RP4 - Investigation into the effect of a named variable on the permeability of cell-surface membranes.
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
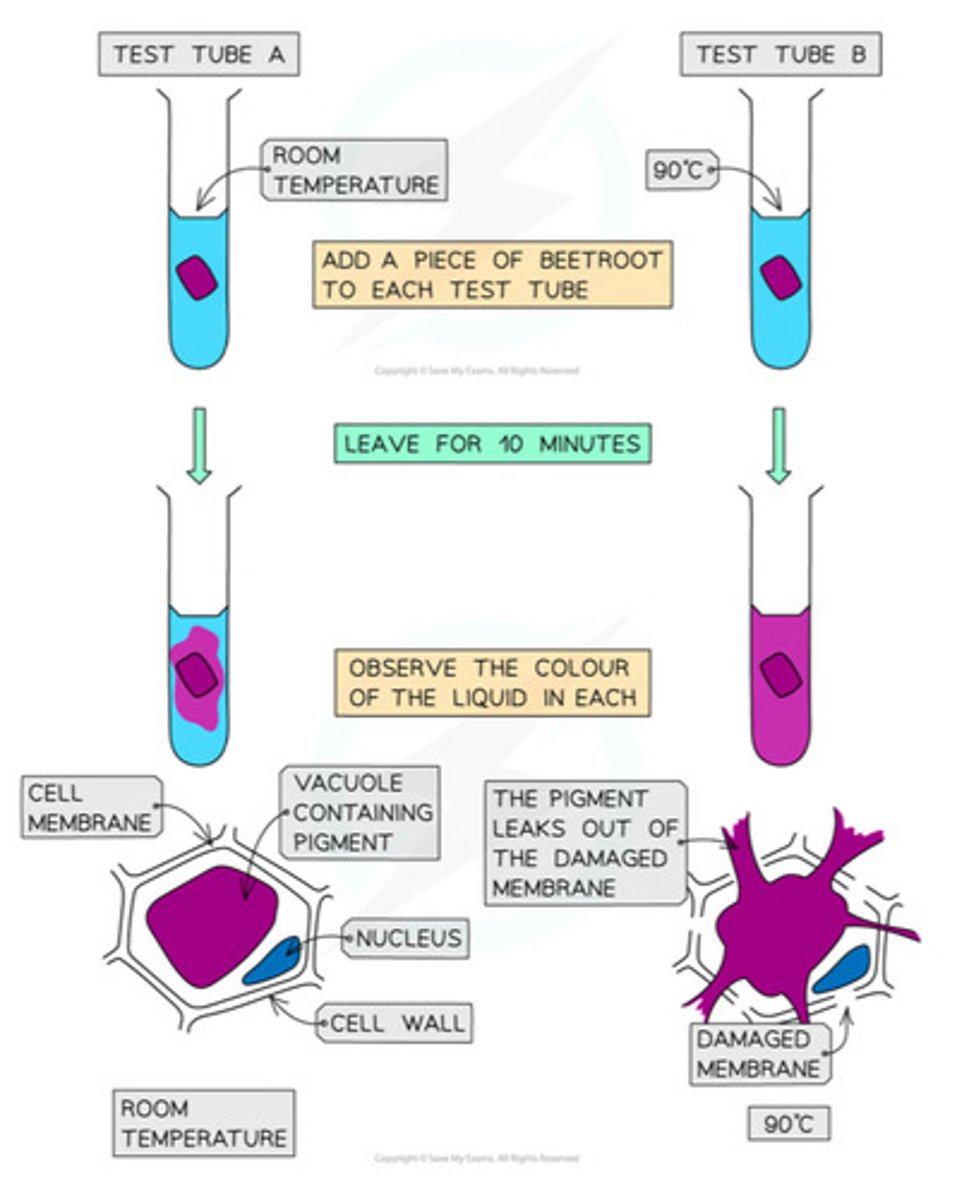
Describe a method to investigate the effect of a named variable (eg. temperature) on the permeability of cell-surface membranes

What does a high absorbance suggest about the cell-membrane?
