Unit 10: Reproductive System Overview
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
Testosterone
male hormone
Fetus
last 7 months of prenatal development
Semen
fluid ejaculation from the penis
Fertilization
sperm cell joins egg
Erection
when the penis becomes engorged with blood and hard
Prostate gland
adds a chemical fluid to the semen
Ovaries
glands that produce the egg cells and hormones
Egg cells
cells produced in the ovaries
Cervix
entrance to the uterus
Seminal vesicles
adds a sugary fluid to semen
Testes
organs that produce sperm
Vas deferens
tube that carries sperm from testes
Ejaculation
when the semen leaves the penis
Puberty
begins at about age 12 or 13
Scrotum
sac that regulates the temperature of the testes
Vagina
female organ of intercourse; birth canal
Fallopian tubes
where fertilization takes place
Embryo
first two months of development in the uterus
Estrogen
a hormone produced in the ovaries
Uterus
houses the fetus during pregnancy
Labia
folds of skin outside the vagina
Epididymis
stores sperm cells
Urethra
brings urine and semen out of the body through the penis
Clitoris
female erectile tissue between the labia
Sperm cells
cells produced in the testes
Placenta
organ that nourishes the fetus
Conception
onset of pregnancy, union of sperm and egg (ovum)
Contraceptive
a device or drug serving to prevent pregnancy
Ectopic
located away from a normal position
Erectile
capable of becoming rigid and elevated when filled with blood
Fertility
capacity of conceive or induce conception
Fibroid
tissue composed of threadlike fibrous structure
Genital
reproductive organ
Gestation
development of young from conception to birth pregnancy
Intercourse
sexual union
Lactation
production and secretion of milk by the mammary glands
Mammography
radiological view of breasts
Menses
normal flow of blood and uterine lining that occurs in cycle in women
Menstrual cycle
the recurring cycle of change of the reproductive organs induced by hormones
Ovulation
release of the egg from the ovary
Sterile
unable to produce offspring
Stillborn
born dead
Cervix
The lower portion of the uterus and a common site of cancer in women.
Fallopian Tube
One of two tubes through which a mature egg travels after ovulation.
Vagina
The female organ of intercourse.
Ovary
Two almond-shaped organs where egg cells are produced.
Uterus
The pear-shaped organ where the lining thickens in preparation for a fertilized egg.
Fimbria
Finger-like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes that help guide the ovum.
Ovum
A mature egg released during ovulation.
Uterine Lining
The tissue that thickens in the uterus in preparation for a fertilized egg.
Menstruation
The process where the egg leaves the body along with the lining of the uterus and a small amount of blood if not fertilized.
Egg cells
Cells produced in the ovaries that can develop into a mature ovum.
Estrogen
A hormone that triggers the development of the female reproductive system.
Progesterone
A hormone that plays a role in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Puberty
