Customer Service and Communication Skills in Business
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Customer
Anyone who uses the service or product of another person, company or group.
Customer Service
A company's ability to supply wants and needs to the customer.
GOOD customer service
The ability of a business to constantly and consistently exceed the expectations of the customer.
Importance of Customer Service
Gives positive impression to future and current clientele, keeps customers willing to come back again, makes customers feel like they are the number one priority.
Steps to Creating Good Customer Service
Make eye contact and greet customer, have a good understanding of the product/service you provide, assume attentive posture to show confidence and a helpful attitude, smile often, if appropriate for the situation.
Customer complaint
Communication that alleges deficiencies during or after purchase.
Average customer with an unsolved complaint
Will tell 9 to 10 other people.
For every complaint received
The average company has 26 unhappy customers that don't complain.
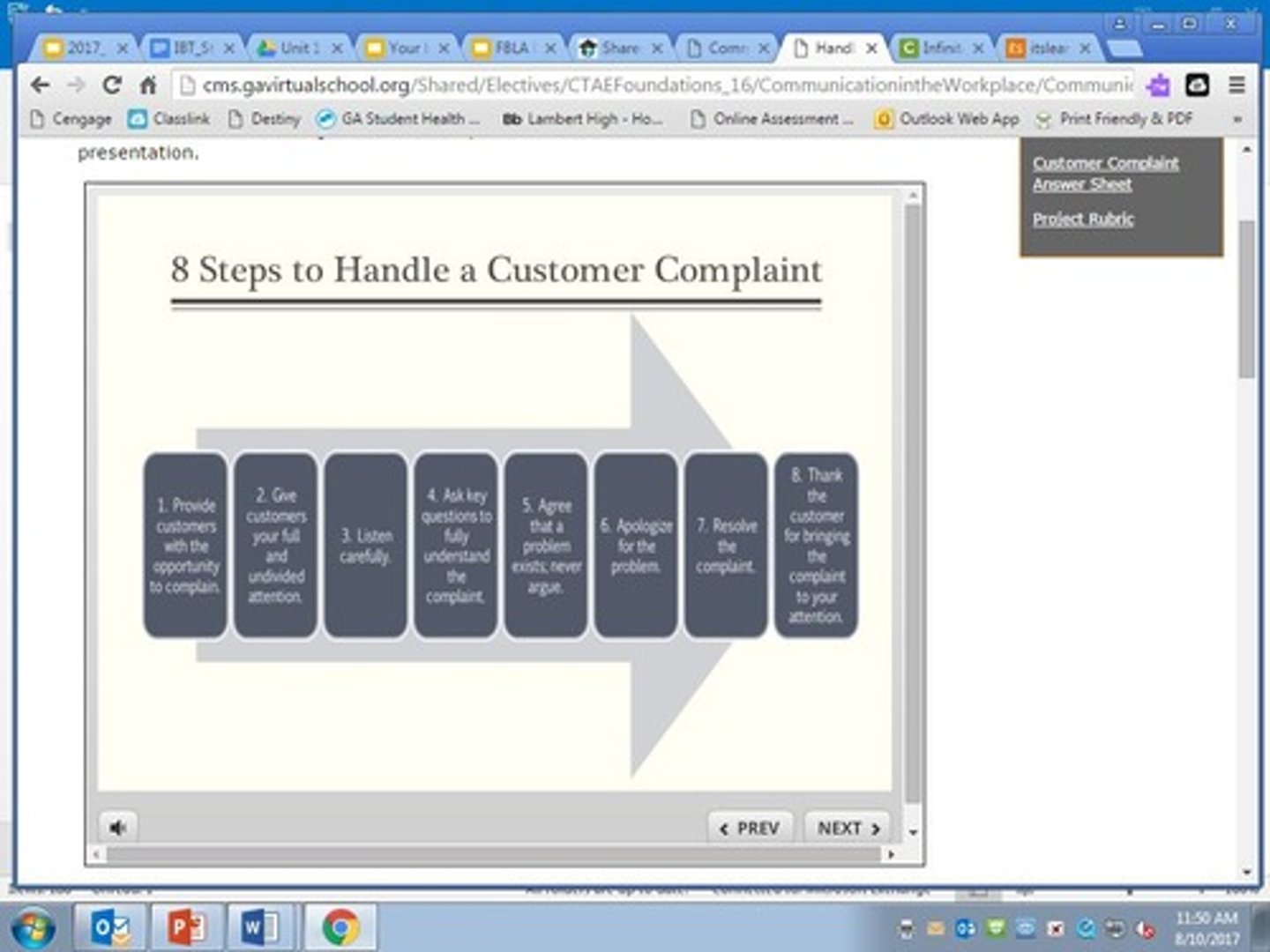
8 steps to handle a customer complaints
(Details not provided in the notes.)