● More permeable / damaged
● As more pigment leaks out making surrounding solution more concentrated (darker)
control variables
- same size/shape cubes
- same age/type/variety of plant tissue
- same volume of water
- length of time left in water bath
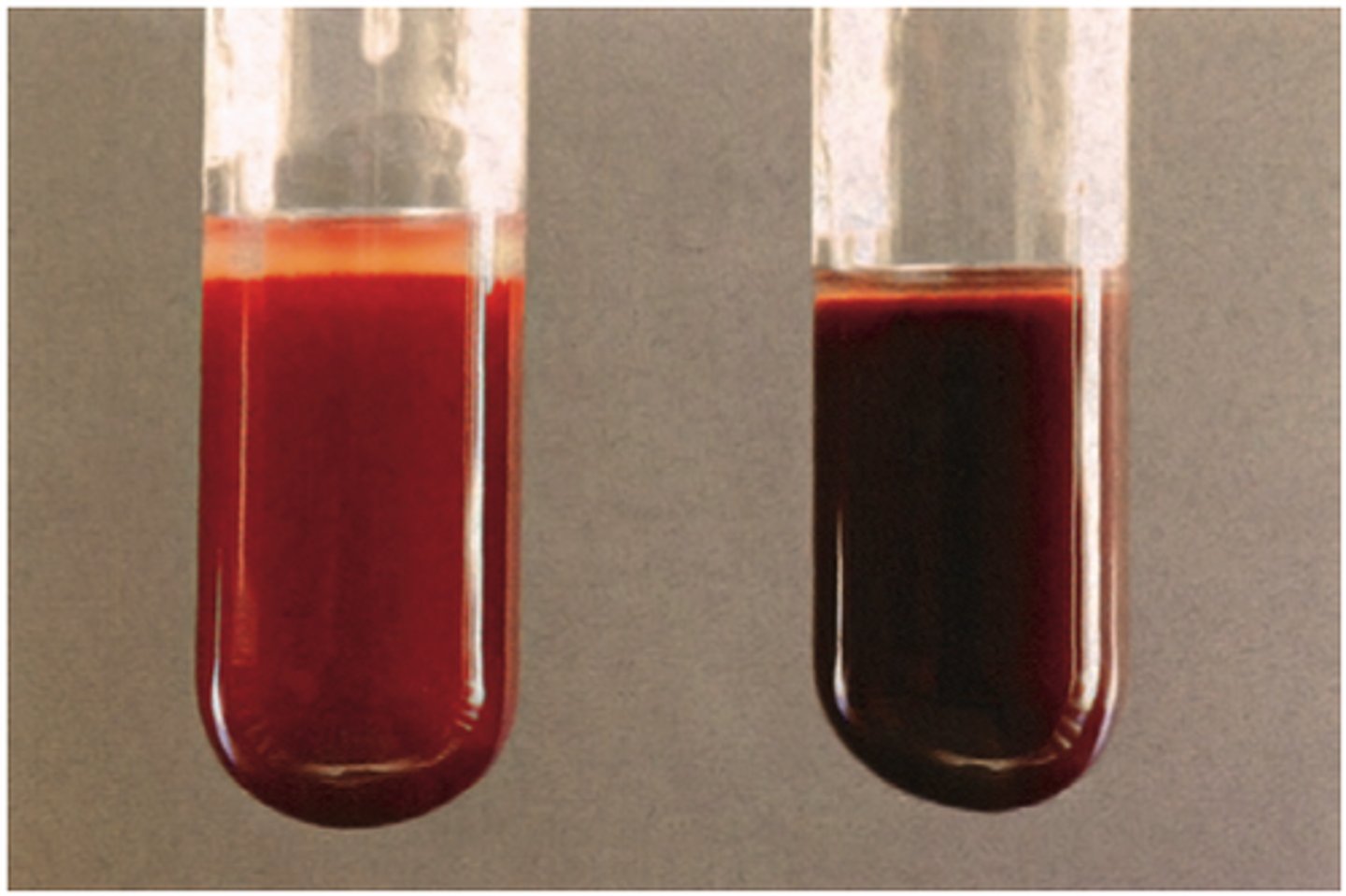
What are the issues with comparing to a colour standard?
● Matching to colour standards is subjective
● Colour obtained may not match any of colour standards

Why wash the beetroot before placing it in water?