The period of physical changes triggered by hormones in a girl.

Sperm cell
The male reproductive cell that fertilizes the ovum.
Bladder
An organ that stores urine.
Seminal Vesicle
A gland that produces a sugary fluid that nourishes sperm.
Prostate
A gland that produces a chemical fluid that is part of semen and is a common site of cancer in men.
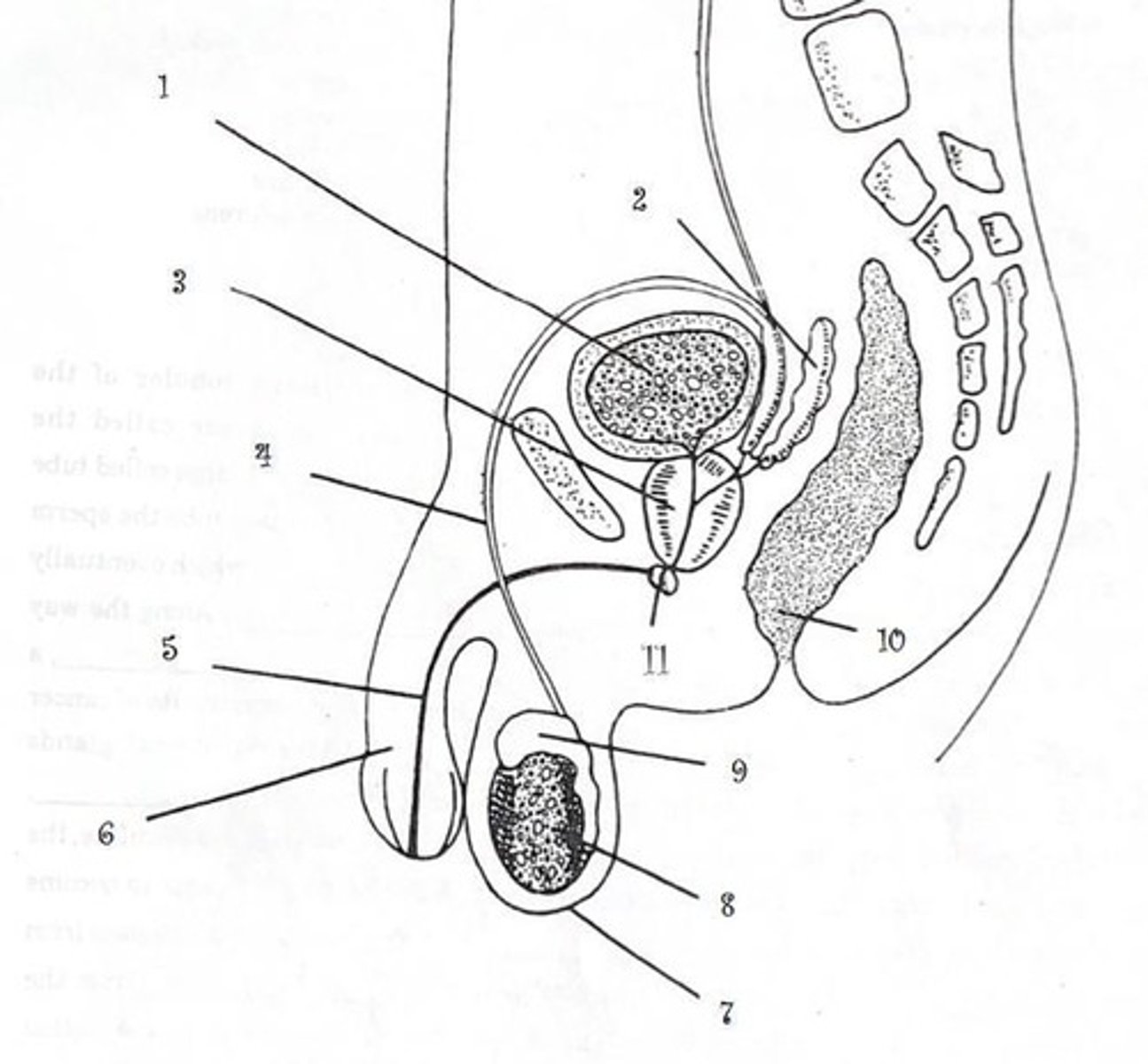
Vas deferens
A larger tube that carries sperm from the epididymis to the penis.
Urethra
The tube that carries semen from the body and also urine from the bladder.
Penis
The external male reproductive organ.
Scrotum
The sac that protects the testes.
Testicle
The gland where sperm is produced.
Epididymis
The coiled tube where sperm is stored after production.
Cowper's Gland
Glands located near the bladder that produce fluid that is part of semen.
Semen
The fluid that is ejaculated from the penis, containing sperm and other fluids.
Orgasm
The climax of sexual excitement, during which semen is ejaculated.
Erection
The process where the penis becomes stiff and hard due to blood engorgement.
Nocturnal emissions
Uncontrolled ejaculation during sleep.
ejaculation of semen
expulsion of semen
Functions of the Reproductive system
to reproduce, includes gonads and ovaries, passing of genetic material to offspring
Sex cells
gametes
Sperm/ova
gametes involved in fertilization
Fertilization
Joining of gametes
Zygote
Conception: 2 weeks
Embryo
2 weeks- 8 weeks
Fetus
8 weeks - birth
Neonate
Birth to one month of age
Testes
4-5 cm, produce spermatozoa
Epididymis
Secrete testosterone, tube on each testes, stores sperm
Seminal vesicle
adds fluid that increases volume and nourishes sperm
Prostate Gland
below bladder, fluid that protects sperm
Urethra
urine and semen excretion
Ovaries
produce: eggs, estrogen, progesterone; hormones prepare egg for fertilization and growth of placenta
Fallopian Tubes
Fertilization occurs in fallopian tube
Uterus
zygote implanted in uterus after fertilization; endometrium is the inner layer of uterus shed during menstrual cycle
Vagina
muscular tube that extends from cervix to outside of body
Vulva
external female genital
labia majora
fold of adipose tissue that protect vaginal opening
mon pubis
fat that joins the vulva
labia minora
folds of skin between labia majora
Clitoris
erectile tissue
mammary glands
breasts (excluded)
Menstruation
Lasts about: 28 days
Week 4 of Fetal Development
Embryo is ¼ inch long, has a head body and tail, eyes and ears can be seen, heart pumps blood to body
Week 5 of Fetal Development
Nose can be seen
Week 6 of Fetal Development
Embryo is ½ inch in length, leg buds are present, increase brain development, gonads start to produce hormones
Week 7 of Fetal Development
Embryo is ¾ inches in length, can move its hands, fingers are defined, internal organs are visible, skull bones are growing at the crown
Week 8 of Fetal Development
Almost 1 inch long, liver is very large, bones begin to form, testes and ovaries are distinguishable, now called a fetus