Developmental Origins of Pigmentation
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What makes melanocytes
neural crests
Melanin
produced by melanocytes and stored in melanosomes; made from tyrosine by the enzyme tyrosinase which gives pigmentation; absorbs UVA and UVB
two forms of melanin
eumelanin (brown and black) and pheomelanin (red and yellow): eumelanin absorbs in both UV and visual
Melanosomes
membrane bound packets of melanin made by melanocytes; coat the nuclei of keratinocytes to protect against UVR; transferred to keratinocyte from melanocyte extensions
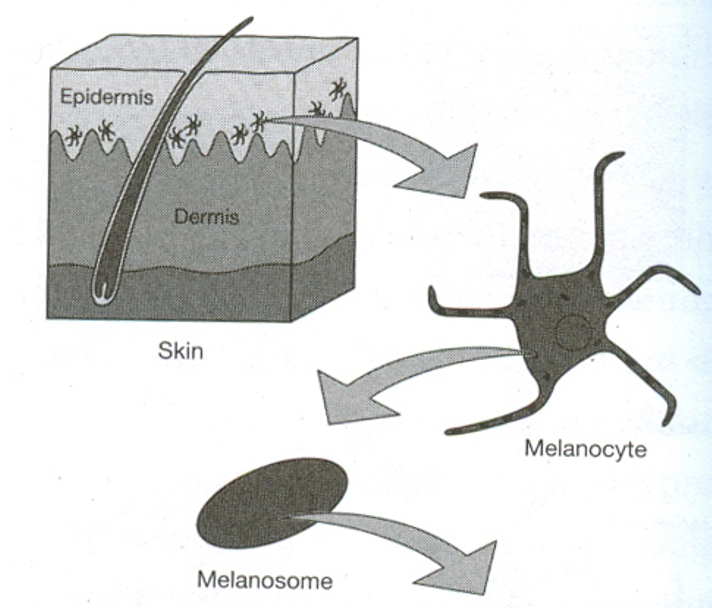
What causes variation in human skin pigmentation
variation in the density and type of melanin (i.e., ratio of eumelanins vs. pheomelanins) and not differences in the density or number of melanocytes.
Can you tell the difference between a reaction norm that shows a very plastic trait (that is, a strong environmental component) versus one that shows no environmental component?
no plasticity means changing the environmental variable changes nothing about the component; plasticity means the environmental variable alters the trait
What causes different reaction norms (e.g., different slopes, different shapes)
because of genetic differences.
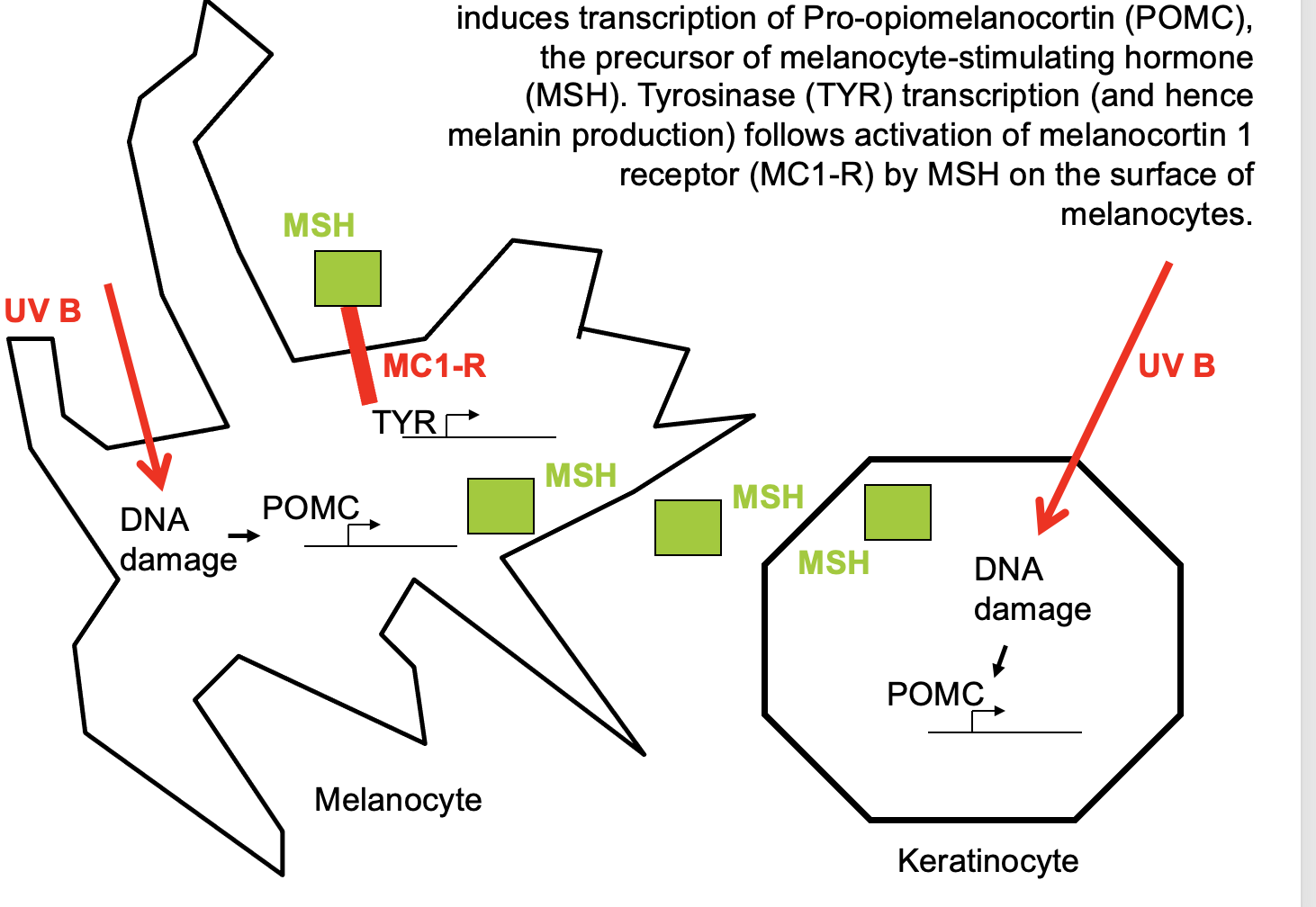
The “tanning response”
involves UVB, DNA damage, and the repair of DNA damage, resulting in increased transcription of POMC (somehow triggered by DNA repair), which produces the hormone MSH, which stimulates increased transcription of tyrosinase through the MC1R receptor, which causes an increase in melanin production in melanocytes.