The Aggressive Customer
Readily complains, often loudly and at length.
Response to The Aggressive Customer
Listen completely.
What not to do with The Aggressive Customer
Be aggressive in return; this customer does not respond well to excuses or reasons why the product/service was unsatisfactory.
The High-Roller Customer
Expects the absolute best and is willing to pay for it; likely to complain in a reasonable manner.
Response to The High-Roller Customer
Always listen respectfully and actively question to fully determine the cause.
The Rip-Off Customer
Their role is not to get the complaint satisfied but to win by getting something that is not entitled to be received.
Response to The Rip-Off Customer
Remain objective; use accurate data to backup your response and ensure the adjustment is within reason of what the company would normally do.
The Chronic Complainer
Never satisfied, feels there is always something wrong.
Response to The Chronic Complainer
Extreme patience is required; listen carefully and never get angry.
Sympathy
A sincere expression of understanding and care for someone's feelings or situation.
Sincere Apology
A genuine expression of regret for a mistake or wrongdoing.
Company Policy
Established guidelines that dictate how employees should behave and respond in various situations.
Meek Customer
A customer who generally does not complain but may share their dissatisfaction with others.
Common Customer Complaint: Rude Associate
A complaint indicating that the employee was disrespectful, requiring an apology and employee training.
Common Customer Complaint: Lack of Help
A complaint expressing that associates are unhelpful, necessitating a greeting and continuous assistance from one employee.
Common Customer Complaint: Associate's Ignorance
A complaint about an associate not knowing how to assist, requiring an apology and employee training.
Common Customer Complaint: Repeated Problems
A complaint from a customer returning with the same issue, requiring urgent resolution.
Common Customer Complaint: Lack of Choice
A complaint indicating that the employee is making decisions for the customer, requiring clear communication and guidance.
Common Customer Complaint: Indifference
A complaint expressing that no one cares about the customer's problem, requiring prompt attention and concern.
Common Customer Complaint: Unhelpful Associate
A complaint about an associate not providing assistance, requiring incentives for good performance and coaching for improvement.
Common Customer Complaint: Competitor's Offer
A complaint comparing services or offers from another store, prompting consideration of competitive benefits.
Importance of Customer Complaints
Customer complaints are vital for identifying areas of improvement within a company.
Types of Customers
Different categories of customers that require tailored approaches for effective service.
Resolved Complaints
Complaints that have been addressed successfully, increasing the likelihood of customer return.
Employee Training
The process of educating employees on proper customer service behaviors and responses.
Customer Engagement
The practice of interacting with customers to understand their needs and concerns.
Incentives for Employees
Rewards given to employees who demonstrate excellent customer service.
Coaching Sessions
Meetings aimed at improving employee performance in customer service.
Scenario Creation
The activity of developing hypothetical situations to practice customer service responses.
Communication
Communication occurs when a sender expresses an emotion or a feeling, creates an idea, or senses the need to communicate.
Communication Process
The communication process is triggered when the sender makes a conscious or an unconscious decision to share the message with another person—the receiver.
