organic chemistry
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
organic vs inorganic
Organic compounds are primarily carbon-based and are usually found in living organisms, while inorganic compounds generally lack carbon or have carbon not bonded to hydrogen and are found in non-living systems.
As the number of bonds increases, the bond energy also
increases
core vs valence
Core electrons are the electrons in the inner shells, and valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell involved in bonding.
nonpolar covalent bond
A nonpolar covalent bond is a type of chemical bond where electrons are shared equally between two atoms.This occurs when the electronegativity difference between the two atoms is very small, typically less than 0.5, according to chemistry resources.
single, double, and triple bonds
A single bond is always a sigma (σ) bond. A double bond consists of one sigma (σ) and one pi (π) bond. A triple bond consists of one sigma (σ) and two pi (π) bonds
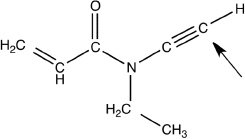
What is the electron geometry and hybridization around the labeled carbon atom (see arrow) in the following molecule?
linear and sp.
Formal Charge
Assign electrons to atoms with the assumption that each co agent bond is perfectly covalent ( equally shared)
in a given covalent bond assign half the electrons to each atom involved in the bond
assign both electrons of a lone pair to the atom on which they appear
2). Compute the formal charge of an atom by comparing the number of electrons assigned to the atom with the atom’s group number
formal charge is 0 if the number of assigned electrons is the same as the atoms group number
each excess electron contributes -1 to the formal charge
each electron that is lacking contributes +1 to the formal charge
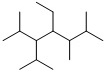
name
4-ethyl-3-isopropyl-2,5,6-trimethylheptane.
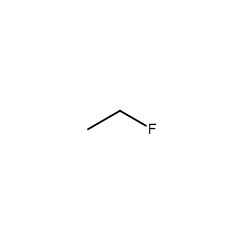
name
fluoroethane