Endocytosis
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is taken up through endocytosis?
Nutrients
Signals
Antibodies
Enzymes
Viruses
Bacteria
Membrane
What are the 3 different fates for endocytosed material?
recycling
transcytosis
degradation
What are the 3 main endocytic pathways?
small scale clathrin endocytic process
micropinocytosis
phagocytosis
What is opsonisation?
process by which antibodies or complement proteins coat pathogens, enhancing their recognition and ingestion by immune cells like macrophages
What type of material does phagocytosis allow to take up?
large particles
What are the 4 steps of phagocytosis of a bacteria?
ligand coated bacteria approaches phagocyte surface receptors
binds to receptors
pseudopod forms from mobilisation of actin in phagocyte cytoplasm, engulfing the bacteria
destruction of bacteria in the phagocyte
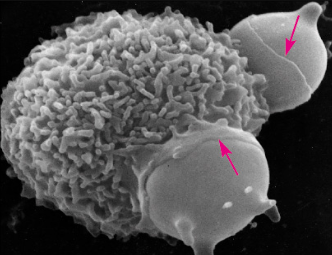
What are the ruffles visible on the membrane of the macrophage? What are the engulfed cells?
actin rich pseudopod
RBCs
What type of cell takes up yeast cells? RBCs?
phagocyte // macrophage
Describe frustrated phagocytosis and cell autonomous
immune cells attempt to engulf a same pathogen but are unable to bc of their incompatible ruffles, called cell autonomous ie has to happen within one single cell
How was membrane recycling proven through use of latex beads
macrophages phagocytosed 1.1 uM of latex beads, by counting the beads it was possible to estimate 30% of total membrane was internalised per hour (invagination of membrane necessary for phagocytosis) but there was no change in cell size
What is the difference between a macrophage and a phagocyte?
macrophage is a specific type of phagocyte, specialised in immunity and tissue repair
Explain the similarity and difference between phagocytosis and micropinocytosis
Mechanistically similar to phagocytosis where cells form actin driven ruffles to engulf material HOWEVER is non selective uptake of material
In which types of cells is micropinocytosis often seen and what purpose does it fulfil?
cancer cells to take up nutrients
What’s the pathway of LDL (cholesterol) from the EC to destruction in a cytoplasmic lysosome?
LDL binds to receptor, clathrin coated pit pinches off and takes up cell membrane + receptor bound to the LDL. The newly formed vesicle is uncoated and fuses with an early endosome, becoming a late endosome and finally a lysosome whose enzymes destroy the LDL
How are LDL receptors recycled during clathrin-mediated endocytosis?
as the receptor and LDL are in the early endosome, a small portion buds off containing the LDL receptor which is returned to the plasma membrane
What did Brown and Goldstein contribute to the understanding of endocytosis?
connection between receptor internalization and regulation of metabolism thanks to cross disciplines
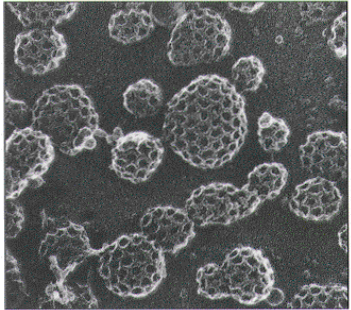
What’s depicted on the photo? What are they made of?
clathrin coated pits and vesicles
plasma membrane + cytosol
Why are clathrins termed triskelia ?
they have 3 arms
Explain the following sentence: “Clathrin triskelia polymerize into lattices “
clathrin molecules come together to form a regular network that helps in the formation of vesicles in cells
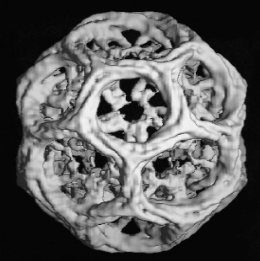
Which protein allows clathrin coated vesicles to pinch off?
dynamin
How is pH gradient related to function of the endocytic pathway? How does it evolve from the plasma membrane to the centre of the cell?
gradient allows maturation of endosomes
pH goes up as we get to the centre of the cell
What are Rab proteins, how are they activated and what is their function?
family of GTPases that act as molecular switches, going from inactive GDP-bound state to active GTP-bound state allowing guidance of vesicles to their target membranes, ensuring proper vesicle formation, transport, docking, and fusion.
What different types of Rab proteins are most important in the function of the endocytic pathway?
5: regulates early endosome formation and vesicle sorting and trafficking
7: late endosome maturation and the fusion of late endosomes with lysosomes
11: recycling endosomes, especially in the recycling of membrane proteins back to the plasma membrane
4: early endosome recycling and sorting
9: protein recycling and retrograde trafficking from late endosomes to the Golgi
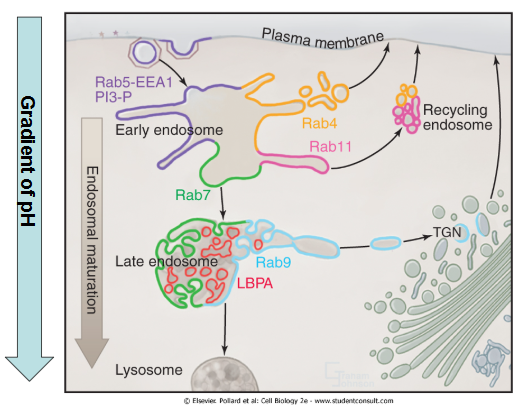
What does overexpression of Rab5 result in? What mediates endosome fusion?
enlarged endosomes
snares
What are lysosomes and what are the 2 main enzymes they contain?
membrane-bound organelles
hydrolases and lipases
What’s the role of hydrolases contained in lysosomes?
catalyse the breakdown of proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids through the addition of water
What’s the role of lipases contained in lysosomes?
catalyse the hydrolysis of lipids, breaking down fats and phospholipids into fatty acids and glycerol
Which vesicles contain cargo for degradation?
ILVs (intraluminal vesicles)
What is the late endosome also termed because of its structure?
Multivesicular Body (MVB)
What mutation of the endocytic system could cause cancers?
mutation in encapsulation of signal molecules = switch off signalling dysregulated ie over-active signalling if signal molecules aren’t capsulated at the right time