Current Electricity and Circuits
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
conventional current
the flow of positive charges (protons)
Positive charges flow from high to low potential
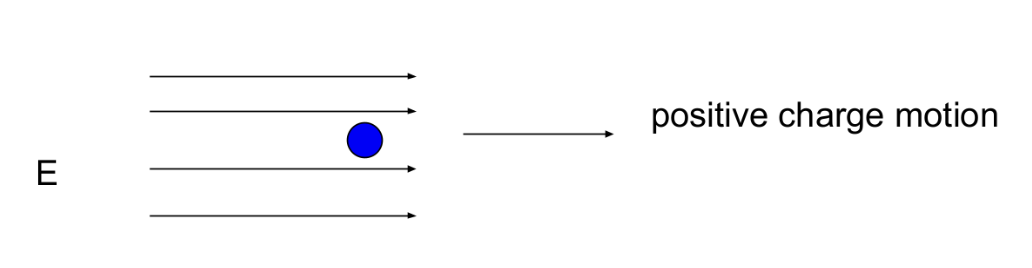
electric current
the flow of negative charges (electrons)
Negative charges flow from low to high potential
battery
an object in which series of chemical reactions occur in which electrons are transferred from one terminal to another.
between these poles there is potential diffrence
voltage
a electrical pressure that pushes and pulls charges
voltage difference
the push/pull that causes charges to move (two points)
A source of energy, a closed path, a device that uses the energy
electrical circuits parts
resistance
the ability of a material to resist the flow of charge
resistor
a circut device that is designed specifically to limit current flow
what affects resistance
length, cross-sectional area, materal and temperature
Kilowatt-Hour (kWh)
the amount of energy consumed in 1 hour at a rate of 1 kW
watt
J/S
conservation on charges
electric charges cannot be created or destroyed; it can only move from one place to another. The total amount of charge in a closed system always stays the same
wire
the medium through which charges flow
current
flow rate
measured in Amperes
amound of slowing water
electromotive force (EMF)
the maximum potential difference a power source can have is called?
It is the same everywhere
How is current distributed in a series circuit?
It increases
What happens to total resistance when more resistors are added in series?
it decreases
How does increasing resistance affect current in a series circuit?
They get dimmer
What happens to light bulbs if current decreases in a series circuit?
It decreases
What happens to circuit current when more resistors are added in series?
The largest resistor
Which resistor uses the most voltage in a series circuit?
The largest resistor
Which resistor uses the most power in a series circuit?
Yes, all of them
Do all resistors in a series affect the total current?
The same as the source voltage
What is the voltage across each resistor in a parallel circuit?
It is smaller
How does the total resistance compare to the smallest resistor in a parallel circuit?
It decreases
What happens to the total resistance when more resistors are added in parallel?
Only the resistance of that branch
What affects the current in each branch of a parallel circuit?
The one with the smallest resistance
Which resistor uses the most power in a parallel circuit?
It increases
What happens to total current when more resistors are added in parallel?
electrons
electric currents transfer ____ from one place to another
lower; higher
electrons flow from a _____ potential to a ______ potential
batteries
____ and generators are devices that plump electrons to an object with a higher concentration of electrons than the original object
electrical
electron pumps convert various forms of energy to ____ energy
amperes
electric currents are measured in _____
ampere
a current flow of one coulomb per second is one _____
Ohm
____ discovered that the ratio of potential difference between the ends of a wire and the current flowing through the wire is a constant
directly
the current that flows through a wire varies ____ as the applied voltage
resistance
the ohm is a unit of electric _____
parallel
a voltmeter should be connected in ____ with the resistance in a circuit
ammeter
a(n) _____ measures the current flowing in a circuit
voltage
electric power is found by multiplying ____ by current
current
the power used by a resistor is directly proportional to its resistance and to the square of the _____ throught the resistor
temperature
in many material, resistance increases when _____ rises
power
the kilowatt hour is a unit for measuring _____
current
the thermal energy produced in a circuit from electric energy varies directly with the resistance, the time interval, and the sqaure of the _____
watts
the product of volt times amperes equals
increase resistance
which change in a circuit would reduce the current flow
sum
In a series circuit, the voltage drop across the entire circuit is equal to the_____ of the voltage drops across the individual resistors.
branches
Total current in a parallel circuit is the sum of the currents in the __________.
series
The total resistance of a(n) __________ circuit is the sum of the individual resistances.
parallel
The voltage across the branches of a(n) __________ circuit is the same everywhere.
parallel
In a(n) __________ circuit, the total resistance is less than any single resistance.
series
The current in a(n) __________ circuit is the same everywhere.
Ohm’s
A(n) __________ law may be applied to an entire circuit or to any part of the circuit.
parallel
In a(n) __________ circuit, each resistor can be operated independently.
series
It is not practical for home circuits to be wired in _________
overloads
A parallel circuit _____ when to many appliances are placed across the circuits
short circuit
A(n) _____ circuit occurs when a piece of low-resistance wire is placed across a circuit.
fuse
A(n) _______ is a short piece of metal that melts if a predetermined current in the line is exceeded.
circuit breaker
A(n) __________ is an automatic switch that cuts off the current if the circuit is overloaded.
voltmeter
A(n) __________ must be built with a very high resistance or it changes the circuit that it is designed to measure.
ammeter
The resistance of a(n) __________ should be very low so that it does not affect the circuit in which it operates.