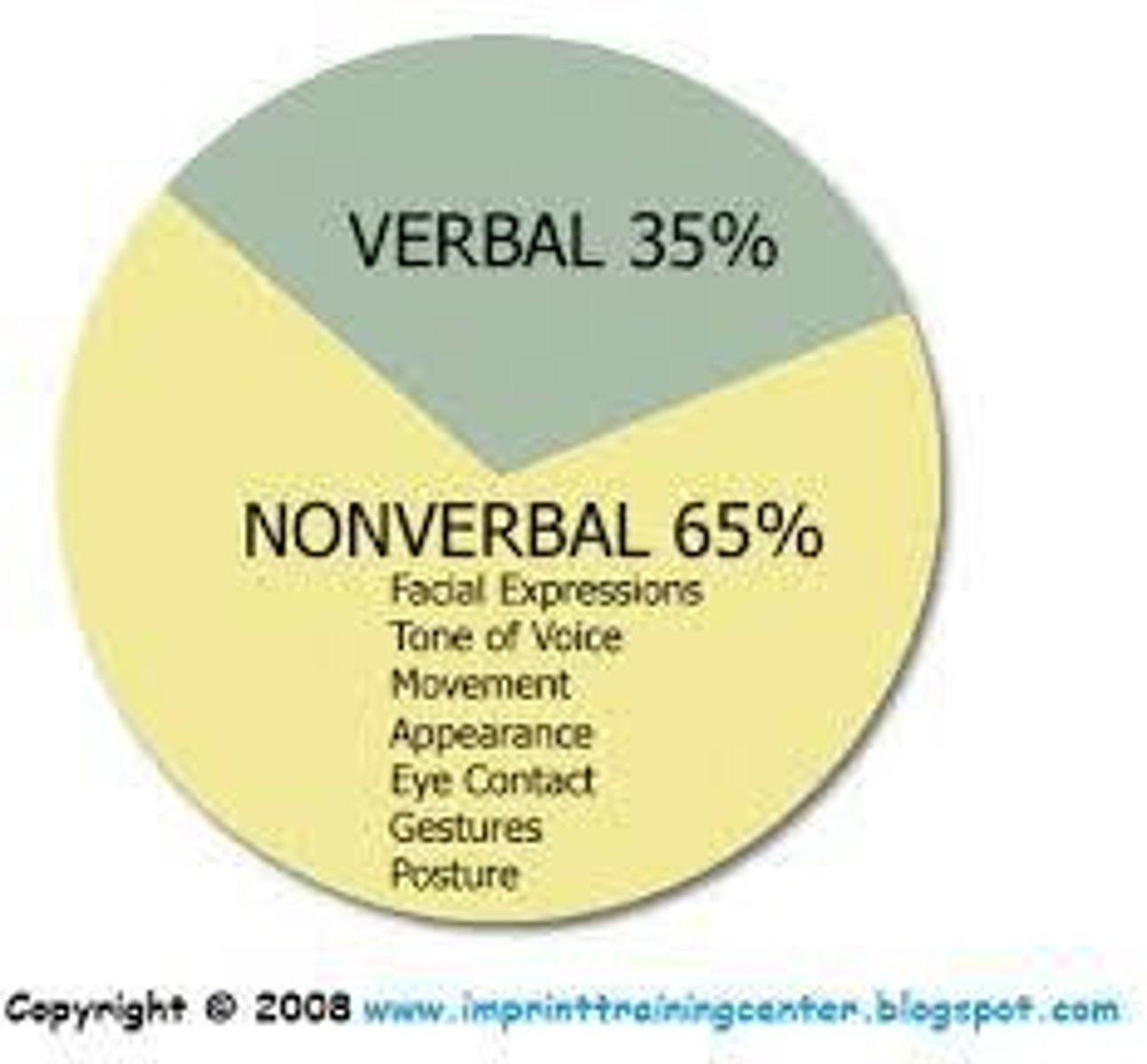
Types of Communication
Verbal (using words), Non-Verbal (no words).
Verbal Communication
Using words to convey messages, which can occur face-to-face, over the phone, or in writing (e-mail, text, letter, etc.).
Non-Verbal Communication
Communication that occurs without words, including eye contact, posture, personal appearance, and timing.
Nonverbal Communications
People telegraph their intentions and feelings, whether they are aware of it or not.
Body Language
A source of nonverbal confirmation or denial of our verbal message.
Nonverbal Cues
Facial expressions, body language, eye contact, dress and physical appearance, gestures.
Nonverbal Cues Trust
When our words send one message and our nonverbal cues send another message, people almost always believe our nonverbal cues.
