation
Parenteral drug administration is often used in
emergency situations
IV (directly enters blood stream)
Drugs BYPASS the GI tract
Best option to CONTROL level of drugs
Topical and transdermal drugs are
absorbed slowly by capillaries and effects last a long time.
For this reason, toxicity should be monitored.
Potency of drug
the amount needed to achieve desired effect.
A lower amount needed to reach desired effect is more potent.
efficacy of a drug
degree to which a drug produces its desired response in a patient. Increasing the dose does not improve the effect.
there is no relationship between potency and efficacy.
potency vs efficacy
potency: amount of drug necessary to produce desired effect
efficacy: ability of drug to achieve desired effect
Adverse reactions to drugs
All adverse reactions are undesirable.
Side effects are predictable, and dose related.
toxic reactions (toxic effects on organs for example) is dose related.
Allergic effects: NOT dose related, and unpredictable.
Type I and Type IV reactions:
Type I- immediate reaction (anaphylactic shock)
Type IV- delayed response (contact dermatitis)
Absorption refers to
entry of drug into the bloodstream.
The rate of absorption depends on:
-route of administration (IV? Oral?)
-pKa of the drug
-drug solubility
-and pH of the media
Distribution refers to
Distribution of drug to other parts of the body, once it reaches the blood stream (after it is absorbed)
Metabolism refers to
How the body breaks down and converts the drug into other substances.
primary site for metabolism is the liver.
Excretion refers to
Drug and metabolites then exit the body.
happen in the kidney- drugs and their metabolites are flushed out through the urine.
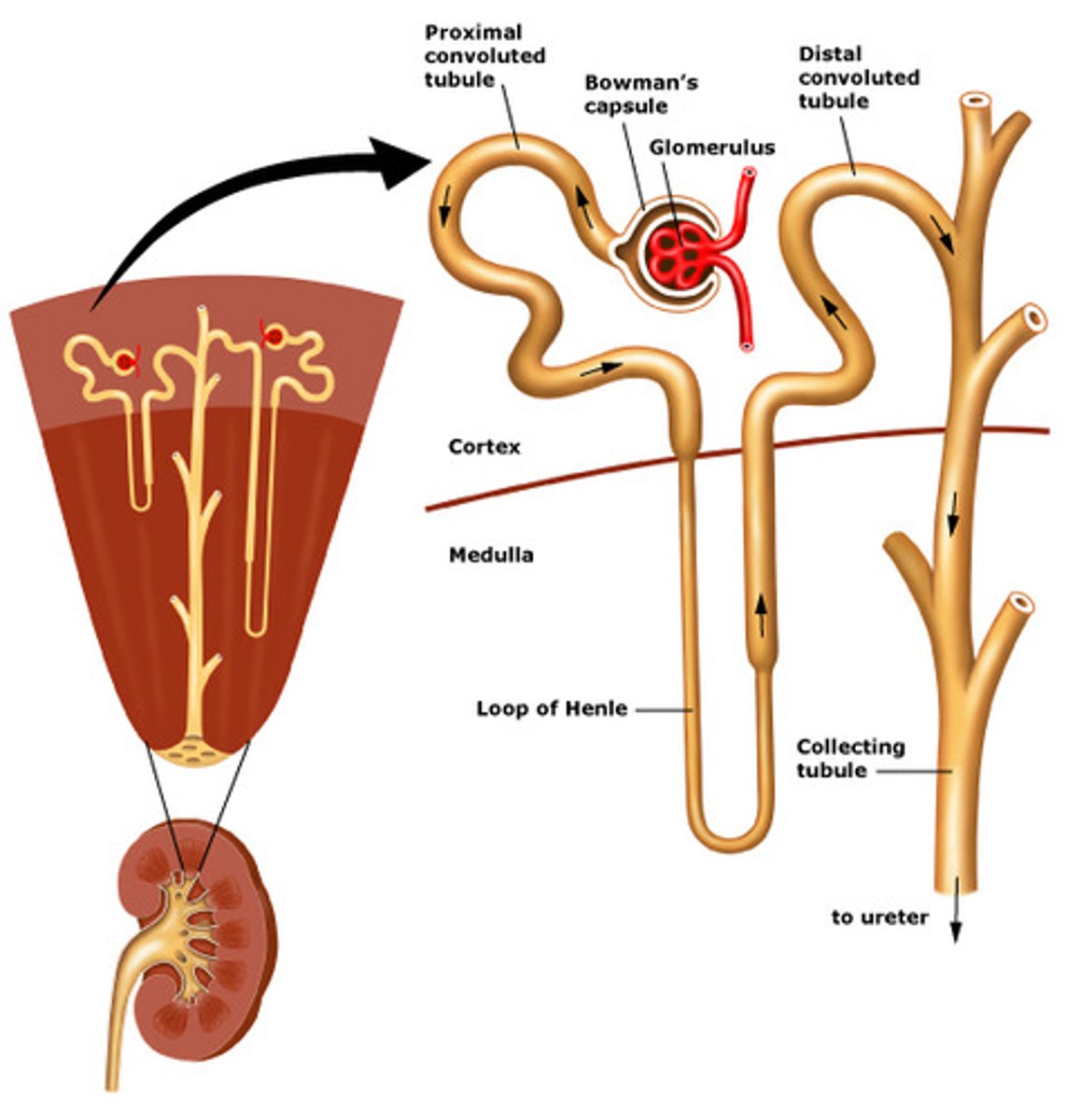
Each kidney contains one million nephrons (microscopic filtering units that filter the blood and result is excreted as urine).
Each nephron has a glomerulus (network of capillaries that performs the initial step in filtering. Each glomerulus is surrounded by a thin-walled Bowmans Capsule).
Nephrons and glomerulus of the kidney
Other ways drugs can be excreted (other than urine)
saliva, GCF, sweat, breast milk, lungs
Antihypertensive medications
-Beta-blockers: (non selective or selective) reduce cardiac output
- Calcium channel blockers relax blood vessels