● Wash off any pigment on surface
● To show that release is only due to [named variable]
![<p>● Wash off any pigment on surface</p><p>● To show that release is only due to [named variable]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9c245c4d-118f-42fa-9ff2-249636dffb7a.jpg)
Why regularly shake each test tube containing cubes of plant tissue?
● To ensure all surfaces of cubes remain in contact with liquid
● To maintain a concentration gradient for diffusion
Why control the volume of water?
● Too much water would dilute the pigment so solution will appear lighter / more light passes through in colorimeter than expected
● So results are comparable
How could you ensure beetroot cylinders were kept at the same temperature throughout the experiment?
● Take readings in intervals throughout experiment of temperature in tube using a digital thermometer / temperature sensor
● Use corrective measure if temperature has fluctuated

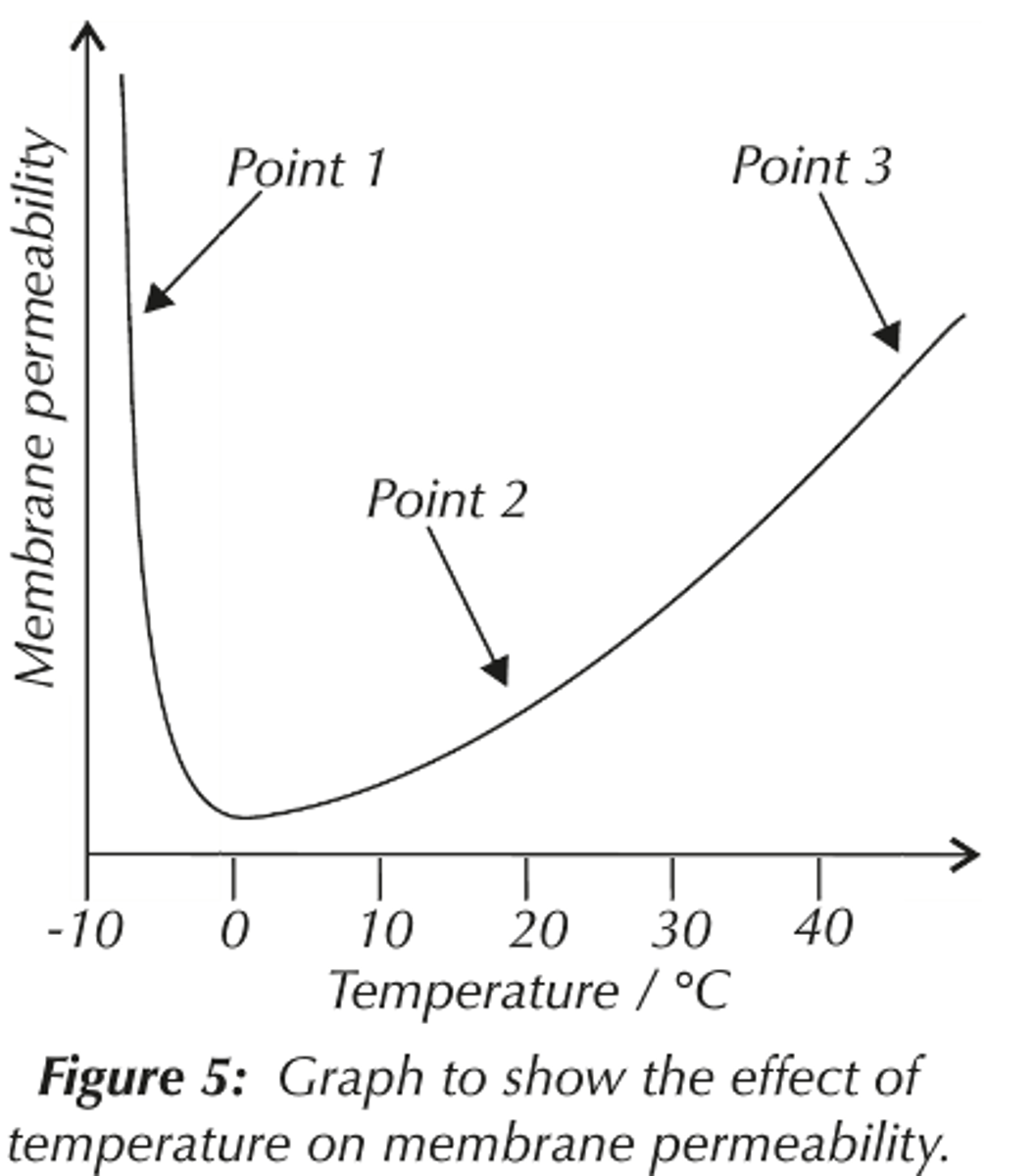
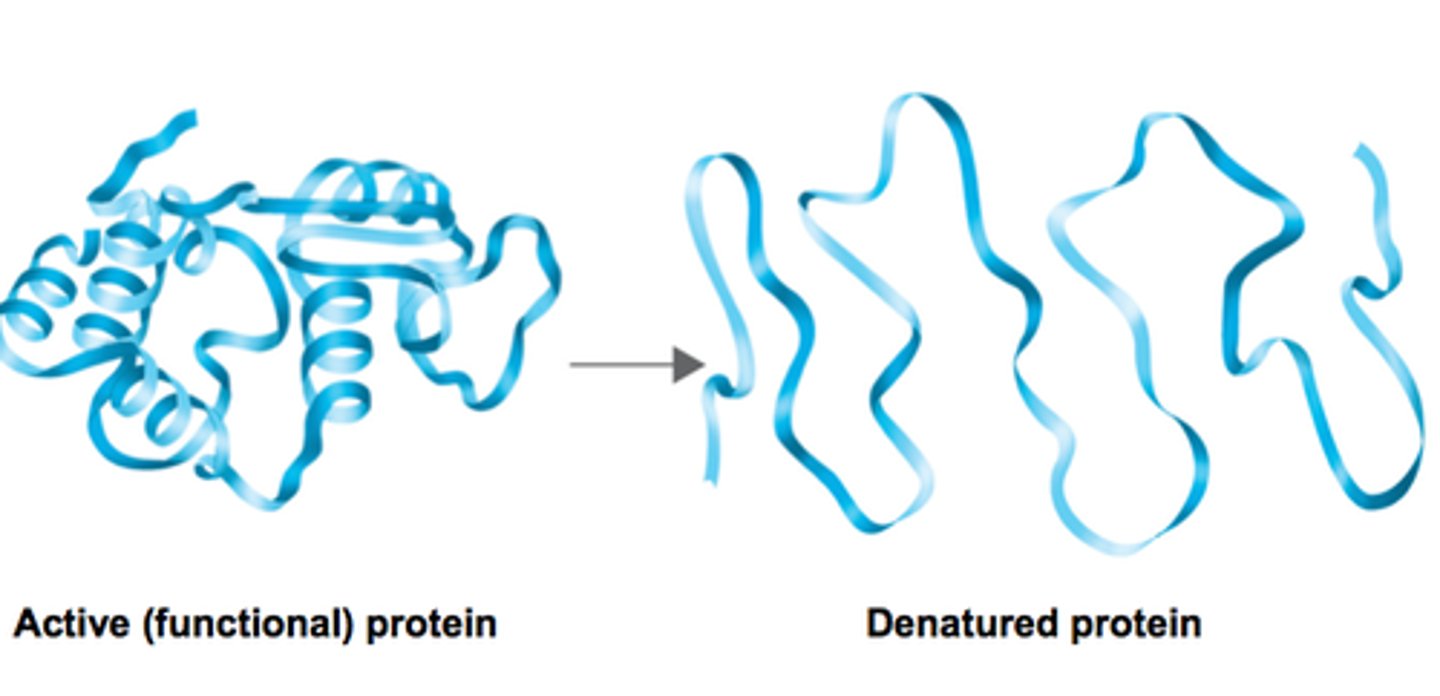
explain how temperature affects permeability of cell-surface membranes
● As temperature increases, permeability increases
○ Phospholipids gain kinetic energy and fluidity increases ○ Transport proteins denature at high temperatures as H bonds break, changing tertiary structure
