(chapter 7) intro to management denis hamilton final review flashcards
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
the 4 elements of organization design
job design, organization structure, integrating and coordinating workflows, organization culture
job design
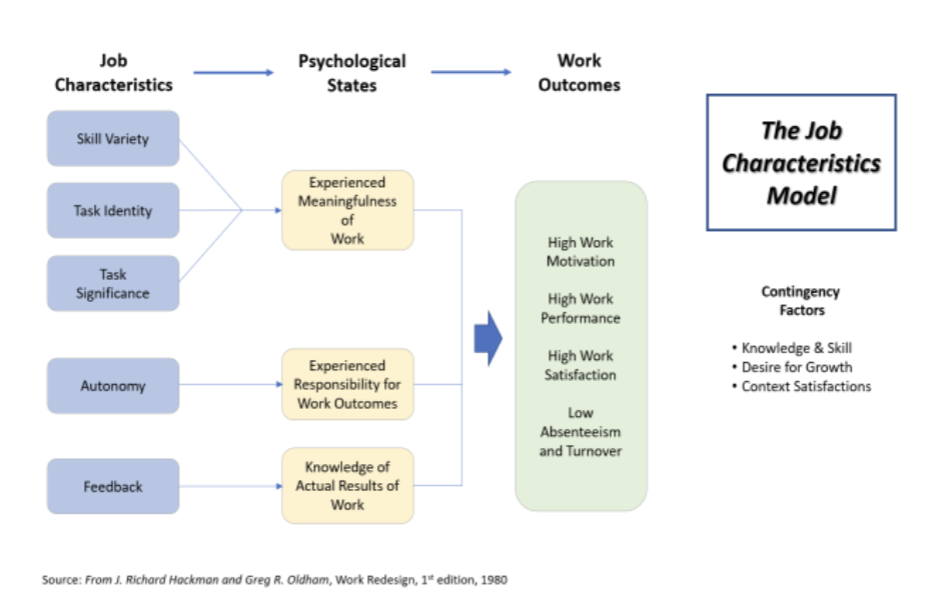
creating jobs in an organization that can be done effectively and efficiently while providing meaningful work for the employee
hackman and oldham job characteristics model
organization structure
the grouping together of jobs into work groups, the delegation of authority and responsibility within an organization, and the formal reporting relationships of employees to supervisors.
3 types of organizational structure
functional structure, divisional structure, matrix structure
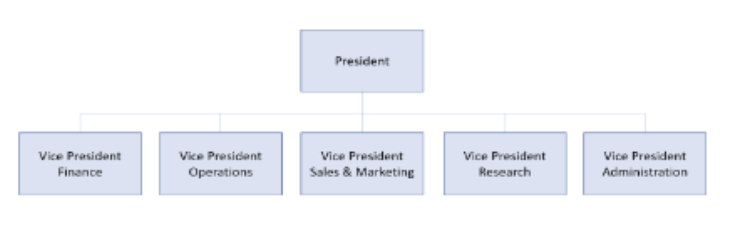
functional structure
groups jobs that require similar skills and experience together into a single work group reporting to the leader of the organization
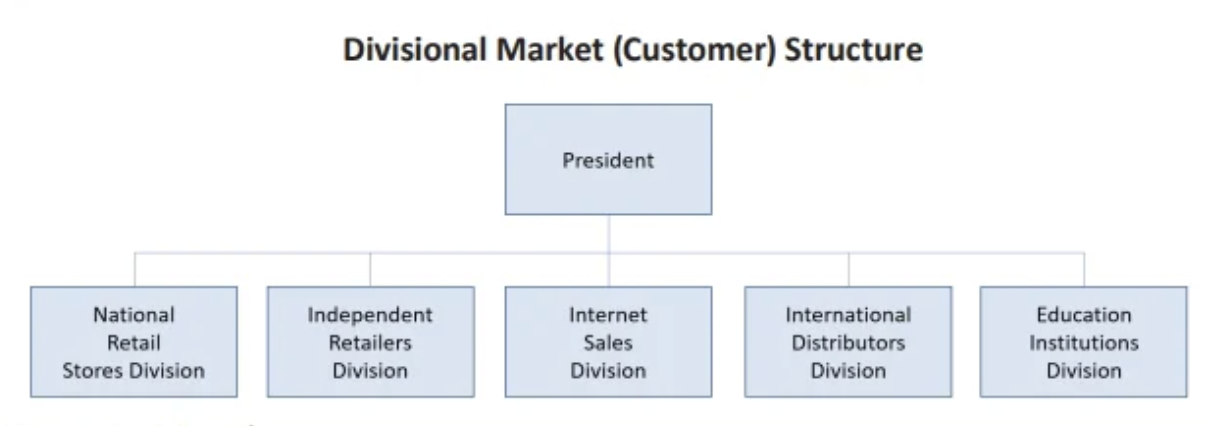
divisional structure
groups jobs together with people of diverse skills and experience who collectively focus on either providing specific products, or serving specific customer groups, or serving specific geographical areas.