-Diuretics remove water and reduce blood volume
- ACE inhibitors reduce constriction of blood vessels.
What is a common side effect of antihypertension medication
orthostatic hypotension.
to prevent this, bring the chair up slowly to allow the patient to adjust.
Diuretics MOA
*First-line agents for mild-mod HTN*
They work by blocking sodium re-uptake in the nephrons (loop of Henle) in the kidneys.
As a result, more water is released from the body, decreasing blood volume and therefore decreasing peripheral resistance.
Examples:
Hydrochlorothiazide
furosemide
Beta Blockers MOA
Block Beta 1, Beta 2 or both receptors.
Beta 1--> causes vasconstriction
Beta 2--> causes bronchiodilation
Examples of non-selective beta blockers
propanolol (Inderal)
timolol (Timoptol)
What beta blockers are CONTRAINDICATED for asthma patients?
non-selective
propranolol
timolol
(Props to Tim!)
Examples of selective beta blockers
atenolol (Tenormin)
metoprolol (Lopressor)
What is the MRD for epinephrine for patients taking non-selective beta blockers?
0.04 mg
What other uses for beta blockers?
angina
antiarrhythmic
anxiety
MI
Calcium Channel Blockers MOA
Stop calcium from entering cells of the heart/blood vessel walls
therefore stopping vasoconstriction
Can cause gingival hyperplasia.
-PINE:
Ex: Procardia (nifedipine), Diltaliziem, amliodipine, vermapil
ACE inhibitors
Stop the enzyme that produces angiotension II in the RAAS system (this substance causes vasoconstriction)
Calcium channel blockers cause
gingival hyperplasia
-dipine
ACE inhibitors can cause
dry cough
-pril
Anti-anginal agent
Nitroglycerin
Vasodilates, taken sublingually to avoid GI tract, quicker onset
Angiotension II Receptor Blockers
ARB's: "Sartan" and "Vasartan: suffixes
-prevent the release of aldosterone (sodium retaining hormone)
-block angiotensin II from the angiotension I receptors found in many tissues
*cause vasodilation and decrease peripheral resistance
*Best for women who are newly diagnosed
-do NOT take during pregnancy
ARBs vs ACE inhibitors
-ARBS don't cause cough, ARBS can't be taken in pregnancy
-Equally effective for treating HTN
-Both are well tolerated
ACE inhibitors block an enzyme that converts angiotensin I from becoming angiotensin II, which prevents the release of aldosterone (which then stops sodium retention, leading to vasodilation.