● At very low temperatures, permeability increases
○ Ice crystals can form which pierce the cell membrane and increase permeability
explain how pH affects permeability of cell-surface membranes
● High or low pH increases permeability
○ Transport proteins denature as H / ionic bonds break, changing tertiary structure
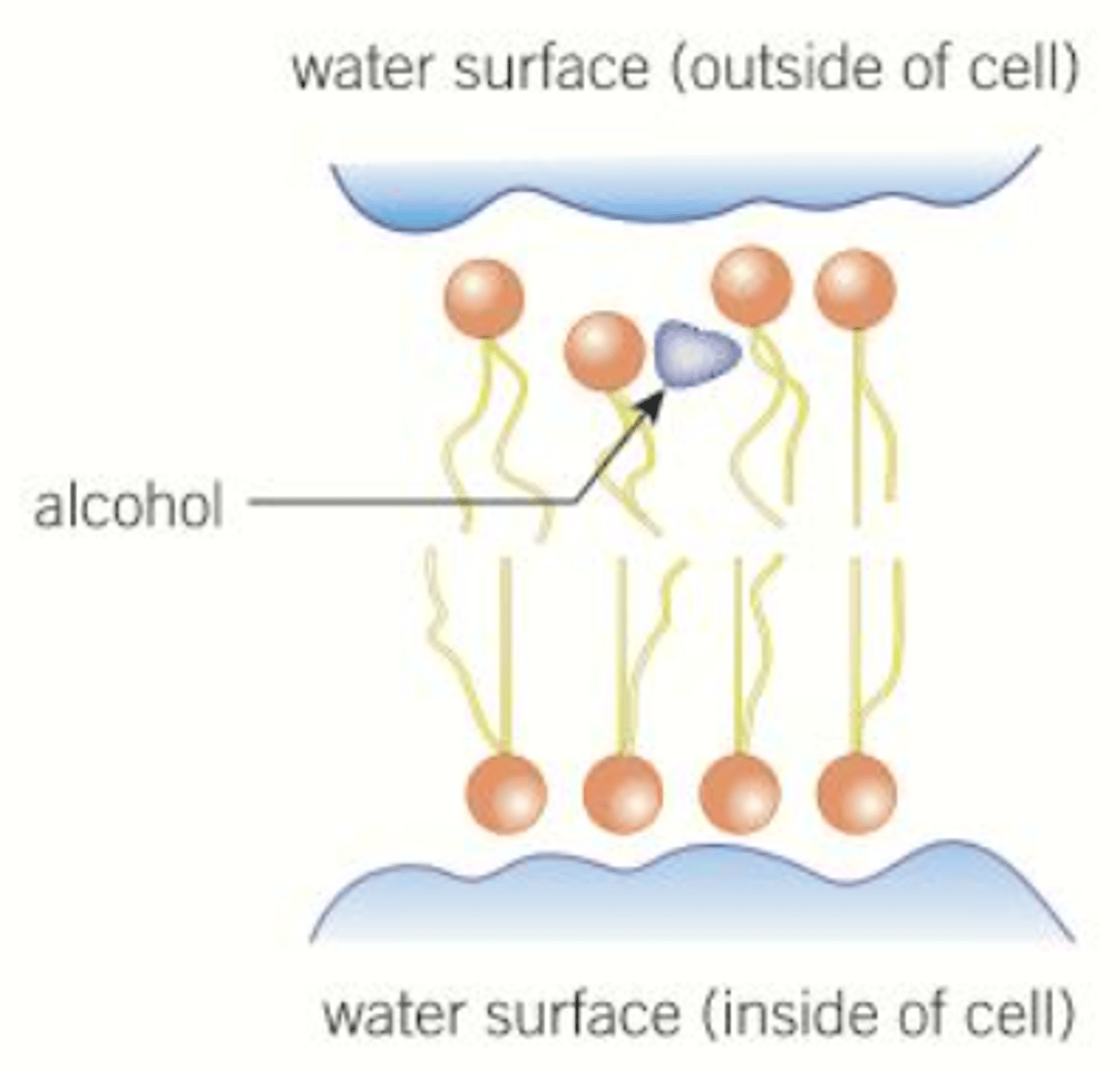
explain how lipid-soluble solvents eg. alcohol affect permeability of cell-surface membranes
● As concentration of alcohol increases, permeability increases
● This is because ethanol (a lipid-soluble solvent) may dissolve phospholipid bilayer, and cause gaps to form