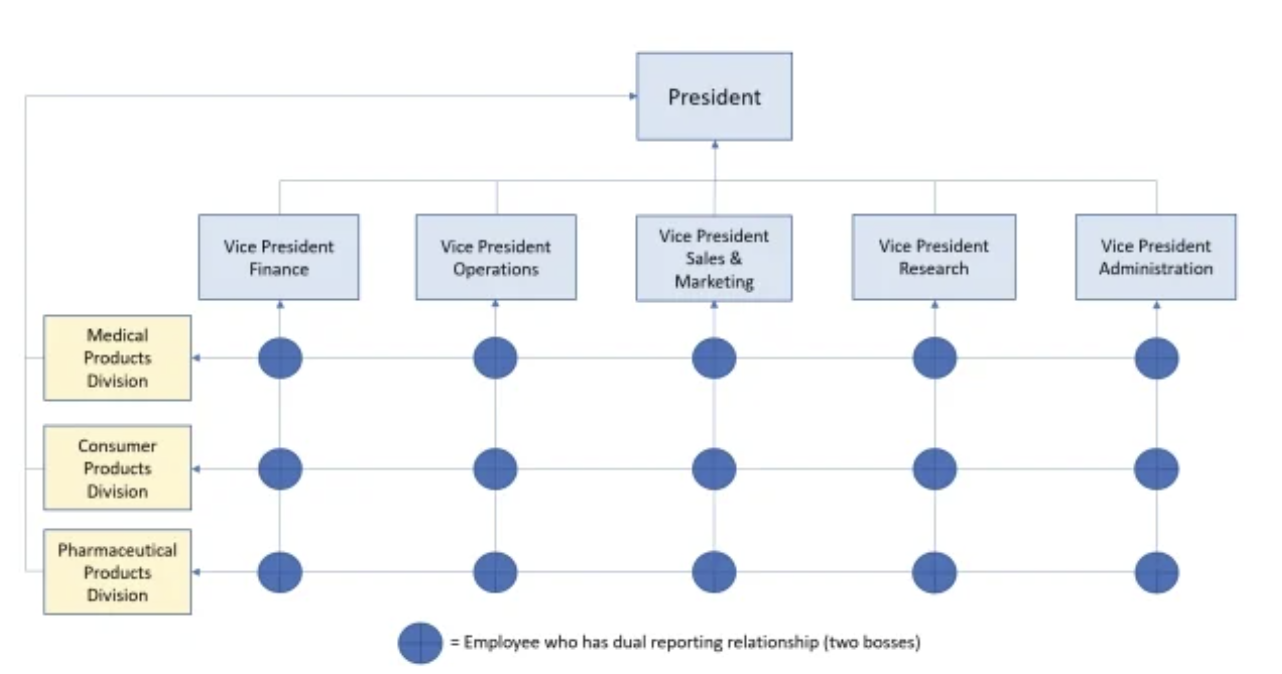
matrix structure
groups jobs together simultaneously by function and division
delegation of authority
in incorporated businesses means, ultimate authority for decisions rests with the shareholders of the business (the individuals or organizations that own the company’s stock)
agency
authority to make most decisions is delegated from those shareholders to a Board of Directors elected by the shareholders. The Board of Directors then delegates some of its authority to a Chief Executive Officer (CEO) appointed by the Board of Directors, who in turn delegates some of her/his authority to subordinates and so forth. The expectation is that each “delegate” is expected to act in the best interest of the shareholders from whom the delegation of authority originates. Shareholders use control mechanisms (such as independent audits) to make sure the authority they delegate is not being misused.