ARBS blocks the receptor site at angiotensin II.
CHF Drugs
ABCDDD
- ACEs & ARBS
- Beta Blockers
- Calcium CB
- Digoxin
- Dilators
- Diuretics (lowers BP)
CHF drugs
Digoxin--> increases force of contraction of the heart
Side effects gag/salivation
Caution with epi, can cause dysrhythmia
Spiralactone--> treats CHF, excessive aldosterone excretion
Potassium sparing diuretics
What is CHF
is a dysfunction of the of the heart as a pump of blood. This results in insufficient oxygen delivery to tissues accompanied by the accumulation of fluid in the lungs.
Side effect of CHF Drug, digoxin
gag reflex/salivation.
Caution with epi (can cause dysrhythmia)
Side effect of CHF drug, (potassium sparing diuretic) Spirolactone
Spironolactone (Aldactone) causes hyperkalemia, and water retention
Antiarhythmic drugs treat
irregular heart rhythms
atrial fibrillation
atrial fibrillation
rapid, random, ineffective contractions of the atrium
Structure of the heart
has four chambers (right and left atriums, right and left ventricles)
SA node triggers electrical impulse to cause atria (upper chambers) to contract. The signal then goes to the AV node which then goes to the purkinjke fibers that cause the ventricles to contract.
IE: SA--->AV--->PF
Classes of antiarrhythmics and MOA
Class I: Sodium Channel blockers (slow electrical impulse conduction in the heart muscle itself.)
Examples of Na Channel Blockers:
-Rhythmodan, Teva-Mixelitine
Class II: Beta-blockers-> slow electrical impulse at SA and AV nodes.
Class III: Potassium channel blockers: blocks repolarization --->slow down impulse in all heart cells. EX: Multaq (
Class IV: Calcium channels---> (-Pine) slow down heart rate at SA and AV nodes.
Examples of CCBs
vermapil, ditalizem, nifedipine
Lidocaine can be used as a
antiarrhythmic drug
Anticoagulation drugs
heparin, warfarin (coumadin), Plavix
reduce the ability of blood to clot after MI or strokes
INR values
2-3
3 means it clots FAST
2-fast, 3-too slow (3 and under is good for dental procedures)
Ideal INR is
3 or BELOW (1 is ideal)
If someone is taking warfarin or coumadin, they should use WHAT for pain?
NOT aspirin or NSAID, use TYLENOL.
Aspirin use as a blood thinner....
often used daily (baby aspirin, 81 mg dose) to prevent MI, is an antiplatlet but does NOT cause excessive bleeding.
If a patient is on a blood thinner (other then aspirin, obviously) they should use what for pain?
Tylenol
Aspirin (by itself) does not cause
NOT cause excessive bleeding
NSAIDs are....
antipyretic
analgesic
anti-inflammatory
NSAIDs MOA
Reversibly inhibit COX-1 & COX-2
Block prostaglandin synthesis (PGEs cause the experience of pain)
COX-1 enzyme
protects stomach lining, decreases fever, promotes platelet aggregation
blocking COX-1 can results in gastric ulceration and renal toxicity
Too much use of NSAIDs can result in
-gastric ulcers (blocks COX-1 which is helpful for protective gastric secretions)
- renal toxicity (blocks COX-1 and can damage kidney)
Blocking of WHAT enzyme is responsible for the NSAID's antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects?
COX-2 inhibition
How do NSAIDs effect temperature?
Affects the hypothalamus (which controls body temperature)
NSAIDs are commonly used for?