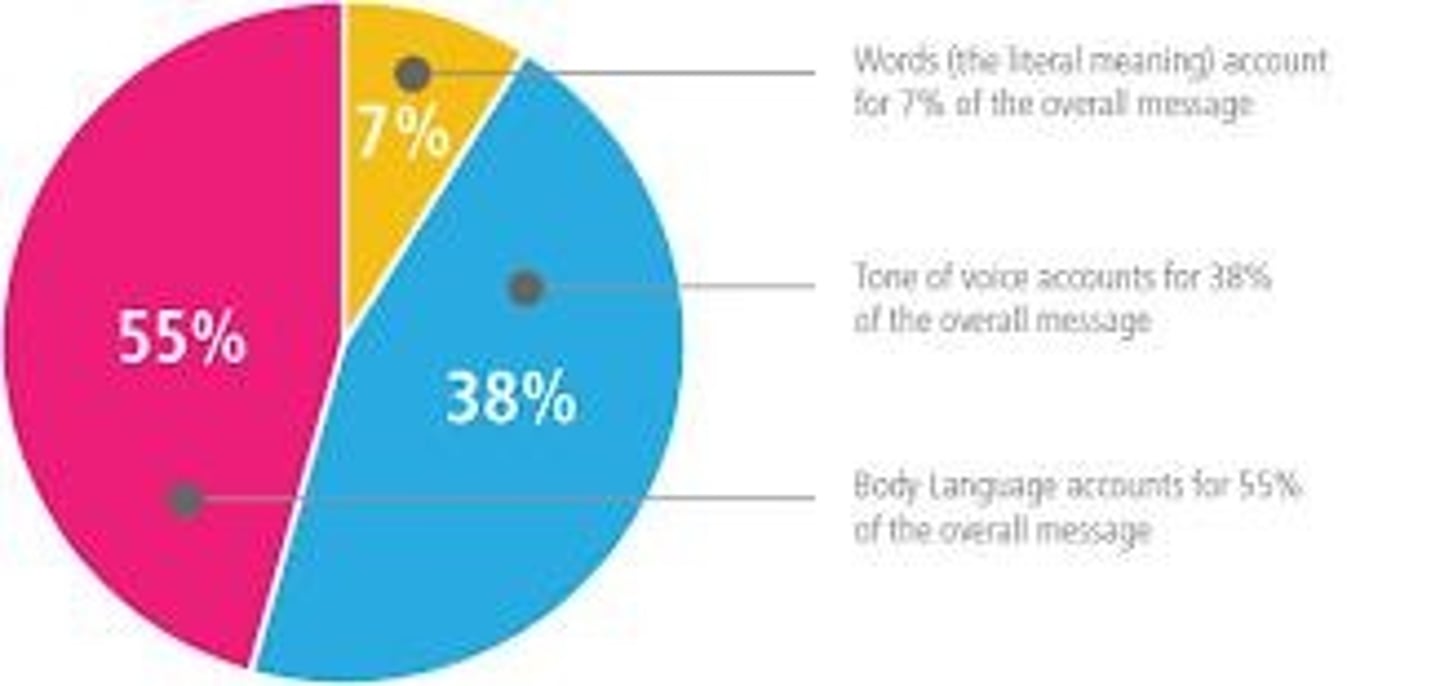
Sources of Communication
Our communication comes from three sources: Words = 7%, Tone of Voice = 38%, Body Language/Gestures = 55%.
Barriers to Communication
Obstacles that hinder effective communication, such as unclear messages, misunderstanding, not listening, and lack of language skills.
Language Barriers
Language that describes what we want to say in our terms may present barriers to others who are not familiar with our expressions, buzz-words, or slang.
Gender Barriers
Distinct differences between the speech patterns in men and women; women speak between 22,000 and 25,000 words a day, while men speak between 7,000 and 10,000.
Childhood Speech Patterns
In childhood, girls speak earlier than boys and at the age of three, have a vocabulary twice that of boys.
Getting the Message Across
Use appropriate tone for situation, make eye contact, use appropriate body language, and ensure your audience is ready to listen.
Effective Listening
In order to comprehend a message, you must be actively listening.
Active Listening
Show interest, don't interrupt the speaker, make eye contact, limit distractions, and ask questions if you don't understand.
Body Language Tips
Strategies to improve communication through nonverbal cues.