centralized organizational structure
most decisions are made, or at least must be approved, by the senior executives at the top of the organization
decentralized organizational structure
many decisions are delegated to lower levels of management with those managers accountable for the consequences of their decisions (good or bad)
span of control
refers to the number of direct reports assigned to a manager, the more direct reports, the broader the span of control. the fewer the number of direct reports, the narrower the span of control
levels of hierarchy
refers to the number of managerial levels between the top and the bottom of an organization. the fewer hierarchical levels, the flatter the organization. the more hierarchical levels, the taller the organization.
five common approaches to integration and coordination
organization structure, liaisons, task forces, cross functional teams, integrating roles
liasons
individuals appointed with the responsibility to coordinate the activities of their group with the activities of one or more other groups
task forces
made up of members of multiple groups who are assembled to address a specific need for coordination
cross functional teams
made up of members of multiple groups who are assembled with ongoing responsibility for managing a key activity of the organization
integrating roles
individuals that in addition to their other responsibilities are charged with being a coordinator of activities with other groups
organization culture
the set of norms, beliefs, values, and attitudes that are shared by a group of individuals within an organization
3 topics in organization culture
understanding an organization’s culture, strong vs weak cultures, changing an organization’s culture
understanding an organization’s culture
dimensions of culture:
content
consensus
intensity of feelings
levels of culture
artifacts
values
assumptions
content
what is deemed important including teamwork accountability and innovation
consensus
how widely norms are shared across people in the organization
intensity of feelings
how people feel about the importance of the norm, to what extent will people be recognized/sanctioned for supporting/violating the norm
artifacts
includes things that can be observed in the organization like the dress code, physical layout, manner in which people address each other, smell and feel of the place; how the individuals inside the organizations react to these artifacts and how it influences their behavior
values
this includes the esposed and documented norms, ideologies, charters, philosophies, wtc. that comprise the apparent values of the organization. to truly identify these, it is necessary to understand how the people in the organization think and feel
assumptions
includes the underlying, taken for granted and usually unconcsious thoughts of members of the organization that determine perceptions, thought processes feelings, and behavior - the root of understanding the culture in an organization
strong vs weak culture
a strong organization culture is one where the majority of the employees share the same norms, beliefs, values, and attitudes as it applies to their work related activities even if they are part of significantly different cultures outside of their workplace
bcg’s 7 dimensions of culture (changing an organization’s culture)
structure vs flexible
controlling vs risk permitting
thinking vs doing
diplomatic vs direct
individualistic vs collaborative
internal vs external

bcg’s 7 levers for moving to target culture (changing an organization’s culture)
leadership
people and development
informal interactions
organization design
resources and tools
values
the agile organization - five trademarks
north star embodied across the organization: clear goals for the organization allow teams to self-identify projects that align with those goals
network of empowered teams: flat organizational structures with limited hierarchy and no middle management. teams are empowered and act autonomously with end-to-end accountability
rapid decision and learning cycles: risk taking, failing, and learning fast are encouraged. continuous people development is a priority
dynamic people model that ignites passion: culture that empowers this agile way of working. emphasis on intrinsic motivation and non-monetary awards. developing expertise of employees is a cornerstone.
next generation enabling technology: technology is seamlessly integrated and core to every aspect of the organization as an enabler for quick identification of opportunities/challenges and quick reaction. this involves full transparency of the organization’s information. the focus is to rapidly unlock value and address business and stakeholder needs