Arthritis
NSAIDs (including Aspirin) adverse effects
-GI ulcers/GI irritation (ESPECIALLY ASPIRIN)
-renal toxicity
-CANNOT be taken with blood thinners (will interfere with bloods ability to clot)
- Excessive use can also cause neuropathy
Name the NSAIDs
Aspirin, ibuprofens (advil, motrin), naproxen (aleve)
Aspirin is also a
antiplatlet agent (but won't cause excessive bleeding like blood thinners would)
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is NOT
NOT anti-inflammatory, NO effect on clotting
(only fever reducer and pain reliever)
ie analgesic and antripyretic
AcetamiNOphen
NO USE for inflammation
I Nap and I feel Alive (NSAIDs)
Aleve, naproxen, advil, aspirin
Tylenol is perfect for
-children
-patients on blood thinners
-patients with kidney disorders
Opiods
Naloxone, naltrexone
Opiods cause...?
respiratory depression and constipation
SLOw + OPIoid=?
SLOPPY
Opioids makes you SLOW.
(slow bowel, breathing, thinking, miosis)
causes constipation
Opiod receptors
mu, kappa, delta
Most pure opioids block
all receptors (mu, kappa, delta) but mostly mu receptors
EX: morphine, hydromorphone, fentanyl, methadone
Pure opioid antagonist (say, for fentanyl) is
Naloxone (Narcan)
What is the most common OPIOID used in dentistry?
Codeine
(Tylenol + codeine= Tylenol #3)
Natural Opioid (opiate)
morphine
semi-synthetic opioids
oxycodone and hydrocodone
Oxycodone combinations
PercoCET= Oxy + aCETaminophen
Percodan= Oxy + aspirin
Nitrous Oxide
Used for patient anxiety OR muscle relaxation (ex, for patient with cerebral palsy)
-Provides STAGE 1 anesthesia
cerebral palsy
paralysis caused by damage to the area of the brain responsible for movement
Nitrous Oxide contradictions
Res[iratory issues (COPD, airway congestion)
Pregnancy
Cystic fibrosis (too much mucous) ,Infections
Emotional illness (manic, depression)
History of substance abuse
Antibacterial agents
Can be: Bacteriocidal or bacteriostatic
Superinfection
overgrowth of normal microbiota that is resistant to antibiotics
Penicillin
DRUG of choice
BACTERIOCIDAL
(amoxicillin, penicillin V, penicillin G, etc)
Clindamycin Side effects
bacteriostatic agent
Side effects: GI cramps and nausea are common
CAN CAUSE C. DIFF INFECTION. This is why it is no longer in pre-med guidelines M
Penicllin = penCIL= ?
BacterioCIdaL
-Linda has Static Hair
Clindamycin is bacteriostatic.
Macrolides
-Zithro's (azithromycin, clarithromycin)
Bacteriostatic agents
Same side effects as clindamycin- GI cramps/nausea
Tetracycline is
bacteriostatic
Atridox: Doxy hyclate gel
Arestin: minocycline microspheres
periostat: Doxycilycine capsules
CAN CAUSE DISCOLORATION of unerupted teeth, CI for children under 9 or pregnant/nursing mothers
Tetracycline (and it's derivatives) can be blocked from absorbing by
milk/antacids.
Periochip
Subgingival sustained release delivery system, containing Chlorhexidine
Periostat
systemic delivery of 20 mg capsule of doxycycline hyclate (oral administration)
WORKS AGAINST AA!
Arestin
minocycline microspheres
Atridox
doxycycline gel
Name 3 bacteriocidal agents (Pe Me Ce!)
Penicillin
Metronidazole
Cephlasporin
Metronidazole is used to treat? (and side effects?)
PDZ
MORE commonly then tetracycline!!
side effects: Black hairy tongue and metallic taste
Antiviral Agents
agent that combats specific viral diseases
A virus needs a host
Common Antivirals and what they treat
Acyclovir---> Herpes simplex 1, Mono, shingles
Docosanol (Abreva) ---> treats oral herpes labialis
Retrovir ---> treats HIV
Anti-TB agents
Rifampin
Isoniazid
Pyrazinamide
Ethambutol
antidepressant drugs
SSRIs--> Newest generation Ex: Celexa, Prozac, Zoloft
TCAs--> Older generation, Amitriptyline (NO EPI!!! )
MAOs --> Nardil
NDRIs --> Bupropion (also used for smoking cessation)
Anti-psychotic medication
Chlorpromazine, clozapine (-Zine, Apine)
Side effects: xerostomia